Bone marrow is key to our health because bone marrow produces blood cells that carry oxygen, fight infections, and help stop bleeding. In children, all bones contain active red marrow, but as we age, this activity shifts to flat bones such as the pelvis, ribs, and sternum.
The way bone marrow produces new cells is a highly complex process known as hematopoiesis, where many specialized stem cells work together to create red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Understanding how bone marrow produces these vital cells helps doctors diagnose, prevent, and treat various blood and immune disorders. Research also shows that the bone marrow environment plays a crucial role in controlling and supporting healthy blood cell production.
Key Takeaways
- Bone marrow is key to making blood cells.
- Red marrow is in charge of making blood cells.
- The process needs many cells working together.
- Bone marrow’s role changes with age.
- Knowing about bone marrow helps prevent diseases.
- The bone marrow environment controls blood cell making.
The Vital Role of Bone Marrow in Human Survival
Bone marrow is at the core of human survival. It’s a spongy tissue that makes the cells we need to live. This tissue is key to our hematopoietic system, creating blood cells essential for life.
What Is Bone Marrow? Medical Definition
Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue inside bones like the hips and thighbones. It produces blood cells. The medical term for it is “medulla ossis.” It has a network of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, that give blood cells the nutrients and oxygen they need.
The Significance of Marrow Medulla Ossium
Bone marrow, or medulla ossa, is a blood cell factory. It makes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells are key for oxygen transport, immune defense, and blood clotting. Without bone marrow, our bodies can’t make these vital cells.
Why Bone Marrow Is Essential for Life
Bone marrow is vital for life because it keeps making blood cells. The table below shows the main functions of the blood cells it produces.
| Blood Cell Type | Function |
| Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) | Oxygen Transport |
| White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) | Immune Defense |
| Platelets (Thrombocytes) | Blood Clotting |
In conclusion, bone marrow is essential for human survival. It produces the blood cells we need to live. Knowing its role helps us understand human health better.
What Bone Marrow Produces: The Complete Blood Cell Factory

The bone marrow is like a factory that makes all the blood cells we need. It creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells help our body work right by carrying oxygen, fighting off germs, and stopping bleeding.
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) for Oxygen Transport
Red blood cells carry oxygen all over our bodies. They have hemoglobin, a special protein that holds onto oxygen. This lets oxygen reach our tissues and organs.
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) for Immune Defense
White blood cells are key to keeping us healthy. They fight off infections and diseases. There are different types, like neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes, each with its own job in protecting us.
Platelets (Thrombocytes) for Blood Clotting
Platelets are tiny pieces made in the bone marrow. They’re important for stopping bleeding. When we get hurt, platelets gather to form a clot and stop the bleeding.
The Continuous Production Process
Blood cells are made all the time, every day of our lives. The bone marrow makes billions of them to replace old or damaged ones. This keeps our blood healthy. It’s all managed by special helpers called growth factors and hormones.
The Anatomy and Structure of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow’s anatomy and structure are key to its function. It’s not just a simple tissue; it’s a complex organ. Its structure allows it to produce blood cells efficiently.
Meshwork of Blood Vessels
Bone marrow has a rich network of blood vessels. This includes arteries, veins, and capillaries. They deliver oxygen and nutrients and remove waste. They also help circulate hematopoietic cells.
Stromal Cells and Their Function
Stromal cells form the bone marrow’s structure. They support hematopoietic cells. Fibroblasts, adipocytes, and osteoblasts each have a unique role. They produce growth factors and cytokines for hematopoietic cells.
Hematopoietic Cells: The Building Blocks
Hematopoietic cells are the precursors to all blood cells. They produce red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells differentiate and mature in the bone marrow, creating essential blood cells.
Extracellular Matrix Components
The bone marrow’s extracellular matrix is made of proteins and glycoproteins. It provides structural support and helps with cell interactions. Components like collagen, fibronectin, and laminin are vital for cell adhesion, migration, and differentiation.
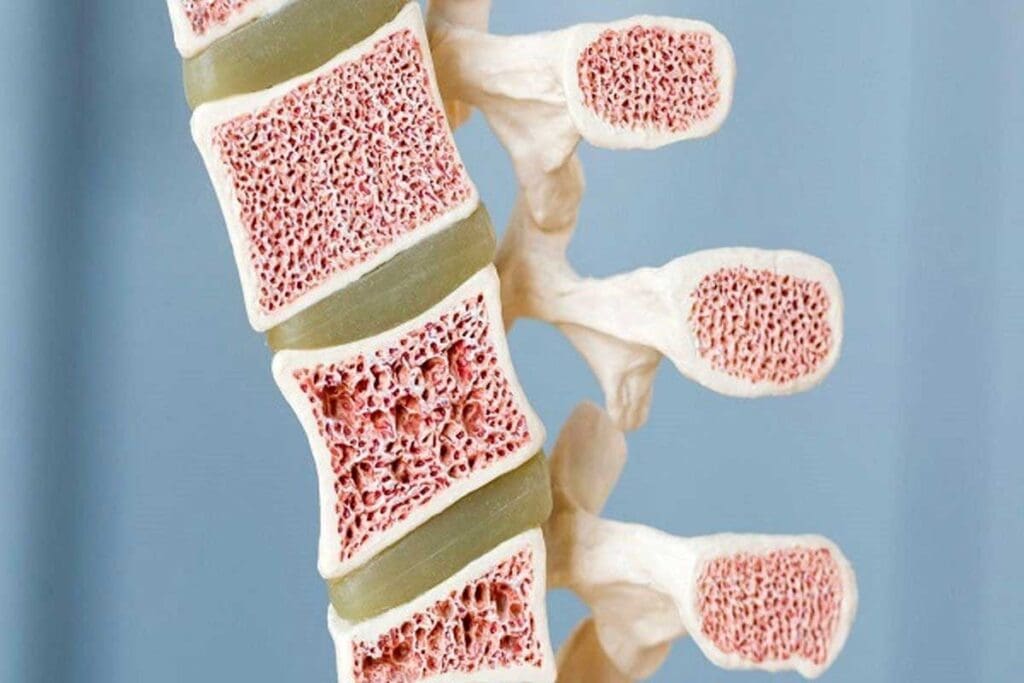
Red vs. Yellow Marrow: Understanding the Two Types
The human body has two kinds of bone marrow: red marrow and yellow marrow. Red marrow makes blood cells, while yellow marrow stores fat. Knowing this helps us understand how bone marrow affects our health.
Red Marrow: The Active Blood Cell Factory
Red marrow is where all blood cells are made. It’s full of stem cells that turn into different blood cells. In adults, you can find red marrow in the pelvis, vertebrae, sternum, and ribs.
Yellow Marrow: Fat Storage and Emergency Reserves
Yellow marrow is mostly fat cells. It’s not as busy making blood cells as red marrow. But it can turn into red marrow if we lose a lot of blood.
How Marrow Changes Throughout Life
As we grow, the mix of red and yellow marrow changes. At birth, most marrow is red. But, as we get older, more of it turns into yellow marrow. Yet, some red marrow stays in key areas like the pelvis and vertebrae.
Visual Differences in Human Bone Marrow Real Pictures
Red marrow looks reddish-brown because of all the blood cells. Yellow marrow is yellow because of the fat. Pictures of human bone marrow show these clear differences.
Do All Bones Contain Bone Marrow? The Surprising Truth
Understanding if all bones have bone marrow involves looking at age groups. Bone marrow is key to making blood cells. But its presence changes with age.
Bone Marrow Distribution in Children
In kids, bone marrow is in all bones. They need lots of blood cells for growth. The marrow in kids is mostly red, making red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Where Is Red Marrow Found in Adults?
In adults, bone marrow shifts. Unlike kids, adults have red marrow mainly in flat bones and long bone ends. For example, red marrow is in the pelvis, vertebrae, sternum, and ribs.
Long Bone Marrow: Structure and Function
Adult long bones, like the femur and humerus, have different marrow. Their shafts have yellow marrow, full of fat cells. But the bone ends have red marrow, making blood cells.
Why Bone Marrow Distribution Changes with Age
The shift in bone marrow with age is natural. As we grow, some red marrow turns to yellow, which stores fat. This change helps the body use less energy for blood cell production in adulthood. Yet, the body keeps enough red marrow in key bones for blood cell needs.
Bone Marrow Cells: The Source of All Blood
Bone marrow is key to human survival, and it’s all thanks to its cells. These cells, including hematopoietic stem cells, are the heart of our blood-making system.
They create every type of blood cell we need, like red and white blood cells, and platelets. This process is complex, with stem cells turning into different cell types. Bone marrow cells are vital for our immune system, carrying oxygen, and clotting blood.
Bone marrow produces many cells that are essential for life. Hematopoietic cells are critical in this process. Their problems can cause serious health issues. Knowing how important bone marrow cells are helps us understand how life is sustained.
FAQ
What is bone marrow?
Bone marrow is a spongy tissue inside some bones, like the hips and thighbones. It makes blood cells. It’s key to the hematopoietic system.
Do all bones contain bone marrow?
No, not all bones have bone marrow. In adults, it’s mainly in the pelvis, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and long bone ends.
What is the difference between red and yellow marrow?
Red marrow makes blood cells. Yellow marrow is fat and stores energy. The mix changes with age.
Where is red marrow found in adults?
In adults, red marrow is in the pelvis, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and long bone ends.
What is the role of hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow?
These stem cells in bone marrow create all blood cell types. This includes red, white blood cells, and platelets.
How does bone marrow distribution change with age?
Kids have red marrow in most bones. As they grow, some turn to yellow marrow. Adults mostly have yellow marrow, with red in specific areas.
What is the function of bone marrow in producing blood cells?
Bone marrow makes blood cells through a complex process. It involves many cell types, like stem cells and their descendants.
What are the different types of blood cells produced by bone marrow?
Bone marrow makes red, white blood cells, and platelets. Each type is vital for life.
Can you describe the structure of bone marrow?
Bone marrow has a network of blood vessels, stromal cells, and hematopoietic cells. It also has an extracellular matrix. All work together to support its function.
What is the significance of bone marrow in human survival?
Bone marrow is vital for survival. It produces blood cells for oxygen transport, immune defense, and blood clotting.
Reference:
PubMed Central. Blood and the cells it contains.



































