At Liv Hospital, we know how important the cervical spine is for our health. The C3 and C4 vertebrae are key for moving our heads and keeping our nervous system working right. Their health is essential for our overall well-being.
Injuries to the C3 and C4 vertebrae can cause big problems. These include breathing issues and tetraplegia. It’s important to understand how vital these vertebrae are and what can happen if they get hurt.
We will look at seven important facts about the C3 and C4 vertebrae. We’ll talk about their role, the dangers of injury, and how to recover. Our aim is to give you all the info you need to make smart choices about your spinal health.
Key Takeaways
- The C3 and C4 vertebrae play a vital role in head movement and nervous system function.
- Injury to these vertebrae can lead to severe complications.
- Knowing the risks and consequences is key for spinal health.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to providing top-notch care and patient-focused excellence.
- Recovering from injuries to the C3 and C4 vertebrae needs a full treatment plan.
The Fundamental Anatomy of C3 and C4 Vertebrae
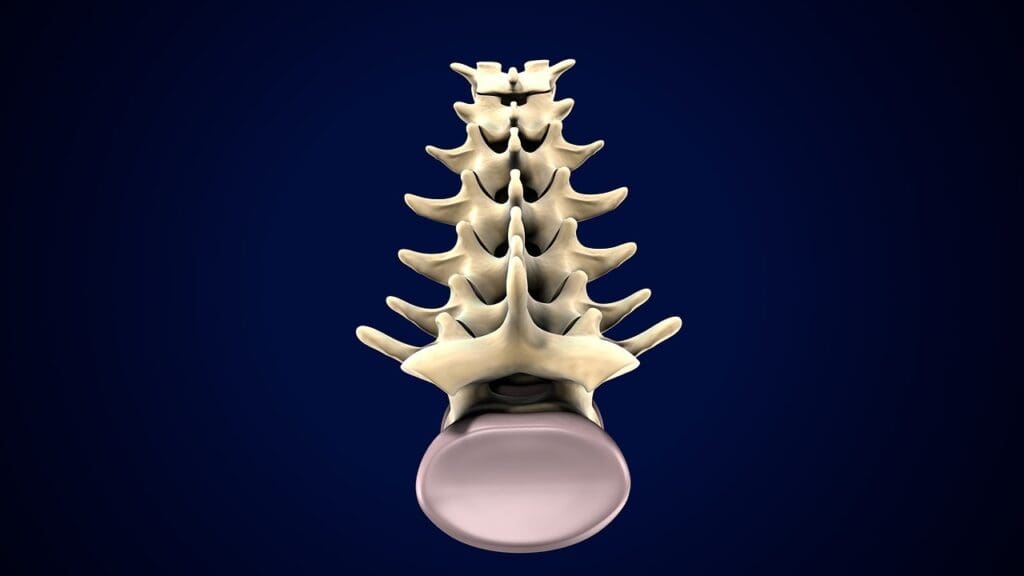
The C3 and C4 vertebrae are key parts of the cervical spine. They help with flexibility, stability, and function. These vertebrae are in the upper part of the spine and support the head. They also help with neck movements.
Physical Characteristics and Structural Design
The C3 and C4 vertebrae look similar to other cervical vertebrae but have special features. They have a smaller body than the lumbar spine. This design allows for more movement.
Key Features:
- Small vertebral body
- Bifid spinous process
- Transverse foramina for vertebral artery passage
These features are important for their function and how they work with other parts.
Mobility Features of C3 and C4 Cervical Vertebrae
The C3 and C4 vertebrae are very mobile. They allow for many neck movements like bending forward, backward, turning, and moving side to side. This is thanks to the discs between them and the design of the facet joints.
Mobility is a key characteristic of these vertebrae. It helps us do daily activities easily.
| Mobility Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Flexion | Forward bending movement |
| Extension | Backward bending movement |
| Rotation | Turning movement around the axis |
Anatomical Relationship with C5 and Surrounding Structures
The C3 and C4 vertebrae are connected to the C5 vertebra and other structures like muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. Knowing these connections is important for diagnosing and treating spine problems.
The C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae work together for the spine’s stability and flexibility. Their connection is key for keeping the spine aligned and working right.
Critical Functions of the C3 C4 and C5 Vertebrae
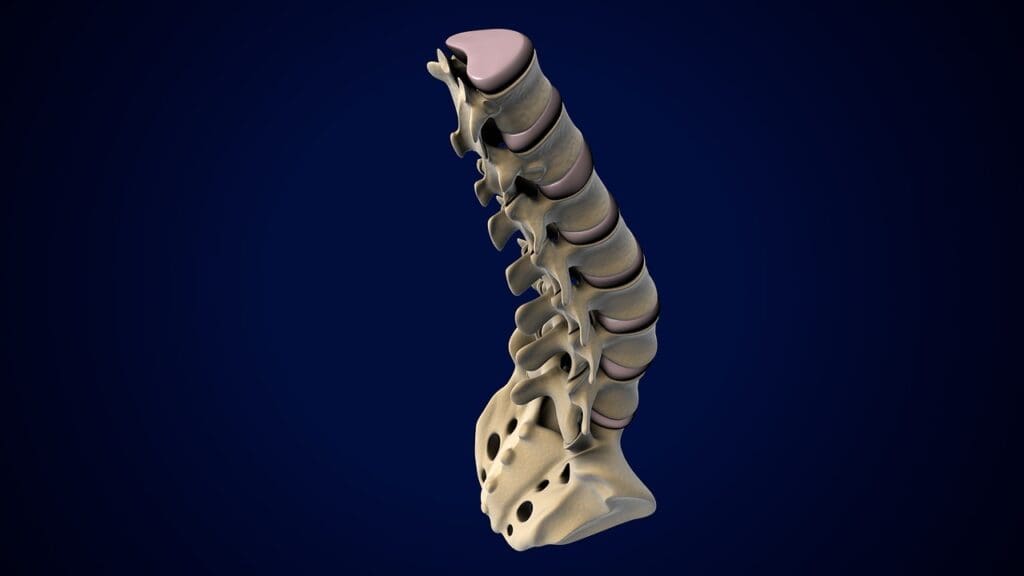
The C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae support the head and protect the spinal cord. They help us move our heads and necks in many ways. This keeps the cervical spine strong and flexible.
Supporting Head Movement and Neck Flexibility
The C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae are key for head movement and neck flexibility. They let us rotate, flex, and extend our necks. Their design, with discs and joints, helps us move smoothly and stay stable.
These vertebrae are vital for daily activities. They help us do simple tasks and complex movements in sports or dance.
Protection of the Spinal Cord and Nerve Pathways
Protecting the spinal cord and nerve pathways is a major job of the C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae. The spinal cord is essential, and damage can be serious. The vertebrae create a safe canal around it.
The C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae are vital for protecting nerve pathways. These nerves control our body functions and help the brain talk to the rest of us.
Role in Overall Cervical Spine Stability
The C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae help keep the cervical spine stable. They work with other parts to keep the spine aligned and prevent injuries.
Keeping these vertebrae healthy is key for spine stability. It’s not just about avoiding injuries. It’s also about managing conditions that can harm their function over time.
Understanding the C3 Spine Location and Its Significance
The C3 vertebra is in the mid-neck area. It helps with head movement and keeps the neck stable. The cervical spine has seven vertebrae, and C3 is the third one. It’s key for the neck’s structure and function.
Precise Position Within the Cervical Spine
The C3 vertebra is between C2 and C4. This spot is important for stress distribution and neck movement. We’ll see how this spot helps the vertebra function and keeps the neck healthy.
Relationship to C2 Above and C4-C5 Below
The C3 vertebra works with C2 and C4-C5 for neck support and flexibility. Knowing how these vertebrae relate helps us understand neck injuries’ effects on the whole spine.
The relationship between C3 and its neighbors is as follows:
| Vertebrae | Relative Position | Functional Significance |
|---|---|---|
| C2 | Above C3 | Forms the atlanto-axial joint, enabling head rotation |
| C3 | Between C2 and C4 | Supports head movement and cervical spine stability |
| C4-C5 | Below C3 | Contributes to neck flexibility and overall cervical spine health |
Anatomical Landmarks for Clinical Identification
Finding the C3 vertebra is key for diagnosing neck issues. The hyoid bone, at C3 level, helps doctors locate it during exams.
Clinical Significance: Knowing where the C3 spine is is essential for correct diagnosis and treatment. It helps pinpoint pain sources, injury extent, and the right treatment.
Neurological Importance of the Spinal C3 C4 Region
The C3-C4 spinal segment is key to many bodily functions. It’s where nerve roots emerge to control important processes. This area is vital for our health.
Nerve Roots and Their Functional Distribution
Nerve roots from C3-C4 control various functions. They send signals for movement and sensation. This ensures our body works well.
Nerve Root Functions: C3 and C4 have unique roles. C3 helps with neck movements and breathing. C4 aids in neck, shoulder, and breathing control.
Impact on Breathing and Diaphragm Control
The C3-C4 region affects breathing and diaphragm control. The phrenic nerve, vital for breathing, gets help from C3, C4, and C5. Damage here can harm breathing.
Respiratory Implications: Injury to C3-C4 can hurt breathing. This might make breathing hard and could need medical help.
Influence on Upper Limb Movement and Sensation
The C3-C4 region also affects upper limb movement and sensation. Though lower cervical segments mainly control the arms, C3-C4’s health is key for arm function.
- The C3 and C4 nerve roots help the cervical plexus. This supplies sensation to the neck and shoulder.
- Damage can cause numbness or weakness in these areas.
Knowing the C3-C4 region’s role shows why injuries need careful handling. This prevents long-term health problems.
Common Injuries to C3 and C4 Vertebrae
Injuries to the C3 and C4 vertebrae are a big worry. They play a key role in neck movement and protecting the spinal cord. These vertebrae are in the cervical spine, which is easily hurt by different injuries.
Mechanisms of Traumatic C3-C4 Injury
High-impact events like car crashes, falls, or sports injuries can hurt the C3-C4 area. The force can cause fractures, dislocations, or sprains in these vertebrae. We’ll look at how these injuries happen and their effects.
The severity of these injuries can range from mild sprains to serious fractures. Knowing how an injury happens helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Comparison with C4 and C5 Injury Patterns
Injuries in the cervical spine can happen at different levels, like C4-C5. Studying these injuries helps us understand the forces at play and their effects on the spinal cord and nerves.
While C3-C4 and C4-C5 injuries share some traits, they also have key differences. For example, injuries at C4-C5 might affect nerve function differently than those at C3-C4.
| Injury Level | Common Injury Types | Nerve Root Impact |
|---|---|---|
| C3-C4 | Fractures, Dislocations | C4 Nerve Root |
| C4-C5 | Fractures, Ligament Sprains | C5 Nerve Root |
Degenerative Conditions Affecting the C3-C4 Region
Osteoarthritis can harm the C3-C4 area, causing pain, stiffness, and less mobility. This condition comes from wear and tear on the spinal joints and discs over time.
We’ll talk about how degenerative changes in the C3-C4 area, like disc wear and facet joint osteoarthritis, affect spinal health.
It’s important to understand both traumatic and degenerative conditions in the C3 and C4 vertebrae. This knowledge helps doctors give the best care to patients with cervical spine injuries.
Recognizing C5 Spinal Cord Injury Symptoms and C3-C4 Complications
Injuries to the C3-C4 spine can cause big problems, like breathing issues. The cervical spine is very important and damage here can affect patients a lot.
Characteristic Signs of Upper Cervical Spine Damage
Damage to the upper spine, like C3 and C4, shows in different ways. People might feel pain, numbness, or weakness in their neck and arms. In bad cases, it can even stop them from breathing properly.
The signs of damage can be small or very big, based on how bad the injury is. We look for symptoms like trouble swallowing, voice changes, or neurological deficits in arms or legs. Spotting these signs early is key for quick help.
Respiratory Complications from C3 C4 Injury
Injuries to C3-C4 can mess with nerves that help us breathe. The phrenic nerve, which comes from the spine at C3, C4, and C5, is at risk. Damage to this nerve can stop the diaphragm from working, leading to breathing trouble. Patients might need a machine to help them breathe.
Respiratory problems are a big worry with C3-C4 injuries. We watch for signs like trouble breathing or low oxygen levels. Quick action is needed to avoid lasting harm.
Diagnostic Approaches and Assessment Methods
Figuring out C5 spinal cord injury symptoms and C3-C4 problems needs a mix of doctor checks and scans. We use advanced imaging like MRI to see how bad the damage is.
Doctor checks include a detailed look at the nervous system to find out where the problems are. We also look at the patient’s past health and how the injury happened. This helps us make a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Treatment Approaches for Spine C3 and C4 Conditions
Dealing with C3 and C4 vertebrae issues needs a mix of treatments. This includes both non-surgical and surgical methods. Every patient is different, so treatments must fit their specific needs.
Conservative Management Strategies
For many, the first step is non-surgical treatment. This aims to ease symptoms and improve function without surgery. It might include:
- Physical therapy to boost neck movement and muscle strength
- Chiropractic care to correct spinal alignment and ease pressure
- Medications like NSAIDs or muscle relaxants for pain relief
- Changes in daily life, like better posture and stress management
“Non-surgical treatment is not just about avoiding surgery,” says a top spine expert. “It’s about starting the healing process and possibly avoiding more serious procedures.” This method works well for those with mild to moderate conditions.
Surgical Interventions and Their Indications
When non-surgical methods fail or the condition is severe, surgery might be needed. Surgical options include:
- Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) to ease spinal cord or nerve pressure
- Cervical laminoplasty to open up the spinal canal
- Artificial disc replacement to keep neck mobility while fixing the disc
Doctors decide on surgery based on how severe the condition is, the patient’s health, and if there are nerve symptoms. “Surgery is key for some C3 and C4 issues,” we say. “It can greatly improve a patient’s life quality.”
Emergency Management of Acute C3-C4 Trauma
Severe injuries to C3 and C4 need quick medical help. Emergency care includes:
- Stabilizing the neck to avoid more harm
- Quick check of nerve function
- Scans like MRI or CT to see the injury’s extent
- Surgery for serious injuries or instability
Quick and right care is vital for acute C3-C4 trauma. “The first steps in treating spine trauma are critical,” we emphasize. “They set the stage for recovery.”
C3 and C4 Injury Recovery: Rehabilitation Protocols
Rehabilitation is key for C3 and C4 spine injury recovery. It helps patients regain strength and mobility. We know how important it is for a full recovery.
Physical Therapy and Mobility Restoration
Physical therapy is essential for C3 and C4 injuries. We use exercises to restore mobility and strength.
Our therapists create personalized plans for each patient. They use various techniques like manual therapy and exercises. We also teach patients about proper posture to avoid further injuries.
Respiratory Support and Management
High cervical injuries like C3 and C4 often need respiratory support. We provide ventilation management and lung function improvement. Our goal is to help patients breathe better and possibly remove ventilators.
Respiratory therapy includes chest physiotherapy and using devices like incentive spirometers. We teach patients and their families how to manage respiratory care at home.
“The key to successful rehabilitation is a multidisciplinary approach that addresses the patient’s physical, emotional, and social needs.”
Innovative Rehabilitation Technologies
We use new technologies to improve recovery. This includes robotic-assisted therapy, exoskeletons, and virtual reality. These tools help patients with strength and mobility.
- Robotic-assisted therapy devices provide precise and consistent movement therapy.
- Exoskeletons support patients in standing and walking, promoting mobility and strength.
- Virtual reality systems offer immersive therapy experiences, boosting engagement and motivation.
These advanced technologies help us create personalized rehabilitation plans. This way, we maximize each patient’s recovery chances.
Conclusion: Protecting and Maintaining C3-C4 Vertebral Health
Keeping the c3 and c4 vertebrae healthy is key for a strong spine. These vertebrae help move our heads and keep our necks flexible. They also protect our spinal cord and nerves.
We’ve talked about how important the c3 c4 vertebrae are for our neck’s stability. To avoid injuries, we need to take care and manage them well.
Knowing how the c3 and c4 vertebrae work helps us take better care of them. This knowledge lets us act early to keep this important area healthy.
To protect and care for the c3 and c4 vertebrae, we need to prevent problems, diagnose them early, and treat them right. Taking care of our spine is essential for our overall health and happiness.
What is the role of the C3 and C4 vertebrae in the cervical spine?
The C3 and C4 vertebrae are key in supporting head movement. They help keep the neck flexible and protect the spinal cord and nerves. They also help keep the spine stable.
What are the possible effects of injuring the C3 and C4 vertebrae?
Injuries to these vertebrae can cause breathing problems and affect arm movement and feeling. They can also lead to other neurological issues. The impact depends on the injury’s severity and type.
How do the C3 and C4 vertebrae relate to the C5 vertebra?
The C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae form a single part of the cervical spine. Together, they help the neck move and protect the spinal cord.
What are the symptoms of a C5 spinal cord injury?
A C5 spinal cord injury can cause breathing issues and weakness or paralysis in the arms. It can also lead to sensory loss. The symptoms vary based on the injury’s extent.
How are injuries to the C3 and C4 vertebrae diagnosed?
Doctors use a mix of clinical checks, imaging like X-rays and MRI, and neurological tests to diagnose these injuries.
What are the treatment options for conditions affecting the C3 and C4 vertebrae?
Treatment options include non-surgical methods, surgery, and emergency care for trauma. The choice depends on the condition’s nature and severity.
What is the importance of rehabilitation after a C3 or C4 injury?
Rehabilitation is vital for regaining mobility and managing breathing issues after a C3 or C4 injury. It includes physical therapy, breathing support, and new rehab technologies. A good rehab program is key to recovery.
How can C3-C4 vertebral health be maintained and protected?
Keeping the C3-C4 vertebrae healthy involves preventive steps like regular exercise and good posture. Avoiding smoking is also important. Seeking medical help quickly if injured or experiencing symptoms is essential.
What is the significance of the C3 spine location?
The C3 spine’s location is important for supporting head movement and keeping the neck flexible. Its exact position and relationship with other structures are key to understanding its function and vulnerabilities.
How do degenerative conditions affect the C3-C4 region?
Conditions like osteoarthritis can harm the C3-C4 region, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. These issues can also raise the risk of injury or neurological problems.


































