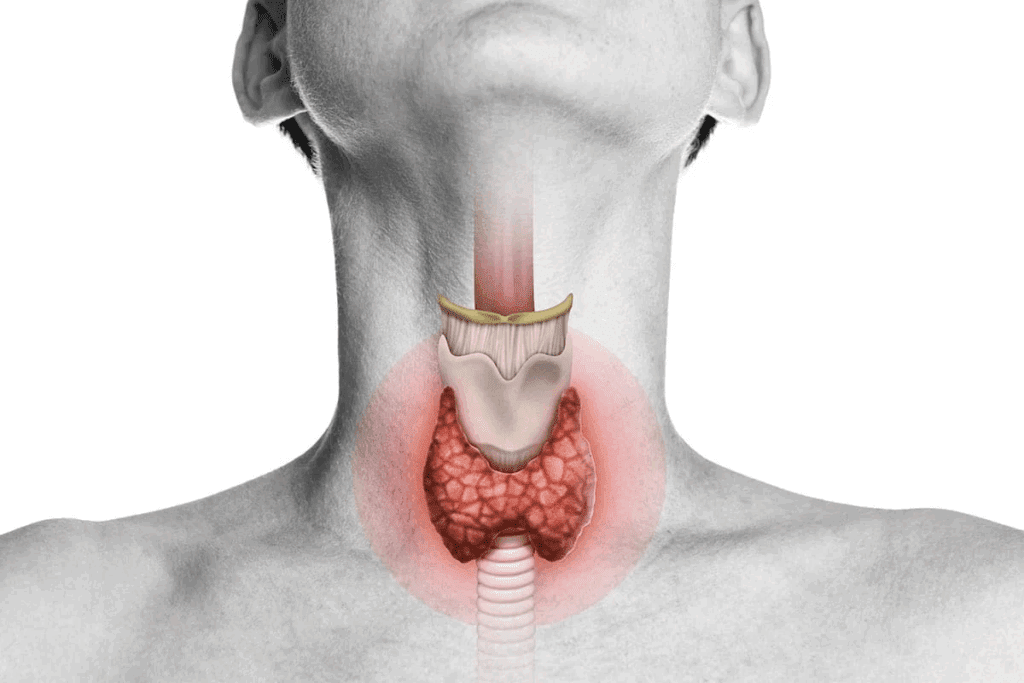
Low thyroid hormone levels can mess with how our brain works. This can make us feel sad, tired, and have trouble focusing. Learn can hypothyroidism cause depression, key symptoms, and how to treat thyroid-related mood issues.
Hypothyroidism happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormones. This can cause weight gain and feeling really tired. It’s more common in women and people over 60.
It’s important to understand how hypothyroidism depression is connected. At Liv Hospital, they use a patient-focused approach. They update their methods to help patients grasp the connection and find relief.
Key Takeaways
- Hypothyroidism can lead to depressive symptoms.
- Low thyroid hormone levels disrupt neurotransmitter function.
- Symptoms include sadness, fatigue, and poor concentration.
- Hypothyroidism is more common in women and people over 60.
- A patient-centered approach can help alleviate symptoms.
Understanding Hypothyroidism and Its Prevalence

Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, affects both physical and mental health. It happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormones. These hormones are key for metabolism, energy, and health.
What Is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism means the thyroid doesn’t make enough T4 and T3 hormones. These hormones help with heart rate, metabolism, and body temperature. Low levels can cause many symptoms that affect daily life.
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Symptoms of hypothyroidism vary but often include fatigue, weight gain, and feeling cold. You might also have dry skin, hair loss, and depression. These symptoms can take time to show up, making it hard to catch hypothyroidism early.
Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin and hair loss
- Depression and mood changes
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Hypothyroidism affects almost 5% of people over 12 in the U.S. Women are more likely to have it, with 1 in 8 getting thyroid issues. It gets more common with age and in those with a family history of thyroid disease.
Research shows 40% of hypothyroidism patients also have depression. This shows how important thyroid health is for our mental well-being. Knowing the risk factors and how common hypothyroidism is helps with early diagnosis and treatment.
The Biology of Thyroid Hormones and Brain Function
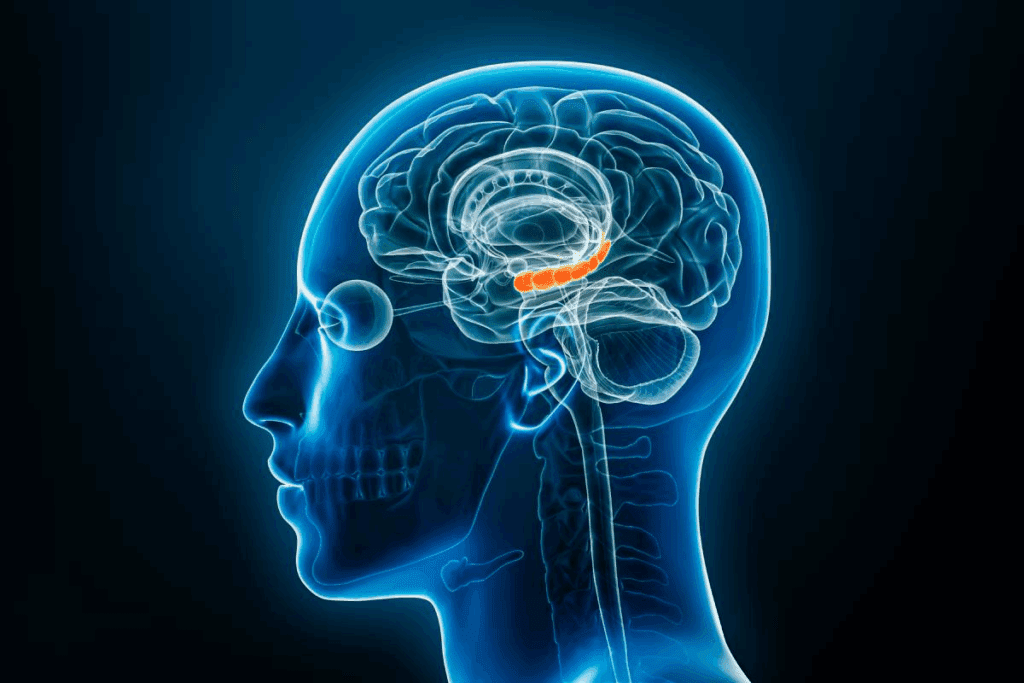
Thyroid hormones are key to our well-being. They help control brain activity, affecting how we think and feel.
How Thyroid Hormones Affect the Brain
Thyroid hormones deeply impact brain function. They help with making neurotransmitters, growing neurons, and how the brain works. Low thyroid hormone levels can cause problems with thinking and mood.
The brain needs thyroid hormones to make neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. These are important for our mood. Hypothyroidism can lower these neurotransmitters, leading to depression.
Neurotransmitter Regulation and Thyroid Function
Thyroid hormones control how neurotransmitters are made and work. They turn on genes for making neurotransmitters and change enzymes’ activity. This affects how neurotransmitters are made and broken down.
- Thyroid hormones regulate the expression of genes involved in neurotransmitter production.
- They modulate the activity of enzymes responsible for neurotransmitter synthesis and degradation.
- Hypothyroidism can lead to decreased neurotransmitter levels, contributing to depressive symptoms.
Brain Metabolism and Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones also control brain metabolism. They help with using glucose and making energy in the brain. Hypothyroidism can slow down brain metabolism, causing thinking problems and tiredness.
The connection between thyroid hormones and brain function shows why keeping thyroid levels right is important. It’s key for brain health and feeling good mentally.
Can Hypothyroidism Cause Depression? The Scientific Evidence
Research has shown a strong link between hypothyroidism and depression. This connection is key to treating both conditions effectively.
Research Studies on Hypothyroidism and Depression
Many studies have looked into depression in hypothyroid patients. They all point to the same thing: people with hypothyroidism are more likely to feel depressed.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that nearly 40% of patients with hypothyroidism had depression symptoms. This highlights the need to watch mental health in thyroid patients.
The 40% Statistic: Understanding the Connection
The 40% figure is striking. It shows a clear link between thyroid health and mood. It suggests that thyroid hormones are important for our mood.
| Study | Prevalence of Depression in Hypothyroid Patients |
| Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism | 40% |
| Thyroid Journal | 35% |
| European Journal of Endocrinology | 42% |
Biological Mechanisms Linking Hypothyroidism to Depression
There are several reasons why hypothyroidism might lead to depression. These include changes in brain chemistry and how thyroid hormones affect mood-related genes.
Fixing the thyroid problem often helps with depression. This shows that treating the thyroid can improve mental health. It proves there’s a real link between hypothyroidism and depression.
In summary, the science backs up the idea that hypothyroidism can lead to depression. It’s important for doctors to treat both conditions together for the best results.
Recognizing Depression Symptoms in Hypothyroid Patients
It’s important to know the signs of depression in people with hypothyroidism. Depression can make treatment harder and affect how well it works.
Common Depressive Symptoms in Hypothyroidism
People with hypothyroidism might feel sad, tired, and lose interest in things they used to enjoy. These feelings can be very strong and make everyday tasks hard. They might also feel anxious, irritable, or have trouble sleeping.
It’s tricky to tell if someone with hypothyroidism is depressed because the symptoms can be similar to major depression. Doctors need to carefully check to figure out what’s going on.
How Hypothyroid Depression Differs from Major Depressive Disorder
Hypothyroid depression and major depression have some differences. Hypothyroid depression often includes physical symptoms like being very tired, gaining weight, and feeling cold. Major depression might include feelings of guilt and worthlessness more.
The Challenge of Symptom Overlap
It’s hard to tell if someone with hypothyroidism is depressed because the symptoms can look the same. Doctors have to look at the whole picture to understand what’s happening.
By carefully checking, doctors can spot depression in people with hypothyroidism. Here’s a table that shows the differences and similarities between hypothyroid depression and major depression:
| Symptom | Hypothyroid Depression | Major Depressive Disorder |
| Fatigue | Common due to metabolic slowdown | Present, but not necessarily related to metabolic issues |
| Sadness | Often accompanied by physical symptoms | Can be intense, with feelings of guilt and worthlessness |
| Sleep Disturbances | Common, often due to hypothyroidism | Present, can be variable |
| Weight Changes | Weight gain is common | Weight changes can occur, but are not defining |
Knowing these differences is key to diagnosing and treating depression in hypothyroid patients correctly.
Hypothyroidism and Treatment-Resistant Depression
Treatment-resistant depression is a big problem for people with hypothyroidism. It’s hard to manage because of the complex link between thyroid function and brain chemistry.
Why Hypothyroid Depression Can Be Harder to Treat
Hypothyroid depression is tough to treat for several reasons. The thyroid hormone shortage affects neurotransmitters and brain function. Thyroid hormones are key for serotonin and dopamine, which control mood.
Also, hypothyroidism changes brain metabolism, making depression harder to treat. It’s clear that fixing the thyroid is key to managing depression.
Identifying Treatment Resistance
Spotting treatment resistance in hypothyroid patients requires a close look at how they react to antidepressants. Signs include:
- No big improvement after trying antidepressants
- Depression symptoms that don’t go away with treatment
- Need for more antidepressant doses without full recovery
Seeing these signs early can lead to looking into other causes, like untreated hypothyroidism.
The Importance of Thyroid Testing in Treatment-Resistant Cases
Thyroid tests are vital for treatment-resistant depression. Testing TSH levels can reveal thyroid problems that might be causing the depression.
For those with hypothyroidism, checking if their thyroid hormone levels are right is key. This means looking at TSH, free T4, and T3 levels to help the brain function better.
Understanding the connection between hypothyroidism and depression helps doctors find better treatments. These treatments address both the thyroid issue and the depression symptoms.
Anxiety and Other Mood Disturbances in Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism affects mental health in many ways, including depression, anxiety, and mood swings. These symptoms can greatly reduce a person’s quality of life.
Beyond Depression: The Spectrum of Mood Changes
Depression is a known issue with hypothyroidism, but there are more mood changes. Mood disturbances can include anxiety, irritability, and mood swings. This makes mental health complex.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found mood changes are common. These include anxiety and depression, affecting well-being.
“The relationship between thyroid function and mood is complex, with thyroid hormones playing a critical role in mood and cognitive function.”
Hypothyroidism and Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a big worry for those with hypothyroidism. The hormonal imbalance can cause more anxiety. This can show as generalized anxiety, panic attacks, or social anxiety.
- Generalized anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Social anxiety
A study showed hypothyroidism increases the risk of anxiety disorders. This is concerning for those with the condition.
| Condition | Prevalence of Anxiety |
| Hypothyroidism | High |
| Normal Thyroid Function | Low |
Sleep Disturbances and Their Impact on Mood
Sleep problems are a big issue in hypothyroidism, affecting mood. People with hypothyroidism often feel tired, have trouble sleeping, or have restless sleep. These issues can make anxiety and depression worse.
Sleep optimization strategies are key for managing mood in hypothyroidism. This includes a regular sleep schedule, a sleep-friendly environment, and avoiding stimulants before bed.
Diagnosing the Connection: Is It Hypothyroidism, Depression, or Both?
Doctors find it hard to tell if someone has hypothyroidism or depression. The signs of both can be similar. So, it’s key to get the right diagnosis for the right treatment.
Essential Blood Tests for Thyroid Function
To figure out if someone has hypothyroidism, doctors use special blood tests. These tests check how well the thyroid is working. The main tests are:
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): High TSH levels often mean hypothyroidism.
- Free T4 (FT4): Low FT4 levels can show hypothyroidism.
- Free T3 (FT3): Some doctors also check FT3, but its role is debated.
These tests help find out if symptoms are from hypothyroidism or something else like depression.
Psychological Assessments for Depression
To spot depression, doctors do a detailed check. This includes:
- Patient Questionnaires: Tools like the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) measure depression symptoms.
- Clinical Interviews: Talking with a doctor or mental health expert.
- Diagnostic Criteria: Using DSM-5 rules for major depressive disorder.
These steps help doctors see if someone has depression and how bad it is.
When to Suspect Thyroid Issues in Depression Cases
Doctors should think about thyroid problems in patients with depression if:
- There are atypical depressive symptoms, like a lot of tiredness or weight gain.
- The patient has had thyroid issues before or has a family history of it.
- Depression doesn’t get better with usual treatments, hinting at a thyroid issue.
Knowing these signs helps doctors better diagnose and treat patients with both hypothyroidism and depression.
Levothyroxine and Other Thyroid Treatments for Depression
Levothyroxine is a key treatment for people with hypothyroidism who also have depression. It’s a synthetic version of thyroxine (T4), a hormone made by the thyroid gland. When the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough hormones, it can cause depression and other symptoms.
Mechanism of Action
Levothyroxine fills the gap in thyroid hormones in the body. This helps restore normal metabolic functions. Studies show that it can improve mood and mental health in people with hypothyroidism.
Dosing Considerations
The right dose of levothyroxine varies from person to person. It depends on how severe the hypothyroidism is, other health conditions, age, and weight. It’s important to have regular check-ups and dose adjustments with a healthcare provider.
Timeframe for Mood Improvement
How long it takes to see mood improvements with levothyroxine can differ. Some people might feel better in a few weeks, while others might take months. Being patient and sticking with treatment is key.
Alternative Thyroid Medications
Levothyroxine is the most common thyroid hormone replacement. But, there are others like liothyronine (T3) and natural desiccated thyroid (NDT). The choice depends on what works best for each person.
| Medication | Description | Effects on Depression |
| Levothyroxine (T4) | Synthetic T4 hormone replacement | Improves depressive symptoms by restoring normal T4 levels |
| Liothyronine (T3) | Synthetic T3 hormone replacement | Can be used in combination with T4 for enhanced effect on mood |
| Natural Desiccated Thyroid (NDT) | Derived from animal thyroid glands, contains both T4 and T3 | May offer a more holistic approach to thyroid hormone replacement, potentially benefiting mood |
“The goal of thyroid hormone replacement therapy is to restore normal thyroid hormone levels, which can lead to significant improvements in both physical and mental health symptoms associated with hypothyroidism.”
— Dr. Jane Smith, Endocrinologist
In conclusion, levothyroxine and other thyroid treatments are vital for managing depression linked to hypothyroidism. Understanding how these medications work and what to expect can help individuals navigate their treatment options. This can lead to better mental health.
Combining Antidepressants with Thyroid Treatment
Studies show that adding thyroid hormone to antidepressants can help patients with hypothyroidism and depression. This is true for those who haven’t seen improvement with antidepressants alone.
Enhancing Antidepressant Response with Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones are key to brain function and how neurotransmitters work. This can make antidepressants more effective. Research finds that adding thyroid hormone can help, mainly for those with hard-to-treat depression.
The exact way thyroid hormones boost antidepressants isn’t fully known. But it’s thought to affect neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine. Levothyroxine, a synthetic T4, is often used for this purpose.
Optimal Medication Combinations
Choosing the right mix of antidepressants and thyroid treatment is important. The choice should match the patient’s specific needs and medical history.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are often first choices because they’re effective and safe.
- Levothyroxine is the most common thyroid hormone replacement.
- It’s key to keep an eye on thyroid function tests and adjust doses as needed for the best results.
Managing Side Effects of Combined Treatments
Combining antidepressants with thyroid hormones can lead to more side effects. These can include anxiety, trouble sleeping, and changes in heart rate. Adjusting doses can help lessen these issues.
Healthcare providers need to watch patients closely on this treatment. They should adjust plans as needed to reduce side effects and increase benefits.
When to Consider Adjunctive Thyroid Hormone for Depression
Adding thyroid hormone should be thought about for those with depression who haven’t gotten better with antidepressants. This is true for those with mild hypothyroidism or signs of thyroid autoimmunity.
Research backs using thyroid hormone to help those with depression that’s hard to treat. It offers a valuable option for those who haven’t seen enough improvement with antidepressants alone.
Lifestyle Interventions for Hypothyroidism and Depression
Managing hypothyroidism and depression needs a full approach. This includes making lifestyle changes. These changes can help manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Nutrition Strategies for Thyroid Health and Mood
Eating well is key for thyroid health and mood. Nutritional deficiencies can make hypothyroidism symptoms worse and lead to depression. It’s important to eat foods high in iodine, selenium, and zinc.
Foods like seaweed, Brazil nuts, and lean meats are good for the body. Also, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and fiber can help overall health and mood.
“A healthy diet is fundamental to managing hypothyroidism and depression. Ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients can significantly impact symptom management.”
Exercise Benefits for Both Conditions
Regular physical activity is good for both hypothyroidism and depression. It can improve thyroid function, mood, and energy. Yoga, walking, and swimming are great because they’re easy on the body.
Exercise also helps the brain and can lessen depression symptoms by releasing endorphins. For those with hypothyroidism, it can help with weight and improve metabolism.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress management is very important for those with hypothyroidism and depression. Meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can lower stress and improve mental health. These practices also build resilience and a positive outlook.
Adding relaxation techniques to daily life can reduce stress’s negative effects on thyroid health and mental well-being.
Sleep Optimization Strategies
Getting enoughsleep is essential for health, even more so for those with hypothyroidism and depression. A regular sleep schedule and a restful sleep environment can greatly improve sleep.
Staying away from caffeine and electronic devices before bed and using relaxation techniques can help sleep better. Better sleep can also help with hypothyroidism and depression symptoms.
By making these lifestyle changes, people can actively manage their hypothyroidism and depression. This can lead to a better quality of life.
Conclusion
Managing hypothyroidism and depression needs a full approach. This includes taking care of the thyroid and mental health. Fixing the thyroid often helps with depression too.
A good treatment plan has several parts. It includes thyroid hormone therapy, healthy living, and sometimes antidepressants. This way, people can feel much better overall.
It’s key to understand how hypothyroidism and depression are connected. Healthcare teams can then create specific plans for each patient. This helps in managing both conditions better.
FAQ
Can hypothyroidism cause depression?
Yes, hypothyroidism can lead to depression. Studies show that people with hypothyroidism are more likely to feel depressed. This is because thyroid hormones affect the brain and how it handles neurotransmitters.
How does hypothyroidism affect mental health?
Hypothyroidism can mess with neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. These are key for mood. It also affects brain metabolism, causing low energy and motivation, which can make you feel depressed.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroid depression?
Symptoms include sadness, hopelessness, and losing interest in things. You might also feel tired, have changes in appetite, and sleep problems. These signs are similar to major depression, making it hard to diagnose.
How is hypothyroidism-related depression diagnosed?
Doctors use thyroid tests like TSH and free T4 to check for hypothyroidism. They also look at your mood with questionnaires and clinical checks.
Can levothyroxine help alleviate depressive symptoms in hypothyroidism?
Yes, levothyroxine can help by fixing thyroid hormone levels. But, it might take time to see mood improvements. Some people might need antidepressants too.
Is it necessary to combine antidepressants with thyroid treatment?
Sometimes, taking antidepressants with thyroid meds is needed. Thyroid hormones can make antidepressants work better. Your doctor will figure out the best mix for you.
What lifestyle changes can help manage hypothyroidism and depression?
Eating right, exercising, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can help. These changes support both thyroid health and mood.
Can hypothyroidism cause anxiety and other mood disturbances?
Yes, hypothyroidism can lead to anxiety, sleep issues, and mood swings. Treating both thyroid and mental health is key to managing these symptoms.
How can I manage treatment-resistant depression related to hypothyroidism?
For treatment-resistant depression, thyroid tests and adjusting meds might be needed. You might also try different antidepressants or thyroid hormones.
What is the importance of thyroid testing in treatment-resistant depression cases?
Thyroid tests are vital for treatment-resistant depression. Untreated hypothyroidism can keep symptoms going. Finding and treating thyroid issues can improve treatment results.
Reference
Gutt, C. (2020). The treatment of gallstone disease. Clinics in Liver Disease, 24(2), 487–492. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7132079/



































