As we get older, our skin changes. For some, this means a higher chance of getting psoriasis. This condition shows up as red, scaly patches on the skin. Knowing the risks and symptoms helps in getting medical help early.
Can you getpsoriasis later in life? Learn the crucial facts on the serious risk of infection and if psoriasis can cause sepsis today.
Key Takeaways
Psoriasis can develop at any age, with a significant number of cases occurring after age 40.
The condition is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Aging skin is more susceptible to psoriasis due to various changes.
Recognizing symptoms early is key for effective management.
Timely medical intervention can greatly improve quality of life.
Understanding Psoriasis: An Overview
Learning about psoriasis is key to managing its symptoms and improving life quality. It’s a chronic condition that needs ongoing care.
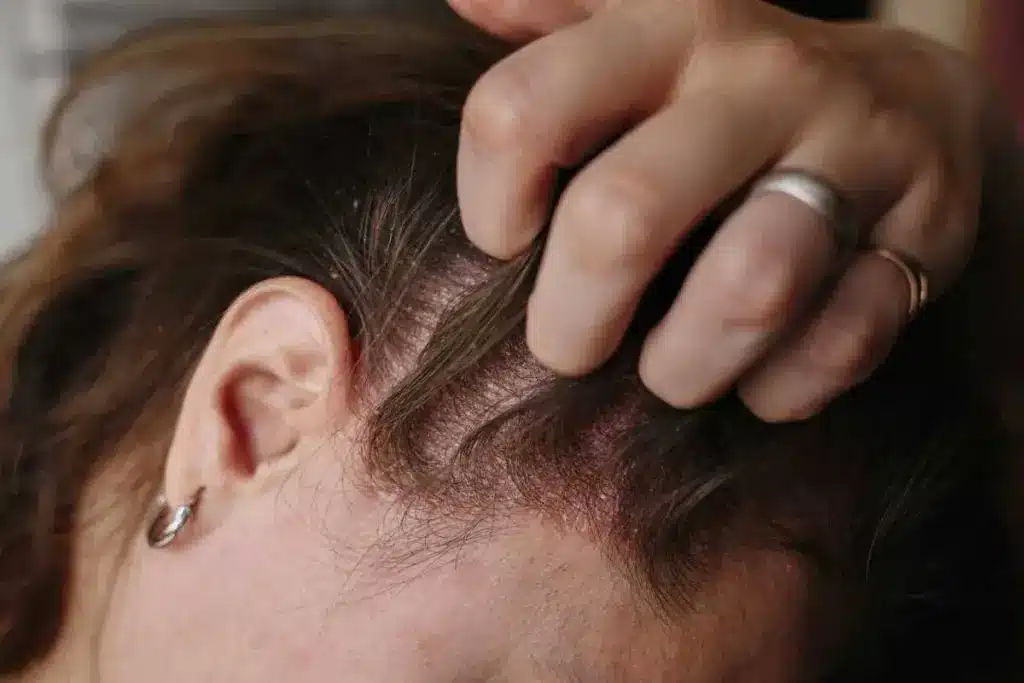
What Is Psoriasis?
[PLACE THE IMAGE HERE]
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes skin inflammation and scaly, red patches. The JAK-STAT signaling pathway is important in its development. It leads to an overactive immune response.
This complex interaction between immune and skin cells causes psoriasis symptoms. Knowing how it works is vital for finding effective treatments.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with its own features. The most common ones are:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common type, with raised, red patches and a silvery white buildup of dead skin cells.
- Guttate Psoriasis: A type that often starts in childhood or young adulthood, appearing as small, dot-like lesions.
- Inverse Psoriasis: A form that affects the folds of the skin, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts, causing smooth, red patches.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white blisters surrounded by red skin, often accompanied by fever, chills, and rapid heartbeat.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare but serious form that can cause widespread redness, scaling, and shedding of the skin.
Common Symptoms to Look For
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary. Common signs include:
Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales.
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed.
Soreness, itching, or burning sensations on the skin.
Nail changes, such as thickening, pitting, or separation from the nail bed.
Joint pain or stiffness, potentially indicating psoriatic arthritis.
Recognizing these symptoms is important for early diagnosis and effective management. If you notice any of these signs, see a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.
Can You Get Psoriasis Later in Life?
Psoriasis can start at any age. It’s important to know what causes it to manage it well. We’ll look at how age, triggers, and gender affect psoriasis later in life.
Can Age Be a Factor?
Research shows that psoriasis risk goes up with age. It can start from infancy to old age. The most common ages for it to start are between 15 and 30, and again between 50 and 60.
A study in a Journal found that psoriasis peaks in the 50-60 age group. This shows age is a big factor in getting psoriasis.
“The incidence of psoriasis has been shown to have a bimodal distribution, with the first peak occurring in adolescence and the second peak in the fifth decade of life.”
Triggers for Late-Onset Psoriasis
Several things can start psoriasis later in life. Hormonal changes, stress, infections, and some medicines are triggers. Knowing these can help manage the condition better.
Hormonal changes: Changes in hormone levels, like during menopause or pregnancy, can start psoriasis.
Stress: Chronic stress can make psoriasis worse or start it in some people.
Infections: Some infections, like streptococcal infections, can start psoriasis.
Medications: Some medicines, like beta-blockers and lithium, can start or make psoriasis worse.
Trigger | Description |
|---|---|
Hormonal Changes | Changes in hormone levels, like during menopause or pregnancy. |
Stress | Chronic stress that can make psoriasis worse or start it. |
Infections | Certain infections like streptococcal infections that can start psoriasis. |
Medications | Certain medicines like beta-blockers and lithium that can start or make psoriasis worse. |
Gender Differences in Psoriasis Onset
Research shows gender differences in psoriasis. Women tend to get it earlier than men. They also see more changes in symptoms during their menstrual cycle or pregnancy.
A study in a Journal found women get psoriasis more before 30. Men get it more after 30.
“There are gender differences in the age of onset and the clinical presentation of psoriasis, with women generally having an earlier onset and more fluctuating course.”
The Connection Between Psoriasis and Sepsis
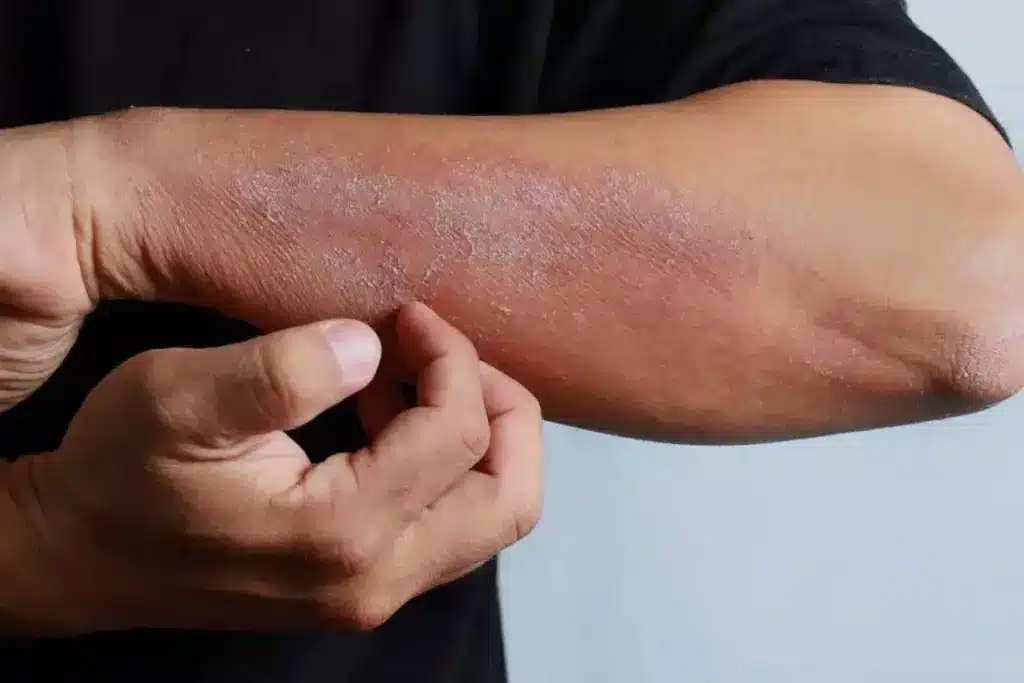
It’s important to understand how psoriasis and sepsis are connected. Psoriasis is more than just a skin issue. It’s an autoimmune disease that affects the body’s immune system.
Immune System Impact
Psoriasis affects the immune system by making it overactive. This leads to inflammation and a higher risk of infections. The body’s immune response is misdirected, attacking its own tissues.
People with psoriasis are more likely to get infections because their immune system is weakened. The inflammation from psoriasis makes it even more critical to manage the condition well.
Understanding Sepsis
Sepsis is a serious condition where the body’s response to infection harms its own tissues and organs. It’s a condition that needs immediate medical help. The link between psoriasis and sepsis comes from the immune system’s imbalance.
Sepsis can come from different infections and can be mild or severe. It’s marked by an intense immune response and widespread inflammation.
Risk Factors for Sepsis in Psoriasis Patients
There are several risk factors for sepsis in people with psoriasis. These include how severe the psoriasis is, other health conditions, and certain medications that weaken the immune system.
Severe psoriasis, with widespread skin involvement, raises the risk.
Having other health issues, like diabetes or heart disease, can make things worse.
Medicines that suppress the immune system, while helpful for psoriasis, increase the risk of infections, including sepsis.
Knowing these risk factors helps healthcare providers give better care to those with psoriasis. This can help lower the chance of severe infections.
Diagnosing Psoriasis in Older Adults
Psoriasis in older adults can be tricky to diagnose because of other health issues and skin problems. As we get older, our skin changes, making psoriasis harder to spot. We’ll look at the signs, why a doctor’s check-up is key, and common mistakes in diagnosis.
Signs and Symptoms in Older Patients
Older adults with psoriasis might show different signs than younger people. Common signs include:
Thickened skin plaques
Scaling on the scalp, elbows, and knees
Nail changes such as pitting or thickening
Joint pain and stiffness in cases of psoriatic arthritis
These symptoms can look like other conditions, so a detailed check-up is important.
Importance of Medical Evaluation
Getting a full medical check-up is key for diagnosing psoriasis in older adults. This includes looking at the patient’s health history, doing a physical exam, and sometimes a skin biopsy. We must also think about any other health issues and medicines that might affect the diagnosis.
Common Misdiagnoses
Psoriasis in older adults is often mistaken for other skin problems like eczema, dermatitis, or fungal infections. Getting the right diagnosis is vital to start the right treatment and improve the patient’s life.
Condition | Common Characteristics | Differential Diagnosis Considerations |
|---|---|---|
Psoriasis | Thickened skin plaques, scaling, nail changes | Presence of psoriatic arthritis, family history |
Eczema | Itchy, inflamed skin, often with a personal or family history of allergies | Absence of characteristic psoriatic nail changes or joint symptoms |
Dermatitis | Inflamed, sometimes itchy skin, often due to irritants or allergens | History of exposure to potentially irritating substances, pattern of skin involvement |
Fungal Infections | Itchy, scaling skin, often with a clear border | Presence of fungal elements on microscopy or culture |
In conclusion, diagnosing psoriasis in older adults needs a careful and detailed approach. We must consider the unique challenges of age and other health issues. By understanding the signs and avoiding common mistakes, we can offer better care for our patients.
Treatment Options for Late-Onset Psoriasis
Psoriasis that starts later in life needs a variety of treatments. These are chosen based on how severe the psoriasis is and the person’s health. The goal is to find what works best for each person.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first choice for psoriasis. They include:
- Corticosteroids: They help reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
- Vitamin D analogues: These help lower skin cell production.
- Topical retinoids: They are vitamin A derivatives that unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
Systemic Medications
For severe psoriasis, systemic medications are used. They work throughout the body and can have a big impact:
- Biologics: They target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Traditional systemic medications: Such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, which suppress the immune system.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Medical treatments aren’t the only way to manage psoriasis. Lifestyle changes and home remedies can also help:
- Dietary changes: Eating a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation and yoga can help manage stress, a known trigger for psoriasis.
- Skin care: Moisturizing regularly to keep the skin hydrated and reduce scaling.
The following table summarizes the treatment options for late-onset psoriasis:
Treatment Type | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Topical Treatments | Corticosteroids, Vitamin D analogues | Reduce inflammation, slow skin cell growth |
Systemic Medications | Biologics, Methotrexate | Target immune system, reduce inflammation |
Lifestyle Changes | Dietary adjustments, Stress management | Reduce triggers, improve overall health |
By understanding and using these treatment options, people with late-onset psoriasis can manage their condition well. This improves their quality of life.
The Role of Stress and Lifestyle
Stress is a big factor in making psoriasis worse. For people with adult onset psoriasis, knowing this is key to controlling symptoms.
Impact of Stress on Psoriasis
Stress can make psoriasis symptoms worse. When we’re stressed, our immune system gets triggered, leading to inflammation and flare-ups. Managing stress is essential to control the condition and improve life quality.
Studies show stress is a big trigger for psoriasis, along with genetics and environmental changes. By dealing with stress, people can manage their psoriasis better.
Managing Stress Effectively
There are many ways to manage stress and help psoriasis symptoms. These include:
Meditation and mindfulness practices
Yoga and other physical activities that promote relaxation
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address underlying stressors
By adding these techniques to daily life, people with psoriasis can lower stress and reduce flare-ups.
“Reducing stress through mindfulness and relaxation techniques can have a positive impact on psoriasis symptoms.”
– Expert Opinion
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle can also help manage psoriasis. This includes:
Eating a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids
Doing regular exercise to improve health and reduce stress
Avoiding known triggers like smoking and too much alcohol
By making these changes, people can manage their psoriasis better and feel better overall.
Knowing psoriasis risk factors and making smart lifestyle choices are important for managing adult onset psoriasis. By being proactive, people can live healthier, more balanced lives despite their condition.
Living with Psoriasis Later in Life
Living with psoriasis later in life can be tough. Our skin’s healing powers change with age, making psoriasis symptoms worse. It’s important to know how to handle these challenges to keep a good quality of life.
Emotional and Mental Health Considerations
Psoriasis affects more than just the skin. It can make you feel self-conscious and lower your self-esteem. “The psychological burden of psoriasis is often underestimated,” says a leading dermatologist. It’s essential to acknowledge the emotional toll of psoriasis and seek support when needed.
People with psoriasis are more likely to feel depressed and anxious. So, it’s key to tackle these mental health issues in treatment plans.
Support Networks and Resources
Having a strong support network is vital for those with psoriasis. This includes family, friends, support groups, and healthcare professionals. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of psoriasis can be incredibly empowering.
There are many resources to help those with psoriasis. These include online forums, educational materials, and counseling services. Using these resources can help manage the condition better.
Coping Strategies for Patients
Developing effective coping strategies is key to managing the psychological impact of psoriasis. Techniques like stress management, mindfulness, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can help.
“Mindfulness practices have been shown to reduce stress and improve overall well-being in individuals with chronic conditions like psoriasis.”
A healthcare provider can help create a personalized coping plan. This plan will include lifestyle changes and stress management tailored to your needs.
Preventative Measures to Consider
Keeping your skin healthy and avoiding known triggers are key to preventing psoriasis flare-ups. As we age, our skin loses its natural moisture and protection. This makes it more likely to get psoriasis symptoms. By taking care of your skin and avoiding triggers, you can lower the chance of psoriasis flare-ups.
Keeping Skin Healthy
Healthy skin is the first step in managing psoriasis. Use gentle skin care products and moisturize often. Also, stay away from harsh soaps that take away your skin’s natural oils.
Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers.
Moisturize immediately after bathing while the skin is wet.
Avoid extreme water temperatures.
Avoiding Triggers
It’s important to know and avoid triggers to prevent psoriasis flare-ups. Common ones include stress, cold weather, and certain medicines.
Trigger | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|
Stress | Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga. |
Cold Weather | Keep the skin moisturized and dress warmly. |
Certain Medications | Consult with a healthcare provider about possible medication interactions. |
Regular Check-ups with Healthcare Providers
Regular visits to healthcare providers are key to managing psoriasis. These visits help catch flare-ups early and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Benefits of Regular Check-ups:
Early detection of psoriasis flare-ups.
Adjustment of treatment plans.
Monitoring for possible side effects of treatments.
Conclusion: Navigating Psoriasis in Later Life
Managing psoriasis in later life needs a full plan. This plan should include medical care, lifestyle changes, and emotional support.
Professional Guidance and Treatment
Getting help from a doctor is key. They can create a treatment plan just for you. This might include creams, pills, or light therapy.
A Holistic Approach to Management
Psoriasis management is more than just medicine. It’s about making lifestyle changes and getting emotional support. Understanding your condition and taking action can greatly improve your life.
Effective Management Strategies
Handling psoriasis well means using many strategies. Work with your doctor to make a plan. This plan should cover medical care, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. Don’t forget about managing stress and taking care of your skin.
FAQ
Can psoriasis develop later in life?
Yes, psoriasis can start at any age, even later in life. It often begins between 15 and 35, but some people first notice symptoms in their 50s or 60s. Knowing the risk factors and symptoms is key to getting help early.
What are the risk factors for developing psoriasis?
Psoriasis risk factors include genetics, environmental triggers, stress, infections, and certain meds. Family history is a big factor. Stress and weakened immune systems also increase risk.
How does age affect the development of psoriasis?
Age can play a role in psoriasis. As we get older, our skin changes, which might raise the risk. Late-onset psoriasis is often due to a mix of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Are there differences in how psoriasis affects men and women?
Yes, men and women with psoriasis have different experiences. Women’s symptoms can change with hormones, while men are more likely to get plaque psoriasis. Treatment responses also vary.
Can stress trigger psoriasis flare-ups?
Yes, stress can make psoriasis worse. Stress management, like meditation or yoga, can help control symptoms and improve health.
What are the treatment options for late-onset psoriasis?
Treatments for late-onset psoriasis include topical creams, systemic meds, and lifestyle changes. The right treatment depends on the condition’s severity and the person’s health. Home remedies and alternative therapies can also help manage psoriasis.
How can I manage psoriasis effectively?
Effective psoriasis management involves keeping the skin moisturized, avoiding triggers, and regular doctor visits. Making lifestyle changes, like diet and exercise, can also help manage symptoms.
What is the connection between psoriasis and sepsis?
Psoriasis can raise the risk of sepsis, a dangerous condition. Understanding this link is important for managing psoriasis and avoiding serious complications.
How can I prevent psoriasis flare-ups?
Preventing flare-ups requires proactive steps like keeping the skin moisturized and avoiding triggers. Regular doctor visits are also key. By following these steps, you can reduce flare-ups and improve your life quality.
References
New England Journal of Medicine. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra0804595



































