Patients, caregivers, and doctors need to understand the many cancer types. There are over 50 different cancer types. Knowing the main types, symptoms, and new research is key.
The World Health Organization and other groups have listed over 100 cancer tumor types. These range from common to rare. We’ll dive into this complex area, sharing insights on different types and important facts about cancers.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch oncology care. Our team keeps up with the latest research. This ensures our patients get the best care possible.
Key Takeaways
- There are over 50 distinct cancer types, with more than 100 documented variations.
- Understanding the different cancer types is key to good diagnosis and treatment.
- Liv Hospital is known for its patient-focused oncology care and staying current with research.
- A detailed list of cancer types helps patients and caregivers understand cancer better.
- Our team is committed to delivering world-class healthcare with full international patient support.
What Is Cancer: Essential Background
To understand cancer, we must first know how normal cells turn bad. Cancer happens when cells grow out of control and spread to other parts of the body.
How Normal Cells Become Cancerous
Turning normal cells into cancer involves many factors. Cells usually grow, divide, and die in a set order. But when this order is broken, cells can grow and divide without stopping.
This can cause a tumor to form. Not all tumors are cancerous. Cancerous tumors can spread to other parts of the body, a process called metastasis.
Key Terminology in Cancer Diagnosis
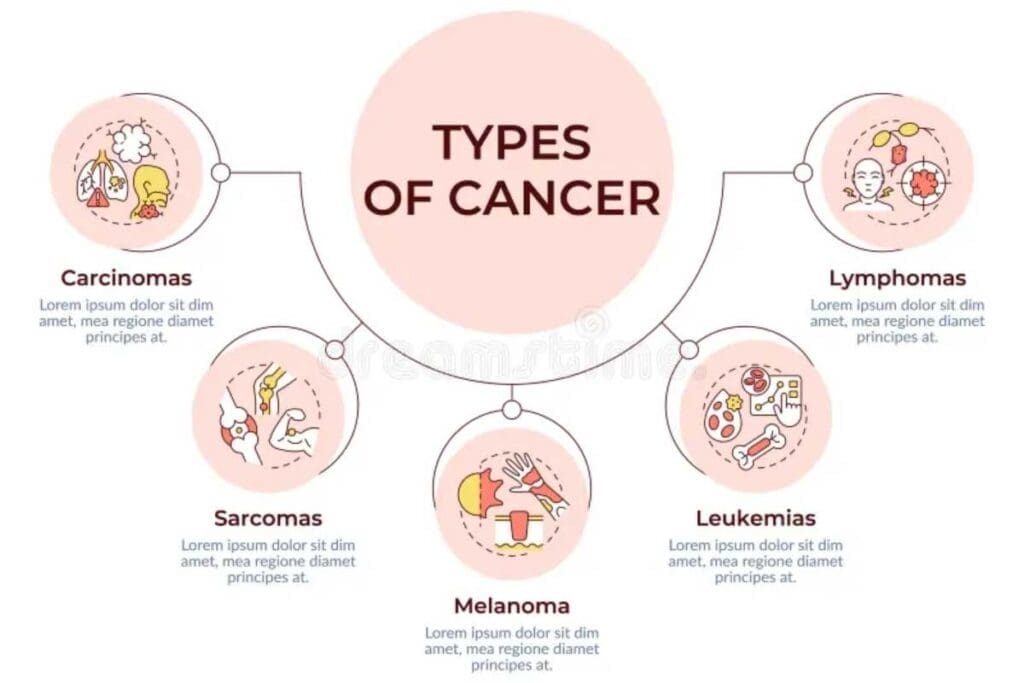
Diagnosing cancer involves knowing the types of cells involved. Carcinomas start in the skin or other organ linings. Sarcomas start in connective tissue, like bones or muscles.
Lymphomas are cancers of the immune system, and leukemias are cancers of the blood. These categories show how different cancer cells can be.
Knowing where cancer starts is key to treatment and understanding the disease. New tests, like the Galleri test, help find and classify cancers better.
Major Cancer Types of Cancer: Classification System
Cancer is a complex disease with many types. It is classified based on where it starts and what it looks like. This helps doctors understand and treat it better.
Carcinomas: Epithelial Tissue Cancers
Carcinomas are the most common cancers. They come from cells in organs and glands. Examples include breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. These cancers are named after the part of the body they start in.
Sarcomas: Connective Tissue Cancers
Sarcomas start in connective tissue, like bones and muscles. They are less common but can grow fast. Osteosarcoma and leiomyosarcoma are examples.
Lymphomas and Leukemias: Blood and Immune System Cancers
Lymphomas and leukemias affect the blood and immune system. Lymphomas start in the lymphatic system. Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are the main types. Leukemias start in the bone marrow and affect the blood. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) are common types.
Other Classification Methods
Cancers can also be classified by their genetics and molecular features. This helps doctors tailor treatments to each patient’s needs.
| Cancer Type | Tissue/Cell of Origin | Examples |
| Carcinomas | Epithelial cells | Breast, lung, colorectal cancer |
| Sarcomas | Connective tissue | Osteosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma |
| Lymphomas | Lymphatic system | Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| Leukemias | Bone marrow | ALL, CML |
Knowing about different cancers and how they are classified is key to improving treatment. By understanding where and how cancers start, we can find better ways to fight them.
Most Common Cancer Types Worldwide
Cancer comes in many forms, but some are more common than others. The American Cancer Society lists breast, lung, colorectal, and prostate cancers as the top types. These cancers affect many people and have different causes and ways to find them.
Breast Cancer: Facts and Statistics
Breast cancer is the leading cancer in women worldwide. It’s more common in countries with better healthcare. Thanks to early detection, more people survive. The American Cancer Society recommends regular mammograms and self-exams.
Lung Cancer: Types and Risk Factors
Lung cancer is the deadliest cancer globally. It’s split into non-small cell and small cell types. Smoking is the main cause of lung cancer deaths. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common and includes types like adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Colorectal Cancer: Detection and Prevention
Colorectal cancer is common and can be caught early. Screening tests find polyps that can turn into cancer. Risk factors include age, family history, and lifestyle choices like diet and exercise.
Prostate Cancer: Demographics and Screening
Prostate cancer is common in older men. Screening with PSA tests can find it early. Men should talk to their doctor about the pros and cons of screening.
| Cancer Type | Estimated New Cases (Globally) | Estimated Deaths (Globally) | Common Risk Factors |
| Breast Cancer | 2.3 million | 685,000 | Genetics, Hormonal factors |
| Lung Cancer | 2.2 million | 1.8 million | Smoking, Air pollution |
| Colorectal Cancer | 1.9 million | 935,000 | Age, Family history, Diet |
| Prostate Cancer | 1.4 million | 375,000 | Age, Family history, Genetics |
Knowing about the most common cancers is key to health efforts and awareness. By understanding breast, lung, colorectal, and prostate cancers, we can fight cancer better.
Digestive System Cancers
Digestive system cancers include many types that affect different parts of the gut. These cancers are hard to spot early, making treatment tough. We’ll look at the different types, their signs, and the challenges in finding and treating them.
Esophageal and Stomach Cancers
Esophageal and stomach cancers are big worries in the digestive system. Esophageal cancer starts in the esophagus’s lining, linked to GERD and diet. Stomach cancer, or gastric cancer, is tied to Helicobacter pylori infection and diet. Finding these cancers early is key to better survival chances.
Pancreatic Cancer: Why It’s Difficult to Treat
Pancreatic cancer is hard to treat because it’s often caught late. Symptoms show up when the cancer is far along, making it hard to find early. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is the most common type. We’re working hard to find better ways to screen and treat it.
Liver and Bile Duct Cancers
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, is linked to liver disease and cirrhosis. Risk factors include hepatitis B and C, alcohol, and aflatoxin. Bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, is hard to diagnose. Knowing these risks helps in prevention and early detection.
Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is rare but serious because of its poor outlook. It’s often found late, making treatment hard. Risk factors include gallstones and chronic inflammation. Early detection and surgery are vital for better results.
In summary, digestive system cancers are complex and need a deep understanding and management. By knowing the risks and improving how we find these cancers, we can improve patient care.
Respiratory System Cancer Types
The respiratory system can get cancer in many ways, with lung cancer being the most common. Cancers can also affect other parts needed for breathing. We’ll look at the different types and what makes them unique.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Subtypes and Treatments
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) is the main type of lung cancer. It breaks down into adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. The treatment for NSCLC depends on the cancer’s stage, type, and the patient’s health.
Some common treatments for NSCLC include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and affected lung tissue
- Targeted therapy that focuses on specific genetic mutations
- Immunotherapy that boosts the body’s immune response against cancer cells
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used to kill cancer cells
Small Cell Lung Cancer: Aggressive Nature
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) grows fast and is very aggressive. It’s linked to smoking and spreads quickly. Treatment often combines chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
The American Cancer Society stresses the need for lung cancer screening in high-risk groups. This can catch SCLC and other lung cancers early.
Mesothelioma: Asbestos Connection
Mesothelioma is a rare cancer that affects the lining of the lungs or abdomen. It’s caused by asbestos exposure. Treatment options are limited, but research aims to improve patient outcomes.
Laryngeal and Tracheal Cancers
Laryngeal cancer hits the voice box, while tracheal cancer targets the windpipe. These cancers are less common than lung cancer but can greatly affect quality of life. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, or both.
Knowing about the different respiratory system cancers is key to finding the right treatment. We’re always learning more to help patients.
Reproductive System Cancers
It’s important to know about reproductive system cancers for early detection and treatment. These cancers can affect both men and women. They impact different parts of the reproductive system.
Female Reproductive Cancers
Female reproductive cancers include cervical, ovarian, and endometrial cancers. These are big health concerns because they are common and can affect women’s health a lot.
Cervical cancer is often caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). It can be prevented with regular screenings and vaccines. Ovarian cancer is less common but is often found late because its symptoms are not clear.
Male Reproductive Cancers
Male reproductive cancers mainly are prostate and testicular cancers. Prostate cancer is very common in men. Doctors recommend regular checks for men over a certain age.
Testicular cancer is rare but affects young men. It’s treatable if caught early.
The American Cancer Society offers great advice on screening and preventing reproductive cancers. For example, regular Pap smears can find cervical cancer early. Prostate cancer screening uses prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests.
| Type of Cancer | Common Risk Factors | Screening Methods |
| Cervical Cancer | HPV infection, smoking | Pap smear, HPV test |
| Ovarian Cancer | Family history, genetic mutations | Pelvic exam, ultrasound |
| Prostate Cancer | Age, family history | PSA test, digital rectal exam |
| Testicular Cancer | Undescended testes, family history | Self-exam, ultrasound |
Early detection and awareness are key to managing reproductive system cancers. Knowing the risks and screening methods helps individuals take care of their health.
Blood and Lymphatic System Cancers
The blood and lymphatic system can get cancer, like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. These cancers affect different parts of the blood and lymphatic system. This leads to different symptoms and treatments.
Leukemia Types
Leukemia is a cancer of the blood cells. It happens when abnormal white blood cells grow too much. There are many types of leukemia, each affecting different blood cells.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): A fast-growing leukemia that affects lymphoid cells.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): A slow-growing leukemia that affects lymphoid cells.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): A fast-growing leukemia that affects myeloid cells.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): A slow-growing leukemia that affects myeloid cells.
The National Cancer Institute says, “Leukemia is a complex disease with various subtypes, each needing specific treatments.”
Lymphoma Types
Lymphoma starts in the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. There are two main types:
- Hodgkin Lymphoma: Has Reed-Sternberg cells.
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL): A group of lymphomas without Reed-Sternberg cells.
NHL can be split into subtypes based on cell type and other features. Knowing these subtypes helps doctors choose the best treatment.
Multiple Myeloma and Other Plasma Cell Neoplasms
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow. It causes anemia, bone pain, and infections. Plasma cell neoplasms include:
- Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS): A condition that can lead to multiple myeloma.
- Waldenström Macroglobulinemia: A rare lymphoma that makes too much IgM antibody.
Research is helping us understand these cancers better. This leads to better ways to diagnose and treat them.
Urinary System Cancers
The urinary system can get several types of cancer. Each one is different. These cancers can really affect your life and need quick medical help.
Kidney (Renal) Cancer
Kidney cancer, or renal cell carcinoma, is a big deal. It starts in the kidney’s lining. This is where waste moves from the blood to the urine.
Kidney cancer is more common in men. It’s linked to smoking, being overweight, and some genetic issues.
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is common in men, too. It’s linked to smoking, chemicals, and infections. You can find more about risk factors for bladder cancer online.
Signs of bladder cancer include blood in urine, painful urination, and needing to pee a lot. Catching it early is key to treating it well.
Urethral Cancer
Urethral cancer is less common than kidney or bladder cancer. It happens in the urethra, where urine leaves the body. Risk factors include irritation and infections.
Urethral cancer might cause bleeding, pain, or trouble peeing. Doctors use imaging and biopsies to diagnose it.
In summary, cancers of the urinary system, like kidney, bladder, and urethral cancers, are serious. Knowing the risks and symptoms is important. Early treatment can help patients a lot.
Endocrine System Cancers
Endocrine system cancers are tumors that affect hormone-producing glands. They can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance and health. We will look at the most common types of these cancers and their characteristics.
Thyroid Cancer: Most Common Endocrine Cancer
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine cancer, found in the thyroid gland. There are several types, including papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Each type has its own characteristics and outcomes.
According to the National Cancer Institute, thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men. It often happens between the ages of 25 and 65.
Types of Thyroid Cancer:
- Papillary thyroid cancer: The most common type, often treatable if detected early.
- Follicular thyroid cancer: Less common, but it can spread to other parts of the body.
- Medullary thyroid cancer: Originates from the parafollicular cells, which produce calcitonin.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer: A rare and aggressive form with a poorer prognosis.
Adrenal Gland Tumors
Adrenal gland tumors are rare and can be benign or malignant. They affect the adrenal glands, which produce hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. Functional tumors can cause hormonal imbalances, while non-functional tumors may not produce hormones but can cause problems due to their size and location.
| Type | Description | Hormonal Impact |
| Functional Tumors | Produce excess hormones | Cushing’s syndrome, Conn’s syndrome |
| Non-functional Tumors | Do not produce hormones | No hormonal impact, but can cause local symptoms |
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) are rare tumors that start in the pancreas. They can be functional, producing excess hormones, or non-functional. The symptoms and treatment depend on whether the tumor is functional or not and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
Pituitary Tumors and Parathyroid Cancers
Pituitary tumors occur in the pituitary gland, a small gland at the base of the brain. Most are benign and can cause hormonal imbalances. Parathyroid cancers are rare and affect the parathyroid glands, which regulate calcium levels in the blood.
Key Facts:
- Pituitary tumors can cause hormonal imbalances or visual disturbances.
- Parathyroid cancers can lead to hypercalcemia due to excess parathyroid hormone.
Nervous System and Brain Cancers
Brain and nervous system cancers include gliomas, meningiomas, and schwannomas. These tumors come from different brain and nervous system cells. Each type behaves differently and needs its own treatment plan.
Gliomas: Astrocytoma, Glioblastoma, and Oligodendroglioma
Gliomas start from the brain’s glial cells. They are split into types based on the cell and tumor grade.
- Astrocytomas come from astrocytes, a type of glial cell. They can be low-grade or high-grade (glioblastoma).
- Glioblastoma is the most aggressive glioma. It grows fast and is hard to treat.
- Oligodendrogliomas start from oligodendrocytes. They usually have a better outlook than astrocytomas.
Meningiomas and Schwannomas
Meningiomas grow from the meninges, which protect the brain and spinal cord. Most are benign and can be treated with surgery.
Schwannomas are benign tumors from Schwann cells. They cover nerve fibers and can appear in the brain.
Medulloblastomas and Other Embryonal Tumors
Medulloblastomas are very aggressive brain tumors that mostly hit kids. They start in the cerebellum.
Other embryonal tumors include PNETs and AT/RT. Both are rare and grow fast.
Spinal Cord Tumors
Spinal cord tumors can be benign or malignant. They grow inside the spinal cord or around it. Symptoms include pain, weakness, and changes in feeling.
| Tumor Type | Origin | Malignancy |
| Gliomas (Astrocytoma, Glioblastoma, Oligodendroglioma) | Glial cells | Variable |
| Meningiomas | Meninges | Mostly benign |
| Schwannomas | Schwann cells | Benign |
| Medulloblastomas | Cerebellum | Malignant |
| Spinal Cord Tumors | Spinal cord or surrounding tissues | Variable |
Rare and Specialized Cancer Types
Rare cancers face unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. They need special care. We’ll look at different rare cancers, like sarcomas, eye cancers, and cancers in children.
Sarcoma Varieties: Bone and Soft Tissue
Sarcomas are rare cancers found in bones and soft tissues. They make up about 1% of adult cancers but are more common in kids. There are over 70 types of sarcomas, each unique.
- Osteosarcoma: The most common bone sarcoma, found in long bones.
- Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Include types like liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma, found in fat and muscle.
Eye Cancers: Retinoblastoma and Ocular Melanoma
Eye cancers are rare but serious. They can affect vision and health. Two main types are:
- Retinoblastoma: A cancer of the retina, mainly in young children. Early detection is key.
- Ocular Melanoma: A melanoma in the eye, different from skin melanoma. It can affect the eye’s uvea.
Skin Cancers Beyond Melanoma
While melanoma is known, other skin cancers are also risky. These include:
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A rare and aggressive skin cancer that looks like a firm, painless nodule.
- Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP): A rare skin cancer that grows slowly but can spread if not treated.
Pediatric-Specific Cancers
Cancers in kids are different from adults, in type and treatment. Some rare cancers in kids are:
- Neuroblastoma: A cancer from immature nerve cells, common in young kids.
- Wilms Tumor: A kidney cancer mainly in kids, often diagnosed before age 5.
It’s vital to understand these rare cancers to improve care. We’re working on new treatments to help patients better.
Conclusion: Advancing Understanding of Cancer Diversity
Understanding the different types of cancer is key to improving research and treatment. As we learn more, we get closer to better care and health strategies.
New research and screening tools, like the Galleri test, are helping detect and treat cancer better. These steps help us understand cancer’s complexities and its role in research.
By learning more about cancer, we can create more effective treatments. This is vital for better patient care. We must keep investing in cancer research to find new ways to fight this disease.
As we learn more about cancer diversity, we can face the challenges of different cancer types. This leads to better health outcomes and a better life for patients everywhere.
FAQ
What are the main types of cancer?
Cancer types are based on where they start. This includes carcinomas, sarcomas, lymphomas, and leukemias.
How many kinds of cancer are there?
There are over 50 different types of cancer. Each has its own challenges in diagnosis and treatment.
What are the most common cancer types worldwide?
Worldwide, the most common cancers are breast, lung, colorectal, and prostate. They are big concerns for public health.
What is the difference between carcinomas, sarcomas, lymphomas, and leukemias?
Carcinomas start in epithelial cells. Sarcomas start in connective tissue. Lymphomas and leukemias affect the lymphatic system and blood cells.
What are the risk factors for different types of cancer?
Risk factors vary by cancer type. They include diet, lifestyle, genetics, and exposure to chemicals or radiation.
How are cancers of the digestive system diagnosed and treated?
Digestive system cancers, like esophageal and pancreatic, are hard to catch early. Treatment often includes surgery, chemo, and radiation.
What are the different types of lung cancer?
Lung cancer is split into non-small cell and small cell types. Each has its own treatment and outlook.
What are the reproductive system cancers in men and women?
Women’s reproductive cancers include cervical, ovarian, and endometrial. Men’s cancers include prostate and testicular cancers.
What are the cancers of the blood and lymphatic system?
Blood and lymphatic system cancers include leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. They affect blood cells, the lymphatic system, and plasma cells.
What are the rare and specialized cancer types?
Rare cancers include sarcomas and eye cancers like retinoblastoma. They need special attention due to their unique challenges.
How can understanding the different types of cancer improve patient outcomes?
Knowing about different cancers helps research and treatment. It leads to better care and health strategies.
What is the significance of cancer classification?
Cancer classification is key for diagnosis, treatment, and research. It helps pinpoint the cancer’s origin and develop targeted therapies.
Are there any cancers that start with the letter L?
Yes, cancers starting with L include leukemia, lymphoma, and laryngeal cancer.
Are there any cancers that start with the letter P?
Yes, cancers starting with P include pancreatic, prostate, and pituitary tumors.
References:
- National Cancer Institute. (2024). Types of cancer. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer























