The carotid arteries are key to our body’s health. They carry blood to the brain. A blockage can cause a stroke.Learn which side of the neck is the carotid artery. Understand that there is one on each side clearly.
The carotid arteries are found on both sides of the neck. They start in the upper chest and go up to the skull.
Knowing where and how the carotid artery works is important for heart health.
Key Takeaways
- The carotid arteries are located on both sides of the neck.
- They originate in the upper chest and travel upward toward the skull.
- The carotid arteries play a critical role in supplying blood to the brain.
- A blockage in the carotid arteries can lead to a stroke.
- Understanding the carotid artery’s location and function is vital for cardiovascular health.
Understanding the Carotid Artery: An Overview
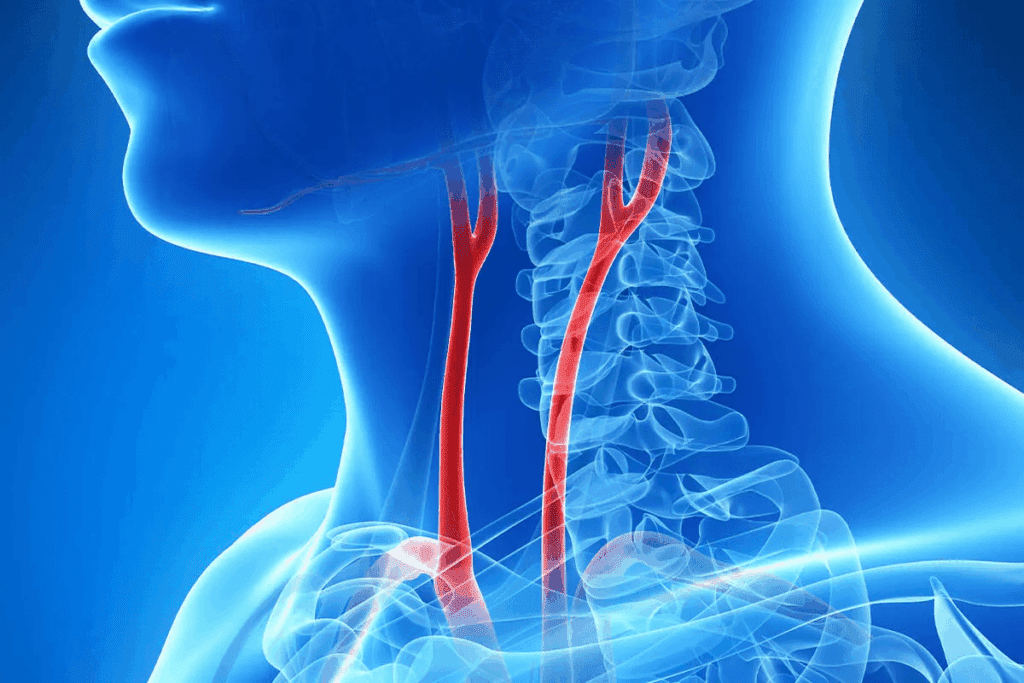
The carotid arteries are two major blood vessels in the neck. They are key for getting oxygen to the brain. This helps with thinking and moving.
Definition and Basic Function
The carotid artery starts at the aortic arch and goes up the neck. It brings oxygen-rich blood to the brain. It’s split into the common carotid artery and then into the internal and external carotid arteries.
Importance in Blood Supply to the Brain
The internal carotid artery is vital for the brain’s blood supply. It’s essential for the brain’s functions, like movement and thinking. Without it, serious brain problems can occur.
| Artery | Function | Area Supplied |
| Internal Carotid Artery | Supplies blood directly to the brain | Cerebral cortex, eyes |
| External Carotid Artery | Supplies blood to the face and neck | Face, neck, scalp |
| Common Carotid Artery | Precursor to internal and external carotid arteries | Neck |
Anatomy of the Carotid Artery System
Knowing the carotid artery’s anatomy is key for diagnosing and treating vascular diseases. This system is complex. It supplies blood to the brain, face, and neck.
Origin and Course
The carotid arteries start from the brachiocephalic trunk and the aortic arch. They go up the neck, in front of the prevertebral fascia. They are covered by the carotid sheath, along with the internal jugular vein and the vagus nerve. This setup is important for understanding their path.
Major Divisions and Segments
The carotid artery system splits into the common carotid artery. It then divides into the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery. The internal carotid artery mainly feeds the brain. The external carotid artery supplies the face and neck.
Relationship to Other Neck Structures
The carotid arteries are near other neck structures. These include the thyroid gland, trachea, and larynx. Knowing these relationships is essential for surgeries and tests in this area.
The Common Carotid Artery: Location and Structure
The common carotid artery is a key blood vessel. It starts differently on the left and right sides of the body. It’s vital for bringing oxygen-rich blood to the head and neck.
This artery is important for the brain, face, and neck. Knowing its structure and location helps us understand its role in blood flow.
Left Common Carotid Artery
The left common carotid artery comes straight from the aortic arch. This makes it unique compared to the right side. It’s key for blood to the left side of the head and neck.
This artery goes up the neck, behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It ends by splitting into the internal and external carotid arteries.
Right Common Carotid Artery
The right common carotid artery starts from the brachiocephalic trunk. This shows the difference in how blood reaches the head and neck.
Like the left artery, the right one also goes up the neck. It splits into the internal and external carotid arteries, serving the right side.
| Characteristics | Left Common Carotid Artery | Right Common Carotid Artery |
| Origin | Directly from the aortic arch | From the brachiocephalic trunk |
| Course | Ascends through the neck, posterior to sternocleidomastoid | Ascends through the neck, posterior to sternocleidomastoid |
| Termination | Divides into internal and external carotid arteries | Divides into internal and external carotid arteries |
The table shows the left and right common carotid arteries start differently. But they follow the same path and end the same way. This highlights their shared role in blood supply to the head and neck.
“The carotid arteries are vital for oxygen-rich blood to the brain. Any issue with them can cause serious brain problems.”
Which Side of the Neck is the Carotid Artery Located?
The carotid arteries are found on both sides of the neck. They are key for bringing blood to the brain. Knowing where they are is important for medical checks.
Bilateral Presence of Carotid Arteries
The carotid arteries are on both the left and right sides of the neck. This setup ensures blood keeps flowing to the brain, no matter what you’re doing.
These arteries work together to keep blood flowing to the brain. This is important to avoid brain problems if one artery gets blocked.
Anatomical Landmarks for Identification
Doctors use certain spots on the neck to find the carotid arteries. One key spot is the thyroid cartilage, or Adam’s apple.
To find the carotid arteries, doctors feel the neck just next to the Adam’s apple. This helps them check the carotid pulse.
Knowing where the carotid arteries are is key for diagnosing and treating blood vessel problems.
| Landmark | Description | Relevance to Carotid Artery |
| Thyroid Cartilage | Commonly known as the Adam’s apple, it is a prominent feature of the neck. | Used as a reference point to locate the carotid arteries. |
| Sternocleidomastoid Muscle | A large muscle that runs from the sternum to the clavicle and mastoid process. | The carotid arteries are located deep to this muscle. |
The Carotid Bifurcation: A Critical Junction
The carotid bifurcation is where the common carotid artery splits into the internal and external carotid arteries. This is key for blood flow to the brain and face. It’s a vital spot for doctors to know about.
Location of the Bifurcation
The carotid bifurcation is found at the top of the thyroid cartilage. It’s around the C3-C4 vertebrae level. This area is critical for medical professionals to spot during exams and surgeries.
Clinical Significance of the Carotid Sinus
The carotid sinus at the bifurcation is a baroreceptor. It senses blood pressure changes. It helps control heart rate and blood vessel tension. Its role in blood pressure regulation is important, and it can cause carotid sinus syndrome in some people.
| Characteristics | Internal Carotid Artery | External Carotid Artery |
| Primary Supply Area | Brain | Face and Neck |
| Branching Pattern | No branches in the neck | Multiple branches |
Internal Carotid Artery: Path and Function
The internal carotid artery is key to the brain’s blood supply. It brings oxygen-rich blood to vital brain areas. It starts at the carotid bifurcation, where the common carotid artery splits into two branches.
This artery goes up through the neck. It enters the carotid canal in the temporal bone. This path is vital for protecting the artery and ensuring it reaches the brain safely.
Course Through the Carotid Canal
The carotid canal is the artery’s path from the neck to the brain. Inside, it’s surrounded by nerves and veins. These are part of a complex network.
After leaving the carotid canal, the artery goes into the cavernous sinus. This is a venous area near the brain’s base. It then splits into branches that feed different brain parts.
Brain Regions Supplied by the Internal Carotid
The internal carotid artery supplies a big part of the brain. This includes the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes. Its branches, like the anterior and middle cerebral arteries, are essential for this.
| Brain Region | Arterial Supply |
| Frontal Lobe | Anterior Cerebral Artery |
| Parietal and Temporal Lobes | Middle Cerebral Artery |
The internal carotid artery is vital for brain health. Problems with it can cause serious brain issues. This shows how important it is for brain function.
External Carotid Artery and Its Branches
The external carotid artery branches off from the common carotid artery. It is key for blood flow to the face and neck. It brings oxygen-rich blood to many structures in these areas.
Major Branches Overview
The external carotid artery has several important branches. The facial artery supplies the front of the face. The maxillary artery gives blood to deeper face structures.
Other branches include the superior thyroid artery, lingual artery, and occipital artery. Each one serves a specific area of the head and neck.
Areas Supplied by the External Carotid
The external carotid artery and its branches cover a wide range. They supply blood to the face’s skin and muscles, as well as neck structures.
The facial artery is vital for the front face, including lips, nose, and cheeks. The maxillary artery supplies deeper areas like teeth, palate, and nasal cavity.
In short, the external carotid artery and its branches are critical. They ensure the face and neck receive the blood they need for health.
How to Locate Your Carotid Pulse
The carotid pulse is a key sign that’s easy to check. Knowing how to find it is important for health checks and heart health.
Safe Technique for Finding the Carotid Pulse
To find your carotid pulse, sit or stand comfortably. Put your index and middle fingers on your neck’s side, below the jaw and next to the windpipe. Press gently until you feel the pulse. Avoid using your thumb because it has its own pulse.
Gentle pressure is key. Too much can mess up your reading. Always check both sides of your neck, but not at the same time, to keep blood flowing to your brain.
Importance in Medical Assessments
Checking the carotid pulse is a key skill in medical checks. It shows heart rate and rhythm. Doctors often check it in emergencies or regular visits to check heart health.
“The carotid pulse is one of the most accessible and reliable indicators of cardiac function.” –
Medical Professional
In medical practice, the carotid pulse helps diagnose and watch heart conditions. It’s a simple yet powerful tool for guiding more medical tests and treatments.
Common Disorders of the Carotid Artery
The carotid artery can face several issues, like disease, atherosclerosis, stenosis, and dissection. These problems can cut down blood flow to the brain. This might lead to a stroke or other brain problems.
It’s key to know about these conditions early. This helps in getting the right treatment fast. We’ll look into each disorder in detail.
Carotid Artery Disease and Atherosclerosis
Carotid artery disease happens when the carotid arteries get narrowed or blocked. This is often because of atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up. This can reduce blood flow to the brain, raising the chance of a stroke.
Carotid Stenosis
Carotid stenosis is when the carotid artery gets too narrow. This usually happens because of atherosclerosis. How severe it is can vary, but it’s a big risk for stroke.
Carotid Dissection
Carotid dissection is when there’s a tear in the carotid artery’s wall. This can cause a stroke. It might happen because of an injury or some vascular conditions.
| Condition | Description | Risk Factors |
| Carotid Artery Disease | Narrowing/blockage due to plaque buildup | Atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, smoking |
| Carotid Stenosis | Narrowing of the carotid artery | Atherosclerosis, age, high cholesterol |
| Carotid Dissection | Tear in the carotid artery wall | Trauma, vascular conditions, connective tissue disorders |
Knowing the signs and risk factors of these carotid artery problems is important. It helps in getting medical help early. This can stop serious issues from happening.
Recognizing Symptoms of Carotid Artery Problems
Knowing the signs of carotid artery disease is key to getting the right treatment. The carotid arteries are vital for blood flow to the brain. Problems here can lead to serious health issues.
Warning Signs of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease symptoms often start with transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or mini-strokes. These can be signs of a stroke to come. Look out for these warning signs:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face or limbs, typically on one side of the body.
- Difficulty in speaking or understanding speech, which can be a sign of reduced blood flow to the brain.
- Sudden vision changes, including blurred vision or loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Dizziness or loss of balance, making it difficult to walk or stand.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or someone else shows any of these symptoms, get medical help right away. Waiting too long can lead to serious problems, like a stroke or even death.
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
| Sudden numbness or weakness | Reduced blood flow to the brain |
| Difficulty speaking or understanding speech | Impaired brain function due to carotid artery disease |
| Sudden vision changes | Potential stroke or TIA |
Early treatment of carotid artery disease can greatly lower stroke and heart disease risks. Knowing the signs and getting medical help fast is very important.
Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches for Carotid Artery Health
Managing carotid artery health requires modern tools and personalized plans. Doctors use various methods to find carotid artery disease. These include ultrasound, angiography, and other imaging to see how blocked the artery is.
Modern Diagnostic Techniques
Modern tools are key in finding carotid artery disease. Ultrasound is often used because it’s safe and shows images in real-time. Angiography gives detailed views but is more invasive. Other methods like MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography) and CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography) are also used for their accuracy.
| Diagnostic Technique | Description | Advantages |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive imaging using sound waves | Real-time imaging, safe, and cost-effective |
| Angiography | Invasive imaging using contrast dye | High detail, accurate stenosis assessment |
| MRA | Non-invasive imaging using magnetic fields | No radiation, detailed images |
Medical and Surgical Interventions
Treatment for carotid artery disease varies. Doctors might prescribe antiplatelet therapy and statins to manage risk. Surgery options include carotid endarterectomy and angioplasty with stenting to keep the artery open.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Changing your lifestyle is key to preventing carotid artery disease. Quit smoking, exercise, and eat a healthy diet. It’s also important to manage hypertension and diabetes.
Health experts say, “Prevention is key in managing carotid artery health. Early detection and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular events.”
Conclusion: The Vital Role of Carotid Arteries in Health
The carotid arteries are key to our health, carrying blood to the brain. Keeping them healthy is vital to avoid strokes and heart problems. It’s important to understand how these arteries work to see their role in heart health.
It’s critical to keep the carotid arteries in good shape for our overall health. Issues like carotid artery disease and atherosclerosis can cause big problems if not treated. Regular health checks and a healthy lifestyle can help prevent these issues.
The role of carotid arteries in our health is huge. By watching for signs of trouble and getting medical help when needed, we can protect our heart health. The importance of these arteries in supplying blood to the brain shows why we must take care of them.
FAQ
Where is the carotid artery located?
The carotid arteries are on both sides of the neck. They are key in sending blood to the brain.
What is the function of the carotid artery?
The carotid arteries send oxygen-rich blood to the brain, face, and neck.
What are the different parts of the carotid artery?
The carotid artery system has the common carotid artery. It splits into the internal and external carotid arteries.
What is the difference between the internal and external carotid arteries?
The internal carotid artery goes to the brain. The external carotid artery goes to the face and neck.
How can I locate my carotid pulse?
To find your carotid pulse, press your fingers on your neck’s side. Do this just below the jawline and feel for the pulse.
What are the symptoms of carotid artery disease?
Symptoms include dizziness, weakness, numbness, or trouble speaking. These signs can warn of a stroke.
What is carotid stenosis?
Carotid stenosis is when the carotid artery narrows due to plaque. It raises the risk of stroke.
How is carotid artery disease diagnosed?
Doctors use tests like ultrasound, CT angiography, or MRI angiography to diagnose it.
What are the treatment options for carotid artery disease?
Treatments include lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and surgeries like carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty.
Can carotid artery disease be prevented?
Yes, it can be prevented or managed with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and not smoking.
What is the significance of the carotid sinus?
The carotid sinus is vital for controlling blood pressure. Its problems can cause heart issues.
What are the branches of the external carotid artery?
The external carotid artery has branches for the face, neck, and scalp. These include the maxillary artery, superficial temporal artery, and occipital artery.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546613/



































