Did you know a simple CBC blood test can tell a lot about your health? It’s a common test used to find blood disorders. It checks different parts of blood, like red and white blood cells and platelets. CBC blood test measures the number, size, and quality of these cells, including hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Doctors use this test to detect conditions such as anemia, infections, and blood cancers. Because the CBC blood test provides comprehensive information about your blood, it is one of the most frequently ordered laboratory tests for overall health assessment and diagnosis.
A CBC test is key in finding health problems. Doctors use it to spot issues like anemia, infections, and leukemia. We’ll look at whyCBC blood tests are important in healthcare.
Key Takeaways
- A CBC is a diagnostic tool used to detect various blood disorders.
- It measures different components of blood, including red and white blood cells and platelets.
- CBC tests help identify health conditions like anemia, infection, and leukemia.
- Understanding CBC results is key for accurate medical diagnosis.
- CBC tests are a vital tool in healthcare, giving insights into overall health.
The Fundamentals of Blood Disorders
Blood disorders are complex and need a deep understanding. They can greatly affect a person’s health and life quality. This section discusses the main types of blood disorders, their health impacts, and early signs to watch for.
Common Categories of Blood Disorders
Blood disorders include anemia, infection, leukemia, and more. Anemia is when you don’t have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin, causing tiredness and weakness. Leukemia is cancer that affects white blood cells, making it hard to fight off infections.
| Disorder Category | Description | Common Symptoms |
| Anemia | Deficiency in red blood cells or hemoglobin | Fatigue, weakness, pale skin |
| Infection | Presence of pathogens in the blood | Fever, chills, confusion |
| Leukemia | Cancer affecting white blood cells | Frequent infections, fatigue, weight loss |
How Blood Disorders Affect Health
Blood disorders can deeply affect your health. For example, anemia can reduce oxygen to tissues, causing tiredness and shortness of breath. Leukemia can weaken the immune system, making you more prone to infections.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to know the early signs of blood disorders. Common symptoms include tiredness, frequent infections, and unexpected weight loss. Spotting these signs early can help get medical help quickly.
We will look at how doctors diagnose and manage blood disorders next. This will help us understand how these conditions are found and treated.
The CBC Blood Test: Primary Tool for Detecting Blood Disorders
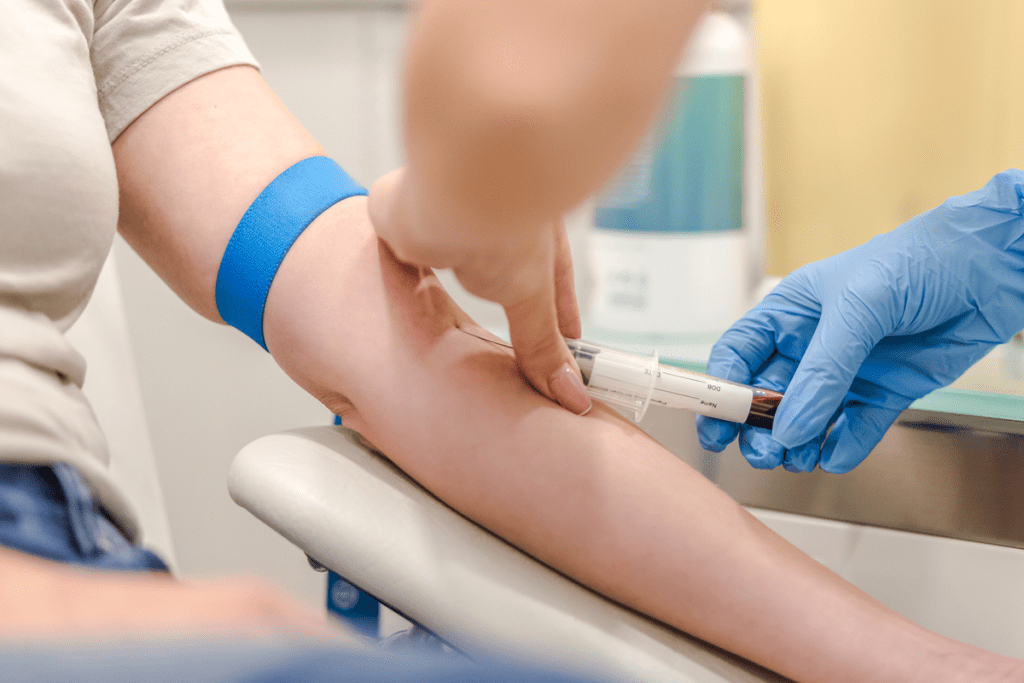
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is key for finding blood disorders. It checks the blood’s parts, like red and white cells, and platelets. Knowing about the CBC test helps doctors diagnose and treat health issues.
What CBC Stands For and Its Purpose
CBC means Complete Blood Count. It’s a test that looks at blood parts to check health and find problems. It helps doctors see if you have anemia, infection, or leukemia. This test is important for understanding your blood health.
How CBC Tests Are Performed
A CBC test takes blood from your arm vein. Then, the blood goes to a lab for checking. It looks at red and white cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and hematocrit levels. This gives doctors a quick look at your blood health.
Comparing Standard CBC vs. CBC with Differential
A standard CBC gives a basic blood overview. But, a CBC with differential shows more about white blood cells. This helps find specific problems, like infections or allergies. Knowing the difference helps doctors make better treatment plans.
Doctors use CBC test results to understand your health. This helps them decide on more tests, treatments, and how to manage blood disorders.
Key Components Measured in a Complete Blood Count
The CBC test checks several important blood cell measurements. These measurements help understand an individual’s health. They also help diagnose different conditions.
Red Blood Cell Count and Indices (RBC, Hgb, Hct, MCV, MCH, MCHC)
Red Blood Cell (RBC) count shows how many red blood cells are in the blood. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the body. The CBC test also looks at other RBC-related indices.
- Hemoglobin (Hgb): measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood, which is essential for oxygen transport.
- Hematocrit (Hct): represents the proportion of blood volume that is occupied by red blood cells.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): indicates the average size of red blood cells.
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH): measures the average amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell.
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC): measures the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
These indices help diagnose various types of anemia and other red blood cell disorders.
White Blood Cell Count and Types
The White Blood Cell (WBC) count shows how many white blood cells are in the blood. White blood cells are key to fighting infections. A CBC test with differential also identifies different white blood cell types.
- Neutrophils
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
Abnormalities in WBC count or types can indicate infections, inflammatory conditions, or immune disorders.
Platelet Count and MPV
The Platelet count measures the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets are vital for blood clotting and preventing excessive bleeding. The Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) measures the average size of platelets, which can indicate platelet production and destruction disorders.
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit Values
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit values are critical in assessing the health of red blood cells. Low hemoglobin or hematocrit levels can indicate anemia, while high levels may suggest dehydration or other conditions.
CBC with Differential: Detailed Analysis of White Blood Cells
The CBC with differential test checks white blood cells, key for spotting infections and diseases. These cells help fight off infections and give clues about our health.
The Five Types of White Blood Cells Measured
This test looks at five types of white blood cells: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type has its own job and reacts differently to health issues.
- Neutrophils: Mainly fight off bacterial infections.
- Lymphocytes: Important in fighting viruses and keeping the immune system balanced.
- Monocytes: Turn into macrophages, which clean up and destroy harmful cells and germs.
- Eosinophils: Help fight parasites and are involved in allergic reactions.
- Basophils: Play a role in inflammation, mainly in allergic responses.
Normal Ranges for Each WBC Type
Knowing the normal ranges for each white blood cell type is key to understanding CBC with differential results. These ranges can vary but generally are:
| Type of WBC | Normal Range (%) |
| Neutrophils | 45-75 |
| Lymphocytes | 20-45 |
| Monocytes | 5-10 |
| Eosinophils | 1-4 |
| Basophils | <1 |
What Abnormal Differential Results Indicate
Abnormal results can point to different health issues. For example, more neutrophils might mean a bacterial infection. More lymphocytes could hint at a viral infection or a problem with the immune system.
Neutrophilia often shows up in bacterial infections, inflammation, and stress. Lymphocytosis is linked to viral infections, like mononucleosis, and some types of cancer.
Manual vs. Automated Differential Analysis
CBC with differential tests can be done manually or automatically. Automated systems give fast and accurate results most of the time. But, manual counts are needed for complex or unusual cases.
We mix automated and manual analysis for the best results. Automated systems are quick, but human experts are needed for tricky cases.
Anemia Detection Through CBC Testing
CBC tests help doctors understand anemia by looking at blood components. Anemia happens when there’s not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. This makes it hard for tissues to get enough oxygen. CBC tests are key in finding out what kind of anemia someone has.
Iron Deficiency Anemia Markers
Iron deficiency anemia is very common. It shows up in CBC tests as low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. The mean corpuscular volume (MCV) is also low, meaning the red blood cells are small. The red blood cell distribution width (RDW) is often high, showing that the red blood cells are not all the same size.
Key markers for iron deficiency anemia:
- Low Hgb and Hct levels
- Decreased MCV
- Elevated RDW
Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency Indicators
Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies cause megaloblastic anemia. This is when red blood cells are too big. CBC tests show an MCV that’s too high, meaning the red blood cells are large. Other signs include a low red blood cell count and a high RDW.
| Parameter | Normal Range | Vitamin B12/Folate Deficiency |
| MCV | 80-100 fL | Increased (>100 fL) |
| RBC Count | 4.32-5.72 million cells/μL | Decreased |
| RDW | 11.8-14.5% | Elevated |
Hemolytic Anemia Signs
Hemolytic anemia is when red blood cells break down too fast. CBC tests show a high reticulocyte count, which means the bone marrow is working hard to make more red blood cells. Other signs include a high lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level and low haptoglobin.
Aplastic Anemia Patterns
Aplastic anemia is rare and means the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. CBC tests show low counts of all blood cells: red, white, and platelets.
CBC findings in aplastic anemia:
- Pancytopenia
- Low reticulocyte count
- Decreased WBC and platelet counts
Detecting Blood Cancers with CBC Blood Tests
Blood cancers like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma can be found with CBC blood tests. These tests give vital info for diagnosis and treatment. We’ll see how CBC tests spot these conditions.
Leukemia Warning Signs in CBC Results
Leukemia affects the white blood cells. A CBC test can show abnormal white blood cell counts. This might mean leukemia. We look for:
- Elevated white blood cell count
- Presence of blast cells
- Anemia or low red blood cell count
- Thrombocytopenia or low platelet count
Lymphoma Indicators
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system. CBC results alone can’t diagnose lymphoma. But, some signs can hint at its presence. These include:
- Abnormal lymphocyte count
- Presence of atypical lymphocytes
- Anemia or low red blood cell count
Multiple Myeloma Markers
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow. CBC tests can show signs of multiple myeloma. These signs are:
- Anemia or low red blood cell count
- Elevated calcium levels
- Renal impairment
To understand CBC results and blood cancers better, let’s look at a table:
| Blood Cancer | CBC Indicators |
| Leukemia | Elevated WBC count, presence of blast cells, anemia, thrombocytopenia |
| Lymphoma | Abnormal lymphocyte count, atypical lymphocytes, anemia |
| Multiple Myeloma | Anemia, elevated calcium levels, renal impairment |
| Myelodysplastic Syndrome | Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, abnormal cell morphology |
Myelodysplastic Syndrome Patterns
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a group of disorders with poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells. CBC tests can show patterns that might mean MDS. These include:
- Anemia or low red blood cell count
- Neutropenia or low white blood cell count
- Thrombocytopenia or low platelet count
- Abnormal cell morphology
In conclusion, CBC blood tests are key in finding blood cancers like leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and myelodysplastic syndrome. By checking different blood parts and features, doctors can spot odd patterns. These patterns might show the presence of these conditions.
Infection and Inflammation Markers in CBC Results
Infection and inflammation markers in CBC test results give us important health insights. When the body finds an invader or gets hurt, it gets inflamed. The CBC test shows the changes in blood cell counts that happen then.
Elevated White Blood Cell Count Interpretation
An elevated white blood cell (WBC) count means the body is fighting off an infection or inflammation. We look at the WBC count to see how serious it is. This helps us decide what tests or treatments are needed.
The normal WBC count is between 4,500 and 11,000 cells per microliter. If it’s higher, it could mean a bacterial infection, inflammation, or stress on the body.
Neutrophilia vs. Lymphocytosis
Neutrophilia is when there are more neutrophils, a type of WBC, often due to bacterial infections. Lymphocytosis is when there are more lymphocytes, which can happen with viral infections or long-term inflammation.
Knowing the difference between neutrophilia and lymphocytosis helps us figure out why the WBC count is high.
Eosinophil and Basophil Abnormalities
Eosinophils and basophils are WBCs that help fight infection and inflammation. Eosinophilia means there are more eosinophils, which can be due to parasites or allergies. Basophilia is less common but can show up in certain blood disorders.
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammatory Patterns
CBC results can tell us if the inflammation is acute or chronic. Acute inflammation has a sudden rise in WBC count, mainly neutrophils, in response to a quick threat like a bacterial infection.
Chronic inflammation has a longer-lasting increase in WBC count, often with changes in lymphocytes or monocytes.
| Inflammatory Pattern | WBC Count Characteristics | Common Causes |
| Acute Inflammation | Sudden increase in neutrophils | Bacterial infections |
| Chronic Inflammation | Sustained elevation in lymphocytes or monocytes | Viral infections, autoimmune diseases |
Bleeding and Clotting Disorders Revealed by CBC
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) test can show important details about bleeding and clotting disorders. It helps find conditions that affect how the body stops bleeding or forms clots. The CBC looks at different parts of the blood, like platelets, which are key in clotting.
A CBC test gives insights into clotting and stopping bleeding. If the results are off, it might mean there’s a problem with bleeding or clotting. This could be due to genes, medicines, or health issues.
Thrombocytopenia: Causes and Implications
Thrombocytopenia is when you have too few platelets, leading to bleeding issues. The CBC checks platelet count to spot thrombocytopenia. It can be caused by bone marrow problems, some medicines, or autoimmune diseases.
Causes and Symptoms: Thrombocytopenia can come from many things, like bone marrow failure or leukemia. Symptoms include easy bruising, nosebleeds, and bleeding that won’t stop after injuries.
Thrombocytosis and Thrombocythemia
Thrombocytosis is when you have too many platelets. It might not cause symptoms but can raise the risk of blood clots. Thrombocythemia is a specific type of thrombocytosis with very high platelet counts, often from bone marrow issues.
Implications: Thrombocytosis and thrombocythemia can increase the chance of blood clots. It’s important to watch and manage them to avoid serious problems.
Von Willebrand Disease Indicators
Von Willebrand disease is a genetic disorder that makes it hard for blood to clot. A CBC isn’t definitive for diagnosing it but can hint at it, like a low platelet count or other blood component issues.
Diagnostic Clues: A CBC might suggest more tests, like von Willebrand factor antigen and activity assays, to confirm von Willebrand disease.
Hemophilia Markers
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that makes it hard for blood to clot, leading to long bleeding. A CBC isn’t used to directly diagnose hemophilia but can show how well blood clots and suggest related conditions.
Further Testing: To diagnose hemophilia, specific clotting factor assays are needed. A CBC can help decide if these tests are necessary.
Interpreting CBC Test Results: Normal vs. Abnormal Values
Understanding CBC test results is key. We look at normal and abnormal values, and consider age and gender. Each part of the CBC test gives us clues about a patient’s health.
Standard Reference Ranges for All CBC Components
Knowing the standard ranges for CBC components is vital. These ranges help us see if a patient’s results are normal or not. For example, a normal white blood cell count is between 4,500 to 11,000 cells per microliter. It’s important to use these ranges to make sure our results are correct.
Slight vs. Significant Deviations
We look at CBC results to find out if they are slightly off or way off. Small changes might not be a big deal and could just need watching over time. But big changes could mean there’s something serious going on, like an infection.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender play a big role in CBC results. For example, men usually have more hemoglobin than women. And as we get older, our white blood cell counts can change. We consider these factors to make sure we’re reading the results right. For example, kids and pregnant women have different results because of their bodies’ changes.
When to Be Concerned About Results
So, when should we worry about CBC test results? We should worry if the results are way off from normal, and if the person is feeling sick or has a history of blood problems. For example, a very low platelet count could mean a risk of bleeding. Or a very high white blood cell count could mean leukemia or another serious disease. It’s always best to talk to a doctor about any worries we have.
When Your Doctor Orders Additional Blood Tests Beyond CBC
Doctors might order more blood tests than just the CBC to understand your health better. These tests can spot many conditions, like blood disorders, infections, and inflammatory diseases.
Peripheral Blood Smear Examination
A peripheral blood smear looks at blood under a microscope. It checks for odd shapes or sizes in blood cells. This can show health problems.
This test can find signs of anemia, infections, or blood cancers. It helps doctors understand what’s causing your symptoms.
Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration
Bone marrow biopsies and aspirations take samples from your bone marrow. They help find and track diseases like leukemia or lymphoma.
In a biopsy, doctors remove bone marrow to check for odd cell growth. Aspiration takes liquid from the bone marrow for analysis.
Specialized Coagulation Studies
Coagulation studies check how well your blood clots. They’re key for diagnosing bleeding disorders or clotting risks.
Tests like prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) are common. They show how well your blood clots and help spot problems.
Genetic and Molecular Testing
Genetic and molecular tests look for specific genetic changes in your blood. They help find genetic disorders, cancer-causing genes, or check treatment success.
Tests like PCR and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are used. They give insights into your genetic makeup and guide treatment.
| Additional Blood Test | Purpose | Conditions Diagnosed or Monitored |
| Peripheral Blood Smear Examination | Examine blood cells for abnormalities | Anemia, infection, blood cancers |
| Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration | Analyze bone marrow for abnormal cell growth | Leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma |
| Specialized Coagulation Studies | Assess blood clotting mechanisms | Bleeding disorders, thrombosis risk |
| Genetic and Molecular Testing | Identify genetic mutations or molecular markers | Genetic disorders, cancer, treatment monitoring |
Preparing for Your CBC Blood Test
To get the most out of your CBC blood test, it’s essential to know how to prepare. A Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is a key tool for healthcare providers. It helps them check your health and find issues like anemia or leukemia. Preparing right can lead to accurate results and a better testing experience.
Fasting Requirements and Restrictions
One common question is whether fasting is required before a CBC blood test. Generally, fasting is not necessary for a CBC test. This is because it checks your blood’s different parts, like red and white cells and platelets. But, if your CBC is part of a bigger blood workup, you might need to fast for 8-12 hours.
It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s specific instructions. Some foods or medications can change test results. So, it’s best to ask your doctor about any doubts.
Medications That May Affect Results
Certain medications can change your CBC results. For example, some drugs can affect white blood cell counts or platelet production. It’s key to tell your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you’re taking. This includes:
- Antibiotics
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressants
Your doctor will tell you if you should keep taking these medications or make any changes before your test.
The Blood Collection Process
The blood collection for a CBC test is quick and simple. Here’s what you can expect:
- A healthcare professional will clean the area where the blood will be drawn, usually the inside of your elbow.
- A tourniquet may be applied to make the veins more visible.
- A sterile needle is inserted into a vein, and a small amount of blood is drawn into a tube.
- The needle is removed, and pressure is applied to the puncture site to stop any bleeding.
Potential Complications and Side Effects
While CBC blood tests are safe, some people might feel minor side effects. These can include:
- Bruising or soreness at the needle site
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting (rare)
If you often faint during blood draws, tell the healthcare professional. They can help make you more comfortable.
Understanding CBC blood test preparation can make your experience better. If you have any questions or concerns, always ask your healthcare provider for help.
Factors That Can Skew CBC Test Results
Many things can change CBC test results. This includes what medicines you take and how hydrated you are. Knowing these can help make sure the test results are right.
Impact of Medications and Supplements
Some medicines and supplements can really change CBC test results. For example, medicines that prevent blood from clotting can change how platelets work. Certain antibiotics can also change white blood cell counts. Always tell your doctor about any medicines or supplements you’re taking before a CBC test.
Examples of medications that can affect CBC results include:
- Anticoagulants, which can affect platelet count
- Corticosteroids, which can increase white blood cell count
- Chemotherapy drugs, which can decrease blood cell counts
Dehydration and Hydration Status
Being dehydrated can make your blood seem thicker. This can make hemoglobin and hematocrit seem higher than they are. On the other hand, being too hydrated can make your blood seem thinner. This can make these values seem lower. It’s important to stay hydrated before a CBC test.
“Proper hydration is key for accurate CBC test results. Dehydration can make hemoglobin and hematocrit seem too high. Too much water can make them seem too low.”
Recent Physical Activity or Stress
Doing a lot of exercise or feeling stressed can change CBC results. Hard exercise can change white blood cell counts. Stress can affect different blood cells. Try to avoid hard exercise before a CBC test.
Altitude and Environmental Factors
High altitudes and some environmental factors can also change CBC results. At high altitudes, your body might make more red blood cells. This can affect hemoglobin and hematocrit values. Exposure to certain toxins can also change blood cell counts.
| Factor | Potential Impact on CBC Results |
| Medications (e.g., anticoagulants) | Affect platelet count and function |
| Dehydration | Falsely elevated hemoglobin and hematocrit |
| Recent Physical Activity | Temporary changes in white blood cell count |
| High Altitude | Increased red blood cell production |
Understanding these factors is key for doctors to correctly read CBC test results. This helps them make the best decisions for patient care.
Conclusion: The Critical Role of CBC Testing in Blood Disorder Management
CBC testing is key in finding and managing blood disorders. It helps doctors see a patient’s health by checking for things like anemia, infections, and leukemia.
We’ve looked at what a CBC includes, like red and white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin. Knowing these details is important for correct diagnosis and treatment plans.
CBC testing gives a full picture of a patient’s blood health. Doctors can spot problems and plan treatments. It also helps track how blood disorders change over time and adjust treatments as needed.
In managing blood disorders, CBC testing is essential. It helps doctors make smart choices, giving patients the best care. As medical tech gets better, CBC testing will keep being a big help in diagnosing and treating blood-related issues.
FAQ
What is a CBC blood test, and what does it measure?
A CBC (Complete Blood Count) test checks different parts of the blood. It looks at red and white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. This test helps doctors find health problems like anemia, infections, and leukemia.
What is the difference between a standard CBC test and a CBC with differential?
A standard CBC counts all white blood cells. A CBC with differential counts specific types of white blood cells. This gives more info on how the immune system is working.
What are the normal ranges for CBC components, and how are they interpreted?
Normal CBC ranges change with age, gender, and other factors. Doctors compare CBC results to standard ranges. They also look at the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
Can a CBC test detect blood cancers, such as leukemia?
Yes, a CBC can spot blood cancer signs like leukemia. But, more tests like bone marrow biopsies are needed for a sure diagnosis.
How does a CBC test help diagnose anemia, and what are the different types of anemia?
A CBC test finds anemia by checking red blood cells, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. It can show different anemia types like iron or vitamin B12 deficiency, and hemolytic anemia.
What factors can affect CBC test results, and how can they be minimized?
Things like dehydration, exercise, and some medicines can change CBC results. To avoid this, follow pre-test instructions like fasting and avoiding hard exercise.
When is a CBC with differential test ordered, and what does it indicate?
A CBC with differential is for more detailed immune system info. It shows signs of infections, inflammation, or allergies.
Can a CBC test detect bleeding or clotting disorders?
Yes, a CBC can find signs of bleeding or clotting problems. This includes issues like thrombocytopenia or thrombocytosis.
How often should I have a CBC test, and why is it important for my health?
CBC test frequency depends on your health needs. Regular tests help monitor chronic conditions, catch issues early, and prevent problems.
Are there any risks or complications associated with CBC blood tests?
CBC tests are usually safe. But, some might get minor issues like bruising or dizziness. Serious problems are rare, but tell your doctor about any worries.
References
MSD Manuals. (2025). Laboratory Tests for Blood Disorders.
https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/blood-disorders/symptoms-and-diagnosis-of-blood-disorders/laboratory-tests-for-blood-disorders



































