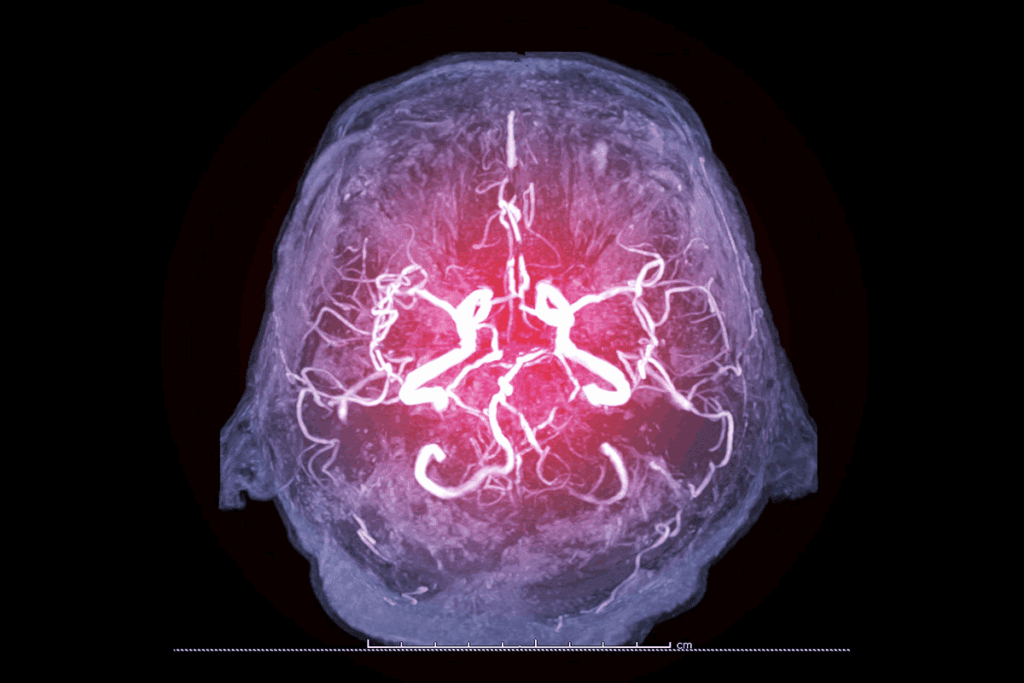
Cerebrovascular diseases encompass various conditions that damage the brain’s blood vessels. This essential guide covers the 4 main cerebrovascular diseases. Learn the differences between stroke, TIA, and aneurysms.
We’re looking at four main conditions: ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), and cerebral aneurysm. These issues affect blood flow to the brain and require immediate medical care.
It’s important to understand these conditions to prevent and treat them effectively. We’ll give you an overview of their importance and how they affect global health.
Key Takeaways
- Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel is blocked.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by bleeding in the brain.
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary disruption of blood flow.
- Cerebral aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel that can rupture.
- Prompt medical treatment is crucial for these conditions.
Overview of Cerebrovascular Diseases
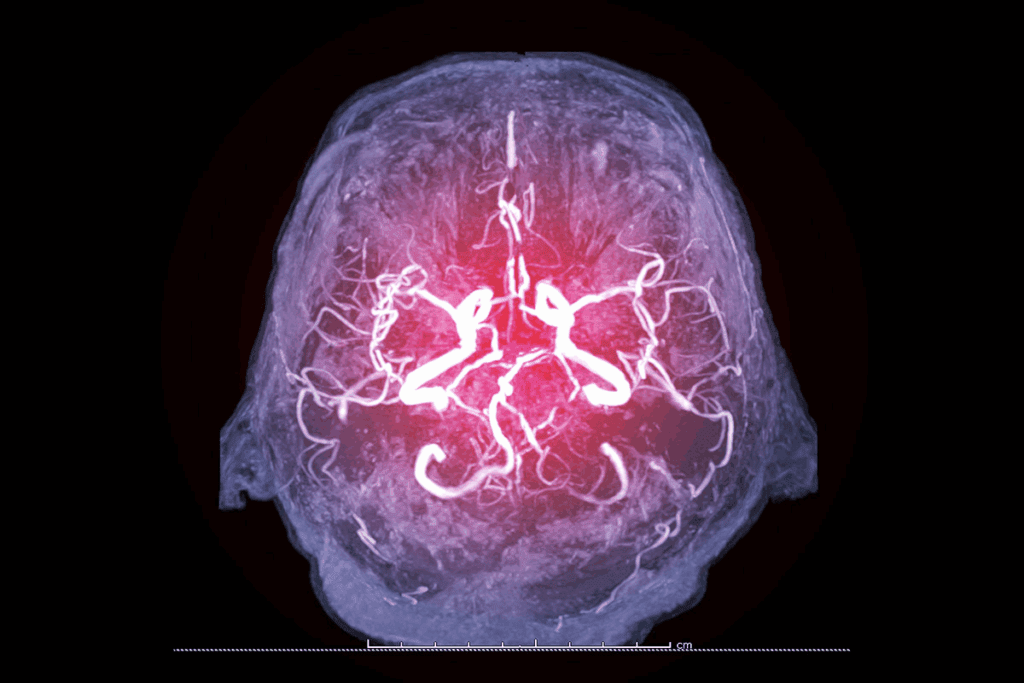
Cerebrovascular diseases pose a significant threat to public health. They affect the blood vessels that supply the brain. This can lead to less oxygen and damage to the brain. Stroke is the most common condition and a major cause of death and disability.
Definition and Medical Significance
Cerebrovascular diseases encompass various conditions that damage the brain’s blood vessels. These can cause significant neurological deficits, affecting a person’s life quality. The damage can be permanent, making quick medical help crucial.
It’s important for both doctors and the public to understand cerebrovascular diseases. Knowing about them helps in taking preventive measures and getting timely treatment. This can help reduce the number of cases and their effects.
Global Prevalence and Impact
Cerebrovascular diseases have a big impact on health worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) says stroke causes millions of deaths each year. It’s a leading cause of death globally.
“The global burden of cerebrovascular disease is substantial, requiring comprehensive strategies for prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation.”
These diseases affect not just individuals but also families and communities. The cost to healthcare and lost productivity is huge. So, it’s important to spread awareness and work on stroke prevention to lessen their impact.
- Cerebrovascular diseases pose a significant threat to public health.ility worldwide.
- The economic and social burden of these conditions is substantial.
- Awareness and prevention are key to reducing the impact of cerebrovascular diseases.
The Brain’s Vascular System
The brain’s blood vessels are key to its function. They form a complex network that brings oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
Anatomy of Cerebral Blood Vessels
The brain gets its blood from two main arteries: the carotid and vertebral arteries. The carotid arteries feed the front two-thirds of the brain. This area handles motor control, language, and thinking.
The vertebral arteries supply the back third of the brain. This includes the cerebellum and brainstem. They are vital for balance and controlling basic functions.
The carotid and vertebral arteries join at the Circle of Willis. This circle is at the brain’s base. It helps spread blood across the brain. Knowing about these blood vessels is key for treating brain diseases.
Normal Blood Flow to the Brain
The brain needs a lot of blood to work and survive. It gets about 15% of the body’s blood, even though it’s only 2% of its mass. This is because the brain is very active and needs constant oxygen and nutrients.
Blood flows into the brain through arteries. It then goes through capillaries, where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged. The deoxygenated blood is then carried away by veins.
| Artery | Region Supplied | Function |
| Carotid Arteries | Front two-thirds of the brain | Motor control, language, cognitive functions |
| Vertebral Arteries | Back third of the brain (cerebellum and brainstem) | Coordination, balance, vital functions |
Understanding how blood flows to the brain is crucial. It helps us see how brain diseases affect us. Keeping the brain’s blood vessels healthy is very important.
Ischemic Stroke: The First Major Cerebrovascular Disease
Ischemic stroke happens when a blood clot blocks an artery to the brain. It’s a big problem worldwide, causing about 80% of all strokes.
Mechanism of Blood Blockage
A blood clot forms in an artery, causing ischemic stroke. This clot can start in the brain or come from the heart. It gets stuck in a smaller artery, called embolism.
Clot formation can be caused by atrial fibrillation or atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis makes arteries narrow and hard, making them more likely to block.
Types of Ischemic Strokes
Ischemic strokes are mainly two types: thrombotic and embolic.
- Thrombotic strokes happen when a clot forms in a brain artery.
- Embolic strokes occur when a clot from elsewhere reaches the brain.
Immediate and Long-term Effects
An ischemic stroke cuts off oxygen and nutrients to brain cells, causing death. The long-term effects depend on the stroke’s severity and where it happens.
Common long-term effects include:
- Physical disabilities like paralysis or weakness.
- Cognitive problems like memory and language issues.
- Emotional changes like depression or anxiety.
Knowing about ischemic stroke is key for prevention and treatment. Recognizing risk factors and symptoms helps get timely medical help. This can lessen the stroke’s impact.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: The Second Major Cerebrovascular Disease
A blood vessel in the brain bursting can cause a hemorrhagic stroke. This is a serious emergency. Hemorrhagic strokes are less common but can be more deadly because of the brain bleeding.
Understanding Vessel Rupture
Many things can cause a brain vessel to rupture. High blood pressure, aneurysms, or arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are some. The rupture leads to bleeding in or around the brain, harming brain tissue.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage happens when bleeding goes directly into the brain. This can cause a lot of damage. It’s often linked to hypertension. Symptoms include sudden headache, weakness, and loss of consciousness.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is when bleeding happens in the space around the brain. It’s usually due to an aneurysm rupture. Symptoms include a sudden, severe headache, often called “the worst headache of my life.”
Knowing about hemorrhagic stroke causes and types is important. It helps in prevention and treatment. Managing risks like hypertension is crucial to lower hemorrhagic stroke rates.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): The Third Major Cerebrovascular Disease
When someone has a Transient Ischemic Attack, it’s a sign they need help fast. A TIA, or “mini stroke,” is when brain blood flow stops briefly. It causes symptoms like a stroke but doesn’t leave lasting damage.
The “Mini Stroke” Explained
A TIA happens when brain blood flow stops for a short time. It causes symptoms like a stroke but they don’t last long. These symptoms can include weakness, trouble speaking, vision changes, dizziness, or losing balance.
Duration and Recovery
TIAs don’t last long, which is why they’re called “mini strokes.” Most people get better quickly. But, having a TIA means you’re at risk for a bigger stroke.
TIA as a Warning Sign
TIAs are a big deal because they warn of a possible major stroke.
“Time is brain” when it comes to TIAs and strokes. The sooner you act, the better your chances of preventing a major stroke.
Knowing the risks and symptoms of a TIA is key to staying safe. By controlling blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol, and living a healthy life, you can lower your risk of a TIA or stroke.
Cerebral Aneurysm: The Fourth Major Cerebrovascular Disease
A cerebral aneurysm is a bulge in a brain blood vessel. It can burst and cause a hemorrhagic stroke. This is a serious health issue, especially if it leads to subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Formation of Arterial Bulges
Cerebral aneurysms happen when an artery wall weakens. This can be due to genetics, high blood pressure, or atherosclerosis. The weakened area bulges, forming an aneurysm.
This bulge is caused by inflammation and damage to the artery wall. Knowing how this happens helps us find better ways to prevent and treat it.
Types of Cerebral Aneurysms
Cerebral aneurysms are classified by their location, shape, and size. The main types are:
- Saccular aneurysms, which are round and the most common.
- Fusiform aneurysms, which are longer and more diffuse.
- Dissecting aneurysms, caused by a tear in the artery wall.
Each type affects the risk of rupture and treatment options differently.
Rupture Risk and Consequences
When a cerebral aneurysm bursts, it causes subarachnoid hemorrhage. This is a serious condition that needs quick medical help. The risk depends on the aneurysm’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
It’s crucial for patients and doctors to understand the risks of aneurysm rupture. This helps in making the right treatment choices. Options include surgery or watching and waiting.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment are key to avoiding severe problems. By learning about cerebral aneurysms, we can improve patient care.
Common Risk Factors for Cerebrovascular Diseases
The risk of cerebrovascular diseases is influenced by many factors. Some can be changed, while others cannot. Knowing these risks helps us prevent and manage these conditions better.
Non-modifiable Risk Factors
Some risks for cerebrovascular diseases are fixed. These include age, gender, heredity, and race. As we get older, our risk of stroke and other conditions grows. Some ethnic groups are more likely to face these risks.
“Genetic factors play a significant role in the risk of stroke,” doctors say. This shows how important family history is in assessing risk.
Lifestyle-related Risk Factors
Our lifestyle choices greatly affect our risk of cerebrovascular diseases. Smoking, being inactive, and eating poorly can lead to high blood pressure and diabetes. These conditions are linked to stroke risk.
Smoking damages blood vessels and affects blood flow. Quitting can greatly lower this risk. Regular exercise and a healthy diet help manage weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol. These are key in preventing cerebrovascular diseases.
Medical Conditions Increasing Risk
Some medical conditions raise the risk of cerebrovascular diseases. High blood pressure is a major risk factor, as it can cause blood vessels to rupture or become blocked. Diabetes also increases risk by damaging blood vessels over time.
Managing these conditions is vital. We must work with healthcare providers to use medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. This helps reduce the risk of stroke and other cerebrovascular diseases.
High cholesterol, atrial fibrillation, and other heart conditions also increase risk. We need to manage these conditions effectively. This involves medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments to minimize risk.
“Prevention is better than cure.” By understanding and addressing risk factors for cerebrovascular diseases, we can prevent these conditions. This improves our overall health outcomes.
Hypertension and Cerebrovascular Diseases
Learning about hypertension and cerebrovascular diseases can save lives. High blood pressure is a big risk for stroke and other brain problems. We’ll look at how high blood pressure affects brain health and why managing blood pressure is key to preventing these diseases.
The Hypertension-Stroke Connection
Hypertension is closely tied to stroke risk because it damages brain blood vessels. High blood pressure weakens blood vessel walls, making them more likely to burst. This is a main cause of hemorrhagic stroke. Also, high blood pressure speeds up plaque buildup in arteries, leading to ischemic stroke.
Research shows controlling hypertension can greatly lower stroke risk. For example, a study found lowering systolic blood pressure by 10 mmHg can cut stroke risk by up to 30%. This highlights how crucial managing blood pressure is for preventing stroke.
Blood Pressure Management for Prevention
Managing blood pressure is essential to prevent brain diseases. This involves making lifestyle changes and, if needed, taking medication. Lifestyle changes include eating a healthy diet, like the DASH diet, and staying active.
- Monitoring blood pressure regularly
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Reducing sodium intake
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Quitting smoking
For many, lifestyle changes alone aren’t enough to control high blood pressure, and medication may be needed. There are many types of blood pressure medications, and the right one depends on the person’s health and other factors.
By understanding the link between hypertension and brain diseases and managing blood pressure, we can greatly reduce stroke and other brain conditions. This approach not only saves lives but also improves life quality for those at risk.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Knowing the warning signs of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases can greatly improve patient outcomes. These diseases, including stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), and cerebral aneurysm, have distinct symptoms. These symptoms need immediate medical attention.
FAST Method for Stroke Recognition
The FAST method is a key tool for spotting stroke symptoms. FAST stands for Face, Arm, Speech, and Time. It helps people quickly recognize stroke signs and act fast.
- Face: Ask the person to smile. Does one side of their face droop?
- Arm: Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- Speech: Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Is their speech slurred or difficult to understand?
- Time: Time is of the essence. If the person shows any of these symptoms, call for emergency services immediately.
Symptoms of Ischemic vs. Hemorrhagic Stroke
Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes have different causes and symptoms. Knowing these differences is key for the right treatment.
Ischemic strokes happen when a brain blood vessel is blocked. Symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden vision changes
- Dizziness or loss of balance
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a brain blood vessel ruptures. Symptoms can be severe and include:
- Severe headache with no known cause
- Vomiting or nausea
- Altered consciousness or confusion
- Seizures
Warning Signs of Aneurysm and TIA
Cerebral aneurysms and TIAs have unique warning signs. An aneurysm may not show symptoms until it ruptures. But sometimes, it can cause:
- Headaches or pain above and behind the eye
- Numbness or weakness on one side of the face or body
- Dilated pupils or double vision
A TIA, or “mini-stroke,” has symptoms similar to a stroke but usually goes away in 24 hours. Symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness
- Difficulty with speech or understanding
- Vision disturbances
- Dizziness or loss of balance
Spotting these warning signs and acting quickly can greatly improve outcomes for cerebrovascular disease patients.
Cerebrovascular diseases pose a significant threat to public health.
Healthcare professionals use many tools to diagnose cerebrovascular diseases. Accurate diagnosis is key to starting the right treatment and helping patients get better.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed initial assessment and physical exam. This is crucial to spot signs and symptoms of cerebrovascular diseases. We look at the patient’s medical history, do neurological exams, and check vital signs to decide on more tests.
A thorough physical exam can uncover important clues. For example, checking cranial nerve function, motor strength, and sensory responses helps pinpoint the problem and figure out the type of disease.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is a big part of diagnosing cerebrovascular diseases. Some common imaging methods include:
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: CT scans are great for finding hemorrhages and big infarctions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI gives detailed brain tissue images, helping spot ischemic strokes and other issues.
- Angiography: This involves injecting a contrast agent to see blood vessels, helping find blockages, aneurysms, or malformations.
Laboratory Tests and Other Diagnostics
Laboratory tests add to imaging studies by giving more info for diagnosis and treatment planning. Some common tests are:
- Blood glucose tests to check for low or high blood sugar
- Complete blood count (CBC) to look for signs of infection or inflammation
- Coagulation studies to check for bleeding or clotting issues
- Lipid profiles to check cholesterol levels
Other tests, like electrocardiograms (ECGs) and carotid ultrasound, help check heart health and find embolism sources.
By combining findings from the initial assessment, imaging, and lab tests, we can accurately diagnose cerebrovascular diseases. This helps us create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Emergency Treatment Options
When a cerebrovascular event happens, time is very important. Quick medical help is key. Emergency treatments for cerebrovascular diseases include many strategies to lessen damage and help patients.
Time-Critical Interventions
Time is crucial in treating cerebrovascular diseases. Thrombolysis is a fast action used mainly for ischemic strokes. Giving thrombolytic agents quickly can greatly help by breaking the clot and bringing blood back to the brain.
Other fast actions include mechanical thrombectomy, where the clot is removed from the blood vessel. These actions need quick diagnosis and are often helped by advanced imaging.
Medication-Based Treatments
Medicine is very important in treating cerebrovascular diseases quickly. For ischemic strokes, intravenous thrombolytics are used to break clots. In hemorrhagic strokes, medicines help control bleeding, manage blood pressure, and stop seizures.
Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are used to stop more clots. The right medicine and when to use it depend on the diagnosis and the patient’s health.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is needed for some cerebrovascular diseases, like ruptured aneurysms or large hemorrhages. Procedures include clipping or coiling of aneurysms to stop bleeding, or removing hematomas to ease brain pressure.
Deciding on surgery depends on the patient’s health, the bleed’s location and size, and any other issues. Surgery needs a skilled team and is usually done in specialized places.
Long-term Management and Rehabilitation
Long-term management and rehabilitation are key to helping patients regain their independence after cerebrovascular diseases. A good recovery plan tackles physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges. This approach helps patients get back on their feet.
Physical and Occupational Therapy
Physical therapy helps patients regain motor skills and mobility. Personalized exercise programs improve strength, balance, and coordination. Occupational therapy enables patients to do daily activities, enhancing their quality of life.
Important aspects of physical and occupational therapy include:
- Customized exercise plans to improve mobility and strength
- Training in the use of assistive devices for daily activities
- Strategies to enhance balance and prevent falls
Speech and Cognitive Rehabilitation
Speech therapy is vital for patients with speech and language issues after a cerebrovascular event. Speech therapists help improve communication skills, addressing problems like aphasia and dysarthria.
Cognitive rehabilitation aims to boost memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. It helps patients manage cognitive impairments and adapt to their condition.
Key components of speech and cognitive rehabilitation include:
- Personalized therapy plans to address specific communication and cognitive challenges
- Techniques to improve memory and concentration
- Strategies to enhance problem-solving and decision-making skills
Psychological Support and Adjustment
Psychological support is crucial for long-term management and rehabilitation. Patients often face emotional and psychological challenges, like depression, anxiety, and frustration.
We offer psychological support through counseling and therapy. This helps patients cope with their condition and adjust to their new circumstances. Support groups also help by connecting patients with others who have faced similar challenges.
The importance of psychological support cannot be overstated, as it significantly impacts a patient’s overall well-being and recovery.
Cerebrovascular diseases pose a significant threat to public health.
To prevent cerebrovascular diseases, it’s key to use a complete plan. This plan should include lifestyle changes and medical care. A proactive approach can greatly lower the risk of these conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy lifestyle choices are vital in preventing cerebrovascular diseases. Eating a balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is important. Also, regular physical activity helps keep your heart healthy.
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol are also key steps. These actions not only lower the risk of cerebrovascular diseases but also boost overall health.
Medical Management of Risk Factors
Managing risk factors through medical care is crucial. This means controlling high blood pressure with medicine and lifestyle changes. It also involves managing diabetes and treating high cholesterol.
Regular visits to healthcare providers are also important. They help monitor and manage these conditions well.
Regular Screening and Monitoring
Regular screenings and monitoring are vital for early detection and prevention. This includes regular blood pressure checks, lipid profile tests, and diabetes screenings.
By being informed and proactive, people can greatly reduce their risk of cerebrovascular diseases.
Recent Advances in Cerebrovascular Disease Treatment
Cerebrovascular diseases pose a significant threat to public health. to new methods and tech. We’re seeing a big shift in how these diseases are treated, leading to better results for patients.
Innovative Therapeutic Approaches
The way we treat cerebrovascular diseases is changing fast. A big step forward is mechanical thrombectomy. This method removes blood clots from the brain’s blood vessels. It has greatly improved outcomes for those with acute ischemic stroke.
New clot-busting medications and other treatments are also making a big difference. They are more precise and effective. This helps lower the risk of problems and improves life quality for patients.
Emerging Technologies and Techniques
New tech is key in improving cerebrovascular disease treatment. Advanced imaging techniques like high-resolution MRI and CT scans help doctors diagnose and treat better. These tools give clear images of the brain’s blood vessels, spotting issues early.
Also, minimally invasive surgical techniques are being developed. They offer safer options than traditional surgeries. These new methods cut down on recovery time and improve results for patients.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also being used. AI can quickly analyze lots of data. It helps find patterns and predict outcomes, guiding treatment plans.
Conclusion
It’s key to understand cerebrovascular diseases to help patients. These include strokes, transient ischemic attacks, and cerebral aneurysms. They really affect brain health and overall well-being.
Preventing strokes and getting timely treatment can improve recovery chances. Managing risks like high blood pressure and vascular disorders helps. This way, people can lower their chance of having a stroke.
New medical tech and treatments offer hope for those with cerebrovascular diseases. We need to keep spreading the word and educating others. This helps make our world a healthier place.
By focusing on brain and vascular health, we can make a big difference. We can help people all over the world. Together, we can create a better future for those with cerebrovascular diseases.
FAQ
What are the four major cerebrovascular diseases?
The four major cerebrovascular diseases are ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), and cerebral aneurysm. These conditions affect blood flow to the brain and require immediate medical attention.
What is the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke?
Ischemic stroke happens when a blood clot blocks an artery. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding in the brain. Knowing the difference is key for timely treatment.
What is a transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
A TIA, or “mini stroke,” is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain. It often warns of a major stroke. Symptoms are like a stroke but usually go away in 24 hours.
What is a cerebral aneurysm?
A cerebral aneurysm is a bulge or sac-like structure on a blood vessel in the brain. If it ruptures, it can cause a hemorrhagic stroke, leading to severe consequences.
What are the risk factors for cerebrovascular diseases?
Common risk factors include hypertension, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, and family history. Understanding and managing these risks can help prevent cerebrovascular diseases.
How is hypertension linked to cerebrovascular diseases?
Hypertension is a significant risk factor for cerebrovascular diseases. It can cause blood vessels to narrow and become more susceptible to blockage or rupture. Managing blood pressure is crucial for prevention.
What are the warning signs of a stroke?
The FAST method is used to recognize stroke symptoms: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, and Time to call for emergency services. Other symptoms may include sudden headache, dizziness, or vision changes.
Cerebrovascular diseases pose a significant threat to public health.
Diagnosis involves initial assessments, imaging techniques like CT or MRI scans, and laboratory tests. These help determine the cause of symptoms and guide treatment.
What are the treatment options for cerebrovascular diseases?
Treatment options vary depending on the condition. They may include medication, surgical interventions, and long-term management and rehabilitation to support recovery.
How can cerebrovascular diseases be prevented?
Prevention strategies include lifestyle modifications, managing medical risk factors, and regular screening. This helps identify potential issues before they become severe.
What is the importance of long-term management and rehabilitation?
Long-term management and rehabilitation are crucial for patients with cerebrovascular diseases. They help restore function, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life.
What recent advances have been made in treating cerebrovascular diseases?
Recent advances include innovative therapeutic approaches and emerging technologies. These are improving patient outcomes and expanding treatment options.
References
The Lancet. Cerebrovascular diseases Ischemic Hemorrhagic stroke TIA aneurysm. Retrieved from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laneur/article/PIIS1474-4422(21)00252-0/fulltext


































