Getting a tumor diagnosis can be scary, and worrying about it coming back after surgery is common. Studies show that tumor recurrence rates vary a lot. This depends on the tumor type and the patient’s health.Learn the crucial rate: how fast do melanoma brain tumors grow back after surgery. Understand the factors influencing recurrence speed clearly.
The path from diagnosis to recovery is tough and emotional. How fast a tumor can come back after surgery depends on many things. These include the tumor type, the surgery method, and the patient’s health.
Looking into tumor recurrence, we must think about the emotional toll on patients. The fear of it coming back can be as hard as the first diagnosis. So, it’s key for doctors to give full support and care.
Key Takeaways
- Tumor recurrence rates vary significantly among different tumor types.
- Individual patient factors play a critical role in determining the likelihood of tumor recurrence.
- Advancements in surgical techniques have improved outcomes for many patients.
- Comprehensive post-surgical care is essential for monitoring and managing recurrence.
- Patient support and education are critical components of care.
The Nature of Tumor Recurrence
It’s key to know why tumors come back after surgery. Tumor recurrence is a big problem in cancer treatment. It happens when cancer cells return after the first treatment seems to work.
Studies show that tiny cancer cells left behind are a big reason for recurrence (Abdelaziz et al., 2021). Even with careful surgery, small cancer cells can stay. These tiny cells can be in the same spot as the original tumor or in other parts of the body.
Why Tumors Return After Surgical Removal
Tumors can come back for several reasons after surgery. One main reason is microscopic residual disease. When cancer is removed, it’s hard to find all cancer cells, even if they’re in nearby tissues or elsewhere.
Microscopic residual disease means tiny cancer cells left after surgery. These small cells can’t be seen by tests or during surgery. But, they can grow into new tumors over time.
Microscopic Residual Disease
Microscopic residual disease is a big factor in tumor recurrence. Even with complete surgical resection, some patients have tiny cancer cells left. These cells can grow and form new tumors.
It’s important to understand and tackle microscopic residual disease to stop or slow recurrence. We need better surgery, more treatments to target remaining cells, and close monitoring for signs of recurrence.
How Fast Do Melanoma Brain Tumors Grow
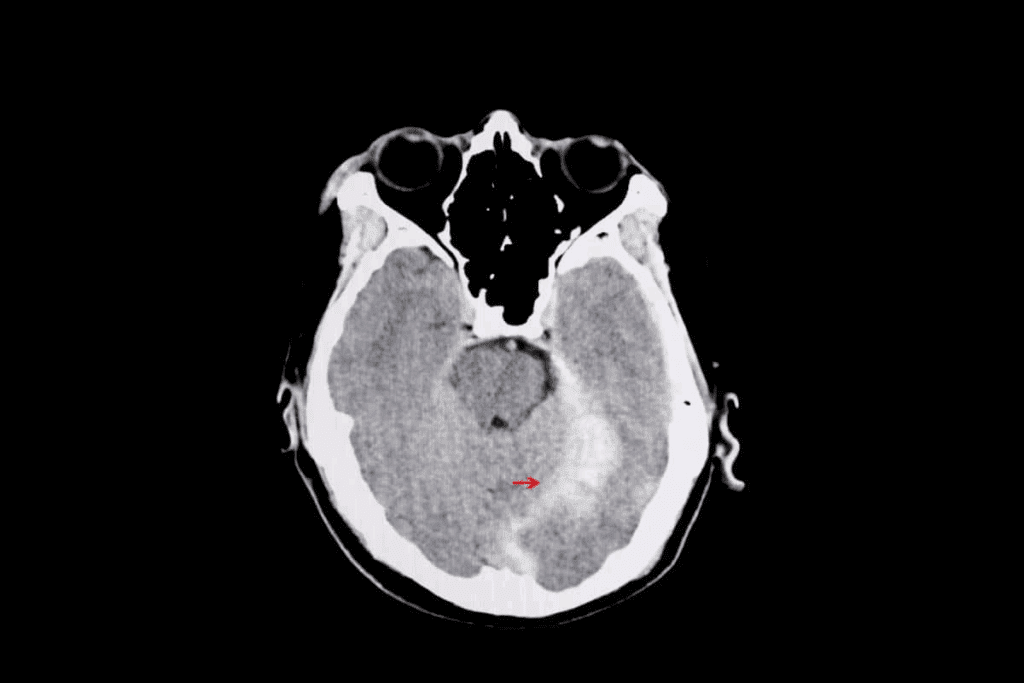
It’s key to know how fast melanoma brain tumors grow to find the best treatments. These tumors grow quickly and aggressively. This can greatly affect how well a patient does.
Melanoma Brain Metastasis Growth Patterns
Melanoma brain metastases grow at different rates. Some grow slowly, while others grow fast. Research shows that how fast they grow can vary a lot between patients. This depends on the tumor’s genetics and the patient’s health.
Doctors group these growth patterns into types based on how fast they grow. Knowing this helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Measuring Growth Velocity in Melanoma Brain Tumors
To measure how fast melanoma brain tumors grow, doctors look at how much they increase in size over time. They use MRI scans for this. These scans show the tumor’s size and how fast it’s growing.
How fast a tumor grows is very important. Fast-growing tumors often mean a worse outcome. This might mean doctors need to treat more aggressively.
Case Studies of Rapid Progression
Many case studies show how quickly melanoma brain metastases can grow. These studies stress the need for constant monitoring and quick action to manage the disease well.
One case study showed a patient with brain metastases that grew at different rates. This case shows how complex treating these tumors can be. It highlights the need for treatment plans tailored to each patient.
Types of Brain Tumors and Their Regrowth Rates
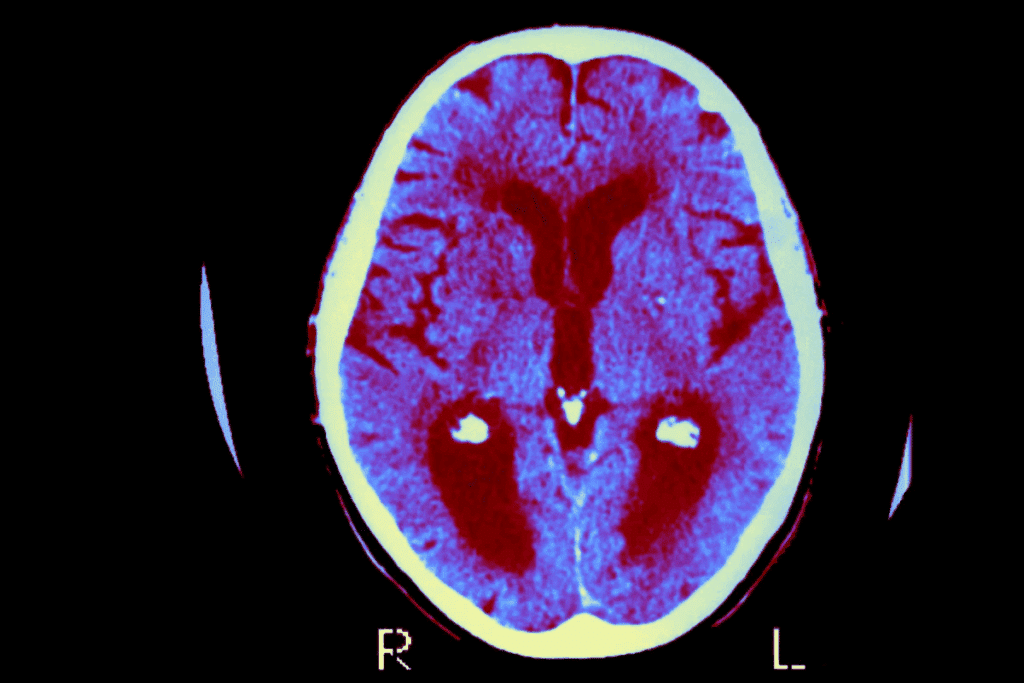
It’s important to know the different types of brain tumors to understand how fast they grow. Brain tumors can be either primary or metastatic. Each type grows differently.
Primary vs. Metastatic Brain Tumors
Primary brain tumors start in the brain. Metastatic tumors spread to the brain from other places. Primary brain tumors can be either benign or malignant. They include glioblastoma, meningioma, and astrocytoma.
Metastatic tumors are usually malignant. They come from cancers like lung, breast, or melanoma. The growth rate of these tumors varies a lot.
Primary tumors like glioblastoma grow fast. Meningiomas grow slower. The growth rate of metastatic tumors depends on the original cancer.
Glioblastoma Recurrence Timeline
Glioblastoma is a very aggressive primary brain tumor. It often comes back quickly. Studies say it usually recurs in 6-9 months after treatment.
Glioblastoma grows fast because it spreads and leaves behind tiny pieces of tumor. These pieces can’t be removed by surgery or radiation.
Meningioma and Other Slower-Growing Tumors
Meningiomas are usually benign. They grow slowly and are found in the meninges, the brain’s protective membranes. Their growth rate is slower than malignant tumors.
Doctors often watch meningiomas, or they might remove them surgically or use radiation. Because they grow slowly, meningiomas can be managed more carefully.
Anatomical Considerations in Tumor Regrowth
Understanding how tumors grow back is key to treating them well. Where a brain tumor is located affects how it grows back and how it’s treated. We’ll look at how different parts of the brain impact tumor return and the challenges they bring.
Frontal Lobe Tumors and Recurrence Patterns
Frontal lobe tumors are common and can cause many symptoms. These include changes in personality, motor skills, and thinking. Because of the frontal lobe’s complex nature, removing tumors is hard, and they often come back.
Complete surgical removal is often not possible because of the tumor’s closeness to important brain areas.
Tumors in the Back of the Head
Tumors at the back of the head, like those in the occipital lobe, can mess with vision. They can lead to blind spots or other vision problems. The occipital lobe’s complex anatomy makes treatment tough, with tumors near vital structures.
Radiation therapy is sometimes used here, when surgery is too risky.
Brain Stem and Deep Brain Tumors
Brain stem tumors are hard to treat because they’re in a key area. This area controls basic functions like breathing and heart rate. Tumors in the brain stem or deep in the brain are hard to remove surgically because of the risk of harming nearby brain tissue.
Advanced radiation techniques and other non-surgical treatments are often used instead.
The location of a brain tumor is very important for understanding how it will grow back and how to treat it. Knowing this helps doctors create better treatment plans and improve patient results.
Biological Factors Influencing Regrowth Speed
Biological factors are key in how fast a tumor can grow back after surgery. These factors include genetics, environment, and body functions. They all work together to affect how quickly a tumor grows.
Genetic Mutations and Growth Rate
Genetic changes are a big deal in tumor regrowth. Some changes can make tumors grow faster by not controlling cell growth. For example, changes in DNA repair genes can make tumors grow quicker.
Genes like TP53, EGFR, and PDGFRA are often changed in aggressive tumors. These changes can make tumors grow faster.
| Gene | Function | Impact of Mutation |
| TP53 | Tumor suppressor gene | Loss of function leads to unchecked cell division |
| EGFR | Receptor tyrosine kinase | Overexpression promotes cell proliferation |
| PDGFRA | Receptor tyrosine kinase | Mutations lead to increased cell growth and survival signals |
Tumor Microenvironment
The area around a tumor, called the tumor microenvironment, affects its growth. This area can either slow down or speed up tumor growth. It depends on the balance of different cells and molecules.
Cells like immune cells, fibroblasts, and blood vessels are part of the tumor microenvironment. They interact with tumor cells, changing how fast the tumor grows. For instance, some immune cells fight tumors, while others help them grow by supporting blood vessel formation.
Blood Supply and Hypoxia
A tumor needs blood to grow because it needs oxygen and nutrients. Tumors create new blood vessels to get what they need. But, this can make parts of the tumor not have enough oxygen, leading to faster growth.
Without enough oxygen, tumors can grow even faster. They start to make more blood vessels and spread. Understanding how blood supply and oxygen levels affect tumors is key to stopping them from growing back.
Patient-Specific Factors Affecting Recurrence
Patient-specific factors are key in figuring out the chance of tumor growth after surgery. These factors are unique to each person. They can greatly affect the chance of recurrence.
Many patient-specific factors can raise the risk of tumor regrowth. Knowing these factors can help manage and lower the risk of regrowth.
Age and Overall Health
A patient’s age and health are very important in figuring out the chance of tumor recurrence. Older patients might face a higher risk because of weaker bodies and immune systems.
A study found that older adults are more likely to see tumor recurrence. This is because their immune response is weaker.
Immune System Function
The immune system is key in fighting cancer cells. Patients with weak immune systems, due to health issues or treatments, face a higher risk of recurrence.
Research shows that a weak immune system can increase the risk of cancer coming back. This highlights how important the immune system is in fighting cancer.
Prior Treatments and Their Impact
Previous treatments, like surgery, chemo, and radiation, can change the chance of tumor recurrence. The success and type of treatments can affect this risk.
Looking at past treatments and their results can give insights into recurrence risk. This helps in making better treatment plans.
| Patient-Specific Factor | Impact on Recurrence | Clinical Considerations |
| Age | Older patients may have higher risk | Consider age in risk assessment |
| Overall Health | Poor health may increase recurrence risk | Optimize overall health pre- and post-surgery |
| Immune System Function | Compromised immunity increases risk | Monitor immune function closely |
| Prior Treatments | Type and effectiveness influence recurrence | Tailor follow-up treatments based on prior outcomes |
Recognizing Tumor Recurrence: Symptoms and Signs
It’s key to spot the signs of brain tumor return early. This can mean a big difference in treatment success. Symptoms of recurrence can be different from the first time.
Do Brain Tumor Symptoms Come and Go?
Symptoms of brain tumors can change. They depend on the tumor’s size, location, and your health. Some symptoms may come and go, while others stay the same.
Intermittent symptoms can be tricky. They might not always mean the tumor is coming back. It’s important to watch your health closely and tell your doctor about any changes.
Headaches Associated with Recurrent Tumors
Headaches are a common sign of tumor return. These headaches can be different in how often they happen and how bad they are. They might also come with nausea or vision problems.
The headaches from a returning tumor can be different from the first time. Keeping track of your headache patterns and telling your doctor about any changes is very important.
Neurological Changes and Warning Signs
Changes in how you feel or move can mean the tumor is back. This could be weakness, numbness, changes in thinking, or mood shifts.
Knowing these warning signs and acting fast is key. Catching it early can help a lot with treatment and results.
We stress the need to be alert and report any new or changing symptoms to your doctor. This way, you can get the help you need quickly. It could make a big difference in your health.
Monitoring and Detecting Recurring Tumors
Early detection of recurring brain tumors is key to better treatment outcomes. After surgery, patients need close monitoring to catch any signs of tumor return early.
Imaging Protocols After Brain Tumor Surgery
Regular imaging is vital for brain tumor patients after surgery. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is often used because it’s very good at spotting tumors again. Doctors usually recommend MRI scans every 3-6 months at first.
The type of imaging used can depend on the tumor, its location, and the patient’s health. For example, contrast-enhanced MRI helps tell apart tumor return from surgery changes.
Blood-Based Biomarkers
Blood tests are becoming a new way to find tumor return. These tests can spot recurrence before imaging can in some cases. We’re seeing progress in using liquid biopsies to find tumor DNA in the blood.
Even though it’s new, blood tests could help with imaging, making monitoring better.
When to Contact Your Doctor
It’s important for patients to know when to call their doctor. New or worsening headaches, seizures, or neurological problems mean you should get in touch right away.
Keep an eye on any changes and tell your doctor. Going to regular check-ups and following the monitoring plan is key for catching and managing recurrence early.
Glioblastoma: Understanding Rapid Recurrence
It’s important for patients and doctors to understand glioblastoma’s quick return. This aggressive brain cancer often comes back fast after treatment.
Speed of Regrowth After Surgery
Glioblastoma grows back quickly after surgery. Studies show it usually comes back in 6-9 months, even with the best treatments. Its aggressive nature means it often comes back, no matter the surgery.
A study in the Journal of Neuro-Oncology found that the second time around, glioblastoma grows even faster. This makes the outlook worse. The tumor’s cells spread out, making it hard to remove completely.
Molecular Mechanisms Driving GBM Regrowth
The reasons glioblastoma comes back are complex. Genetic changes, the tumor’s environment, and signaling pathways play a big role. Key factors include changes in the PI3K/AKT pathway, TP53 mutations, and cancer stem cells. These help the tumor grow back and fight treatments.
“The presence of glioblastoma stem cells, which are thought to be responsible for the initiation and recurrence of glioblastoma, poses a significant challenge to achieving long-term remission.”
Scientists are studying how to target these genetic changes. But glioblastoma’s variety makes it hard to find a single treatment. Different parts of the tumor can have different genes.
| Molecular Mechanism | Impact on GBM Regrowth |
| PI3K/AKT Pathway Alterations | Promotes tumor growth and survival |
| TP53 Mutations | Disrupts normal cell cycle regulation, contributing to tumor aggressiveness |
| Glioblastoma Stem Cells | Thought to be responsible for tumor initiation and recurrence |
Life Expectancy After GBM Recurrence
The outlook for glioblastoma patients who experience a recurrence is not good. Life expectancy is usually short, from a few months to a year. This depends on age, health, and how much treatment they’ve had.
Knowing what affects life expectancy after recurrence helps make better treatment choices. Some may try surgery or clinical trials. Others might choose palliative care to improve their quality of life.
Treatment Strategies for Recurrent Brain Tumors
Recurrent brain tumors are a big challenge. They need a treatment plan made just for the person. The plan depends on the tumor type, where it is, the patient’s health, and past treatments.
Surgical Options for Recurrence
Surgery might be an option for some recurrent brain tumors. It’s considered if the tumor is easy to reach and the patient can handle it. Reoperation can help with symptoms and might improve survival chances. But, it’s important to think about the risks and benefits carefully.
- Tumor Location: Some tumors are easier to remove surgically.
- Patient Health: The patient’s health and recovery ability are key.
- Tumor Type: The tumor’s type and how aggressive it is also matters.
Radiation Therapy Approaches
Radiation therapy is often used for brain tumors that can’t be removed by surgery. There are different ways to do radiation, like stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or fractionated radiation therapy. The choice depends on the tumor and if it’s been treated with radiation before.
- SRS is good for smaller, more localized tumors.
- Fractionated radiation therapy is better for bigger or more spread-out tumors.
Systemic Treatments and Targeted Therapies
Systemic treatments, like chemotherapy and targeted therapies, are used for brain tumors that come back. They’re helpful for tumors that have spread or can’t be treated locally.
- Chemotherapy: It works for some types of brain tumors.
- Targeted Therapies: These therapies target specific tumor molecules.
It’s vital to have a care plan that covers all aspects of a patient’s life. By using different treatments and supportive care, we can make life better and possibly extend it for these patients.
Can Recurrent Brain Tumors Be Cured?
The question of whether recurrent brain tumors can be cured is complex. It depends on several factors. These include the type of tumor, its location, and the patient’s overall health.
To answer this question, we need to understand what “cure” means in brain cancer. A cure means the tumor is gone for good. But, some brain tumors can come back even after treatment.
Defining “Cure” in the Context of Brain Cancer
In brain cancer, a “cure” is often about long-term remission. This means the tumor is gone, and the patient feels no symptoms for a long time.
Long-term remission is a big win. It gives patients hope and a better quality of life. But, it’s important to remember that the risk of the tumor coming back is always there.
Long-term Remission Possibilities
Some patients with recurrent brain tumors can get long-term remission. This can happen through surgery, radiation, or other treatments. The chance of getting long-term remission depends on the tumor type, its genetics, and how well the patient responds to treatment.
For instance, some slow-growing tumors like meningiomas might have a better chance of long-term remission. But, aggressive tumors like glioblastoma might have a lower chance. Yet, treatment can greatly improve a patient’s quality of life.
When Cure Is Not Possible: Focus on Quality of Life
If a cure is not possible, the focus shifts to improving the patient’s quality of life. This means managing symptoms, reducing complications, and improving overall well-being.
Palliative care is key in this area. It helps relieve symptoms and stress from serious illnesses. The goal is to help patients live comfortably and actively, even with a recurrent tumor.
Understanding the possibilities and limits of treating recurrent brain tumors helps patients and their families make informed decisions. They can focus on what matters most to them.
Survival Statistics and Prognosis
When a brain tumor comes back, many questions come up. Questions about survival and what the future holds are key. Knowing these things helps patients and their families face what’s next.
Survival rates for brain tumors that come back vary a lot. This depends on the tumor type, where it is, and the patient’s health. We’ll look into these rates to help understand what’s possible.
Recurrent Brain Tumor Survival Rates by Type
Each brain tumor type has its own survival rate when it comes back. For example, glioblastoma, a fast-growing cancer, has a tough prognosis. On the other hand, meningioma, a slower-growing tumor, might have a better chance.
- Glioblastoma: The survival time for glioblastoma that comes back is usually short. It can range from a few months to a year.
- Meningioma: Most meningiomas are not cancerous. They tend to have a better survival rate, even when they come back. Treatment often includes surgery or radiation.
Melanoma Brain Metastasis Prognosis
Melanoma that spreads to the brain is very challenging. The outlook is generally not good. But, new treatments like targeted therapy and immunotherapy have helped some patients.
How well a patient does depends on several things. These include how many tumors are in the brain, if symptoms are present, and the patient’s overall health. Treatment options include surgery, radiation, and systemic treatments like chemotherapy and targeted therapy.
Interpreting Statistics for Individual Cases
Survival statistics are based on big groups of people. They might not exactly match what will happen to one person. Many things, like age and health, can affect a person’s outcome.
When looking at survival statistics, it’s important to think about the specific situation. Talking to a healthcare provider can give more tailored advice. This helps in making better choices about care.
By understanding survival rates and what the future might hold, patients and their families can better handle the challenges of brain tumors coming back. They can make more informed decisions about their care.
Living With the Risk of Recurrence
Living with the risk of tumor recurrence is tough for patients and their families. The uncertainty after surgery is hard to handle. It’s key to have a strong support system.
Follow-up Care Schedules
Regular check-ups are vital to watch for recurrence. Patients must keep up with their follow-up appointments and scans. This helps catch any problems early and gives peace of mind.
A typical follow-up schedule includes:
- Regular MRI or CT scans
- Clinical check-ups with the neurosurgeon or oncologist
- Review of any new symptoms or concerns
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
The mental toll of recurrence risk is real. Anxiety, fear, and depression are common. It’s important to find ways to cope.
Effective coping strategies include:
- Mindfulness and meditation practices
- Support groups, either online or in-person
- Counseling or therapy sessions with a mental health professional
Using these strategies can help manage anxiety and improve life quality.
Support Resources for Patients and Families
Access to the right support is critical for patients and families. This includes medical, emotional, and practical help.
Some valuable resources are:
- Patient advocacy organizations
- Online forums and communities
- Local support groups
These resources help patients and families deal with recurrence risk better.
Research Frontiers in Preventing Tumor Regrowth
Recent breakthroughs in cancer research have opened new avenues for preventing tumor regrowth. Researchers are exploring new strategies to tackle the challenge of tumor recurrence. We are seeing big advancements in fields like novel therapeutics, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine.
Novel Therapeutic Approaches
New therapeutic approaches are being explored to prevent tumor regrowth. Targeted therapies are being developed to attack cancer cells while protecting healthy tissue. Targeted therapies have shown great promise in reducing recurrence in various cancers.
Another area of research is anti-angiogenic therapy. This aims to cut off the blood supply to tumors, stopping their growth. It has been very effective in treating certain brain tumors.
Immunotherapy Advances
Immunotherapy is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer. It uses the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells more effectively. Cancer vaccines and checkpoint inhibitors are examples of immunotherapies showing great promise.
One exciting development in immunotherapy is CAR-T cell therapy. It involves modifying a patient’s T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. This approach has shown remarkable success in treating certain blood cancers.
Personalized Medicine and Genomic Profiling
Personalized medicine is changing cancer treatment by tailoring therapies to individual patients. Genomic profiling helps identify genetic mutations driving tumor growth. This allows for targeted therapies that address these mutations.
By using genomic profiling in clinical practice, we can better predict recurrence risk. This is very promising for treating glioblastoma and other aggressive brain tumors.
Conclusion
Knowing how fast a tumor can grow back after surgery is key for patients and doctors. Tumor recurrence depends on the tumor type, its location, and the patient’s health.
In this article, we’ve looked into the challenges of tumor recurrence. We’ve seen how tumors can grow back and the new treatments being developed. Despite the challenges, research and new treatments offer hope for fighting brain tumors.
As we learn more about brain tumors, we’re getting closer to better treatments. The future looks bright with new therapies, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine. There’s hope for better outcomes for those affected by brain tumors.
FAQ
How fast can a tumor grow back after surgery?
Tumors can grow back at different rates. This depends on the tumor type, where it is, and the patient’s health. Some tumors, like glioblastoma, can grow back quickly. Others, like meningioma, may grow back slower.
Can brain tumor symptoms come and go?
Yes, symptoms can change. This depends on the tumor’s location and the brain tissue around it. Symptoms can be constant or come and go, and their severity can change over time.
What are the signs of tumor recurrence?
Signs of recurrence include headaches, changes in the nervous system, seizures, and cognitive decline. The symptoms depend on the tumor’s location and type.
How is tumor recurrence detected?
Doctors use imaging like MRI or CT scans to detect recurrence. They also look for biomarkers in the blood. Regular check-ups are key for early detection.
Can glioblastoma be cured?
Glioblastoma is hard to cure, but some patients can live long without it coming back. Yet, many tumors do come back. The chance of survival varies based on many factors.
How fast does glioblastoma grow back after surgery?
Glioblastoma can come back quickly, often in a few months. The exact rate depends on how much of the tumor was removed and the tumor’s molecular makeup.
What are the treatment options for recurrent brain tumors?
Treatment options include surgery, radiation, and systemic treatments. The best option depends on the tumor type, location, and the patient’s health.
Can recurrent brain tumors be cured?
The idea of “cure” for recurrent brain tumors is complex. Some patients can live long without symptoms, while others need ongoing care to manage symptoms and slow tumor growth.
How do patient-specific factors affect recurrence?
Factors like age, health, immune system, and past treatments can affect recurrence risk and treatment success. Each patient is different.
What is the prognosis for melanoma brain metastases?
Prognosis for melanoma brain metastases varies. It depends on the disease extent and treatment success. While statistics can guide, each case is unique.
How can patients cope with the risk of tumor recurrence?
Patients can manage recurrence risk by following up regularly, using support resources, and finding ways to deal with the emotional impact of cancer.
What research is being done to prevent tumor regrowth?
Researchers are working on new treatments, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine to stop tumor regrowth and improve outcomes for brain tumor patients.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11156256/


































