Learn what surgery has the surgery highest failure rate. Understand the procedures that often require revisions or don’t achieve the desired outcome clearly. When looking at surgical options, both patients and doctors worry about complications. Some procedures have much higher failure rates than others. For example, spinal fusion surgeries have failure rates between 20% and 40%, studies show. This shows how key it is to know about surgical failure rates and what causes them.
We will dive into the details of surgical procedures and their results. We’ll look at surgery complication rates and unsuccessful surgery statistics. By studying these, we hope to give a full picture of the risks with different surgeries.
Key Takeaways
- Spinal fusion surgeries have high failure rates, ranging from 20% to 40%.
- Understanding surgical failure rates is key for both patients and doctors.
- Surgical complication rates vary a lot across different procedures.
- Things like patient health and surgical technique affect failure rates.
- Knowing about unsuccessful surgery statistics helps set realistic expectations.
Defining Surgical Failure and Success Metrics

To understand surgical failure rates, we need to know what makes a surgery fail. It’s not just about immediate problems or long-term results. It also includes how happy the patient is after the surgery.
How Medical Professionals Define “Failed” Surgeries
Doctors look at many things to say if a surgery was a success or not. They check:
- Complication rates: How often bad things happen during or after surgery.
- Revision rates: How many times a surgery needs to be done again.
- Patient-reported outcomes: How happy the patient is and their quality of life after surgery.
Different Types of Surgical Outcome Measurements
There are many ways to measure how well a surgery goes:
- Objective measures: Like how many people die, how many complications there are, and how long they stay in the hospital.
- Subjective measures: What the patient says about their pain and life quality after surgery.
- Composite measures: A mix of different outcomes to get a full picture of success.
The Difference Between Complications and True Failures
It’s key to know the difference between complications and true surgical failures. Complications are unexpected problems during or after surgery. They don’t always mean the surgery failed. True failures happen when the surgery doesn’t do what it was meant to do, even without big complications.
Knowing these definitions helps doctors and patients. By using clear metrics, we can see how often surgeries don’t work out. This helps us try to make surgeries more successful.
Key Factors Contributing to Surgical Failures
Understanding what leads to surgical failures is key to reducing risks. Data shows that patient, procedure, and post-op factors all matter. They determine if a surgery is a success.
Patient-Related Risk Factors
Patient health is a big factor in surgery success. Studies point out that comorbidities and age are important. For example, diabetes or heart disease can increase surgery risks.
Other factors like obesity, smoking, and overall health also play a part. They can slow healing, raise infection risks, and extend recovery. Knowing these can help doctors prepare better for patients.
Surgeon Experience and Hospital Volume
The surgeon’s experience and the hospital’s surgery volume are also key. Research shows that experienced surgeons have better results. They’re more skilled and familiar with the surgery.
Hospitals that do more surgeries also tend to have better results. They have smoother processes and better staff. Choosing a skilled surgeon and a reputable hospital is important.
Procedural Complexity and Technical Challenges
The surgery’s complexity is another big factor. More complex surgeries are riskier. They involve complex procedures and technical challenges.
Surgeons need to be ready for unexpected problems. They must have the skills to handle complex anatomy. New techniques and technology help, but complexity remains a challenge.
Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation
Good post-op care and rehab are essential for success. Proper wound care, pain management, and rehab can greatly affect recovery.
A solid post-op plan can prevent complications and improve patient satisfaction. It’s important for doctors to clearly explain post-op care and follow-up.
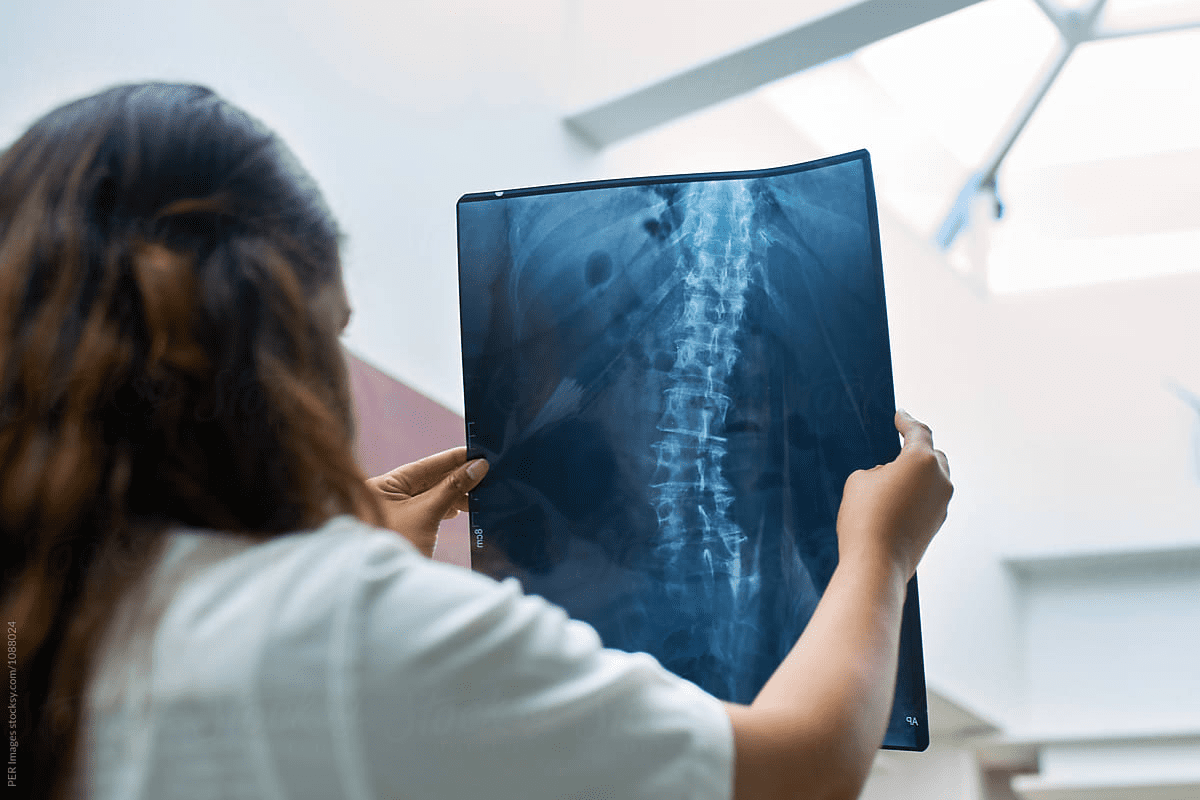
Spinal Fusion: A Leading Contender for Highest Failure Rate
Spinal fusion surgeries are common but risky. They join vertebrae to stabilize the spine and ease pain. But, their complexity often leads to failure.
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) Statistics
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) happens when patients keep feeling pain after spinal surgery. Studies show that a big number of patients with spinal fusion suffer from FBSS. It’s estimated that 20% to 40% of patients face this issue.
Key statistics on FBSS include:
- Up to 40% of spinal fusion patients may not achieve desired outcomes.
- FBSS can result from various factors, including inadequate surgical technique, insufficient fusion, or hardware failure.
- Patients with FBSS often require additional medical interventions, which can include further surgery, pain management, or physical therapy.
Why Up to 40% of Spinal Fusions Don’t Achieve Desired Outcomes
Several reasons contribute to the high failure rate of spinal fusion surgeries. These include patient-related risks, surgical technique, and post-operative care. Inadequate patient selection and insufficient pre-surgical planning are key factors.
Adjacent Segment Disease and Long-term Complications
Adjacent Segment Disease (ASD) is a complication after spinal fusion surgery. It’s when the spinal segments next to the fused area degenerate. This can cause more pain and might need more surgery.
Long-term complications of spinal fusion include:
- Adjacent Segment Disease (ASD)
- Pseudoarthrosis (failure of the bones to fuse)
- Hardware failure or loosening
- Chronic pain and disability
Risk Factors Specific to Spinal Procedures
Several factors specific to spinal procedures can affect success rates. These include the patient’s health, any existing conditions, and the surgeon’s experience.
Healthcare providers can improve spinal fusion surgery outcomes by understanding these risks. They should carefully choose patients, use precise surgical techniques, and provide thorough post-operative care.
Bariatric Weight Loss Surgery Complications
Bariatric weight loss surgery is effective for many but comes with complications. It’s important to know the risks and complications of these procedures.
Gastric Bypass Failure and Revision Rates
Gastric bypass surgery, or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is complex and can have complications. Failure rates can be as high as 20-30%, often needing revision surgery. Revision rates for gastric bypass surgery can range from 5-15%, depending on the surgeon’s experience and patient selection.
“The need for revision surgery after gastric bypass is often due to complications such as stricture, marginal ulcer, or internal hernia.”
Gastric Sleeve and Lap-Band Long-term Outcomes
Gastric sleeve and lap-band surgeries are popular but have long-term complications. Gastric sleeve surgery can lead to leaks or stenosis, while lap-band surgery has risks like band slippage or erosion.
- Gastric sleeve complications: leaks, stenosis, and nutritional deficiencies
- Lap-band complications: band slippage, erosion, and pouch dilation
Weight Regain as a Measure of Procedural Failure
Weight regain after surgery is a big concern and can mean the procedure failed. Reasons for weight regain include poor diet, lack of follow-up care, and hormonal changes. Studies suggest that up to 50% of patients may experience significant weight regain within 2-5 years after surgery.
Metabolic Complications After Bariatric Procedures
Bariatric surgery can cause metabolic problems like nutritional deficiencies and metabolic bone disease. Patients undergoing bariatric surgery require lifelong nutritional supplementation and monitoring to avoid deficiencies in vitamins and minerals like vitamin B12, iron, and calcium.
Metabolic Complication | Prevalence | Management |
Vitamin B12 deficiency | High | Lifelong supplementation |
Iron deficiency | Moderate to High | Iron supplements, dietary changes |
Osteoporosis | Moderate | Calcium and Vitamin D supplements, bone density monitoring |
Joint Replacement Revision Statistics
Joint replacement revision rates are key to measuring the success of orthopedic surgeries. As we advance in medical tech and surgery, knowing what affects these rates is vital.
Knee Replacement Failure Rates and Causes
Knee replacement surgeries are very common. Yet, some need a second surgery. We look at why this happens.
About 5% to 10% of knee replacement patients need a second surgery within 10 to 15 years. Reasons include infection, implant loosening, and wear and tear.
Hip Replacement Complications and Longevity
Hip replacement surgeries are often successful. But, like any surgery, they can have complications. We explore these issues and how they affect how long the replacement lasts.
Problems like dislocation, infection, and nerve damage can occur. Better implants and surgery methods have helped, but some patients need a second surgery.
Shoulder and Ankle Replacement Outcomes
Shoulder and ankle replacements are less common but growing. We talk about their success rates and challenges.
These surgeries face unique challenges due to the joints’ complexity. Success rates are improving with better techniques and implants.
Implant Materials and Their Impact on Failure Rates
The materials in joint implants greatly affect their success and longevity. We examine how different materials influence failure rates and patient results.
Different materials like metal, ceramic, and polyethylene are used in implants. Each has its benefits and drawbacks, affecting the surgery’s success.
Cosmetic Surgery: High Expectations and Disappointment
Many people get cosmetic surgery hoping for the best. But, the reality often falls short of their dreams. The cosmetic surgery industry is huge, but it comes with its own set of risks and problems.
Rhinoplasty: Why It Has Among the Highest Revision Rates
Rhinoplasty, or nose surgery, is a common choice. Yet, it often needs a second surgery because of its complex nature and how hard it is to please everyone.
Research shows that up to 20% of those who get rhinoplasty might need a second surgery. This is due to issues or results that don’t meet their expectations.
Breast Augmentation Complications and Reoperations
Breast augmentation is also a favorite among those looking for cosmetic changes. While it’s generally safe, it can cause problems like capsular contracture, implant rupture, and scarring.
Studies reveal that up to 30% of breast augmentation patients might need more surgery within 10 years. This is because of complications or results that aren’t what they hoped for.
Facelift and Body Contouring Failure Statistics
Facelifts and body contouring, like abdominoplasty, also face challenges and high revision rates. The complexity of these surgeries and individual factors play a big role in the risk of not getting the desired results.
We’ve put together a table to show the complication and revision rates for different cosmetic surgeries:
Procedure | Complication Rate | Revision Rate |
Rhinoplasty | 15-20% | 10-15% |
Breast Augmentation | 10-20% | 20-30% |
Facelift | 5-15% | 5-10% |
Abdominoplasty | 10-20% | 5-15% |
The Psychological Impact of Failed Cosmetic Procedures
The emotional toll of failed cosmetic procedures is real. Patients might feel let down, anxious, and even depressed after things don’t go as planned.
It’s key for patients to have realistic hopes and to know all about the possible risks and complications of cosmetic surgery.
Cardiac Procedures with Concerning Outcomes
Exploring cardiac procedures, we see the risks and outcomes they carry. These surgeries are complex, using various techniques and technologies.
Long-term Results of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) helps improve heart blood flow. Yet, its long-term success varies. Success depends on the patient’s health, the surgeon’s skill, and post-op care.
Key statistics for CABG long-term results include:
- Most patients see relief from angina symptoms.
- Survival rates improve, mainly for complex cases.
- Some may need more surgeries due to graft issues or disease.
CABG Outcome | Short-term | Long-term |
Survival Rate | High | Variable |
Symptom Relief | Significant | Generally maintained |
Need for Repeat Procedure | Low | Moderate |
Cardiac Stent Restenosis and Failure Rates
Cardiac stenting opens narrowed arteries. Yet, it risks restenosis or stent failure.
Factors influencing cardiac stent outcomes include:
- Stent type (bare metal vs. drug-eluting)
- Patient factors such as diabetes and renal disease
- Antiplatelet therapy adherence
Emerging Alternatives to Traditional Cardiac Surgeries
New, less invasive cardiac surgeries are emerging. These aim to improve outcomes and patient recovery.
Some emerging alternatives include:
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Minimally invasive cardiac surgery
- Robotic-assisted cardiac procedures
Surgery Highest Failure Rate: Comparative Analysis
Looking into surgical failure rates means comparing different medical fields. We need to look at both short-term and long-term results. This helps patients and doctors make better choices about surgery.
Statistical Comparison Across Surgical Specialties
Different surgeries have different failure rates. For example, spinal fusion can fail in 20% to 40% of cases. But, heart surgeries like CABG often have lower failure rates. We’ll dive into these differences and what causes them.
- Spinal fusion: 20-40% failure rate
- CABG: Lower failure rate compared to spinal fusion
- Bariatric surgery: Variable failure rates based on procedure type
Short-term vs. Long-term Failure Metrics
It’s key to separate short-term and long-term failure rates. Short-term failures happen right after surgery. Long-term failures can come from disease coming back or implants failing. We’ll see how each field views these rates differently.
Surgical Specialty | Short-term Failure Rate | Long-term Failure Rate |
Orthopedic | 5% | 15% |
Cardiac | 3% | 10% |
How Failure Rates Have Changed Over Time
New surgical methods, technology, and care have changed failure rates. We’ll look at these changes, showing where things have gotten better and where they need more work.
By understanding how surgical failure rates compare, we can make better choices. This leads to better surgery results for everyone.
Organ Transplantation Rejection and Survival Rates
The field of organ transplantation has made big strides, but there are ongoing challenges. Many patients with failing organs get new ones, thanks to transplants. But, success depends on the organ type and the patient’s health.
Kidney Transplant Outcomes and Rejection Statistics
Kidney transplants are common and often successful. Studies show a 95% one-year survival rate. Yet, chronic rejection can harm long-term survival. Matching the donor and recipient, the right treatment, and care after transplant are key.
Key Statistics for Kidney Transplant Outcomes:
Time Frame | Graft Survival Rate |
1 Year | 95% |
5 Years | 80% |
10 Years | 60% |
Heart and Lung Transplant Survival Curves
Heart and lung transplants face high risks and lower success rates. Heart transplant survival at one year is about 85%, and lung transplants around 80%.
Factors Affecting Transplant Success
Many things can affect transplant success. These include matching between donor and recipient, organ quality, treatment, and post-transplant care. Knowing these factors helps improve transplant success and lower rejection risk.
- Donor-recipient HLA matching
- Immunosuppressive regimen
- Post-transplant monitoring and care
- Recipient’s overall health and compliance
Healthcare providers can boost transplant success by focusing on these areas. This leads to better outcomes for patients.
Complex Neurosurgical Procedures and Their Outcomes
Complex neurosurgical interventions are often needed but come with risks. They have varying success rates that patients need to know. These procedures are very detailed and can have complications.
We will look at the results of several important neurosurgical procedures. This includes brain tumor resection, aneurysm treatment, deep brain stimulation, and spinal cord stimulation.
Brain Tumor Resection Complications and Recurrence
Removing a brain tumor is a complex procedure. It can save lives but also has risks like neurological damage and infection. There’s also a chance the tumor could come back.
The chance of a brain tumor coming back varies. For example, glioblastoma, a fast-growing brain cancer, often comes back after surgery.
“The surgical management of brain tumors remains a challenging task, with tumor recurrence being a significant concern. Advances in surgical techniques and adjuvant therapies are critical in improving patient outcomes.”
Aneurysm Treatment Success Rates: Clipping vs. Coiling
Treating an aneurysm can be done by clipping or coiling. Both methods have their own success rates and risks.
Treatment Method | Success Rate | Complication Rate |
Clipping | 85-90% | 5-10% |
Coiling | 80-85% | 10-15% |
Choosing between clipping and coiling depends on the aneurysm’s location, size, and the patient’s health.
Deep Brain Stimulation Effectiveness for Movement Disorders
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used to treat movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease. It involves placing an electrode in the brain.
Research shows DBS can greatly improve symptoms in patients with movement disorders. It can greatly improve their quality of life.
Spinal Cord Stimulator Failure and Revision Rates
Spinal cord stimulation is used for chronic pain. While it works for many, there’s a risk of device failure and the need for more surgery.
- Device failure rates range from 10-20%.
- Revision surgery is needed in up to 30% of cases.
- Complications can include infection, hardware malfunction, and loss of effectiveness.
It’s important for patients to know these risks before considering spinal cord stimulation.
Options After Failed Surgery: Revision Procedures
When surgery doesn’t work out, patients face a tough choice: should they try revision surgery? This choice needs careful thought and a good grasp of the options available.
When to Consider Revision Surgery
Revision surgery isn’t always the first step after a failed procedure. The decision to undergo revision surgery depends on several factors. These include why the first surgery failed, the patient’s health, and their personal wishes.
Patients might choose revision surgery if the first procedure didn’t meet their goals. Or if complications have come up that surgery can fix.
Success Rates of Second and Third Attempts
The success of revision surgeries can change a lot. It depends on the first surgery, how complex the case is, and the surgeon’s skill. Studies show that while revision surgeries can work, they often don’t succeed as well as the first time.
For example, the success rate of spinal fusion revision surgery can be between 50% and 80%. This depends on the patient’s health and the surgeon’s experience.
Alternative Treatments When Surgery Fails
Not every failed surgery needs a second try. Alternative treatments might include physical therapy, pain meds, or other non-surgical methods.
The choice between more surgery and these alternatives depends on the failed surgery’s details and the patient’s wishes.
Managing Expectations for Revision Procedures
It’s key to manage what you expect from revision surgery. Patients need to understand the possible results and risks of these procedures.
Talking to your surgeon about what you hope to achieve is vital. This way, you can know if revision surgery is likely to meet your goals.
Minimizing Your Risk of Surgical Failure
Understanding what can go wrong with surgery is key to a good outcome. By taking steps ahead of time, you can lower your risk of problems. This makes your recovery more likely to be successful.
Choosing the Right Surgeon and Hospital
Finding a skilled surgeon is very important. Look into their qualifications, experience, and past results. Also, the hospital’s quality matters. Choose one with good ratings for your surgery.
Patient Preparation and Pre-surgical Optimization
Getting your body ready for surgery helps a lot. Eat well, exercise, and manage health issues. Follow your surgeon’s advice on what to do before surgery.
Setting Realistic Expectations Before Surgery
It’s important to know what your surgery can and can’t do. Talk openly with your surgeon about what to expect. Understand the risks and how likely you are to get the results you want.
The Importance of Following Post-Operative Instructions
Following your surgeon’s post-op advice is essential. Stick to your medication, go to follow-ups, and avoid heavy work. These steps help avoid complications and ensure the best results.
Technology’s Role in Reducing Surgical Failures
Technology has changed surgery a lot, making it safer. Now, surgeries are more precise and have fewer problems. This has made care better for everyone.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Impact on Outcomes
Robotic surgery is a big deal in medicine. It lets surgeons do complex tasks better. This means less blood loss, fewer infections, and faster healing times.
AI and Predictive Analytics in Surgical Planning
AI and predictive analytics are changing how we plan surgeries. They look at lots of data to help surgeons make better choices. This can prevent problems before they start.
Emerging Technologies Improving Success Rates
New tech like advanced imaging and 3D printing are making surgeries better. They help with planning and doing surgeries that were hard before. This makes surgeries safer and more possible.
The Learning Curve of New Surgical Technologies
New tech is great, but it’s hard for surgeons to learn at first. They need a lot of training to use it well. Hospitals are working hard to teach surgeons, so patients get the best care.
As tech keeps getting better, we’ll see even fewer surgery problems. By using new tech and training surgeons, we can make care even better.
How to Interpret Surgical Success Statistics as a Patient
Surgical success statistics can be tricky to understand. But, knowing how to read them is key for patient empowerment. As patients, we must grasp the data behind surgical outcomes to make informed decisions.
Understanding Relative vs. Absolute Risk
It’s important to know the difference between relative and absolute risk. Relative risk compares risks between groups. Absolute risk shows the actual chance of an event happening. For example, a study might say a technique cuts complications by 50% (relative risk). But if the original risk was 2%, the actual benefit is only 1%.
Essential Questions to Ask Your Surgeon About Outcomes
To understand surgical success statistics, ask your surgeon specific questions. You might ask, “What are the success rates for this procedure in your hands?” or “What are the most common complications, and how often do they occur?” Asking these questions helps you understand what to expect.
Red Flags in Surgical Outcome Reporting
When looking at surgical outcome data, watch out for red flags. These include unusually high or low success rates, unclear complications, or missing long-term data. Be wary if the information seems too good (or bad) to be true or unclear.
Finding Reliable Sources for Surgical Success Data
For reliable surgical success data, check reputable medical journals, government health databases, or professional medical organizations. It’s important to check the source’s credibility and understand the data’s context. Peer-reviewed journals and government health reports are usually trustworthy.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About High-Risk Surgeries
Exploring surgeries with high failure rates shows how important it is to know the risks. Surgeries like spinal fusion, bariatric weight loss, and joint replacement have big risks. It’s vital for patients to be well-informed before deciding.
Studies highlight the need for patient education and making informed choices. Knowing the risks and benefits helps patients understand their options better. We must look at why surgeries fail, like patient risks, surgeon skill, and how complex the surgery is.
Patients should talk to their doctors about their risks, learn about the surgeon’s experience, and check the hospital’s success rates. Taking these steps helps reduce the chance of surgery failure and improves outcomes.
FAQ
What is considered a surgical failure?
Surgical failure happens when a procedure doesn’t work as planned. This can lead to ongoing or worsening symptoms. It might also mean needing more treatments.
What are the most common reasons for surgical failure?
Surgical failures often come from patient risks, inexperienced surgeons, and complex procedures. Poor post-op care and unexpected problems also play a part.
Which surgical procedures have the highest failure rates?
Spinal fusion, bariatric surgery, and some heart surgeries often have higher failure rates. But, these rates can change based on the situation and the patients involved.
How can I minimize my risk of surgical failure?
To lower your risk, pick a skilled surgeon and a good hospital. Get ready well for your surgery. Follow your doctor’s advice after surgery. And, have clear expectations about what will happen.
What are the options if a surgery fails?
If surgery doesn’t work, you might need another surgery, try different treatments, or manage symptoms in other ways. The best choice depends on your health and the situation.
How do surgeons define success in surgical procedures?
Surgeons measure success by symptom relief, better function, and no big complications. The exact measures can change based on the surgery and the patient’s health.
Can technology help reduce surgical failure rates?
Yes, new tech like robotic surgery, AI, and predictive analytics can help. They make surgeries more precise and improve care before and after surgery.
How can I interpret surgical success statistics?
Understanding success stats means knowing the context, like the patients and how success is measured. Talk to your surgeon about these details for better insight.
Are some hospitals or surgeons more prone to surgical failures than others?
Yes, failure rates can differ between places and doctors. This is due to things like how often they do surgeries and their experience. Choosing a busy, experienced center can help.
What role does patient preparation play in surgical success?
Getting ready for surgery is key. It helps spot and reduce risks. It also makes sure you’re as healthy as possible for the surgery.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5913031/



































