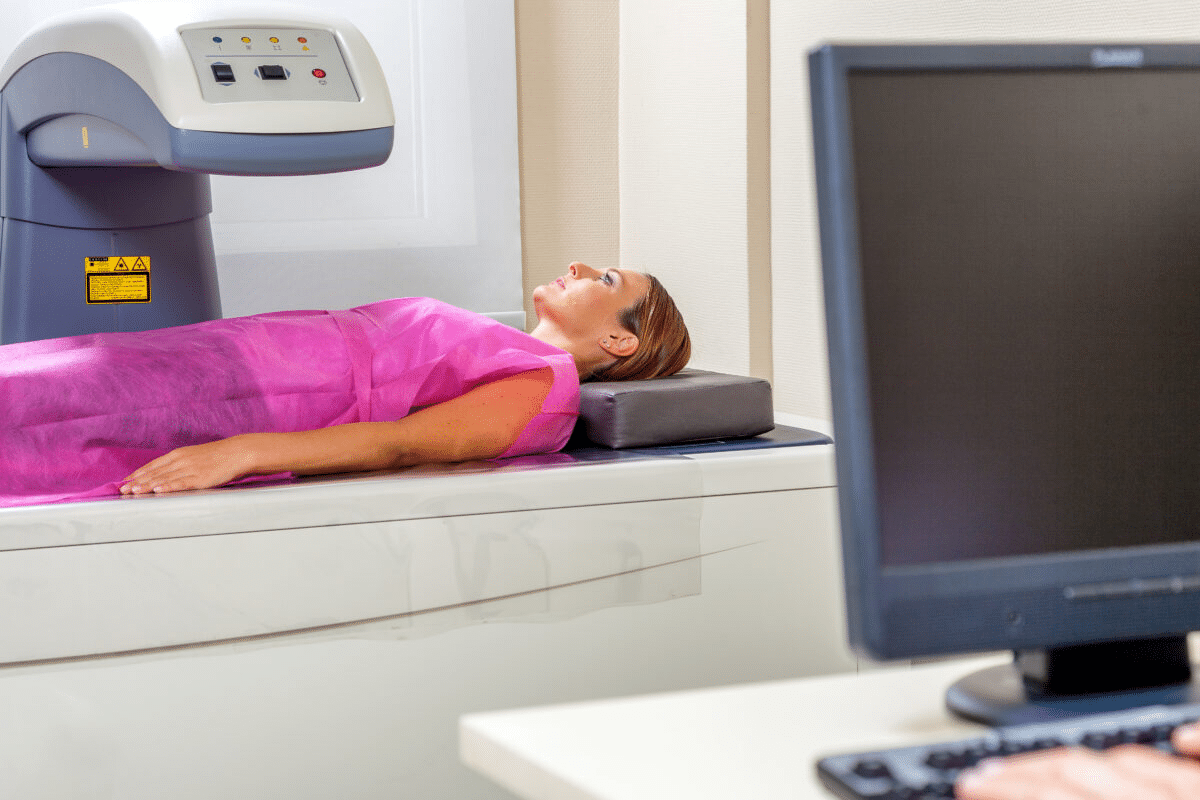
Does a DEXA scan show bone cancer? Get the best expert answers on DEXA capabilities and how doctors screen for skeletal diseases effectively. Many patients ask if a DEXA scan can find bone cancer. The answer is no. DEXA scans are made to check bone mineral density and see if you might get osteoporosis. They are not for finding cancer.
Even though DEXA scans might show odd bone density patterns, they can’t spot cancerous tumors. They don’t have the detail needed for cancer diagnosis.
At Liv Hospital, we aim to give you the right diagnosis and treatment. We’ll talk about what DEXA scans can and can’t do for bone cancer. We’ll also look at better ways to find cancer.
Key Takeaways
- DEXA scans are designed to measure bone mineral density and assess osteoporosis risk.
- They are not intended to diagnose cancer or detect cancerous tumors.
- Unusual bone density patterns may warrant further investigation.
- Alternative imaging modalities are more effective for cancer diagnosis.
- Liv Hospital is committed to providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Understanding DEXA Scans: Purpose and Technology
DEXA scan technology is all about measuring bone density. These scans, or Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry scans, are key for checking bone health. We use DEXA scans to create detailed images of bones, helping us spot and track conditions like osteoporosis.
What is a DEXA Scan?
A DEXA scan is a safe, non-invasive test that uses X-rays to check bone mineral density. It works by sending out two kinds of X-rays: high-energy and low-energy. The difference in how these beams are absorbed by the body lets us figure out bone density. This info is vital for checking bone health and spotting osteoporosis.
How DEXA Scan Technology Works
DEXA scan technology measures how much X-ray energy bones absorb. It sends out two energy levels, which are absorbed differently by bone and soft tissue. By looking at these absorption rates, the scan can accurately measure bone mineral density. This whole process is quick and painless, taking less than 10 minutes.
The amount of radiation from a DEXA scan is very small, similar to what we get from the environment for a few hours. This makes DEXA scans a safe choice for patients of all ages.
Primary Clinical Applications
DEXA scans are mainly used for measuring bone density and assessing osteoporosis. They help us see how likely someone is to break a bone and check if treatments for osteoporosis are working. By checking bone health, doctors can make better choices for patient care, like suggesting lifestyle changes or medication.
Some main uses of DEXA scans include:
- Diagnosing osteoporosis and assessing fracture risk
- Monitoring changes in bone density over time
- Evaluating the effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments
Understanding DEXA scan technology and its uses helps us see why bone health is so important. It encourages us to take steps to keep our bones strong.
The Primary Function of DEXA Scans: Bone Density Measurement
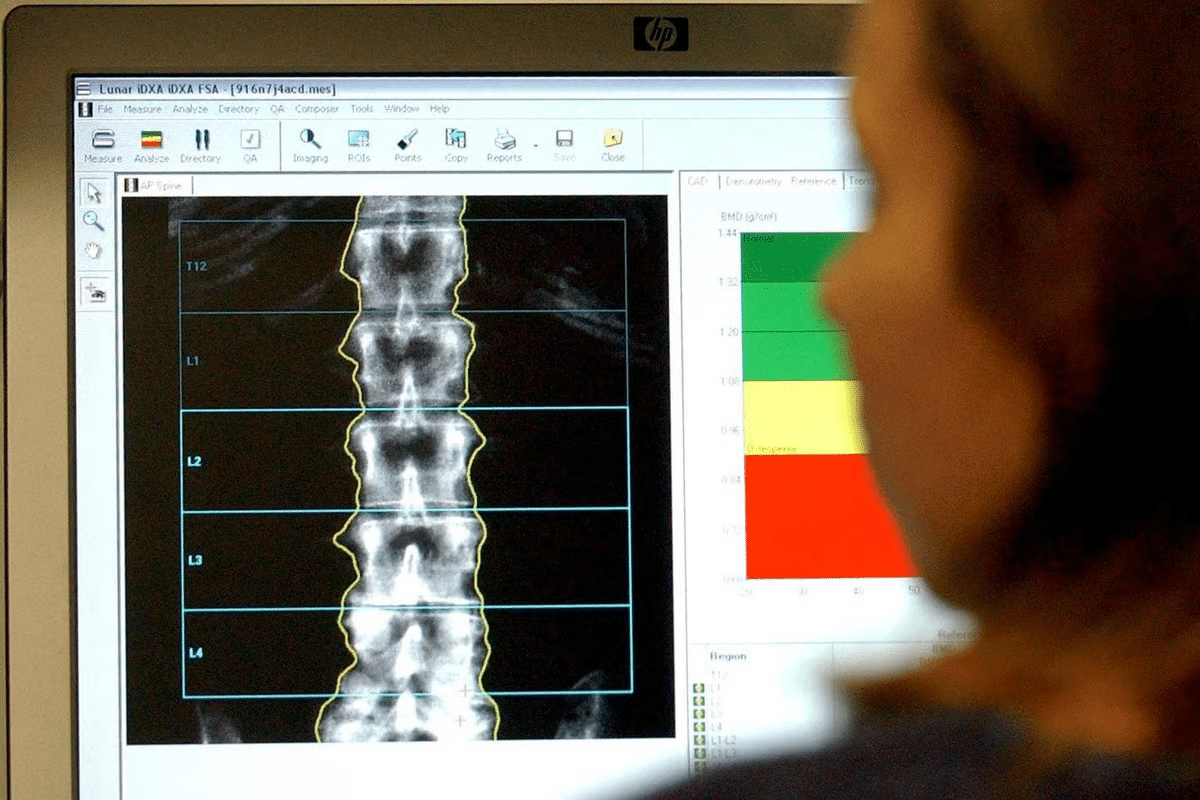
DEXA scans measure bone mineral density to check bone health. They detect minerals like calcium in bones. This helps find the risk of osteoporosis, a condition where bones lose strength.
Evaluating Bone Mineral Density
Bone mineral density (BMD) shows how healthy bones are. DEXA scans give a precise BMD reading. This helps doctors see if you might break bones easily.
The scan uses a low-dose X-ray to see the spine, hip, or other bones. It then analyzes these images to find bone density. This gives a T-score, comparing your BMD to a healthy young adult’s.
Osteoporosis Assessment and Diagnosis
DEXA scans are the best way to find osteoporosis. They check bone density to spot risks early. Osteoporosis often doesn’t show symptoms until a bone breaks.
This makes it key to catch it early with DEXA scans. It helps prevent breaks and manage the disease well.
- Identifying individuals with low bone mass
- Diagnosing osteoporosis
- Assessing fracture risk
- Monitoring the effectiveness of osteoporosis treatment
Fracture Risk Prediction
DEXA scans also predict fracture risk. They look at bone density and other factors. Spotting high-risk patients early helps start treatment sooner.
The FRAX tool helps with this. It shows the chance of major osteoporotic fractures in 10 years. This helps doctors make better treatment plans.
Can a DEXA Scan Detect Bone Cancer? Limitations and Capabilities
Understanding if DEXA scans can find bone cancer involves knowing their strengths and weaknesses. DEXA scans are great for checking bone health by measuring bone mineral density. But, their role in spotting bone cancer is more complicated.
DEXA Scan Resolution and Sensitivity
DEXA scans are made to measure bone density, not find cancer. They are not as good at spotting the changes bone cancer makes. They might show unusual bone density changes, but they’re not sure signs of cancer.
Why DEXA Scans Aren’t Designed for Cancer Detection
DEXA scans aren’t for finding cancer because they can’t see the small details needed. They give a general idea of bone density, which can be affected by many things like osteoporosis or fractures. For finding cancer, you need more advanced imaging.
Incidental Findings: When DEXA Scans Reveal Abnormalities
Even though DEXA scans aren’t for cancer, they can sometimes find things that need more looking into. They might show unusual bone density patterns or changes that could mean different things, like bone problems. If this happens, you’ll need more tests to figure out what’s going on.
In short, while DEXA scans can’t always find bone cancer, they’re very important for checking bone health. It’s key for both patients and doctors to know what they can and can’t do.
Bone Cancer: Types and Diagnostic Challenges
Bone cancer, whether it starts in the bone or spreads to it, is hard to diagnose. We will look at the different types of bone cancer and the challenges in finding out if someone has it.
Primary vs. Metastatic Bone Cancer
Bone cancer can be either primary or metastatic. Primary bone cancer starts in the bone. Metastatic bone cancer comes from other parts of the body. Knowing the difference is key for the right treatment.
- Primary Bone Cancer: This includes osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma. Each needs its own way of being diagnosed.
- Metastatic Bone Cancer: This is more common and often comes from cancers like breast, prostate, or lung. Finding where the cancer started is part of diagnosing it.
How Bone Cancer Affects Bone Structure
Bone cancer can change the bone’s structure, causing problems. Osteolytic lesions destroy bone tissue, while osteoblastic lesions cause abnormal growth. These changes are seen in imaging studies and help doctors diagnose bone cancer.
Key Diagnostic Indicators Physicians Look For
Doctors use several important signs to find bone cancer. These include:
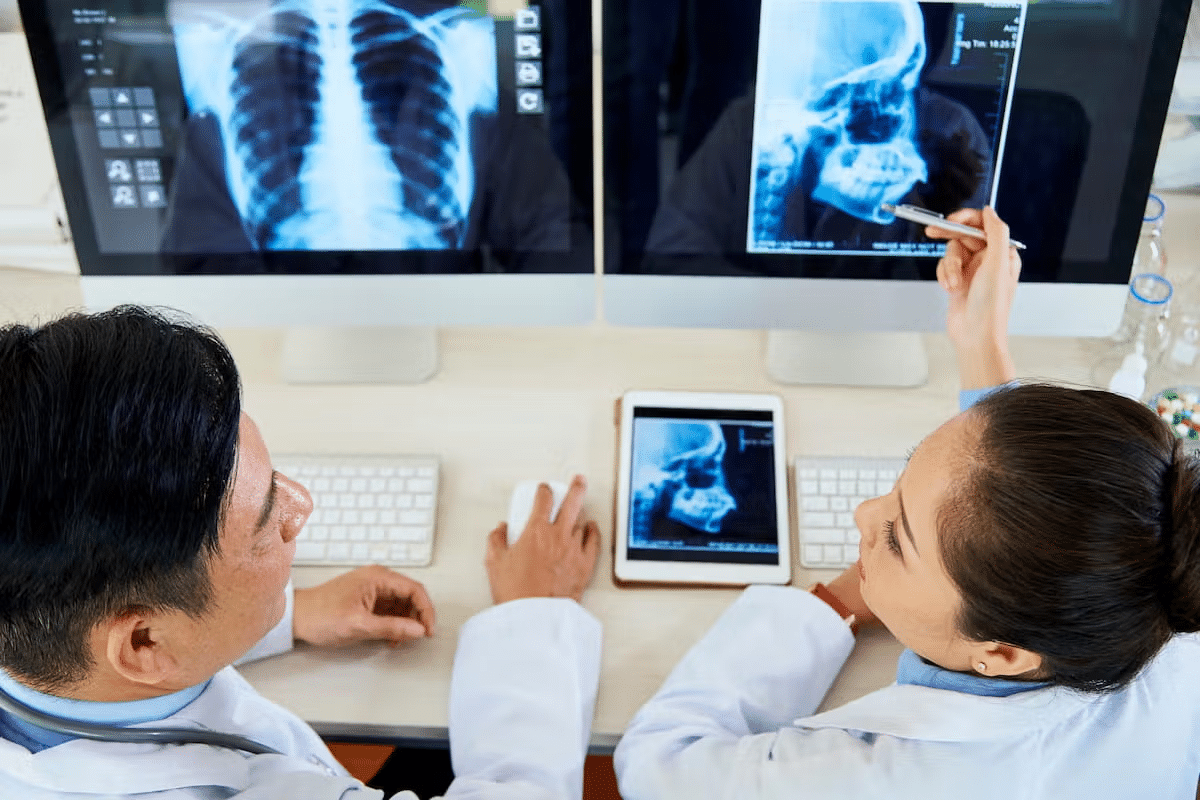
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans show the size and type of bone lesions.
- Biopsy: A biopsy confirms cancer cells and the type of bone cancer.
- Clinical Evaluation: Patient history, symptoms, and physical exams also help in diagnosing bone cancer.
By using these methods together, doctors can accurately diagnose and treat bone cancer. This helps improve patient care.
Superior Imaging Modalities for Bone Cancer Detection
For finding bone cancer, some imaging methods are better than others. DEXA scans are good for checking bone density. But, more advanced methods are needed to find bone cancer accurately.
MRI: Detailed Soft Tissue and Bone Marrow Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is great for spotting bone cancer. It shows soft tissue and bone marrow in detail. MRI helps see how far tumors have spread, which is key for knowing the cancer’s stage.
CT Scans: 3D Visualization of Bone Structure
Computed Tomography (CT) scans give a 3D view of bones. They help find tumors and check bone health. CT scans are good for looking at bone and finding tumor calcifications.
Bone Scintigraphy (Bone Scan): Detecting Metabolic Activity
Bone scintigraphy, or a bone scan, uses radioactive material to spot active bone areas. It’s good at finding cancer spread in bones and checks the whole body.
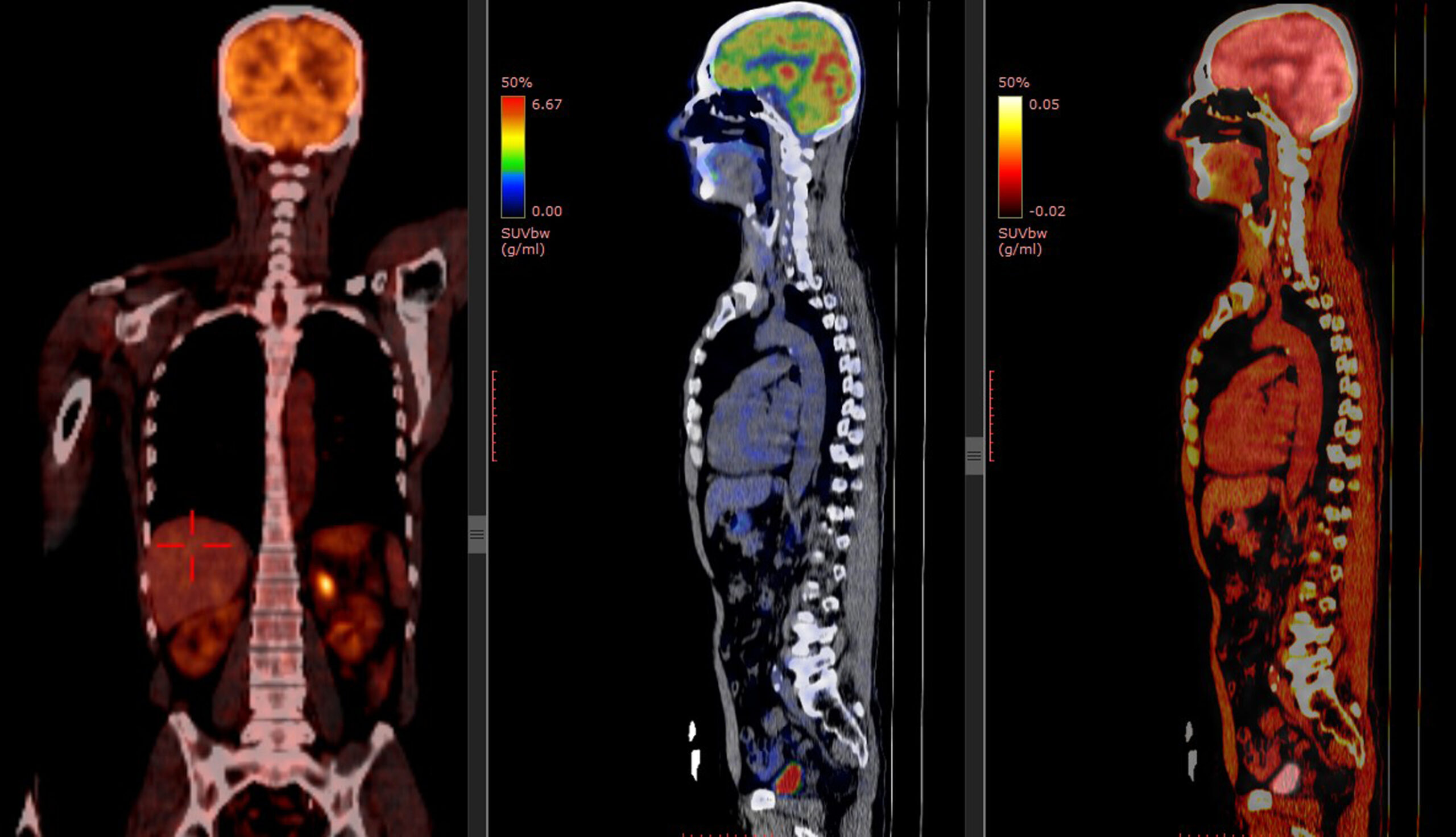
PET Scans: Identifying Cancer Cell Activity
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are top-notch for finding cancer cells. They use special tracers to see where cells are active. This helps see how cancer has spread and if treatments are working.
In summary, while DEXA scans have their uses, advanced imaging like MRI, CT scans, bone scintigraphy, and PET scans are better for bone cancer. These tools give the detailed info needed for accurate diagnosis and treatment plans.
When DEXA Scans Might Indicate Possible Bone Abnormalities
DEXA scans can sometimes spot unusual bone density patterns or changes that need more tests. They are mainly used to check bone mineral density and spot osteoporosis. But, they can also hint at other bone issues that need looking into.
Unusual Bone Density Patterns
DEXA scans might show bone density patterns that don’t fit with common bone problems. These can include diffuse or focal areas of increased or decreased bone density. Such findings might point to conditions like bone metastases, Paget’s disease, or other bone issues.
Localized Density Changes
Localized density changes mean specific spots where bone density is way off from the rest. These can show up on a DEXA scan. For example, a scan might show a vertebra with much lower density, hinting at a fracture or other problem.
These changes can sometimes hint at conditions that need medical care. In such cases, more tests are usually needed to figure out the cause and how big the problem is.
Follow-up Procedures When Abnormalities Are Detected
If a DEXA scan shows possible bone issues, more tests are usually suggested. These might include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): To get detailed images of soft tissues and bone marrow.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans: To see the bone structure in 3D and spot small changes.
- Bone scintigraphy (Bone Scan): To check how active bones are metabolically.
We team up with patients and their doctors to pick the best follow-up tests. This depends on the patient’s specific needs and situation.
DEXA Scans in Cancer Patient Care: Monitoring Bone Health
As cancer treatment gets better, checking bone health with DEXA scans is key. Patients with breast, lung, or prostate cancer face a higher risk of losing bone and breaking bones.
Bone Health Concerns During Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatments like chemo, hormone therapy, and radiation harm bones. They can make bones weaker, raising the chance of osteoporosis and fractures. DEXA scans help track these changes and guide doctors.
Keeping bones healthy is vital for cancer patients. DEXA scans help doctors spot problems early and act fast.
Monitoring Treatment-Induced Bone Loss
Bone loss from treatment is a big worry for cancer patients. DEXA scans are a trusted way to watch bone density changes. This info is key for adjusting treatments to protect bones.
|
Cancer Type |
Common Treatments |
Bone Health Risks |
Monitoring Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Breast Cancer |
Hormone therapy, chemotherapy |
Osteoporosis, fractures |
Regular DEXA scans |
|
Prostate Cancer |
Hormone therapy, radiation |
Bone loss, osteoporosis |
DEXA scans at diagnosis and follow-up |
|
Lung Cancer |
Chemotherapy, targeted therapy |
Bone metastases, osteoporosis |
Baseline DEXA scan, regular monitoring |
Fracture Risk Assessment in Cancer Survivors
Cancer survivors face a higher risk of fractures due to bone loss from treatment. DEXA scans measure bone density to assess this risk. This helps doctors find who’s most at risk and suggest ways to prevent fractures.
Key factors in fracture risk assessment include:
- History of fractures
- Bone mineral density as measured by DEXA scans
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Use of medications that affect bone health
Understanding these factors and using DEXA scans helps us care for cancer survivors better. This way, we can help them live a good life despite their challenges.
The Diagnostic Journey: From Suspicious Findings to Definitive Diagnosis
When DEXA scans show something suspicious, patients start a complex and emotional journey. This path includes many steps, from the first scan to getting a clear diagnosis. It’s important for us to support our patients at every step.
Initial Imaging and Referral Process
The first step is usually more tests to learn about the suspicious findings. We might suggest MRI or CT scans for a closer look. Then, we send patients to specialists for focused care.
Referral to specialists is key. Depending on the findings, patients might see oncologists, orthopedic doctors, or others. These experts bring the needed knowledge.
Biopsy and Pathological Confirmation
Often, a biopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This means taking tissue from the area and checking it for disease signs. We aim to make this process as easy as possible for patients.
The biopsy results are vital for planning treatment. Our team works with pathologists and specialists to ensure accurate diagnosis and care.
Patient Experience and What to Expect
We focus on the patient experience, giving the support and care needed. This time can be tough, both physically and emotionally. We’re here to make it as smooth as we can.
Patients can expect a caring and thorough approach. Our team is ready to answer questions, offer guidance, and provide reassurance during the diagnostic process.
Conclusion: The Role of DEXA Scans in Comprehensive Bone Health
DEXA scans are key in checking bone health by showing bone density and osteoporosis risk. They help us see how healthy our bones are. But, they can’t replace other tests for cancer.
DEXA scans can spot bone issues that might need more tests. For cancer patients, they help keep an eye on bone health. This way, we can stop fractures before they happen.
In short, DEXA scans are very important for bone health checks. They work best when used with other tests. This way, we can give patients the right care and improve their health.
FAQ
Does a DEXA scan show bone cancer?
DEXA scans are not made to find bone cancer. They might show some things by chance, but they’re not good for diagnosing cancer. For finding bone cancer, MRI, CT scans, and PET scans work better.
Can a bone density test detect cancer?
Bone density tests, like DEXA scans, check bone health and find osteoporosis. They’re not for finding cancer, but might show something odd that needs more looking into.
What does bone cancer look like on a bone scan?
Bone cancer might show up as spots of more or less activity on a bone scan. But, these scans can’t tell for sure if it’s cancer. To really know, a biopsy and lab tests are needed.
Will a DEXA scan show cancer?
DEXA scans aren’t for finding cancer. They help see how strong your bones are and spot osteoporosis. They might find something odd, but they’re not good for cancer checks.
Can a DEXA scan detect bone metastases?
DEXA scans don’t usually find bone metastases. For finding cancer spread to bones, MRI, CT scans, and PET scans are better.
Are DEXA scans useful for cancer patients?
Yes, DEXA scans help cancer patients. They check bone health during treatment, see if bones are losing density, and figure out fracture risk in survivors.
What are the limitations of DEXA scans in detecting bone abnormalities?
DEXA scans have limits in finding bone problems. They don’t catch cancer or specific bone issues well. They might miss some bone problems.
What should I expect if I have a suspicious finding on a DEXA scan?
If a DEXA scan finds something odd, your doctor might want more tests or a biopsy. You’ll get a full check to figure out what’s going on.
How do DEXA scans contribute to comprehensiv bone health?
DEXA scans help with bone health by checking density and spotting osteoporosis. They help doctors find who’s at risk of bone fractures and plan how to stop or treat bone loss.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. DEXA Scan Inadequate for Bone Cancer Detection. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK45513/