The human body can work without some organs. But what if we lose our appendix? Studies show the appendix might help our immune system and gut health. Even though it’s seen as a leftover organ, losing it can lead to unexpected problems. Discussing the minimal Effects of Living Without an Appendix on the body’s digestive and immune systems.
We’ll look into the health implications of not having an appendix. This includes how appendectomy affects our health. Knowing these effects of living without an appendix helps us understand our body better.
Key Takeaways
- The appendix may have a role in our immune system and gut health.
- Removing the appendix can have unforeseen health consequences.
- Understanding the effects of living without an appendix is key for our health.
- Recent studies have shown the appendix’s importance.
- The impact of appendectomy on health is a big area of research.
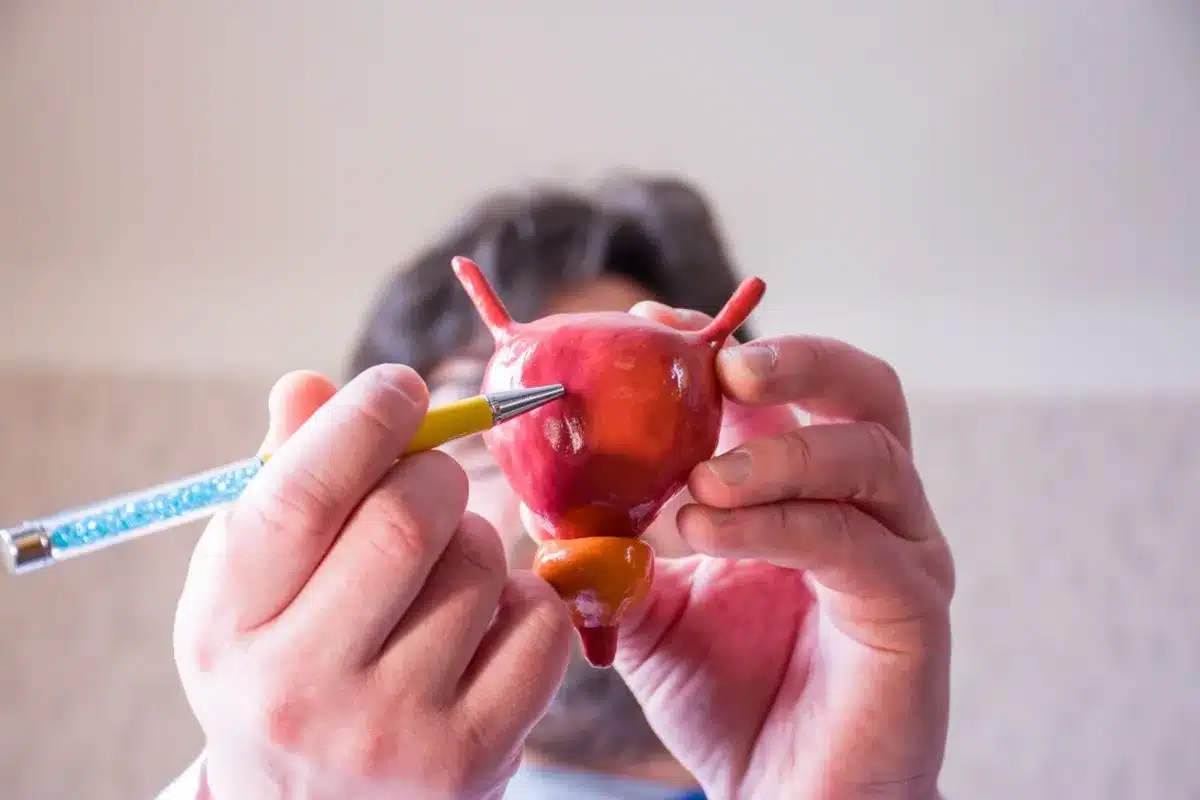
The Appendix: Understanding Its Function and Purpose

For years, the appendix was seen as useless. But recent studies have changed our view. It’s a small, tube-like structure attached to the large intestine. Knowing its role can help us understand its importance for our health.
Historical Perspective on Appendix Function
Long ago, people thought the appendix was useless. They believed it was leftover from our ancestors. This idea came from seeing people without an appendix live normally without digestive problems.
“The appendix is a small, finger-like pouch connected to the large intestine, and its function has been a topic of debate among anatomists and physicians for centuries.”
— A reflection on the historical view of the appendix
Modern Scientific Understanding
Now, we think the appendix might be useful. Research shows it could hold good bacteria. This helps our gut after sickness, keeping it healthy.
Aspect | Historical View | Modern Understanding |
Function | Considered vestigial with no significant function | Believed to be a reservoir for beneficial bacteria |
Role in Health | Removal not associated with significant health issues | May aid in recovery from gut infections |
The Appendix as an Immune Organ
The appendix is full of lymphoid tissue. This is key for our immune system. It helps make antibodies and activate immune cells. This means the appendix might play a big role in our immune system, mainly when we’re young.
The appendix’s role in our health is complex. While it might need to be removed, understanding it can help us see its long-term effects on our health and immune system.
Appendectomy: When and Why It’s Performed
An appendectomy is a common emergency surgery. It involves removing the appendix, a small tube-like structure attached to the large intestine. Sometimes, the appendix gets inflamed or infected, leading to appendicitis. If not treated, it can cause serious problems, making surgery urgent.
Emergency vs. Elective Appendectomy
Most appendectomies are emergency surgeries. They are done when symptoms of appendicitis appear, like severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Sometimes, an appendectomy is planned if someone has had appendicitis before or has other health issues.
Emergency appendectomy is the usual choice. It aims to stop the appendix from bursting and causing more harm. Prompt surgery is key to avoid serious infections like peritonitis.
Surgical Approaches and Techniques
There are different ways to remove the appendix. The main methods are:
- Open Appendectomy: This traditional method involves making a single incision in the lower right abdomen to access and remove the appendix.
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy: A minimally invasive technique that uses several small incisions, a laparoscope, and specialized surgical tools to remove the appendix. This approach often results in quicker recovery times and less postoperative pain.
The choice between these methods depends on the severity of the appendicitis, the patient’s health, and the surgeon’s preference.
“The laparoscopic approach has revolutionized the treatment of appendicitis, providing a less invasive option with fewer complications and faster recovery.” –
A renowned surgeon
Immediate Post-Surgical Recovery
After an appendectomy, patients stay in the hospital for a while. They manage pain, watch for complications, and slowly get back to normal activities.
Most people can get back to their usual life in a few weeks. But, recovery time can vary. It depends on the patient’s health, the surgery type, and if any issues came up during or after the surgery.
Short-Term Effects of Living Without an Appendix
After an appendectomy, your body starts to heal. Knowing what to expect in the first few weeks is key. We’ll help you understand what happens right after surgery.
Physical Recovery Timeline
The time it takes to recover from an appendectomy varies. It depends on the surgery type and your body. Usually, it takes a few weeks to fully heal. You might be back to normal in 2-4 weeks. But, always listen to your doctor’s advice.
Common Post-Surgical Symptoms
After surgery, you might feel pain, nausea, and tiredness. Managing pain is very important. Your doctor will help you find ways to feel better.
Watch out for these symptoms:
- Mild to moderate pain at the surgical site
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or feeling weak
- Mild fever
Normal vs. Concerning Recovery Signs
It’s important to know the difference between normal and concerning signs. Normal signs include mild pain and swelling that get better over time. But, some symptoms need quick medical help.
Normal Recovery Signs | Concerning Recovery Signs |
Mild pain manageable with medication | Severe pain not relieved by medication |
Mild swelling or bruising | Increasing swelling or redness around the incision site |
Gradual improvement in symptoms | Fever above 101.5°F (38.6°C) |
Ability to perform daily activities | Vomiting or inability to keep down fluids |
Knowing the short-term effects and what to watch for can help your recovery. Always follow your doctor’s advice for a safe and smooth healing process.
Impact on Digestive Health and Function
The appendix is now seen as important for gut health, even though its exact role is debated. It may act as a home for good bacteria that help with digestion and boost the immune system. This is based on research that suggests its function goes beyond being a leftover from evolution.
Changes in Digestive Processes
After an appendectomy, some people might notice changes in how their body digests food. These changes can show up as constipation or diarrhea. The appendix helps keep the gut’s balance of bacteria, and losing it could upset this balance.
Studies show the appendix helps store good bacteria for the gut. Without it, the body might take longer to get over infections or could be more prone to digestive problems.
Potential Gastrointestinal Issues
Some research links appendix removal to a higher risk of gut problems. These can include:
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis might be more likely after an appendectomy.
- Gastrointestinal infections: Losing the appendix’s role in storing good bacteria could make it harder to fight off infections.
- Other digestive issues: Some people might experience bloating, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel habits after surgery.
Nutritional Absorption Considerations
The appendix is part of the digestive system, and removing it could affect how we absorb nutrients. It doesn’t directly absorb nutrients but is important for the balance of gut bacteria. An imbalance, or dysbiosis, can make it harder to absorb nutrients and might lead to deficiencies.
To avoid problems, those who have had their appendix removed should eat a diet full of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Doctors might also suggest probiotics or supplements to help with gut health.
It’s key for those who have had their appendix removed to be aware of these possible changes. Talking to a healthcare provider about any concerns is important. Understanding how appendix removal affects digestion can help patients stay healthy.
The Appendix and Immune System Function
The appendix is more than just a small part of our digestive system. It plays a key role in our immune response. It’s filled with lymphoid tissue, which is important for our Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT).
Role in Immune Response
The lymphoid tissue in the appendix helps our immune system. It aids in the growth of lymphocytes, which fight off pathogens. The appendix also stores good bacteria. This helps repopulate the gut after illness.
Key functions of the appendix in immune response include:
- Supporting the development of GALT
- Aiding in the maturation of lymphocytes
- Serving as a reservoir for beneficial bacteria
Changes in Immunity After Appendectomy
Removing the appendix might change how our body fights off infections. Some studies show a slight increase in infection risk, mainly in the gut.
But, our bodies can adjust. Other parts of our immune system can take over. The full impact of losing the appendix is something scientists are studying.
Research on Infection Risk Post-Appendectomy
Many studies have looked into if removing the appendix raises infection risk. Some say yes, others say no. It’s a mixed bag.
More research is needed to understand how losing the appendix affects our immune system and infection risk.
Gut Microbiome Alterations After Appendix Removal
The appendix is now seen as more than just a leftover part. It’s believed to hold good bacteria that help the gut after sickness. Scientists are looking into how losing the appendix changes our gut’s bacteria.
The Appendix as a Bacterial Reservoir
The appendix is thought to be a safe spot for good bacteria. It keeps them safe during times of stomach upset like diarrhea. The appendix acts as a biofilm reservoir, helping the gut get back to normal after sickness. Studies show it’s full of different kinds of bacteria.
Changes in Gut Flora Composition
Removing the appendix might change the types of bacteria in our gut. People without an appendix might have different gut bacteria than those who have one. These changes could affect how well we digest food and our overall health.
Gut Microbiome Aspect | With Appendix | Without Appendix |
Bacterial Diversity | High diversity of beneficial bacteria | Reduced diversity, potentially leading to imbalance |
Pathogen Resistance | Enhanced resistance thanks to good bacteria | Potential decrease in resistance |
Recovery from Illness | Faster recovery with appendix’s help | Slower recovery, possibly longer illness |
Potential Long-Term Microbiome Effects
The long-term effects of losing the appendix on our gut’s bacteria are being studied. It’s thought that changes in our gut’s bacteria could affect our immune system. This might raise the risk of some stomach problems.
We’re learning more about how the appendix and our gut’s bacteria are connected. More research is needed to understand the effects of removing the appendix. This will help doctors make better choices for their patients.
Potential Long-Term Complications of Appendectomy
An appendectomy can fix the immediate problem of appendicitis. But, it’s important to think about the long-term issues that might happen after surgery.
Bowel Obstruction Risk
Bowel obstruction is a serious long-term problem. It happens when the intestine gets blocked. This can cause severe pain, vomiting, and constipation. People who had an emergency appendectomy are at higher risk.
Chronic Abdominal Pain
Some people might have ongoing abdominal pain after surgery. This pain can come from adhesions, nerve damage, or other issues. It’s key to talk to a doctor about any pain that doesn’t go away.
Incisional Hernias
Incisional hernias are another possible long-term issue. They happen when tissue bulges through the surgical scar. The risk depends on the surgery method, wound infection, and the patient’s health.
Adhesion Formation
Adhesions are bands of tissue that can form after surgery. They can cause bowel obstruction or chronic pain. While not all adhesions are a problem, they are common after abdominal surgery.
Complication | Description | Risk Factors |
Bowel Obstruction | Partial or complete blockage of the intestine | Emergency surgery, adhesions |
Chronic Abdominal Pain | Persistent pain in the abdominal region | Nerve damage, adhesions, underlying conditions |
Incisional Hernias | Tissue protrusion through the surgical scar | Surgical technique, wound infection, patient health |
Adhesion Formation | Formation of fibrous tissue bands between organs or the abdominal wall | Abdominal surgery, infection, individual healing processes |
It’s important for patients to know about these possible long-term issues after an appendectomy. Following post-op care and going to follow-up appointments can help catch any problems early.
Appendectomy and Risk of Other Health Conditions
Recent studies have looked into how appendectomy might be linked to serious health issues. We’re learning more about the appendix’s role in our health. This research has uncovered possible long-term effects of removing it.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Some studies suggest a link between appendectomy and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). This includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The appendix helps with the gut’s immune function. Removing it might upset the balance of gut bacteria, leading to IBD in some people.
Colorectal Cancer Risk
There’s been interest in how appendectomy affects colorectal cancer risk. The appendix is part of the large intestine. Its removal might change the risk of colorectal cancer. Some studies hint at a connection, but more research is needed to confirm this.
Cardiovascular Considerations
New evidence points to a possible link between appendectomy and heart health. Inflammation is key in heart diseases. Removing the appendix could affect body-wide inflammation. Ongoing research aims to find out if there’s a direct link to heart health.
We’re learning more about how different body systems interact. We’re also finding out how surgeries like appendectomy affect our health. As research continues, we’ll understand better how to reduce risks and improve outcomes for those who’ve had their appendix removed.
Psychological Impact of Emergency Surgery and Living Without an Organ
Having an emergency appendectomy can change a person’s life. It affects them not just physically but also emotionally. The sudden surgery can cause a range of feelings, from anxiety and fear to relief and gratitude.
Processing Unexpected Medical Emergencies
Being diagnosed with appendicitis and needing emergency surgery can be very shocking. Patients might feel anxious, fearful, and relieved all at once. It’s important for doctors to offer emotional support during this time.
This support helps patients deal with their feelings and adjust to their new situation. We know that the emotional impact of such an event is big. It’s key to address these feelings for a full recovery. By guiding and supporting, we help patients get through this tough time.
Body Image and Perception
After an emergency appendectomy, some people might feel different about their body. They might feel a loss or change in their body. It’s important to acknowledge these feelings and reassure them that losing an appendix is common and sometimes necessary.
We stress the need for open talks between patients and doctors. This helps clear up any worries or wrong ideas about the surgery and what comes after.
Coping Strategies and Support
It’s important for patients to find ways to cope with the emotional effects of emergency surgery and living without an appendix. This can include talking to loved ones, doing things that reduce stress, and following the doctor’s advice after surgery.
We suggest that patients keep in touch with their healthcare team. They should report any worries or symptoms during recovery. This way, they get the support and advice they need to recover well.
Coping Strategies:
- Seeking support from loved ones
- Engaging in stress-reducing activities
- Following post-operative care instructions
- Staying connected with healthcare providers
Lifestyle Adjustments After Appendix Removal
After an appendectomy, making lifestyle changes can greatly help your recovery. Life without an appendix means making several key adjustments.
Dietary Considerations
Diet is very important after removing the appendix. At first, eat foods that are easy on your stomach. Later, add foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support your health.
Drinking lots of water is also key. Some foods might make you uncomfortable or upset your stomach. Talk to a healthcare provider or nutritionist to create a diet plan that’s right for you.
Food Type | Recommended | To Avoid |
Fruits | Bananas, applesauce | Citrus fruits, berries |
Vegetables | Cooked carrots, green beans | Raw vegetables, cabbage |
Grains | White rice, toast | Whole grains, spicy foods |
Physical Activity Guidelines
Physical activity is important too. Rest first to let your body heal. Then, start with light activities like walking to improve circulation and strength.
Listen to your healthcare provider about when to start exercising again. Avoid too much activity to prevent problems.
Long-Term Health Monitoring
Watching your health long-term after an appendectomy is key. Be aware of risks like bowel obstruction or hernias. Tell your doctor if you notice any unusual symptoms.
Going to regular check-ups helps catch and manage problems early. Eating well and staying active keeps you healthy overall.
Special Considerations for Different Age Groups
The effects of removing the appendix vary by age. Each age group has its own needs and challenges. This means different care is needed for each group.
Children and Adolescents
Young people who have their appendix removed face unique recovery paths. It’s important to watch their digestive health and immune system growth. Their bodies are constantly changing.
Parents should notice any changes in their child’s appetite or bowel habits after surgery. A balanced diet is key for their recovery and health.
Adults and Middle-Aged Individuals
Adults and those in middle age may face different issues after the surgery. They might need to make lifestyle changes like eating differently and staying at a healthy weight. This can help avoid problems.
They should also be aware of the risk of adhesions or bowel obstruction later on. Regular doctor visits can catch any problems early.
Elderly Patients
Elderly people may have more risks and complications after surgery. They need close monitoring and care to avoid and manage these issues.
They should watch for signs of infection or other complications and tell their doctor right away. Keeping their health in check, including any chronic conditions, is important during recovery.
Age Group | Key Considerations | Potential Complications |
Children and Adolescents | Monitoring digestive health and immune system development, balanced diet | Changes in appetite and bowel habits |
Adults and Middle-Aged | Lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, healthy weight | Adhesions, bowel obstruction |
Elderly Patients | Close monitoring, post-operative care, managing chronic conditions | Infection, post-surgical complications |
Current Research on Appendix Function and Post-Appendectomy Health
Research on the appendix is revealing new insights into its role in our health. We’re learning more about its importance for our well-being.
Emerging Scientific Understanding
Recent studies have changed what we know about the appendix. It’s no longer seen as just a leftover part. The appendix is believed to act as a reservoir for beneficial bacteria, helping to repopulate the gut after illness.
“The appendix serves as a safe house for beneficial bacteria, allowing them to repopulate the gut after a diarrheal illness or other infection.” – This quote from a leading researcher in the field highlights the appendix’s role in gut health.
Ongoing Clinical Studies
Many studies are looking at how appendectomy affects health. They’re studying immune function, gut health, and disease risk. For example, a study found that those who had their appendix removed were more likely to get inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Investigating the role of the appendix in immune system development
- Examining the impact of appendectomy on gut microbiota
- Assessing the long-term risk of various diseases post-appendectomy
Future Directions in Appendix Research
As we learn more about the appendix, research will evolve. We might explore new treatments for appendicitis that keep the appendix. Future research may also explore the possibility of appendix transplantation or other innovative treatments.
“As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the appendix, we may uncover new avenues for preventing and treating diseases related to the gut and immune system.”
A leading gastroenterologist
By deepening our understanding of the appendix, we can improve care for those who have it removed. This will help us develop better treatments.
Conclusion: Living a Healthy Life Without an Appendix
The appendix might seem important, but losing it doesn’t always mean health problems. Many people stay healthy without an appendix. With the right care, you can avoid big issues after its removal.
Not having an appendix means making some changes in your life. You need to watch your digestion, look out for complications, and eat well. Knowing how appendix removal affects you helps you stay healthy.
Scientists are always learning about the appendix and its role in health. They might find out more about it soon. For now, people who had their appendix removed can live well with the right care.
FAQ
What are the immediate effects of living without an appendix?
After an appendectomy, recovery can take several weeks. Symptoms include abdominal pain, fatigue, and bowel changes. Most people can get back to normal in a few weeks.
How does appendix removal affect digestive health?
Removing the appendix can cause digestive issues like diarrhea or constipation. But for most, these problems are short-lived. Digestive health usually returns to normal over time.
Can living without an appendix increase the risk of infections?
Some studies suggest a slight increase in infection risk after removing the appendix. But for most, the impact on the immune system is minimal.
Are there any long-term complications associated with appendectomy?
Long-term issues can include bowel obstruction, chronic pain, and hernias. These complications are rare but possible.
How does appendix removal affect the gut microbiome?
The appendix helps keep beneficial bacteria in the gut. Removing it can change gut flora. But the body often adjusts, and the gut microbiome can rebalance.
Are there any dietary recommendations after appendix removal?
Eat a balanced, easy-to-digest diet after surgery. Start with bland foods and gradually add variety. Drinking plenty of water is also key.
Can appendix removal impact physical activity?
Patients should start with light exercises a few weeks after surgery. Gradually increase activity as recovery allows.
Is there a higher risk of other health conditions after appendectomy?
Some research links appendectomy to increased risks of diseases like inflammatory bowel diseases or colorectal cancer. But more research is needed to confirm this.
How does age affect recovery and health after appendix removal?
Recovery time varies with age. Younger people tend to heal faster than older adults. Elderly patients may need closer monitoring.
What are the psychological impacts of undergoing an emergency appendectomy?
Emergency surgery can be stressful and affect mental health. Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends can help manage these effects.
How can one monitor their health after appendix removal?
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are important. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and watching for unusual symptoms helps monitor health after surgery. Report any concerns to your doctor.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3015275/