Cushing syndrome is a hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high cortisol levels. Learn about its definition, types, and medical scope.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and Definition
The human body is a masterpiece of biological engineering, orchestrated by a complex network of chemical messengers called hormones. These invisible signals travel through your bloodstream, dictating everything from your energy levels and weight to your mood, growth, and fertility. When this delicate balance is disrupted, the effects can be devastating.
At Liv Hospital, the Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism serves as the “Control Center” for your health. We do not simply treat symptoms; we act as medical detectives to identify the root cause of the imbalance. Whether you are struggling with a thyroid nodule, unmanaged diabetes, or a rare pituitary tumor, our approach is defined by Precision Metabolism.
We combine the latest diagnostic technology—from high-resolution ultrasonography to dynamic hormone suppression tests—with advanced therapeutic options. Liv Hospital is one of the few centers in the region offering TOETVA (Scarless Thyroid Surgery) and integrated Nuclear Medicine therapies, ensuring that your treatment is not only effective but also minimally invasive and aesthetically superior.
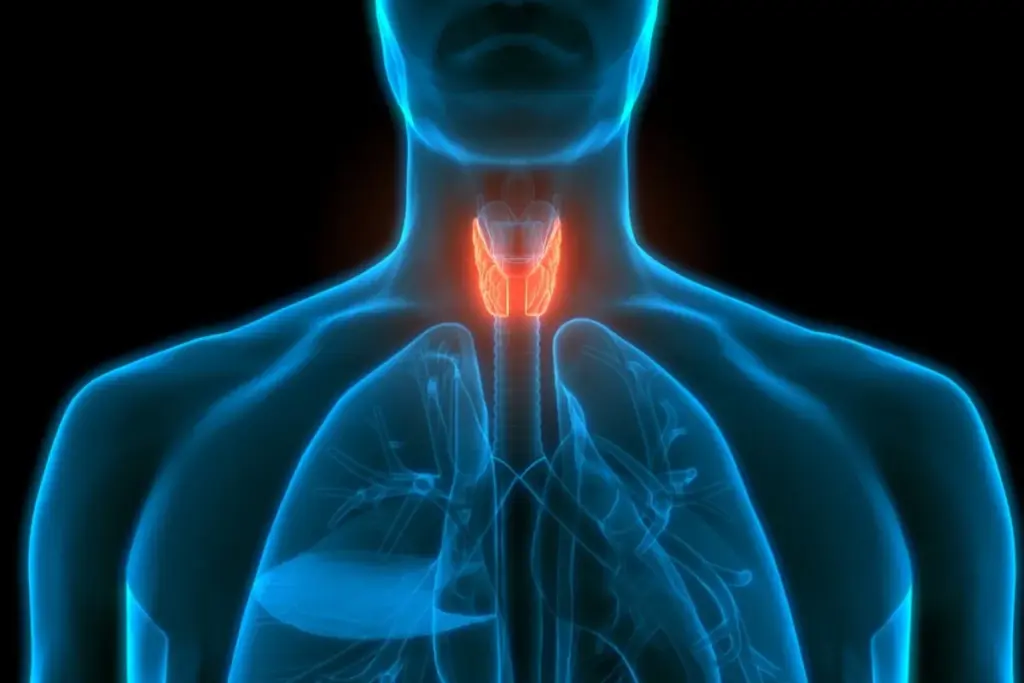
Endocrinology is the branch of medicine that deals with the Endocrine System—the glands that produce hormones. Think of your body as an orchestra. The organs (heart, lungs, liver) are the musicians, but the endocrine glands are the conductors. If the conductor is too fast (Hyperthyroidism) or too slow (Hypothyroidism), the music falls apart.

Thyroid disorders are the most common endocrine issue we treat. Our center is renowned for its comprehensive “Nodule-to-Surgery” pathway.
Many patients come to us with a “suspicious lump.” We use High-Resolution Ultrasonography with Doppler flow to assess the nodule’s risk instantly. If needed, we perform a Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNA) under ultrasound guidance.

For Hyperthyroidism (Graves’ Disease) or Thyroid Cancer remnants, we work seamlessly with our Nuclear Medicine Department.
For decades, thyroid surgery meant a visible scar across the neck. Liv Hospital is a pioneer in TOETVA (Transoral Endoscopic Thyroidectomy Vestibular Approach).

Diabetes is not just about “high sugar”; it is a vascular disease that threatens the eyes, kidneys, and heart. We move beyond basic metformin prescriptions to offer Next-Generation Diabetes Management.
Managing Type 1 diabetes is a 24/7 job. We use technology to lighten the burden.
For Type 2 patients, our goal is often Remission—getting off medication entirely.
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized organ at the base of the brain. Tumors here can cause havoc, from giantism (Acromegaly) to milk production in men (Prolactinoma).
The adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys. When they malfunction, they can cause dangerous hypertension or physical changes.
Endocrinologists often work closely with other specialists. They team up with endocrine surgeons for thyroid or parathyroid surgery, ophthalmologists for eye checks in diabetes or Graves’ disease, and dietitians to help manage diabetes and obesity. This teamwork provides complete care for complex health issues.
Hormones are the fuel of reproduction. We treat the hormonal barriers to fertility and wellness.
Osteoporosis is a silent thief. It steals bone mass until a hip or spine fracture occurs.
Obesity is a hormonal disease, not a willpower failure. Our Endocrinologists lead the Medical Weight Loss Program.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Hormones are chemical messengers released into the bloodstream to affect distant organs over a more extended period, while neurotransmitters are chemicals released by nerve cells to send rapid signals across a synapse to a neighboring cell.
It is called the master gland because it produces stimulating hormones that control the function of the thyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs, effectively acting as the manager of the endocrine system.
Yes, you can live without a thyroid gland, but you must take synthetic thyroid hormone replacement medication daily for the rest of your life to maintain metabolism and bodily functions.
Yes, hormonal imbalances can significantly impact mental health, causing symptoms such as anxiety, depression, mood swings, and cognitive fog, as the brain is susceptible to hormonal fluctuations.
Obesity is increasingly recognized as a metabolic and endocrine disease because fat tissue acts as an active endocrine organ, releasing hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism, and obesity often involves resistance to hormones like insulin.


We look into the anterior pituitary gland, also called the adenohypophysis. It’s at the brain’s base, in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. This small
Revising sleeve gastrectomy to gastric bypass is now a common choice in bariatric surgery. About 9-11% of all bariatric surgeries today are revisions after sleeve gastrectomy sleeve
If you’ve had weight loss surgery but didn’t get the results you wanted, finding the right bariatric revision surgeon is key revision weight loss surgery.
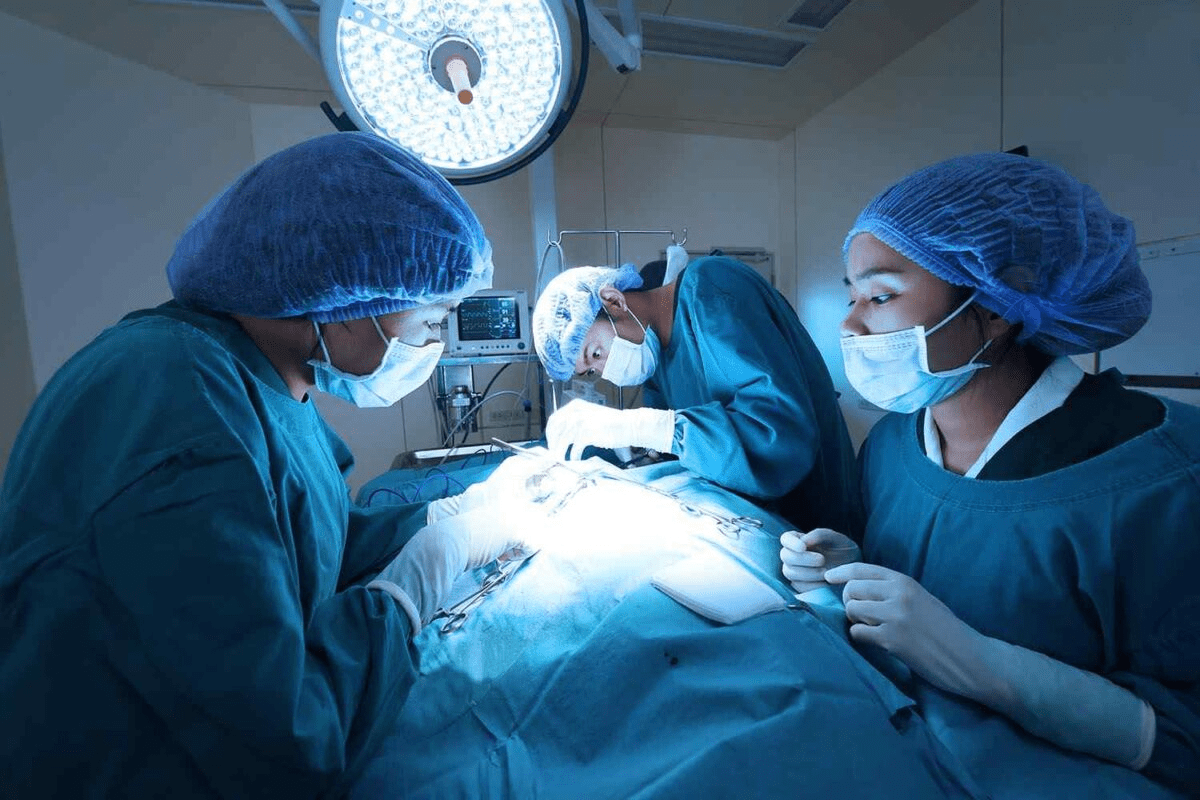
Gastric bypass surgery, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, changes the stomach’s size to help with weight loss. It makes a small pouch at the
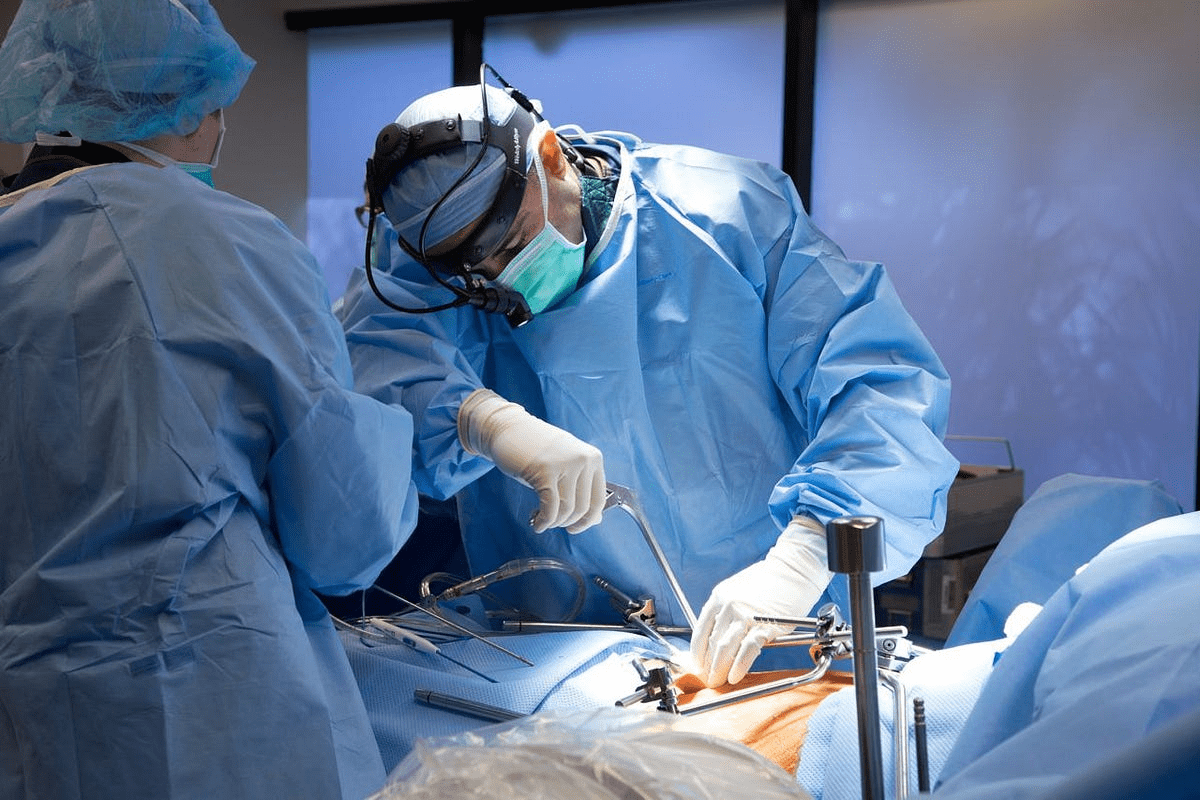
Gastric sleeve surgery is a big step in weight loss. It changes how much your stomach can hold. Surgeons take out about 80-85 percent of
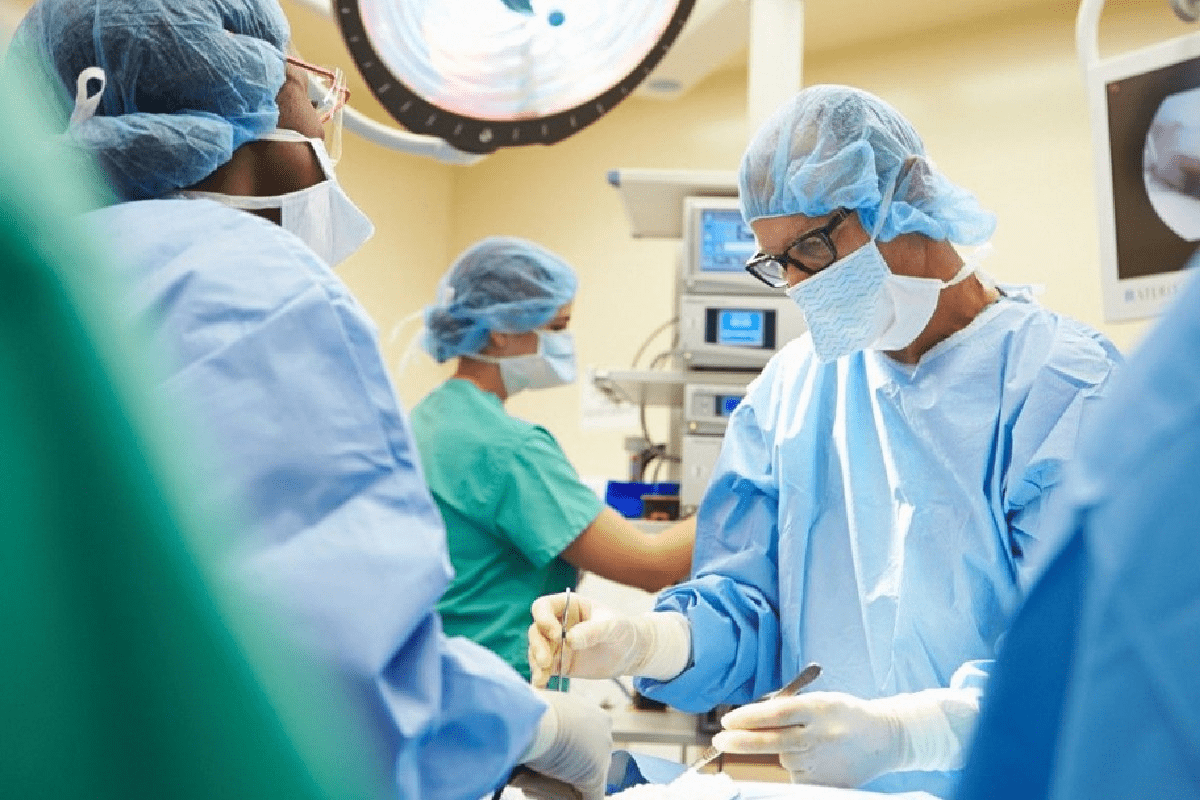
Patients who don’t lose enough weight or gain it back after sleeve gastrectomy might consider gastric bypass. Studies show that about 4.7% of people need

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)