Carotid artery stenosis is a big risk for stroke, hitting thousands globally. Nearly 1 in 5 strokes is caused by carotid artery stenosis. This shows how vital quick and effective treatment is.Learn what degree of stenosis is considered for carotid endarterectomy. Understand the threshold for surgical intervention clearly.
Carotid endarterectomy is a key surgery for carotid artery stenosis. Deciding on this surgery depends on the severity of stenosis and overall health. Knowing the stenosis degree for carotid endarterectomy is key for both patients and doctors to make smart choices.
Key Takeaways
- Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove plaque buildup in the carotid arteries.
- The degree of stenosis is a critical factor in determining the need for carotid endarterectomy.
- Symptomatic patients with severe stenosis are typically considered for surgery.
- The severity of stenosis is assessed through imaging tests, such as ultrasound or angiography.
- Carotid endarterectomy can significantly reduce the risk of stroke in patients with severe carotid stenosis.
Understanding Carotid Artery Stenosis
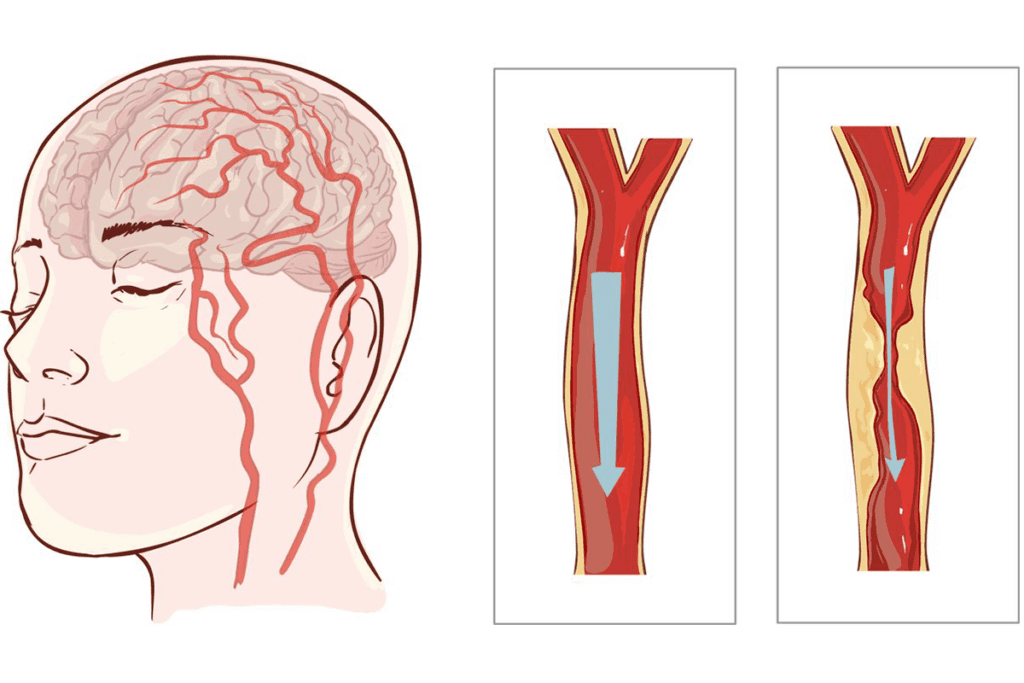
It’s key to understand carotid artery stenosis to diagnose and treat carotid artery disease. This condition is when the carotid arteries narrow due to plaque buildup. It’s a major part of carotid artery disease.
Definition and Pathophysiology
Carotid artery stenosis happens when plaque builds up in the carotid arteries, causing them to narrow. The atherosclerotic process is when lipids, inflammatory cells, and fibrous elements gather, forming plaque.
Atherosclerotic Process
The atherosclerotic process is complex. It starts with lipids entering the arterial wall and then an inflammatory response. As the plaque grows, it narrows the artery, reducing blood flow.
Hemodynamic Effects
The narrowing of the carotid arteries can cause hemodynamic effects. This reduced blood flow to the brain can lead to transient ischemic attacks or strokes. The severity of stenosis determines the risk of these events.
A medical expert notes, “The degree of carotid stenosis is key in deciding if surgery is needed, like carotid endarterectomy.” This shows how important it is to accurately measure stenosis severity.
Clinical Significance of Carotid Stenosis
Carotid stenosis is linked to a higher stroke risk. The more severe the stenosis, the higher the stroke risk. This makes it a major concern for health.
Relationship to Stroke Risk
Carotid stenosis increases stroke risk in two main ways. Knowing these ways helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Embolic Mechanisms
Embolic mechanisms happen when pieces of thrombi or plaque break off. These pieces block blood flow in other parts of the brain, causing a stroke. “The majority of strokes in patients with carotid stenosis are due to embolic events.”
Hypoperfusion Mechanisms
Hypoperfusion mechanisms occur when severe stenosis cuts off blood flow to the brain. This leads to brain ischemia. It’s often linked to hemodynamic issues.
A medical expert said,
“Carotid stenosis is a significant predictor of stroke, and its management is critical in preventing stroke-related morbidity and mortality.”
Methods for Measuring Carotid Stenosis
Accurate measurement of carotid stenosis is key for making medical decisions. Different imaging methods are used to check how severe the stenosis is. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses.
Ultrasound Evaluation
Ultrasound is a popular, non-invasive way to check carotid stenosis. It uses two main methods:
Velocity Criteria
Peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end-diastolic velocity (EDV) help figure out how severe the stenosis is. Higher numbers mean more severe stenosis.
B-mode Imaging
B-mode imaging lets doctors see the carotid artery and plaque up close. This helps them judge how severe the stenosis is.
CT Angiography
CT angiography gives detailed pictures of the carotid arteries. It’s great for accurately measuring stenosis, even in tough cases.
Measurement Techniques
CT angiography uses image reconstruction to measure stenosis precisely. It’s very accurate and reliable.
MR Angiography
MR angiography is another non-invasive way to check carotid stenosis. It gives clear images without using harmful radiation.
Advantages and Limitations
MR angiography is good because it’s non-invasive and doesn’t use radiation. But, it’s not for everyone, like those with metal implants or who get anxious in tight spaces.
| Imaging Modality | Advantages | Limitations |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, cost-effective | Operator-dependent, limited by patient factors |
| CT Angiography | High sensitivity and specificity | Involves radiation, contrast agents |
| MR Angiography | No radiation, high-resolution images | Contraindicated in certain patients, higher cost |
What Degree of Stenosis is Considered for Carotid Endarterectomy?
Guidelines now clearly state when carotid endarterectomy is needed. This decision is based on how severe the stenosis is, symptoms, and the patient’s overall health.
Historical Evolution of Stenosis Criteria
The rules for when to do carotid endarterectomy have changed a lot. This change came from big studies that showed what works best.
Early Surgical Thresholds
At first, doctors had different ideas about when to do the surgery. This was because there wasn’t much research back then.
Impact of Major Trials
Big studies like the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) and the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST) changed things. They showed that carotid endarterectomy can really help people with severe stenosis.
“The NASCET trial showed that carotid endarterectomy helps a lot, leading to new guidelines.”
NASCET Collaborators
Current Consensus Guidelines
Today, doctors follow guidelines that are based on solid research. These guidelines look at how severe the stenosis is and if the patient has symptoms.
American Heart Association/American Stroke Association
The American Heart Association/American Stroke Association says to do carotid endarterectomy for certain patients. This includes those with symptoms and 50-99% stenosis, or those without symptoms but with 60-99% stenosis, if the risk of surgery is low.
European Society for Vascular Surgery
The European Society for Vascular Surgery also supports carotid endarterectomy for some patients. They stress the need to look at each patient’s situation and health problems.
In summary, the rules for when to do carotid endarterectomy have gotten clearer. Clinical judgment is key in deciding if surgery is right for each patient.
Evidence from Major Clinical Trials
Landmark clinical trials have greatly shaped how we manage carotid artery stenosis. These studies have shown that carotid endarterectomy is effective in preventing strokes.
NASCET Trial Findings
The North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) was a key study. It showed that carotid endarterectomy helps symptomatic patients. The trial grouped patients by stenosis level.
Severe Stenosis Outcomes
Those with severe stenosis (70-99%) saw a big drop in stroke risk after surgery. The trial found a 17% absolute risk reduction at 2 years.
Moderate Stenosis Outcomes
For those with moderate stenosis (50-69%), the benefits were less but significant. NASCET showed a 6.5% absolute risk reduction at 5 years.
ECST Trial Results
The European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST) also looked at carotid endarterectomy’s effectiveness. Though similar to NASCET, ECST had some methodological differences.
Key Differences from NASCET
ECST measured stenosis differently, which made comparing results tricky. Yet, both trials agreed that carotid endarterectomy helps those with severe stenosis.
ACAS and ACST for Asymptomatic Patients
The Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study (ACAS) and the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial (ACST) focused on asymptomatic patients. These studies showed that carotid endarterectomy can lower stroke risk in this group.
Risk Reduction Metrics
ACAS found a 5.9% absolute risk reduction at 5 years for asymptomatic patients who had surgery.
Number Needed to Treat
The number needed to treat (NNT) to prevent one stroke was about 20 in ACAS. This shows how effective the procedure is.
| Trial | Patient Group | Absolute Risk Reduction | NNT |
| NASCET | Symptomatic, Severe Stenosis | 17% | 6 |
| ACAS | Asymptomatic | 5.9% | 20 |
Guidelines for Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis
Guidelines for symptomatic carotid stenosis stress the need for quick evaluation and treatment. This is to prevent strokes. Patients with serious stenosis need fast assessment and might need carotid endarterectomy.
Current guidelines suggest urgent checks for those with symptoms like transient ischemic attack or minor stroke. Carotid endarterectomy is seen as a key treatment for these patients, mainly those with severe stenosis.
Doctors treating patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis must know these guidelines. The American Heart Association and other groups have set carotid endarterectomy recommendations. These are based on big clinical trials.
By sticking to these guidelines, doctors can spot who will benefit most from carotid endarterectomy. This helps lower stroke risk and improves patient results.
FAQ
What is carotid endarterectomy, and how does it relate to carotid stenosis?
Carotid endarterectomy is a surgery that removes plaque from the carotid arteries. It helps prevent strokes in people with severe carotid stenosis.
What degree of stenosis is typically considered for carotid endarterectomy?
The decision for carotid endarterectomy depends on symptoms and health. Usually, those with 70% or more stenosis are considered for the surgery.
How is carotid stenosis measured, and which imaging modalities are used?
Doctors use ultrasound, CT angiography, and MR angiography to measure carotid stenosis. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses.
What are the benefits and risks associated with carotid endarterectomy?
The surgery can greatly lower stroke risk in those with severe stenosis. But, it also comes with risks like stroke, heart attack, and death during or after surgery.
What do major clinical trials, such as NASCET and ECST, tell us about carotid endarterectomy?
The NASCET and ECST trials showed carotid endarterectomy helps symptomatic patients with severe stenosis. The ACAS and ACST trials found benefits for asymptomatic patients with significant stenosis too.
How do guidelines recommend managing symptomatic carotid stenosis?
Guidelines suggest urgent evaluation and possible carotid endarterectomy for symptomatic patients with significant stenosis.
What is the role of carotid endarterectomy in stroke prevention?
Carotid endarterectomy is key in preventing strokes. It removes plaque from the carotid arteries, reducing stroke risk in those with severe stenosis.
How has the degree of stenosis considered for carotid endarterectomy evolved over time?
The criteria for carotid endarterectomy have changed a lot. This is due to major trials and guidelines, leading to more evidence-based recommendations.
What are the indications for carotid endarterectomy in asymptomatic patients?
Asymptomatic patients with stenosis of 60% or more might be considered for surgery. This depends on their overall risk and health.
How do healthcare providers determine the need for carotid endarterectomy?
Doctors decide on carotid endarterectomy based on a detailed evaluation. This includes stenosis degree, symptoms, health, and individual risk assessment.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8370069/


































