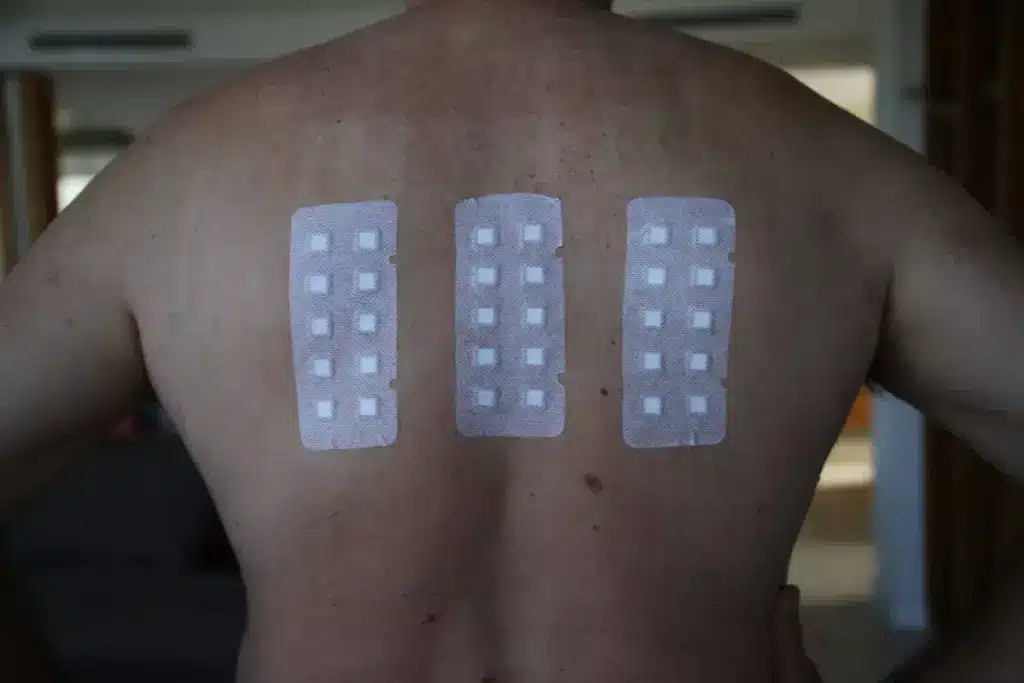
Did you know millions of people worldwide have contact dermatitis? This skin condition is often diagnosed with an allergy patch test. This tool is key to finding out what’s causing the problem.
An allergy patch test works by putting small amounts of possible allergens on the skin. This is usually done on the back. It helps see if there’s a bad reaction. Knowing about this skin patch test is important for patients to get ready and know what to expect.
This article will explain what happens during an allergy test on back. We’ll cover how long it takes and what the results mean for your health.
Key Takeaways
- An allergy patch test is used to diagnose contact dermatitis.
- The test involves applying possible allergens to the skin.
- Results are usually ready in a few days.
- The test is done on the back.
- Knowing about the test helps patients prepare better.
Understanding Allergy Patch Tests
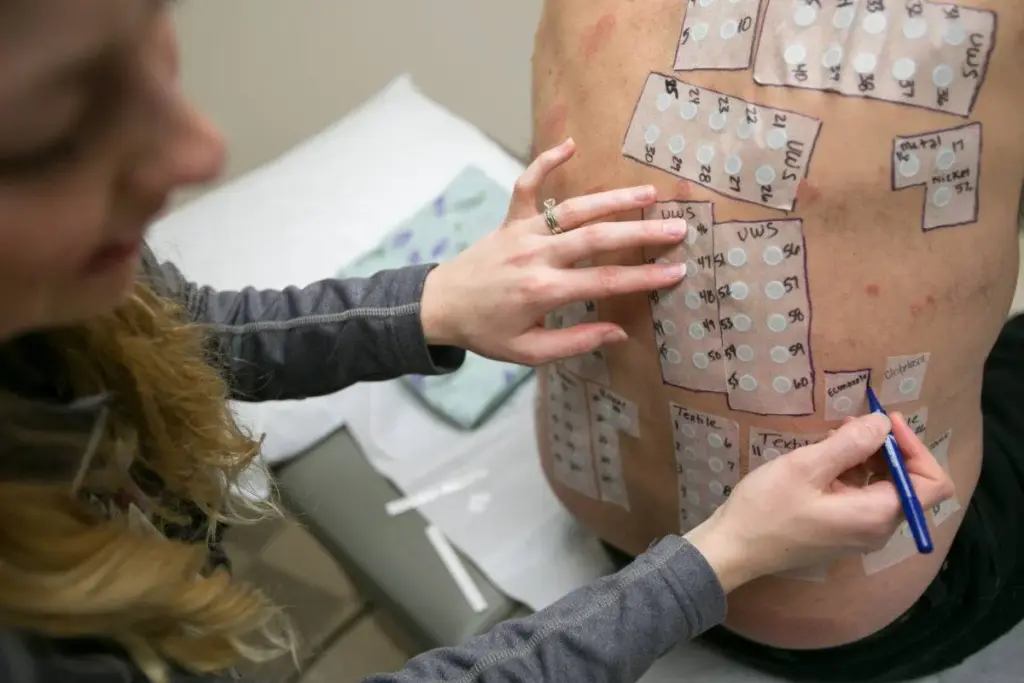
Learning about patch testing is key for those with allergic contact dermatitis. This test helps find out if a certain substance causes skin inflammation. It’s a way to figure out what’s causing the problem.
What Is a Patch Test?
A patch test applies small amounts of possible allergens to the skin, often on the back. These are held in place by adhesive patches. The TRUE test includes common allergens known to cause skin reactions.
Common Allergens Tested
Tests look for metals like nickel and cobalt, fragrances, preservatives, and rubber chemicals. The choice of allergens depends on the suspected allergy and the test type. For example, a customized allergen panel might be used for certain jobs.
Difference Between Patch Tests and Other Allergy Tests
A patch test is different from an allergy scratch test. It finds delayed hypersensitivity reactions, not immediate ones. It’s great for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis, which can hurt the skin over time.
Unlike blood tests or prick tests, patch tests watch the skin’s reaction over days. This makes them a key tool for doctors to find the cause of skin problems.
The Complete Patch Test Timeline
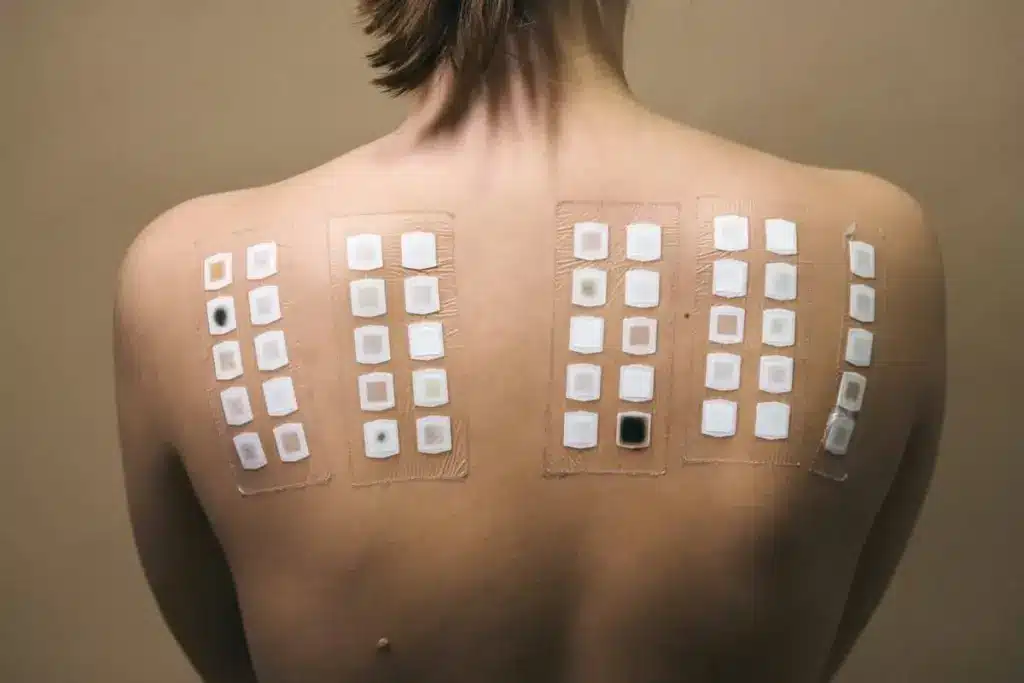
The journey to find out what you’re allergic to starts with a first meeting. It goes on with many follow-ups. Knowing this timeline helps patients get ready for what’s coming.
Initial Consultation (Day 0)
The first step is a meeting with a doctor. They check if you need a patch test. They talk about your health, symptoms, and past allergies. This meeting makes the test fit your needs.
Test Application Day (Day 1)
On the test day, the doctor gets your skin ready. They put patches with different allergens on your back. The patch test procedure makes sure the patches stay in place.
First Check-up (48 Hours/Day 3)
48 hours later, you go back to the patch test clinic. The doctor checks the patches and your skin’s reaction. Some reactions show up early, others take time. They note any positive signs.
Final Reading (72-96 Hours/Day 4-5)
The last check is 72 to 96 hours after the patches go on. This is key for seeing the patch test results. The doctor looks at your skin again. They compare it to the first check-up. This helps figure out your allergies and how to treat them.
Knowing the dermatology patch test timeline helps patients prepare. By the end, they’ll know their allergies and how to handle them.
Why Doctors Recommend Patch Tests
The allergen patch test is a key tool for finding out what causes skin allergies. Doctors suggest it for those with signs of allergic reactions. It helps figure out the exact allergen causing the problem.
It’s great for finding out what’s causing a skin issue that’s hard to spot. Doctors put small amounts of possible allergens on the skin. Then, they watch for reactions to find out what’s causing the allergy.
Diagnosing Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common skin issue. It makes the skin red, itchy, and inflamed. It happens when the skin meets an allergen or irritant. Patch testing is key in finding out what’s causing it.
“Patch testing is essential for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis, as it allows for the identification of specific allergens that may not be immediately apparent.”
Journal of Dermatology
To do a patch test, doctors put patches with different allergens on the back. These patches stay on for days to see if a reaction happens. Then, a doctor looks at the results to see if there’s an allergy.
Identifying Unknown Allergens
Many people react to something without knowing what it is. Patch testing can find these unknown allergens. It’s helpful for those who can’t avoid certain products or substances.
- Common allergens tested include metals like nickel and cobalt.
- Fragrances and preservatives in personal care products are also frequently tested.
- Some patch tests include less common allergens depending on the patient’s history.
Confirming Suspected Allergies
Some people think they might be allergic to something. Patch testing can prove it. It’s good for those who want to be sure before changing their daily life.
|
Allergen |
Common Sources |
Reaction |
|---|---|---|
|
Nickel |
Jewelry, buckles, coins |
Redness, itching |
|
Fragrances |
Perfumes, soaps, lotions |
Eczema, dermatitis |
|
Cobalt |
Medical equipment, jewelry |
Skin discoloration, itching |
Knowing what causes a reaction helps avoid it and manage symptoms better. Doctors say patch testing is a good way to diagnose and manage skin allergies.
Who Should Consider Getting a Patch Test
Edit
Full screen
Delete
patch test for skin allergies
If you’re dealing with ongoing skin problems, a patch test could help find the cause. It’s great for people with skin allergies or conditions made worse by certain things.
Common Symptoms Indicating Need for Testing
Some signs suggest you might need a skin allergy test. Look out for:
- Unexplained rashes or irritation on the skin
- Redness or itching that won’t go away with over-the-counter treatments
- Skin reactions from new products or the environment
Medical Conditions That Benefit from Patch Testing
People with specific health issues can really benefit from patch testing for skin allergies. These include:
- Contact dermatitis
- Eczema
- Chronic skin irritation
Occupational Considerations
Some jobs put you at risk for allergens, making a patch test essential. These jobs are:
- Healthcare workers exposed to latex or disinfectants
- Hairdressers and beauticians who handle chemicals
- Construction workers exposed to metals and other materials
When to Postpone Testing
Even though a patch test clinic is helpful, there are times to wait. These include:
- During an active flare-up of a skin condition
- If you’re taking certain medications that could affect test results
- When you’ve recently changed your skin care routine a lot
Preparing for Your Patch Test
Edit
Full screen
Delete
patch test preparation
Getting ready for your patch test is important for good results. Knowing what to do before the test can really help.
Medications to Avoid Before Testing
Some medicines can mess with your patch test results. Tell your doctor about any drugs you’re taking. Topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines should be stopped before the test. They can hide skin reactions.
- Oral corticosteroids may need to be tapered off or stopped before testing.
- Immunosuppressant drugs can affect test results and should be discussed with your doctor.
Skin Preparation Guidelines
Before the test, avoid using moisturizers, creams, or lotions on your back for 3 days. Make sure your skin is clean and oil-free on test day.
Avoid too much sun and hard activities that make you sweat a lot. These can change your skin and test results.
What to Wear to Appointments
Wear loose, comfortable clothing on test day. This helps avoid irritation and keeps patches in place. Don’t wear tight clothes that might rub against the patches.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
Ask your doctor questions before the test. This helps you understand what’s happening. Some important questions are:
- What are the most common allergens tested in a patch test?
- How long will the patches remain on my skin?
- Are there any specific aftercare instructions I should follow?
- How will I receive my test results, and what do they mean?
Being well-prepared helps your patch test go smoothly. It also makes sure the results are accurate. If you have any worries or questions, talk to your healthcare provider.
The Patch Test Procedure Step by Step
Edit
Full screen
Delete
patch test application process
A patch test involves applying small amounts of possible allergens to the skin. It checks for reactions. This tool is key for finding out what causes allergic contact dermatitis.
Initial Assessment
First, a healthcare professional does an initial assessment. They look at the patient’s medical history and symptoms. They also examine the affected skin area.
The goal is to find out what might cause an allergic reaction. Then, they decide how to do the patch test.
Allergen Application Process
Small patches with different allergens are applied to the skin, usually on the back. These patches stay on for a few days. This lets the healthcare provider see how the skin reacts.
They make sure the patches are put on right. This ensures the test results are accurate.
Securing the Patches
After applying the patches, they need to stay in place. This is done with hypoallergenic adhesive or tape. Patients are told how to take care of the patches.
This helps them stay on during the test.
Post-Application Instructions
Patients get instructions on patch care after application. They’re told to avoid activities that might remove the patches. This includes not sweating too much or swimming.
They’re also told to watch for any skin reactions. If they feel uncomfortable or have concerns, they know what to do.
By following these steps, the patch test helps find out about skin allergies. It helps doctors diagnose and treat allergic contact dermatitis well.
What to Expect During the Testing Period
Edit
Full screen
Delete
patch test aftercare
Knowing what to expect during the patch testing period can make it easier. It’s important to follow certain guidelines to get accurate results. This helps you prepare and reduces stress.
Activity Restrictions
Try to avoid activities that might mess up the test results. Avoid strenuous exercise and activities that make you sweat a lot. Also, don’t swim or take long baths as they can remove the patches.
Showering and Bathing Guidelines
It’s okay to shower or bathe during the test period. But be gentle around the patch area. Avoid harsh soaps or exfoliating products on the skin with patches. When showering, pat the area dry gently; don’t rub or scrub.
|
Activity |
Recommended Action |
|---|---|
|
Showering |
Gently pat dry around the patch area |
|
Bathing |
Avoid submerging the patch area in water |
|
Exercise |
Avoid strenuous exercise that causes excessive sweating |
Managing Discomfort
Some people might feel discomfort or itching during the test. To ease this, try a cold compress or over-the-counter anti-itch creams. But always check with your doctor first.
When to Call Your Doctor During Testing
If you have severe itching, redness, or any unusual reactions, call your doctor. They can help manage symptoms and ensure the test results are good.
By following these tips and knowing what to expect, you can get accurate patch test results. This makes the process smoother and less stressful.
Different Types of Patch Tests Available
There are many patch testing methods, each with its own uses and benefits. Patch testing is key for finding skin allergies. Knowing the different types helps patients and doctors pick the best test.
TRUE Test System
The TRUE Test System is a common patch testing method. It uses pre-made panels with common allergens on the skin. It’s easy to use and follows a set standard, making it a favorite among dermatologists.
Customized Allergen Panels
For people exposed to specific substances, customized panels are better. These panels match the person’s job or environment, focusing on their allergies.
Specialized Industry-Specific Tests
Workers in certain fields, like construction or healthcare, face unique allergens. Special tests for these industries help find work-related allergies.
Comparative Test Durations
How long a patch test lasts varies by type and skin reaction. Here’s a table showing typical test times:
|
Test Type |
Typical Duration |
Key Features |
|---|---|---|
|
TRUE Test System |
3-4 days |
Standardized, easy to apply |
|
Customized Allergen Panels |
4-7 days |
Tailored to individual needs, flexible |
|
Industry-Specific Tests |
3-5 days |
Designed for specific occupational exposures |
Knowing about the various patch tests helps both individuals and healthcare providers. Whether it’s the TRUE Test or a custom test, the aim is the same. It’s to find skin allergies accurately and treat them effectively.
Reading and Interpreting Patch Test Results
Patch test results can be tricky, but knowing them is key for managing allergies. When you see your doctor again, usually 72 to 96 hours after the test, they’ll tell you if you’re allergic to anything.
Positive Reactions: What They Look Like
A positive test shows up as a skin reaction where the allergen was applied. You might see redness, swelling, or blisters. The reaction’s strength can vary, and your doctor will rate it to see how sensitive you are.
The doctor uses a scale from mild to severe to understand your allergy level. It’s important to talk to your doctor about what the results mean and how to stay away from allergens.
Negative Results
A negative test means no allergic reaction was found for the tested substances. But, it’s important to remember that a negative result doesn’t always mean you’re not allergic. It might just mean the tested allergen wasn’t the problem.
Your doctor might suggest more tests or talk about other reasons for your symptoms.
Irritant vs. Allergic Reactions
Telling irritant from allergic reactions is key for a correct diagnosis. Irritant reactions are not allergies but skin irritation from the test substance. Your doctor will check to see if it’s an allergy or irritation.
- Allergic reactions take time to develop and can get worse after the patch is off.
- Irritant reactions happen fast and usually go away once the irritant is removed.
Delayed Reactions
Sometimes, reactions to patch tests can show up later, even after the final reading. If you get new symptoms or reactions, you should call your doctor right away.
Though rare, delayed reactions can give more clues about your allergies and might need more checking.
Potential Side Effects and Complications
While patch testing is safe, it’s good to know about possible side effects. It’s a tool to find out what causes skin problems. But, like any test, it has risks.
Common Reactions During Testing
Most people get mild reactions when they test patches. But, some might get:
- Irritation at the patch site, which is usually mild and temporary
- Redness and itching, showing a possible allergic reaction
- Local edema (swelling) at the patch site
These reactions usually stay in the patch area and go away when the patches are removed.
Rare Complications
Though rare, severe reactions can happen. These might include:
- Active sensitization, becoming sensitized to an allergen during the test
- Permanent hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation at the test site
- Flare-up reactions, making a previous skin problem worse
For more info on managing these reactions, check out the American Academy of Dermatology.
Allergic Reaction to Patch Test Materials
In rare cases, people might be allergic to the patch test materials. This can cause mild irritation to a severe allergic reaction.
|
Symptom |
Description |
Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Mild Irritation |
Redness, itching under the patch |
Monitor, may resolve on its own |
|
Moderate Reaction |
Increased redness, swelling |
Consult doctor, may require topical treatment |
|
Severe Reaction |
Significant swelling, blistering |
Immediate medical attention required |
Managing Side Effects
It’s important to manage side effects well for the patch test to work. This includes:
- Keeping the test area dry to prevent the patches from falling off
- Avoiding strenuous activities that cause excessive sweating
- Not removing or tampering with the patches
- Using topical corticosteroids or oral antihistamines as directed by a healthcare provider to alleviate discomfort
Knowing about side effects and complications helps patients prepare for patch testing. It also tells them how to handle any bad reactions.
Patch Test Accuracy and Limitations
Patch testing is very useful but has its own challenges. Knowing these challenges helps us understand the results better.
False Positives and False Negatives
One big issue with patch testing is false positives and false negatives. False positives can make us avoid things we don’t need to. False negatives might mean we miss a real allergy.
- False positives can happen because of irritants or other things.
- False negatives might be because the allergen wasn’t strong enough or the test wasn’t applied right.
Factors Affecting Test Reliability
Many things can make patch test results less reliable. These include:
- The quality of the allergens used.
- How well the person applying the patches does it.
- Things specific to the patient, like their skin condition and medicines.
Complementary Testing Methods
Sometimes, we use other tests to check patch test results or get more info. These can be:
- Repeat open application tests (ROAT).
- Use tests.
- Intradermal tests in certain cases.
When Retesting May Be Necessary
Retesting might be needed if the first results aren’t clear, if we think of new allergies, or if we change how we’re exposed to allergens. It’s key to talk to a healthcare provider to figure out what to do next.
Cost and Insurance Coverage for Patch Testing
Understanding the costs of a patch test is key. Patch testing helps find out what causes skin allergies.
Average Costs in the United States
The price of patch testing changes based on several things. This includes how many allergens are tested and the provider’s fees. On average, it can cost between $200 and $1,000 or more.
|
Service |
Average Cost |
|---|---|
|
Initial Consultation |
$100-$200 |
|
Patch Test Application |
$50-$150 |
|
Follow-up Visits |
$50-$100 per visit |
Insurance Coverage Guidelines
Many insurance plans do cover patch testing, but it varies. Always check with your insurance to see what’s covered. For more on allergy testing costs, visit https://affderm.com/how-much-is-an-allergy-test/.
Questions to Ask Your Provider
Before getting a patch test, ask your provider about costs and what’s included. Some questions to ask include:
- What is the total cost of the patch test?
- Are there any additional fees for follow-up visits?
- Does the cost include any necessary medications or treatments?
Financial Assistance Options
If costs are a problem, there are ways to get help. Some providers offer payment plans or fees based on income. Also, some non-profit groups help with the cost of tests.
Finding a Qualified Patch Test Provider
Choosing the right patch test provider is key. They must be qualified to give accurate results. This is important for treating allergic contact dermatitis effectively.
Dermatologists vs. Allergists
Dermatologists and allergists can do patch tests. But, they focus on different things. Dermatologists deal with skin issues like contact dermatitis and have lots of patch test experience. Allergists work on allergies and immune problems. They can also help with patch tests, which is good if you have many allergies.
Specialized Patch Test Clinics
Some clinics are experts in patch testing. They use the TRUE Test System and custom panels. This gives you detailed tests that fit your needs. Look for clinics known for their accurate and reliable tests.
Questions to Ask Before Scheduling
Before your patch test, ask important questions. Here are some:
- What experience do you have with patch testing?
- What testing methods do you use?
- How will you determine the allergens to be tested?
- What is the cost, and is it covered by insurance?
Typical Wait Times for Appointments
Wait times for patch tests vary. It depends on the provider and where you are. Here’s what you might find:
|
Provider Type |
Average Wait Time |
|---|---|
|
Dermatologist |
2-6 weeks |
|
Allergist |
3-8 weeks |
|
Specialized Patch Test Clinics |
1-4 weeks |
Always call ahead to check wait times. This helps you plan better.
Living With Patch Test Results
Understanding how to live with your patch test results is key to avoiding allergens and reducing allergic reactions. After receiving your results, you’ll need to take proactive steps to manage your allergies effectively.
Creating an Allergen Avoidance Plan
The first step in managing your allergies is to create an allergen avoidance plan. This involves identifying the allergens you’ve tested positive for and finding ways to avoid them in your daily life. Start by making a list of the allergens you’re sensitive to and then research ways to minimize exposure.
For instance, if you’re allergic to nickel, you’ll need to avoid jewelry and clothing that contains nickel. If you’re allergic to certain fragrances, you’ll need to choose fragrance-free products.
Reading Product Labels
Reading product labels is key to avoiding allergens. Look for products labeled as hypoallergenic or fragrance-free, as these are less likely to contain common allergens. Be aware of ingredient names that may trigger allergies, such as fragrances, dyes, or preservatives.
|
Product Type |
Common Allergens to Avoid |
Safer Alternatives |
|---|---|---|
|
Skincare Products |
Fragrances, preservatives |
Fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products |
|
Jewelry |
Nickel, cobalt |
Stainless steel, titanium, or nickel-free jewelry |
|
Detergents |
Dyes, fragrances |
Fragrance-free, dye-free detergents |
Finding Suitable Alternatives
Finding alternatives to allergens is key to managing your allergies. This might involve switching to different brands or types of products that are less likely to cause allergic reactions. For example, if you’re allergic to latex, you can opt for vinyl or nitrile gloves instead.
When to Consider Retesting
It’s also important to know when to consider retesting for allergies. If you notice changes in your allergic reactions or if your symptoms persist despite avoiding identified allergens, it may be necessary to undergo retesting. Also, if you’re introducing new products or materials into your environment, retesting can help identify any new allergens.
By following these steps and staying informed, you can effectively manage your allergies and reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Patch Tests for Special Populations
Patch testing for special populations needs careful approaches. Each group has its own needs that healthcare providers must consider. This ensures accurate and safe results.
Children and Patch Testing
Children’s skin is very sensitive, so patch testing must be done with extra care. The amount of allergen used might need to be less. It’s also important to watch for any signs of discomfort or bad reactions.
Key considerations for pediatric patch testing include:
- Using lower concentrations of allergens
- Reducing the number of allergens tested
- Monitoring for signs of irritation or discomfort
Elderly Patients
Elderly patients have thinner skin, which can easily get irritated. They might also be taking many medicines that could affect the test results. Healthcare providers need to keep these things in mind when looking at the test results.
|
Consideration |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Skin Condition |
Thinner skin in elderly patients may increase the risk of irritation. |
|
Medication Interference |
Multiple medications can potentially affect patch test results. |
Pregnant Women
Patch testing during pregnancy needs to be done with caution. Some allergens might cause bad reactions. It’s often recommended to wait until after pregnancy for non-essential tests.
It’s very important for pregnant women to tell their healthcare provider about their pregnancy before patch testing.
Patients with Existing Skin Conditions
For people with skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, patch testing is more complicated. The skin’s condition at the test site can affect the results. If there are active lesions, the testing might need to be adjusted.
Healthcare providers can make patch testing safe and effective for different groups by understanding their unique needs. This way, they can tailor the testing to get the best results.
Advances in Patch Testing Technology
New technologies in patch testing are changing how we diagnose allergies. These changes make patch testing more accurate and efficient. They also improve the experience for patients.
Digital Tracking and Analysis
Digital tracking and analysis are big steps forward in patch testing. This tech lets doctors watch how patients react more closely. It also gives detailed data for analysis.
With digital tools, doctors can share test results easily. This helps everyone involved make better decisions together.
New Allergen Detection Methods
Scientists are finding new ways to detect allergens. This means we can test for more substances. It’s key for spotting new allergens and making tests more complete.
New methods make patch tests more reliable. They cut down on mistakes in test results. This leads to better treatment plans for patients.
Reduced Testing Time Innovations
There are also efforts to make patch testing faster. This lets doctors give patients results quicker. Patients can start their treatment plans sooner.
New materials, better ways to apply patches, and advanced reading tech are part of these efforts. They help find reactions faster and more accurately.
Future Developments
The future of patch testing looks bright. Technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning will help a lot. They will make patch testing even better.
As research goes on, we’ll see even more advanced testing methods. These might include non-invasive or barely invasive techniques. These changes will keep improving how we diagnose and treat allergies.
Conclusion
Allergy patch testing is a key tool for finding out what causes skin allergies. It involves putting allergens on the skin and watching for reactions over a few days. This helps people know what to avoid to manage their symptoms.
A patch test summary gives a detailed look at the testing and what it shows. This info is key for making a plan to avoid allergens and finding safe alternatives.
In short, the results of an allergy patch test conclusion can greatly improve someone’s life by lowering the chance of allergic reactions. By listening to experts and staying up-to-date on patch testing overview, people can handle their allergies better and keep their skin healthy.
FAQ
What is an allergy patch test?
An allergy patch test is a way to find out what causes skin allergies. It involves putting small amounts of possible allergens on the skin. Then, the skin is watched for reactions over several days.
How long does an allergy patch test take?
It usually takes about a week. The patches are put on the first day. The final check is between 72 to 96 hours later.
What are the common allergens tested in a patch test?
Common tests include metals like nickel and cobalt, fragrances, preservatives, rubber chemicals, and some medicines. The tests depend on what the person thinks they might be allergic to and their job.
How does a patch test differ from other allergy tests?
Patch tests look for delayed reactions, which take days to show up. Blood tests or prick tests find immediate reactions.
Can I shower or bathe while wearing the patches?
Usually, you’re told not to get the patches wet. This means you might not be able to shower or bathe during the test. Your doctor will give you specific instructions.
What should I do if I experience discomfort during the patch test?
If you’re uncomfortable, call your doctor. They might suggest over-the-counter pain relievers. Always follow their advice.
How are patch test results interpreted?
Results show if you’re allergic to something. A positive reaction means you are allergic. A negative result means you’re not.
Can patch tests cause allergic reactions?
Yes, they can. In rare cases, reactions can be serious. Always follow up with your doctor as they say.
Are patch tests covered by insurance?
Many insurance plans cover patch testing. But, coverage can vary. Check with your insurance and talk to your doctor about costs before the test.
How can I prepare for a patch test?
To prepare, avoid certain medicines and make sure your skin is clean and dry. Wear loose clothes and be ready to talk about your health and symptoms with your doctor.
Can children undergo patch testing?
Yes, kids can get patch tests. The test might be adjusted for their age and skin. Pediatric dermatologists might be involved.
What are the common side effects of patch testing?
Side effects include skin irritation, itching, and redness. Rarely, there can be severe reactions or infections.
How often should patch testing be repeated?
It depends on your situation. If your symptoms change or you’re exposed to new allergens, you might need to be tested again. Your doctor will tell you when.
Can patch tests be performed on pregnant women?
Yes, pregnant women can get patch tests. But, there are special precautions and considerations. Tell your doctor about your pregnancy to get the right care.
What are the advances in patch testing technology?
New tech includes digital tracking and analysis, better methods for finding allergens, and ways to make tests faster. These changes make patch testing more accurate and efficient.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34105598/