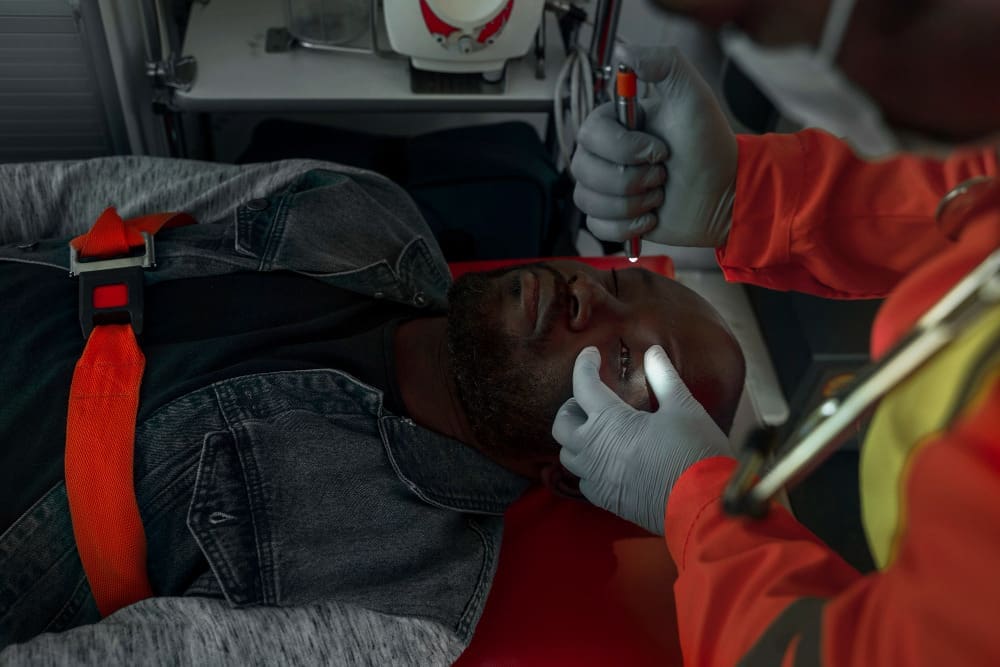
Knowing the signs of a stroke is key to quick medical help. The FAST acronym helps spot common stroke symptoms. At Liv Hospital, we stress the need to act fast when these signs appear.
The FAST acronym comes from American Heart Association. It’s a critical part of stroke care around the world. By knowing what F.A.S.T means, people can help save lives.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the FAST acronym is key to spotting stroke symptoms.
- Acting F.A.S.T. can greatly improve survival and recovery chances for stroke patients.
- Knowing the FAST acronym helps get medical help quickly.
- Liv Hospital stresses the importance of quick action to stroke symptoms.
Understanding Stroke: A Life-Threatening Emergency
It’s vital to understand what a stroke is to act fast. A stroke, or brain attack, happens when blood flow to the brain stops or slows down. This prevents brain cells from getting oxygen and nutrients.
What Happens During a Stroke
When the brain doesn’t get enough blood, brain cells can get damaged. This can lead to loss of function or even death. The damage’s extent depends on how long and where the stroke happens. Early detection using the stroke test acronym, FAST, is critical for minimizing damage.
The FAST acronym helps spot stroke victims fast. It stands for Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, and Time to call emergency services. Knowing the fast stroke meaning helps people react quickly when a stroke occurs.
Types of Strokes and Their Differences
There are mainly three types of strokes: ischemic, hemorrhagic, and transient ischemic attack (TIA). Each type has its own traits and needs different treatments.
| Type of Stroke | Cause | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Ischemic Stroke | Blockage of a blood vessel | Most common type, often caused by a blood clot |
| Hemorrhagic Stroke | Rupture of a blood vessel | Less common but more deadly, often associated with high blood pressure |
| Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) | Temporary blockage | Often referred to as a “mini-stroke,” it’s a warning sign for a future stroke |
Knowing the differences between these strokes is key to proper care. Being aware of risk factors and symptoms is important for quick medical help.
Stroke Statistics and Impact in the United States
It’s important to know the facts about stroke to understand its big impact on America. Stroke is a major health issue that affects millions in the U.S. every year.
Annual Incidence and Mortality Rates
Stroke is a top cause of death and disability in the U.S. The American Heart Association says someone in the U.S. has a stroke every 40 seconds. Also, someone dies from a stroke every 3 minutes and 33 seconds.
Looking at the numbers, we see stroke is a big public health problem. It needs quick action and prevention to tackle it.
| Year | Stroke Incidence | Stroke Mortality Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 795,000 | 37.6 per 100,000 |
| 2020 | 808,000 | 38.2 per 100,000 |
| 2021 | 823,000 | 38.8 per 100,000 |
Economic and Social Burden
Stroke has a big economic and social cost. The costs of stroke are over $100 billion a year in the U.S.
Stroke affects not just the person but also their family, community, and healthcare system. The long-term care and rehab for survivors add up to the cost.
Disparities in Stroke Occurrence and Outcomes
Stroke hits some groups harder than others in the U.S. This shows we need to focus on certain areas to help.
Age, gender, ethnicity, and income level all play a part in who gets stroke and how they do. Knowing this helps us find ways to lessen stroke’s impact.
The Critical Importance of Early Detection
Acting quickly is key during a stroke. Early detection is vital to reduce damage. Understanding how to treat strokes effectively is essential.
The “Time is Brain” Principle
The “time is brain” idea shows how fast action is needed. Every minute matters because the brain loses neurons without blood flow. This means quick medical help is critical to save brain function.
How Minutes Can Save Lives and Function
In stroke cases, every minute counts. Quick medical care reduces brain damage. Studies show this leads to better survival and function for patients.
For example, using thrombolytic therapy quickly can clear clots. This can restore blood flow and reverse stroke symptoms. This shows how vital early detection and action are.
The Treatment Window for Effective Intervention
The time to treat a stroke is short, usually 4.5 to 6 hours. Knowing this window helps doctors choose the best treatments.
During this time, treatments like thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy can help. The FAST acronym reminds us of the urgency and need for fast action.
Understanding early detection and stroke treatment is key to better patient outcomes. The “time is brain” principle is not just a saying. It’s a call to act quickly and effectively in medical emergencies.
The FAST Acronym for Stroke: A Life-Saving Tool
The FAST acronym is key in the battle against stroke. It stands for Face, Arm, Speech, and Time. It’s a simple way to spot stroke symptoms early.
Origins and Development of the FAST System
In the late 1990s, researchers in the UK created the FAST acronym. They wanted a tool that was easy for everyone to use. The FAST acronym was influenced by earlier stroke assessment scales, but it was made simpler for emergencies.
The creators of FAST used what we know about stroke symptoms. They focused on face drooping, arm weakness, speech issues, and the need for quick action. This made FAST a key part of stroke awareness globally.
Scientific Validation of the FAST Method
Many studies have shown FAST works well in spotting stroke patients. Using FAST can cut down on delays before getting medical help. The scientific community sees FAST as a valuable tool for everyone.
“The FAST acronym has been instrumental in educating the public about stroke symptoms and the importance of acting quickly.”
Why FAST Has Become the Global Standard
FAST is popular because it’s easy to remember and very effective. It gives a clear guide to recognizing stroke symptoms. This helps people get help fast. FAST is now a big part of worldwide efforts to fight stroke.
We think FAST will keep saving lives and helping patients all over the world.
F – Face Drooping: The First Warning Sign
The “F” in FAST stands for Face Drooping, a key warning sign. It means someone might be having a stroke. Facial asymmetry or drooping is one of the first signs.
How to Identify Facial Asymmetry
Facial asymmetry happens when one side of the face weakens or becomes paralyzed. To spot this, we can do a simple test. Ask the person to smile or show their teeth.
If their smile is uneven, it could be a stroke sign. Another test is to ask them to stick out their tongue. If it deviates to one side, it might be a stroke.
Simple Tests Anyone Can Perform
There are easy tests for facial drooping. First, ask the person to smile. An uneven smile could mean a stroke.
Another test is to ask them to stick out their tongue. If it goes to one side, it might be a stroke. These tests are simple and can be very helpful.
What Causes Facial Drooping During Stroke
Facial drooping in a stroke is usually from brain damage. This damage happens when blood flow to the brain stops. It affects the muscles controlling the face.
This damage can cause weakness or paralysis on one side of the face. Knowing this makes it clear why we need to act fast when we see these signs.
By spotting face drooping as a stroke warning, we can quickly get help. The FAST acronym is a simple way to detect strokes. It’s easy for everyone to use.
A – Arm Weakness: Testing Motor Function
One of the key signs of a stroke is sudden arm weakness. A stroke can harm many body functions, including how we move. Spotting arm weakness early is key for quick medical help.
During a stroke, arm weakness shows as trouble moving or lifting the arm. It might also feel numb or tingly. It’s important to spot these signs fast to get medical help right away.
Recognizing Sudden Weakness or Numbness
Sudden weakness or numbness in the arm is a big sign of a stroke. Look for:
- Difficulty lifting or moving the arm
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the arm
- Weakness on one side of the body
How to Test Arm Strength Properly
Testing arm strength is easy and quick:
- Ask the person to lift both arms and hold them at shoulder height.
- See if one arm drops or if they struggle to hold it up.
- Check for weakness by gently pressing on the arms.
Why Arm Weakness Occurs During Stroke
Arm weakness in a stroke happens because blood flow to the brain stops. This affects the brain’s motor control areas. It can cause weakness or paralysis in the arms.
| Cause | Effect on Arm |
|---|---|
| Interruption of blood flow to the brain | Weakness or numbness in the arm |
| Damage to motor control areas | Paralysis or trouble moving the arm |
Knowing why arm weakness happens and spotting it early can help a lot in a stroke emergency. Quick action and medical help can lessen a stroke’s effects and improve recovery.
S – Speech Difficulties: Communication Changes
When a stroke happens, one key warning sign is speech problems. These can show up as slurred or confused speech. The FAST acronym helps us spot these signs. It stands for Face, Arm, Speech, and Time.
Recognizing Speech Problems
Speech issues during a stroke might include slurred words or trouble finding the right words. It’s important to check if someone can understand and express themselves clearly.
Types of Speech Difficulties
There are different speech problems that can happen during a stroke. These include dysarthria (slurred speech) and aphasia (trouble with words or understanding). Knowing these signs is key, as every minute is critical.
The FAST acronym is a lifesaver for spotting stroke symptoms. Knowing what FAST stands for helps us act fast in emergencies. It reminds us that Face, Arm, Speech, and Time are all important signs.
What does the FAST acronym stand for in stroke detection?
FAST stands for Face, Arm, Speech, and Time. These are key signs to spot during a stroke.
What is the significance of the FAST acronym in identifying stroke signs?
Using FAST can greatly improve survival and recovery. It helps in early detection and treatment.
What happens during a stroke?
A stroke happens when the brain’s blood supply is cut off. This can be due to a blockage or a rupture, causing brain cell damage.
What are the different types of strokes?
There are mainly three types of strokes: ischemic, hemorrhagic, and transient ischemic attack (TIA or mini-stroke).
What are the statistics on stroke incidence and mortality rates in the United States?
Stroke is a top cause of death and disability in the U.S. It has high annual incidence and mortality rates.
Why is early detection critical in stroke treatment?
Early detection is key because “time is brain.” The sooner treatment starts, the more brain cells can be saved.
What is the treatment window for effective intervention in stroke?
The window for effective treatment varies. But, getting medical help within a few hours of a stroke is very important.
How can I identify facial asymmetry during a stroke?
Check for facial asymmetry by asking the person to smile. If one side droops, it could be a stroke sign.
How can I test for arm weakness during a stroke?
Test for arm weakness by asking the person to lift both arms. If one arm is weak or drifts down, it may be a stroke.
What are the different types of speech problems that occur during a stroke?
Speech problems can include slurred speech, trouble finding words, or understanding speech.
What is the first warning sign of stroke?
The first sign of stroke is often facial drooping, or facial asymmetry.
Why does arm weakness occur during a stroke?
Arm weakness happens because the brain’s motor areas are affected. This leads to muscle function problems.
How can I identify slurred or confused speech during a stroke?
Look for unclear or nonsensical speech by talking to the person. Listen for slurred or confused speech.
References
Wikipedia. FAST (stroke). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FAST_(stroke)