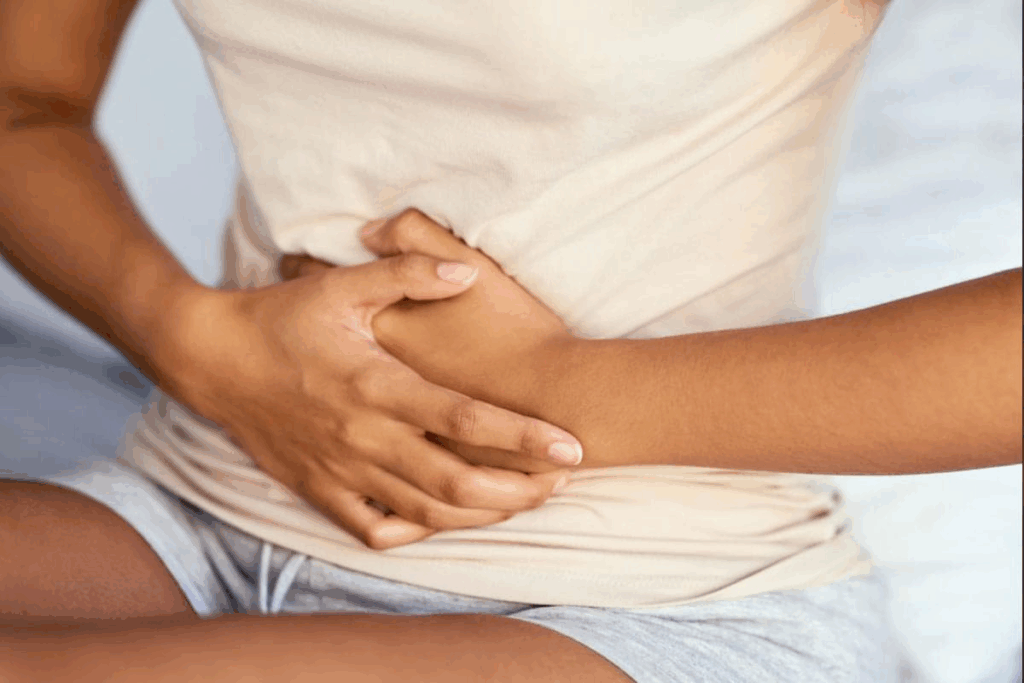
Gastrointestinal bleeding is a serious issue that affects many worldwide each year. It’s a life-threatening condition if not addressed promptly. We aim to help you spot the critical signs that need immediate medical care.The ultimate, critical list of GI bleed red flags. These 5 shocking symptoms, from vomiting blood to dizziness, mean go to the ER now.
It’s vital to recognize the emergency GI signs early. Ignoring these signs can cause serious harm, including organ failure and death. We stress the need for quick action and awareness in dealing with gastrointestinal bleeding.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the severity of gastrointestinal bleeding is key.
- Spotting emergency GI signs can save lives.
- Quick action is needed for GI bleeding.
- Knowing GI bleed red flags is essential for timely medical help.
- Ignoring GI bleed signs can lead to severe health issues.
Understanding GI Bleeds: An Overview
It’s key to know about GI bleeding to catch it early and treat it right. GI bleeding happens in the GI tract, which is from the mouth to the colon.
What is a GI Bleed?
A GI bleed is when blood leaks from the GI tract. It can show up as vomiting blood, black stools, or rectal bleeding. The severity can vary a lot.
Types of GI Bleeds
GI bleeds are mainly divided into upper and lower types. Upper bleeds happen in the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum. Lower bleeds occur in the small and large intestines.
- Upper GI Bleeds: Symptoms include vomiting blood or black stools.
- Lower GI Bleeds: Symptoms are bright red blood or maroon stools.
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms
Spotting GI bleeding symptoms early is vital. Quick action can lead to better treatment. This might include medicines, endoscopy, or surgery.
Knowing the major signs of GI bleeds is critical. Look out for vomiting blood, black or tarry stools, and abdominal pain. Being aware can save lives.
Common Symptoms of GI Bleed
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding shows itself in many ways, some very alarming. It’s key to know these signs to get help fast. We’ll look at the common signs that GI bleeding might be happening.
Vomiting Blood: What It Indicates
Vomiting blood, or hematemesis, is a big warning sign of GI bleeding. It means there’s bleeding in the upper part of your stomach. The blood might look bright red or like coffee grounds because it’s been digested a bit. Vomiting blood is a medical emergency that needs quick action.
Blood in your vomit can come from many things, like ulcers or tears in your stomach. If you see this, get medical help fast.
Black or Tarry Stools
Black or tarry stools, known as melena, are another serious sign of GI bleeding. This happens when blood gets digested in your gut, making your stools look like tar. Melena usually means bleeding in the upper GI tract, but it can sometimes point to lower GI bleeding too.
If you see melena, you should see a doctor right away. It’s a sign of serious bleeding in your GI tract.
Abdominal Pain and Discomfort
Abdominal pain or discomfort can also be a sign of GI bleeding. This pain can be mild or very bad and might be in one spot or all over. Severe abdominal pain, with symptoms like vomiting blood or black stools, needs quick medical check-up.
Bloody diarrhea is another worrying sign of GI bleeding, mainly if it lasts a long time or is very bad. We need to watch for these signs and get medical help if they happen.
Identifying Severe Symptoms
It’s important to know the severe symptoms of GI Bleeds to get medical help fast. A GI Bleed can cause symptoms that are very serious. We’ll look at these signs to help you know when to get urgent care.
Bright Red Blood in Stool
Bright red blood in stool means you’re bleeding in the lower part of your GI tract. This is a big warning sign. It usually means the bleeding is near the anus.
Fainting or Dizziness
Fainting or feeling dizzy can happen if you lose a lot of blood. This loss can lower your blood pressure. It can also make your brain get less blood, causing dizziness or fainting. These are serious signs that need quick medical help.
Rapid Heart Rate and Low Blood Pressure
A fast heart rate and low blood pressure can mean you’re in shock. Shock is a serious condition from losing too much blood. Your body tries to keep up by beating faster, but if it can’t, you might not get enough blood. Seeing these signs means you need emergency care right away.
Symptom | Description | Possible Indication |
Bright Red Blood in Stool | Blood visible in stool, often bright red | Lower GI Bleeding |
Fainting or Dizziness | Feeling lightheaded or passing out | Significant Blood Loss |
Rapid Heart Rate and Low Blood Pressure | Increased heart rate with decreased blood pressure | Shock due to Severe Blood Loss |
Risk Factors for GI Bleeds
It’s important to know the risk factors for GI bleeds to catch them early. Age, health conditions, and some medicines can raise the risk.
Age Considerations
As we get older, the risk of GI bleeding goes up, more so after 60. Our stomach and intestines’ lining gets thinner with age, making them more likely to bleed.
Underlying Health Conditions
Some health issues can make GI bleeding more likely. These include:
- Ulcers: These are open sores in the stomach or intestines that can bleed easily.
- Cancer: Tumors in the GI tract can cause bleeding.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can lead to chronic inflammation and increase the risk of bleeding.
- Liver disease: Cirrhosis and other liver conditions can cause portal hypertension, leading to varices that are prone to bleeding.
Medications That Increase Risk
Some medicines can also raise the risk of GI bleeding. These include:
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): Long-term use of NSAIDs like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen can irritate the stomach lining and increase the risk of ulcers and bleeding.
- Anticoagulants: Medications that thin the blood, such as warfarin, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban, can increase the risk of bleeding, including GI bleeding.
- Antiplatelet drugs: Medications like clopidogrel can prevent platelets from clotting, increasing the risk of bleeding.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help for GI Bleeds is key. It helps in treating the issue and avoiding serious problems. GI Bleeds can be scary, and it’s important to know the difference between urgent and serious symptoms.
Emergency Signs to Watch For
Certain symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe Bleeding: Vomiting blood or passing black, tarry stools are signs of significant bleeding that require urgent attention.
- Signs of Shock: Symptoms such as fainting, dizziness, or a rapid heart rate can indicate that the body is going into shock, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Significant Changes in Vital Signs: A drop in blood pressure or an increase in heart rate can signal severe blood loss.
These emergency signs should not be ignored, and immediate action is necessary to prevent serious outcomes.
Differences between Mild and Severe Bleeding
Not all GI Bleeds are the same. Knowing the difference is important for the right response.
Mild Bleeding might show as occasional blood in the stool or mild belly pain. It needs a doctor’s check-up but might not need emergency care unless it gets worse or has other bad symptoms.
Severe Bleeding is heavy or constant bleeding, a lot of pain, or signs of shock. It needs quick medical help to keep the patient safe and find the cause.
Diagnostic Procedures for GI Bleeds
To manage GI bleeding well, knowing the diagnostic procedures is key. These tests help find the source and extent of the bleed. They are vital for a proper diagnosis.
Common Tests and Examinations
Several tests are used to diagnose GI bleeding. These include:
- Endoscopy: Allows doctors to see the upper GI tract.
- Colonoscopy: Examines the lower GI tract.
- Imaging Tests: Like CT scans or angiography, to find the bleeding source.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests for anemia, infection, or other issues.
These tests help find the cause and how severe the bleeding is. They guide doctors to the best treatment.
Preparing for Diagnostic Procedures
Preparation is important for effective tests. Patients need to:
- Follow a special diet before the test.
- Stop certain medications that might affect the test.
- Have someone to take them home after.
Following these steps helps the test go well.
Follow-up Care After Diagnosis
After diagnosis, follow-up care is key. It includes:
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups.
- Treatment Plans: Following the doctor’s advice, which might include medication or lifestyle changes.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Making diet and lifestyle changes to prevent future bleeds.
A good follow-up plan helps recovery and lowers the risk of future bleeds.
Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Preparation |
Endoscopy | Examine the upper GI tract | Fasting, stopping certain medications |
Colonoscopy | Examine the lower GI tract | Bowel preparation, dietary changes |
Imaging Tests (CT Scan) | Identify the source of bleeding | Contrast dye, fasting |
Treatment Options for GI Bleeds
Managing GI bleeds needs a detailed plan. This plan might include medical, surgical, and lifestyle changes. Each patient’s situation is different. So, the treatment must fit the cause and how bad the bleeding is.
Medical Interventions
Medical treatments are key in handling GI bleeds. Endoscopy is a common method to find and fix bleeding in the gut. A doctor can see the bleeding spot and use treatments like cauterization or clipping to stop it. Also, medicines like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help heal the stomach and lower bleeding risk.
Other treatments might include vasoconstrictors to slow blood flow or clotting factors to help blood clot. The right treatment depends on where, how bad, and why the bleeding is happening.
Surgical Options: When Needed
If medical treatments don’t work or the bleeding is severe, surgery might be needed. Surgery aims to fix or remove the bleeding source. The surgery type varies based on the bleed’s location and cause.
Surgery is usually considered for serious bleeding, unstable conditions, or when other treatments fail. New surgical methods, like minimally invasive surgery, have made surgery safer for GI bleed patients.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
To prevent future GI bleeds, making lifestyle changes is key. Patients should avoid NSAIDs and other stomach irritants. Eating a diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains helps the gut stay healthy.
Quitting smoking and drinking less alcohol also lowers GI bleed risks. Stress management, like meditation or yoga, can improve gut health too.
Preventive Measures Against GI Bleeds
To prevent GI bleeds, we need to make changes in our diet, manage health conditions, and get regular check-ups. These steps can greatly lower the chance of a GI bleed.
Dietary Tips to Reduce Risk
Eating a balanced diet is key to keeping your gut healthy. Some foods can upset your stomach or make health problems worse, leading to a GI bleed. Here are some tips to help:
- Avoid spicy and acidic foods that can irritate the stomach lining.
- Eat more fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for better digestion.
- Drink lots of water to stay hydrated.
- Drink less alcohol, as it can irritate your stomach and increase bleeding risk.
Following these dietary tips can lower your risk of GI bleeds. Also, watch out for food allergies and intolerances, as they can cause stomach problems.
Managing Existing Conditions
If you have health issues, like stomach problems, managing them well is important. This means:
- Following your doctor’s treatment plan for ulcers, gastritis, or esophagitis.
- Keeping an eye on conditions that can lead to bleeding, like liver disease or bleeding disorders.
- Knowing the side effects of medicines, like NSAIDs and anticoagulants, which can cause bleeding.
By managing your health conditions and working with your doctor, you can lower your risk of a GI bleed.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular health check-ups are essential for your overall health and catching problems early. For your gut, they help in:
- Finding and treating gut issues early.
- Keeping an eye on your gut’s health and fixing any problems quickly.
- Changing treatment plans as needed to manage long-term conditions.
Regular check-ups are critical in preventing GI bleeds. By keeping up with your health appointments, you can greatly reduce your risk.
Preventive Measure | Description | Benefit |
Dietary Adjustments | Avoiding irritants, increasing fiber intake | Reduces stomach irritation, promotes digestive health |
Managing Existing Conditions | Adhering to treatment plans, monitoring conditions | Prevents exacerbation of conditions, reduces GI bleed risk |
Regular Check-ups | Early detection, monitoring GI health | Enables timely intervention, improves overall GI health |
Patient Experiences: Real Stories
Patient stories and case studies give us a deeper look at GI bleeding and how to manage it. By hearing real-life experiences, we learn about the challenges patients face. We also learn valuable lessons from their journeys.
Case Studies of GI Bleed Incidents
Many case studies show how different GI bleeding incidents can be. For example, a patient in their mid-40s had severe bleeding due to an unknown condition. Thanks to diagnostic tests, the condition was found, and treatment began.
An elderly patient was taking medication that raised their risk of bleeding. Quick medical help and changing their meds helped manage the issue.
Key Takeaways from Case Studies:
- The importance of early diagnosis and treatment
- The role of medication management in preventing GI bleeding
- The need for personalized care plans based on individual patient risk factors
Lessons Learned from Patients
Patients who have had GI bleeding share important lessons. One key lesson is knowing the risk factors and symptoms of GI bleeding.
“Understanding my condition and being proactive about my health made a significant difference in my recovery.” –
A GI bleed survivor
They also highlight the value of support groups and resources. Connecting with others who have gone through similar experiences can offer emotional support and practical advice.
Support Groups and Resources
Support groups are vital for many patients’ recovery. These groups let people share their experiences, get support, and learn from others who have faced similar challenges.
There are also many resources for patients and caregivers. These include educational materials, counseling services, and online forums. Using these resources can greatly help manage GI bleeding and improve life quality for those affected.
Recommended Resources:
- National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC)
- Gastrointestinal Society
- Local support groups and online forums
Myths and Misconceptions About GI Bleeds
Myths about GI bleeding can confuse people and delay treatment. This condition is serious and needs quick medical help. It’s often misunderstood.
Debunking Common Myths
Many myths surround GI bleeds. Some people think they always show clear symptoms. But, some GI bleeds might not show symptoms at all or have mild ones.
- Myth: GI bleeds only happen in older adults. Reality: While older age is a risk, GI bleeds can happen to anyone at any age.
- Myth: Bleeding always stops on its own. Reality: Some bleeds might stop without help. But, serious cases need medical care to avoid big problems.
Understanding Reality vs. Fiction
It’s important to know what’s real and what’s not about GI bleeds. Misunderstandings can cause delays in getting the right help.
Myth | Reality |
GI bleeds are always accompanied by severe pain. | Pain isn’t always there; some people might feel mild discomfort or no pain at all. |
Over-the-counter medications are safe for everyone. | Some over-the-counter meds, like NSAIDs, can raise the risk of GI bleeding in certain people. |
The Role of Education
Learning the truth about GI bleeds is key. Knowing the facts helps people get medical help when they should.
We suggest that people at risk or who have had GI bleeds learn about the signs, symptoms, and risk factors. This knowledge helps them make better health choices.
Resources for Further Information
To learn more about GI Bleeds, check out these reliable sources. We’ve gathered a list of trusted websites, books, and support groups. They offer valuable info and help.
Trusted Medical Websites
For the latest on GI health, online resources are key. Here are some top sites:
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): Has detailed info on health topics, including GI Bleeds.
- American Gastroenterological Association (AGA): A top source for GI health info and expert advice.
Resource | Description | URL |
NIH | Comprehensive health information | https://www.nih.gov/ |
AGA | Gastrointestinal health expertise | https://www.gastro.org/ |
Books and Publications on GI Health
For those who like to read deeply, there are many books and publications on GI health and GI Bleeds.
- “Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and Management” – A detailed guide to GI Bleeds.
- “The GI Tract: A Guide to Gastrointestinal Health” – Covers GI health and common issues, like GI Bleeds.
Support Organizations
Support groups are essential for those dealing with GI Bleeds. They offer help and a sense of community.
- Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation: Provides resources, support, and advocacy for IBD and GI conditions.
- GI Alliance: Offers educational resources and support for GI disorders.
By using these resources, you can learn more about GI Bleeds. Stay updated on research and find support from others who get it.
Summary: Key Takeaways on GI Bleed Red Flags
It’s important to know the signs of GI bleeding to get help fast. We’ve looked at symptoms, risk factors, and how to diagnose GI bleeds.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
The key signs include vomiting blood, black or tarry stools, and stomach pain. Also, look out for bright red blood in stool, fainting, or a fast heart rate. Spotting these signs early can make a big difference in treatment.
The Role of Early Detection
Finding GI bleeds early is key. By spotting the signs and getting medical help quickly, you can lower the risk of serious problems. This also boosts your treatment success chances.
Staying Informed
Knowing about GI health and risks helps you prevent and detect problems early. We suggest checking out reliable medical sources and talking to doctors. This way, you can learn more about GI bleeds and how to stay safe.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a GI bleed?
Symptoms include vomiting blood, black or tarry stools, and abdominal pain. Bloody diarrhea is also a sign. These symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away.
How can I identify if my symptoms are severe?
Severe symptoms include bright red blood in stool and fainting. Dizziness, rapid heart rate, and clammy skin are also signs. If you see these, get help fast.
What are the risk factors for GI bleeding?
Risk factors include age and health conditions like ulcers or cancer. Certain medications can also increase the risk. Knowing these can help you stay safe.
When should I seek medical attention for GI bleeding?
Seek help for heavy bleeding or signs of shock. If you have a history of GI issues, get medical help too. Knowing when to act is key.
What diagnostic procedures are used to identify GI bleeding?
Doctors use endoscopic and imaging techniques to diagnose. Preparing for these tests and following up with your doctor is important. It helps get the right treatment.
What are the treatment options for GI bleeding?
Treatments include stopping the bleeding medically or surgically. Lifestyle changes can also help prevent future episodes. Your doctor will choose the best treatment for you.
How can I prevent GI bleeding?
Preventive steps include eating right and managing health conditions. Regular check-ups are also important. These steps can lower your risk of GI bleeding.
Are there any myths about GI bleeding that I should be aware of?
Yes, there are myths about GI bleeding. Learning the truth about GI health is important. It helps you stay informed and safe.
Where can I find reliable resources for more information on GI health?
Reliable resources include medical websites and books. Support groups focused on GI health are also good sources. They offer trusted information and support.
Why is early detection of GI bleeding important?
Early detection is key because it improves outcomes. Spotting the signs early and getting help fast can save lives.
What should I do if I’m experiencing dizziness or lightheadedness along with GI bleeding symptoms?
Dizziness or lightheadedness with GI bleeding symptoms means you’ve lost a lot of blood. Seek medical help right away. These could be signs of shock or severe anemia.
Can certain medications increase the risk of GI bleeding?
Yes, some medications like NSAIDs or anticoagulants can raise the risk. Talk to your doctor about your meds. They can help you understand the risks and take steps to stay safe.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK411/




































