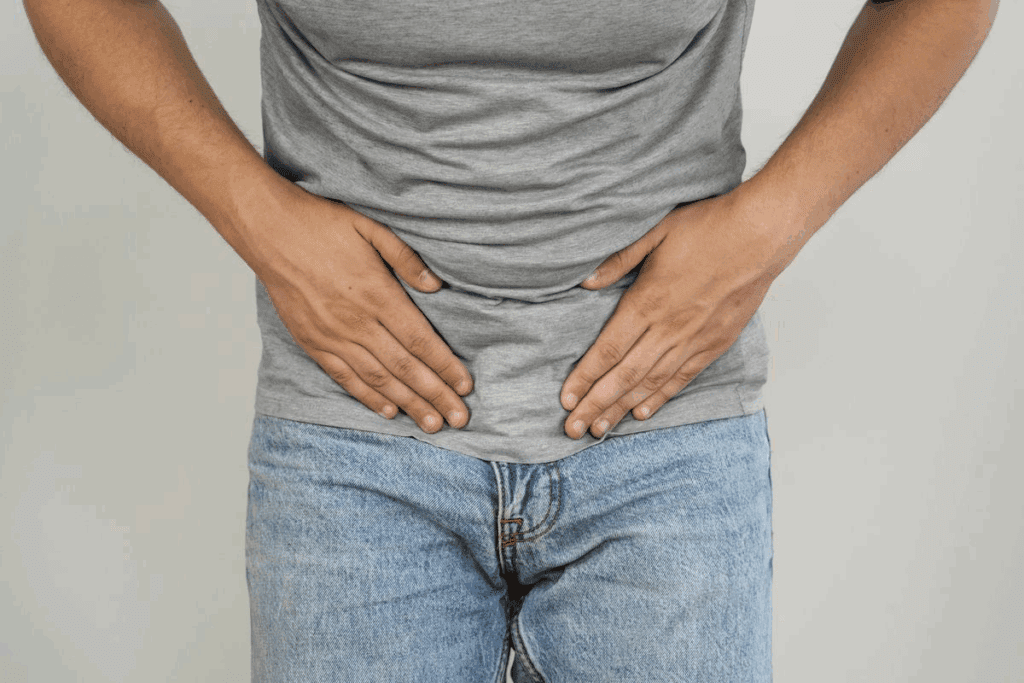
Many athletes and people who are active often feel groin pain. This pain usually comes from muscle strain or sports injuries. It can really hurt, making it hard to perform and even daily tasks.What are the top groin pain causes? We explore the 5 most surprising reasons, from a hidden hernia to a critical nerve issue, in our ultimate guide.
Groin pain causes can vary a lot. They include muscle strains, hernias, hip problems, and nerve issues. Knowing what’s causing the pain is key to feeling better and getting the right treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Groin pain can result from various injuries and medical conditions.
- Muscle strains are a common cause of groin pain, specially in athletes.
- Hip-related issues can also contribute to groin pain.
- Nerve-related problems may be a source of groin pain.
- Understanding the cause is essential for effective treatment.
- Proper diagnosis is key to alleviating discomfort.
Understanding Groin Anatomy
Knowing the anatomy of the groin is key to treating pain there. The groin, or inguinal region, links the abdomen to the thighs. It has many structures like muscles, tendons, and nerves that can cause pain.
Key Muscles and Ligaments
The groin is held together by important muscles and ligaments. The adductor muscles help move the thigh. The pectineus muscle aids in hip movement. The inguinal ligament adds extra support.
Nerve Supply in the Groin
The nerves in the groin come from the lumbar plexus. The ilioinguinal nerve and genitofemoral nerve give sensation to the area. Damage to these nerves can cause pain or numbness.
Major Blood Vessels
The groin also has major blood vessels. The femoral artery and femoral vein are vital for blood flow. The femoral artery splits into smaller ones, bringing oxygen to the leg.
Structure | Description | Function |
Adductor Muscles | Group of muscles including adductor longus, brevis, and magnus | Thigh adduction and movement |
Pectineus Muscle | Muscle located in the upper thigh | Hip flexion and adduction |
Inguinal Ligament | Ligament connecting the pubic bone to the anterior superior iliac spine | Supports the groin area |
Ilioinguinal Nerve | Nerve providing sensation to the groin and genital area | Sensory innervation |
Femoral Artery | Major artery supplying blood to the lower limb | Blood circulation |
Common Causes of Groin Pain

Groin pain can come from muscle strains, sports injuries, and overuse. We’ll dive into these causes to understand how they happen and how to manage them.
Muscle Strains and Tears
Muscle strains and tears are common in athletes, mainly those in sports needing quick changes, kicking, or jumping. The adductor muscles are often strained. This stretching can cause groin pain.
Symptoms include sudden pain, bruising, and trouble walking. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy also helps to strengthen the muscles.
Injuries from Sports Activities
Sports activities often lead to groin pain. Soccer, football, and hockey, with their fast movements, can strain the groin. Athletes should wear protective gear and do warm-up exercises to lower injury risk.
Common sports injuries include:
- Groin strains
- Hip flexor strains
- Stress fractures
Preventing injuries means proper training, conditioning, and using the right techniques during sports.
Overuse Injuries in Athletes
Overuse injuries happen when athletes stress their muscles and tendons too much without enough rest. This can cause tendonitis, where tendons get inflamed. Spotting the signs early is key.
Symptoms include ongoing pain, swelling, and less performance. To manage, change activities, take rest days, and do physical therapy to boost flexibility and strength.
Groin Pain Due to Hernias
Groin pain often comes from hernias. These happen when tissue bulges through weak spots in the abdominal muscles. It’s not just uncomfortable; it can be serious if not treated.
Hernias are common. Knowing their causes and symptoms is key to managing them well.
Inguinal Hernia Explained
An inguinal hernia happens when tissue bulges through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles in the groin. It’s more common in men. This is because of how their bodies are built.
The inguinal canal is where these hernias usually occur. When intestine or other tissue pushes through, it causes a bulge or swelling. This is often painful, worse when coughing, lifting, or bending over.
Symptoms include a bulge in the groin, pain when straining, and a feeling of heaviness. If the hernia becomes incarcerated or strangulated, it can cause severe pain. This needs immediate medical help.
Femoral Hernia Overview
A femoral hernia happens just below the inguinal ligament, where the femoral artery goes into the thigh. It’s more common in women because of their wider pelvis. Femoral hernias are less common but more dangerous because they can easily become incarcerated or strangulated.
Symptoms are similar to inguinal hernias, with a bulge in the upper thigh and pain when straining. Because of their location and risk of complications, femoral hernias often need quick surgery.
Groin pain from a hernia can be scary. It’s important to get medical help to find out why you’re in pain and what to do. Both inguinal and femoral hernias can really affect your life. But with the right care, you can get better and do your usual activities again.
Hip-Related Issues
Groin pain often comes from hip problems like arthritis, labral tears, and bursitis. These issues can really hurt your quality of life. They make moving hard and cause pain.
Arthritis of the Hip Joint
Arthritis in the hip joint is a common cause of groin pain. Osteoarthritis is a disease that wears down the cartilage in the hip. This leads to bone rubbing on bone and pain.
Symptoms include pain in the groin or thigh, stiffness, and trouble moving. Doctors use physical exams and tests like X-rays or MRI to diagnose it. Treatment can be physical therapy, medicine, or even surgery for severe cases.
Labral Tear in the Hip
A labral tear is a tear in the cartilage ring around the hip socket. It can cause pain in the groin, mainly when you move your hip. Tears can happen from injury, too much use, or abnormal structure.
Doctors use physical exams and MRI arthrography to find a labral tear. Treatment might be physical therapy, medicine, or surgery to fix the tear.
Bursitis and Its Effects
Bursitis in the hip is inflammation of the bursae. These are fluid-filled sacs that protect joints and reduce friction. Hip bursitis can hurt the groin or outer hip, making it hard to move.
To treat bursitis, doctors aim to reduce swelling and pressure. This can be done with rest, physical therapy, and medicine. Sometimes, they might use corticosteroid injections if it doesn’t get better.
Reproductive System Concerns
Certain health issues in the reproductive system can cause groin pain. This requires a detailed medical check-up. The reproductive system is connected to the groin, leading to discomfort and serious problems.
Understanding Testicular Torsion Risks
Testicular torsion is a serious condition where the spermatic cord twists. This cuts off blood to the testicle. It causes severe pain and swelling in the groin.
If not treated quickly, it can result in losing the testicle. We urge immediate medical help if symptoms get worse or don’t go away.
Symptoms of Testicular Torsion:
- Severe pain in one testicle
- Swelling of the testicle
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abnormal positioning of the testicle
Ovarian Cysts and Pain
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries. They are usually harmless but can cause pain if they rupture or twist. The pain can be mild or severe, with symptoms like bloating and irregular periods.
Condition | Symptoms | Complications |
Ovarian Cysts | Groin pain, bloating, irregular periods | Rupture, torsion, infertility |
Testicular Torsion | Severe testicular pain, swelling, nausea | Loss of testicle, infertility |
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs. It causes pain in the lower abdomen and groin, fever, and abnormal vaginal discharge. PID is serious and needs quick treatment to avoid infertility.
“Pelvic inflammatory disease is a significant cause of morbidity among women of reproductive age, and its diagnosis and treatment are critical to preventing long-term sequelae.”
Source: CDC Guidelines
We emphasize the need to recognize symptoms of these reproductive system issues. Seeking medical care quickly is key to avoiding serious problems.
Nerve-Related Causes
Nerve problems are a big reason for groin pain. Conditions like meralgia paresthetica and sciatica are common. They happen when nerves get compressed or irritated, causing pain in the groin.
Meralgia Paresthetica
Meralgia paresthetica is when the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve gets compressed. This nerve sends signals to the thigh. The compression leads to numbness, tingling, and burning pain in the groin and thigh.
The symptoms of meralgia paresthetica can vary. But, they often include a burning or numb feeling on the outer thigh. Tight clothes, obesity, or other factors can cause it. Treatment aims to relieve the compression, manage pain, and fix any underlying issues.
Sciatica and Its Influence
Sciatica is pain that goes down the sciatic nerve. This nerve starts in the lower back, goes through the hips, and down each leg. Sciatica can sometimes cause groin pain because of the nerve’s wide path. We’ll look at how sciatica affects groin pain and treatment options.
Sciatica pain can be mild or severe. It often comes with numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs. Treatment usually includes physical therapy, pain management, and sometimes surgery to ease the nerve pressure.
Conditions Affecting Joints
It’s important to know about joint conditions and their role in groin pain. Diseases like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can really hurt your quality of life. They cause ongoing pain and make it hard to move around.
Osteoarthritis in the Groin Area
Osteoarthritis is a disease that wears down the cartilage in joints. This can happen in the groin area too. It leads to pain, stiffness, and less ability to move.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis in the groin include:
- Pain in the groin that may radiate to the thigh or knee
- Stiffness, specially after resting
- Limited mobility and flexibility
- A grinding sensation in the joint
Rheumatoid Arthritis Connection
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease where the body attacks its own joints. It can hit many joints at once, including those in the groin. It’s different from osteoarthritis because it affects joints on both sides of the body and has other symptoms too.
The connection between rheumatoid arthritis and groin pain is multifaceted:
- Inflammation and pain in the groin joint
- Morning stiffness that lasts for hours
- Systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever
- Potential for joint deformity if left untreated
Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis need a detailed treatment plan. This might include medicine, physical therapy, and changes in your lifestyle. Knowing what’s causing your groin pain is key to finding the right treatment.
Groin Pain in Children
Groin pain is common in kids and often means they need to see a doctor. It’s important to find out why they’re in pain. This can be anything from a minor issue to something more serious.
Pediatric Causes of Groin Pain
There are many reasons why kids might feel pain in their groin. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH): This is when the hip joint doesn’t form right, causing pain.
- Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease: It’s when the hip joint doesn’t get enough blood, leading to pain and trouble moving.
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE): This is when the ball at the top of the femur slips out of the hip socket, causing pain.
These conditions show why it’s key to get a proper medical check-up for groin pain in kids.
When to Consult a Doctor
If your child has groin pain, watch their symptoms closely. You should see a doctor if:
- The pain gets worse or is very bad.
- There’s swelling, redness, or warmth in the groin area.
- They have trouble walking or moving.
- They also have a fever.
Seeing a doctor early can help figure out why your child is in pain. It ensures they get the right treatment and care.
Diagnostic Procedures for Groin Pain
Healthcare professionals use many ways to find out why you have groin pain. These steps help figure out the cause and plan the best treatment. We’ll look at how they do this, including physical checks and imaging tests.
Physical Examination Techniques
A physical check is often the first step. It looks at how well you move, if it hurts, and how strong your muscles are. They also do special tests to see if it’s a hernia or a hip problem.
The physical check might include:
- Looking at the groin for swelling or bruises
- Feeling the groin for tenderness or lumps
- Checking how well the hip moves
- Testing the strength of nearby muscles
Imaging Tests Overview
Imaging tests are used with physical checks to get a clearer picture. They help spot muscle strains, hernias, or joint problems.
Some common imaging tests for groin pain are:
Imaging Test | Description | Use in Diagnosing Groin Pain |
X-ray | Uses X-rays to show bones and joints | Good for finding bone breaks or joint problems |
Ultrasound | Uses sound waves to see soft tissues | Helps find hernias, muscle strains, or soft tissue injuries |
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | Uses a magnetic field and radio waves to see soft tissues | Shows detailed images of muscles, tendons, and joints, helping with complex issues |
Treatment Options for Groin Pain
Managing groin pain requires different approaches. The right treatment depends on the cause, how severe it is, and the patient’s health.
Benefits of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often the first step for groin pain, mainly from muscle strains or overuse. A physical therapist creates a custom workout plan. This plan aims to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and aid in healing.
Key benefits of physical therapy include:
- Strengthening the muscles around the groin
- Improving flexibility and range of motion
- Enhancing recovery and reducing the risk of future injuries
Role of Medication and Injections
Medications and injections are key in managing groin pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help lessen pain and swelling.
Medication/Injection Type | Purpose | Benefits |
Over-the-counter pain relievers | Reduce pain and inflammation | Easily accessible, effective for mild to moderate pain |
Corticosteroid injections | Decrease inflammation | Quick reduction in swelling and pain |
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections | Promote healing | Utilizes the body’s own healing factors |
Surgical Interventions for Groin Pain
In some cases, surgery is needed to fix the root cause of groin pain. Surgery is usually considered when other treatments don’t work or if the condition is severe.
Surgical options may include:
- Hernia repair
- Orthopedic procedures to correct hip or joint issues
- Other surgeries to address specific causes of groin pain
We know each patient is different. The best treatment plan is made just for them, based on their unique needs and condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Groin pain can be a sign of many issues, some serious. It’s important to know when to get help.
Identifying Severe Symptoms
Severe pain, swelling, or trouble walking are warning signs. These could mean vascular problems. If you notice these, get medical help fast.
Recognizing Emergency Situations
Signs like sudden severe pain or trouble moving a leg are emergencies. So are signs of infection like redness, swelling, and fever. If you see these, get emergency care right away.
We aim to give top-notch healthcare to everyone, including international patients. If you’re worried about groin pain, see a doctor. They can check and treat you properly.
FAQ
What are the most common causes of groin pain?
Groin pain can come from many sources. Muscle strains, hernias, and hip problems are common. Nerve issues and reproductive system problems also play a role. Conditions like osteoarthritis and bursitis can cause pain too.
How do muscle strains and tears cause groin pain?
Muscle strains and tears happen when muscles in the groin get stretched or torn. This often happens from sudden movements or too much use. It leads to pain, swelling, and trouble moving.
What is the difference between an inguinal hernia and a femoral hernia?
An inguinal hernia happens when tissue bulges through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. A femoral hernia occurs when tissue pushes through the femoral canal wall. Both can cause pain, but they need different treatments.
Can hip-related issues cause groin pain?
Yes, hip problems like arthritis and bursitis can cause groin pain. These issues can lead to inflammation and pain in the hip. This pain can spread to the groin area.
What are the symptoms of testicular torsion?
Testicular torsion is a serious issue that needs quick medical help. It shows as severe testicular pain, swelling, and tenderness. You might also feel nausea and vomiting.
How is groin pain in children diagnosed and treated?
Children’s groin pain can stem from muscle strains, hernias, or hip issues. Doctors use physical exams, medical history, and imaging tests to diagnose. Treatment varies based on the cause and might include surgery or conservative methods.
What diagnostic procedures are used to determine the cause of groin pain?
Doctors use physical exams, X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI to find the cause of groin pain. Sometimes, they do diagnostic injections. These steps help identify the problem.
What are the treatment options for groin pain?
Treatment for groin pain depends on the cause. It might include physical therapy, medication, injections, or surgery. We create treatment plans that meet each patient’s needs.
When should I seek medical attention for groin pain?
See a doctor for severe groin pain, swelling, or tenderness. Also, seek help if you have fever, nausea, or vomiting. A history of trauma or injury to the groin area is another reason to get medical help.
Can nerve-related causes like meralgia paresthetica and sciatica cause groin pain?
Yes, nerve issues like meralgia paresthetica and sciatica can cause groin pain. These conditions involve nerve compression or irritation. They lead to pain, numbness, and tingling in the groin area.
How can I prevent groin pain?
To avoid groin pain, stay active, stretch, and strengthen your muscles. Wear the right gear during sports and manage any health conditions you have.
What are the signs of serious conditions that cause groin pain?
Look out for severe pain, swelling, or tenderness, fever, nausea, or vomiting, and trouble walking. If you notice these symptoms, get medical help right away.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4617224/



































