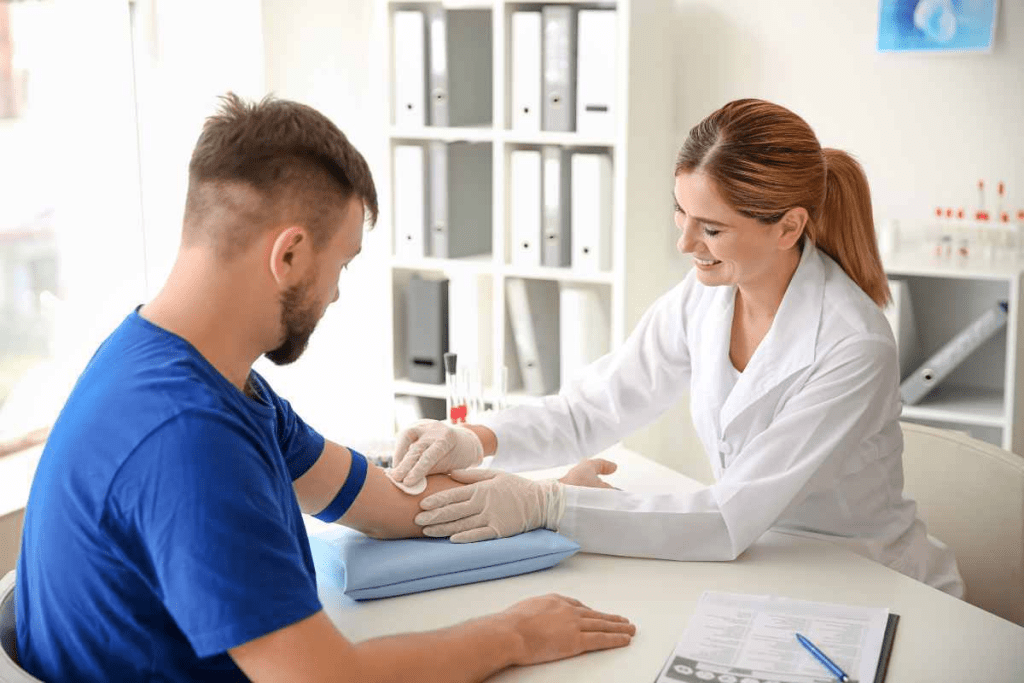
Blood disorders affect millions of people around the world. The American Society of Hematologist says over 1.6 million people in the United States get diagnosed with a blood disorder each year. Treating these conditions requires specialized care from a doctor who knows a lot about blood-related diseases.A blood doctor, also known as a hematologist, is a medical specialist. They are trained to diagnose and treat blood disorders, like anemia, bleeding disorders, and blood cancers.
Seeing a hematologist is very important for people with blood-related issues. They offer personalized care and treatment plans that fit each person’s needs.
Key Takeaways
- A hematologist is a medical specialist trained to diagnose and treat blood disorders.
- Blood disorders affect millions of people worldwide, requiring specialized care.
- Consulting a hematologist is critical for patients with blood-related issues.
- Hematologists provide personalized care and treatment options for blood disorders.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for patients with blood disorders.
Understanding Hematology and Blood Disorders
Keeping your blood healthy is key to feeling good. Hematology is a branch of medicine that studies blood and blood disorders. It helps diagnose and treat blood-related conditions.
What is hematology?
Hematology is the study of blood and its problems. It looks at blood cells to find and fix blood issues. Hematologists are doctors who deal with blood disorders, from anemia to blood cancers.
“Hematology has grown a lot, giving patients better care for blood problems,” says a top hematologist.
The importance of blood health
Blood health is essential for your well-being. It carries oxygen, fights infections, and stops bleeding. Problems with blood can cause serious health issues. Knowing how important blood health is can help you avoid blood disorders.
Studies show that healthy blood prevents anemia, clotting issues, and blood cancers. Taking care of your blood can greatly improve your life quality.
What is a Hematologist?
Hematologists are key in healthcare, focusing on blood disorders. They help manage issues that affect blood function.
Hematologist Definition and Role
A hematologist is a doctor who deals with blood disorders. They examine patients, interpret tests, and create treatment plans. Each plan is made for the patient’s specific needs.
They handle many blood issues, like anemia and blood cancers. Hematologists use tests and biopsies to find the cause of a patient’s problem.
How Hematologists Differ from Other Specialists
Hematologists focus on blood and its disorders. This focus lets them understand and treat blood issues better.
They have more training than general doctors in blood disorders. They work with other doctors to give complete care to patients.
Hematologists are very helpful for complex blood issues. Their specialized care improves patient health.
Education and Training of Hematologists
Becoming a hematologist takes a lot of hard work and dedication. These doctors focus on blood disorders and diseases. They have to go through a lot of education and training.
Medical School and Residency Requirements
To start, one must finish medical school. This can be either an MD or a DO degree. It takes four years after a bachelor’s degree.
After medical school, they need to do a residency in internal medicine. This lasts for three years. They learn to diagnose and treat many adult diseases, including blood-related ones.
Specialized Fellowship Training
Next, they must get into a hematology fellowship program. These programs last from two to three years. They focus on blood disorders like anemia and blood cancers.
Some hematologists might also do a fellowship in hematology and medical oncology. This gives them even more knowledge.
Here’s a quick look at how a hematologist gets educated:
| Educational Step | Duration | Description |
| Medical School | 4 years | Earning an MD or DO degree |
| Internal Medicine Residency | 3 years | Gaining experience in adult medicine |
| Hematology Fellowship | 2-3 years | Specialized training in blood disorders |
Common Blood Disorders Treated by Hematologists

Hematologists deal with many blood-related issues. These include anemia, bleeding disorders, and blood cancers. They work with other doctors to give patients the care they need.
Anemia and Related Conditions
Anemia means not enough red blood cells or poor quality ones. This makes it hard for tissues to get oxygen. Hematologists treat different types of anemia. They might suggest diet changes, iron supplements, or other treatments.
Bleeding Disorders
Bleeding disorders, like hemophilia, make it hard for blood to clot. This leads to too much bleeding. Hematologists use clotting factors and other treatments to stop bleeding. They also look into gene therapy for future treatments.
Clotting Disorders
Clotting disorders make blood clot too much. This can cause problems like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Hematologists use medicines to stop clots and prevent serious issues.
Blood Cell Cancers
Blood cell cancers, like leukemia, affect the blood and bone marrow. Hematologists and oncologists team up to find and treat these cancers. They use chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplants.
| Blood Disorder | Description | Common Treatments |
| Anemia | Deficiency in red blood cells or their quality | Iron supplements, dietary changes, addressing underlying causes |
| Bleeding Disorders | Conditions where blood doesn’t clot properly | Clotting factor concentrates, gene therapy |
| Clotting Disorders | Conditions where blood clots too easily | Anticoagulant medications |
| Blood Cell Cancers | Cancers affecting blood, bone marrow, or lymphatic system | Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, stem cell transplantation |
Hematologists are key in treating blood disorders. They work with teams to help patients get better.
The Overlap Between Hematology and Oncology
Hematology and oncology are closely related, mainly in treating blood cancers. Hematologists and oncologists team up to care for patients with blood disorders. These disorders might turn into cancer or are already cancerous.
Understanding Hematologist-Oncologists
A hematologist-oncologist is a doctor who knows how to treat blood disorders and cancer. They are key in managing diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. These conditions affect the blood, bone marrow, or lymphatic system.
These doctors can handle a patient’s care from start to finish. They use their knowledge of both fields to create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
When Cancer Affects the Blood
Cancer can show up in the blood in different ways, like leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma. Hematologist-oncologists are experts in treating these blood cancers. They use a mix of treatments, including chemotherapy and targeted therapy.
Working together, hematologists and oncologists make sure patients get the best treatment. This teamwork helps improve treatment results and the patient’s quality of life.
Diagnostic Methods Used by Hematologists
Hematologists use many ways to find and treat blood problems. These methods help find the cause of blood issues and plan the right treatment.
Blood Tests and Analysis
Blood tests are key in hematology. They check blood samples for different parts, like red and white blood cells. Blood tests can spot issues like anemia, infections, and leukemia. Automated analyzers give detailed info about the blood’s makeup.
Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration
A bone marrow biopsy takes a small bone marrow sample for study. It helps find blood disorders, like cancers. Bone marrow aspiration gets a liquid sample for analysis. These steps give important info on blood cell production and function.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Hematologists also use new ways to diagnose. These include molecular tests for genetic issues, flow cytometry for cell analysis, and cytogenetic analysis for chromosomal changes. These diagnostic techniques help find complex blood disorders. They let doctors create treatments that fit each patient’s needs.
Treatment Approaches in Hematology
Managing blood disorders well needs a deep understanding of treatment options in hematology. Hematologists use many strategies to treat blood-related issues. This includes anemia, bleeding disorders, and blood cancers.
Medication Therapies
Medications play a key role in treating many blood disorders. Anticoagulants stop clots from forming. Clotting factors help those with bleeding disorders like hemophilia. Medicines that boost red blood cell production treat anemia.
Blood Transfusions and Products
Blood transfusions are vital in hematology. They help those with severe anemia or undergoing chemotherapy. Red blood cell transfusions are given to those with low red blood cells.
Platelet transfusions are for people with low platelet counts to prevent or treat bleeding. Plasma transfusions are used for clotting factor deficiencies or severe bleeding.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation, or bone marrow transplantation, treats some blood cancers and disorders. It replaces the patient’s diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. These can come from the patient (autologous transplant) or a donor (allogeneic transplant).
The right treatment depends on the diagnosis, condition severity, and patient health. Hematologists work with other healthcare teams to find the best treatment for each patient.
When Should You See a Hematologist?
Certain symptoms can mean you have a blood disorder. This calls for a visit to a hematologist for the right diagnosis and treatment. Blood disorders show up in many ways. It’s key to know when you need a specialist’s help.
Common Symptoms Requiring Hematological Evaluation
Several symptoms may mean you need a hematologist’s check-up. These include:
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
Seeing these symptoms doesn’t always mean you have a blood disorder. But, it’s a sign to talk to your primary care doctor or a hematologist.
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
| Fatigue | Anemia or low red blood cell count |
| Frequent Infections | Immune system disorder or low white blood cell count |
| Easy Bruising | Platelet disorder or clotting issue |
Referral Process from Primary Care
Your journey to see a hematologist starts with your primary care doctor. If they think you might have a blood disorder, they’ll send you to a hematologist for more tests and treatment.
The referral process includes:
- A detailed medical history and physical check by your primary care doctor.
- First tests, like a complete blood count (CBC).
- A referral to a hematologist if the tests show a possible blood disorder.
Knowing the symptoms that need a hematologist’s check and how to get a referral is important. It helps make sure you get the right care for your health issues.
What to Expect During Your First Hematology Appointment
Knowing what to expect at your first hematology appointment can ease your worries. It’s a key step in figuring out and treating your blood disorder.
Preparation Tips
To get the most from your first appointment, being ready is key. Here are some tips:
- Gather your medical history: Collect any important medical records, like past test results and current medications.
- List your symptoms: Write down your symptoms, including when they happen and how long you’ve had them.
- Prepare questions: Make a list of questions for your hematologist, like what might be causing your symptoms and what treatment you might need.
Being ready will help you get the most from your appointment. It ensures you don’t miss important details to discuss with your hematologist.
Typical Examination Procedures
At your first hematology appointment, you’ll go through several tests to find out what’s wrong. These might include:
- Blood tests: Your hematologist might do blood tests to check your blood cell count and look for any issues.
- Physical examination: A detailed physical check will be done to look for signs of illness or disease.
- Medical history review: Your hematologist will look over your medical history to find possible reasons for your symptoms.
“The first appointment is key in starting the patient’s treatment journey. It’s important to be thorough and address all the patient’s concerns.”
By knowing what to expect, you can feel more confident at your first hematology appointment.
The Multidisciplinary Approach: How Hematologists Work with Other Specialists
Hematologists often team up with other specialists to tackle blood disorders. This teamwork makes sure patients get care that fits their needs perfectly.
Collaboration with Oncologists
Hematologists and oncologists work together a lot. This is because many blood issues are linked to cancer. They create treatment plans that cover both the blood and cancer sides of a patient’s health.
Partnerships with Primary Care Physicians
Primary care doctors are key in spotting patients who might need a hematologist. Hematologists help these doctors manage blood disorder patients. This teamwork leads to early detection and better care for blood-related problems.
Working with Surgeons and Other Specialists
Hematologists also team up with surgeons and other experts. For example, they work with surgeons for patients needing surgery for bleeding issues. This ensures the patient’s health is fully considered.
| Specialist | Role in Hematology | Examples of Collaboration |
| Oncologists | Manage cancerous blood disorders | Coordinated treatment plans for leukemia, lymphoma |
| Primary Care Physicians | Initial patient evaluation and referral | Guidance on managing anemia, referrals for further testing |
| Surgeons | Surgical interventions for patients with blood disorders | Managing bleeding risks during surgery, post-operative care |
Insurance Coverage and Costs for Hematology Care in the US
Knowing your insurance coverage is vital for managing hematology care costs. Hematology treatments can be pricey. Insurance helps make these treatments more accessible.
Understanding Insurance Coverage for Blood Disorders
Most health insurance plans cover hematology care. This includes tests and treatments for blood disorders. But, coverage can differ a lot between insurance providers and plans.
It’s important to check your insurance policy. This way, you’ll know what’s covered and what you might have to pay for yourself.
Key aspects to consider include:
- Deductibles and copays
- Coverage for specific treatments like blood transfusions or chemotherapy
- Network providers and out-of-network care
Financial Assistance Programs and Resources
For those facing financial hurdles, there are help programs available. These include patient assistance programs (PAPs) from drug companies, non-profit financial aid, and government programs like Medicaid.
Patients should ask their healthcare provider or insurance company about these options. They can help understand what’s available and who’s eligible.
Living with Chronic Blood Disorders
Living with chronic blood disorders can be tough, but it’s possible to live well. Conditions like anemia, bleeding disorders, and clotting disorders need ongoing care. This care helps prevent serious problems and improves life quality.
Long-term Management Strategies
Managing chronic blood disorders long-term means a mix of medical care, lifestyle changes, and regular checks. Patients should team up with their hematologist to create a care plan that fits them.
- Adhering to prescribed medication regimens
- Making dietary changes to support blood health
- Engaging in regular physical activity tailored to their condition
Monitoring and adjusting treatment plans as needed is key. It helps manage symptoms and avoid serious issues.
| Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Medication Adherence | Taking prescribed medications as directed | Controls symptoms, prevents complications |
| Dietary Changes | Adjusting diet to support blood health | Improves overall health, reduces symptoms |
| Physical Activity | Engaging in appropriate exercise | Enhances well-being, improves circulation |
Support Resources for Patients
Patients with chronic blood disorders have access to many support resources. These include patient groups, online forums, and counseling services. These help with emotional support, practical tips, and a sense of community.
Connecting with others who face similar challenges can be very helpful.
Conclusion
Managing blood disorders well needs a hematologist’s help. These doctors are key in finding and treating blood-related issues. This includes anemia, bleeding problems, and blood cancers.Knowing how hematologists are trained helps patients understand their care better. They work with other doctors to create treatment plans that fit each person’s needs. For those with ongoing blood disorders, seeing a hematologist is vital. It helps in managing the condition and improving life quality. With proper care, patients can keep their health in check.
FAQ
What does a hematologist do?
A hematologist is a doctor who focuses on blood disorders. They treat conditions like anemia, bleeding, and blood cancers.
What is hematology?
Hematology is the study of blood disorders and diseases. It involves diagnosis, treatment, and management.
Does seeing a hematologist mean I have cancer?
No, seeing a hematologist doesn’t mean you have cancer. They treat many blood disorders, not just cancer.
What kind of doctor is a hematologist?
A hematologist is a doctor with special training in blood disorders. They work alone or with a team.
How do I find a hematologist near me?
To find a hematologist, ask your doctor for a referral. You can also check with your insurance or search online.
What are the common symptoms that require hematological evaluation?
Common symptoms needing a hematologist include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. Also, easy bruising, bleeding, and frequent infections.
What diagnostic tests are used in hematology?
Hematology uses blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and advanced tests like flow cytometry and genetic testing.
What treatment approaches are used in hematology?
Treatments include medications, blood transfusions, and stem cell transplants. The choice depends on the disorder.
How do hematologists work with other specialists?
Hematologists team up with oncologists, primary care doctors, and surgeons. They work together for patient care.
Are there financial assistance programs available for hematology care?
Yes, there are programs to help with the costs of hematology care. This includes insurance and patient assistance.
How can I manage chronic blood disorders?
Managing chronic blood disorders needs a long-term plan. This includes regular doctor visits, following treatment, and making lifestyle changes.
What is the role of a hematologist-oncologist?
A hematologist-oncologist specializes in blood cancers. They treat leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
References
- Pastori, D., & Radu, A. (2024). Factor V Leiden Thrombophilia. GeneReviews ®. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1368/
- American Society of Hematology. (2022). ASH Clinical Practice Guidelines: Thrombophilia Testing. https://www.hematology.org/education/clinicians/guidelines-and-quality-care/clinical-practice-guidelines/venous-thromboembolism-guidelines/thrombophilia



































