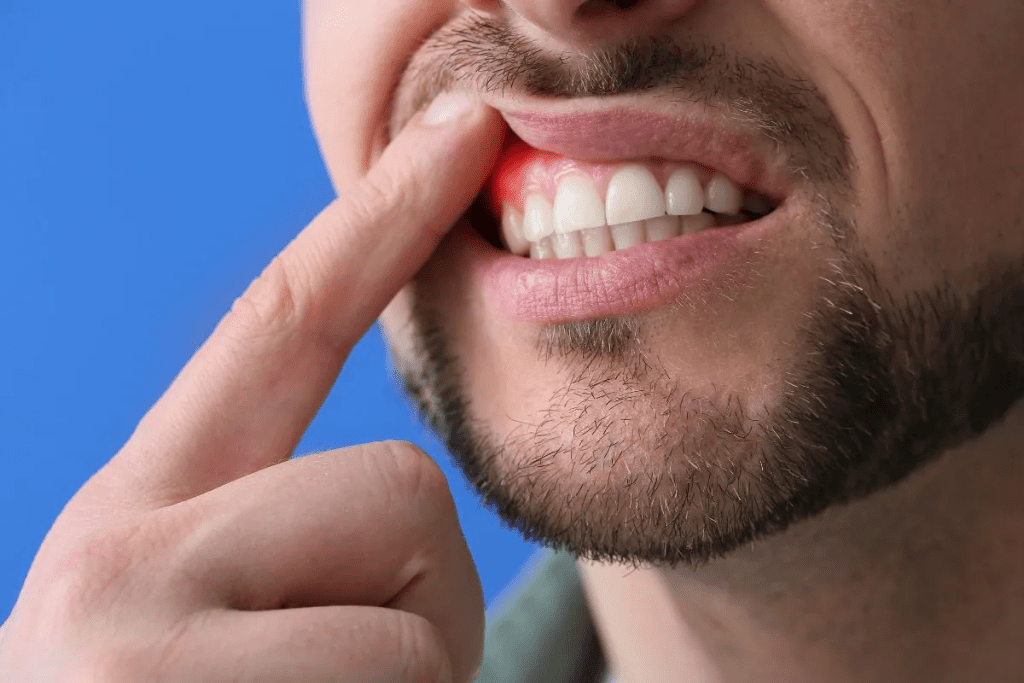
A bleeding disorder, like hemophilia, makes it hard for the body to form blood clots. This is key to stopping bleeding. Studies show about 1 in 5,000 males worldwide are born with hemophilia. This makes knowing its symptoms very important.
So, what is hemophilia? It’s a genetic disorder that stops the body from making blood clots. This leads to bleeding that doesn’t stop. Knowing the symptoms of bleeding disorders is key for early diagnosis and treatment.
This article will look at the 9 most common symptoms of bleeding disorders. We’ll explore how to identify and manage them.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding bleeding disorders is key for early diagnosis.
- Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that affects blood clotting.
- Spotting symptoms early can lead to timely treatment.
- Untreated bleeding disorders can have serious health effects.
- Knowing about the disorder can help improve patient care.
Understanding Bleeding Disorders
Bleeding disorders happen when the body can’t stop bleeding properly. This leads to too much or too long bleeding. It’s about how the body’s clotting process fails.
Definition and Overview
A bleeding disorder or clotting disorder is when blood can’t clot right. This causes bleeding inside the body or outside. It can be due to genetics, some medicines, or health problems.
These disorders are split into types based on their causes. They can be due to missing clotting factors, platelet issues, or blood vessel problems. Knowing the cause helps find the right treatment.
Understanding the mechanics of blood clotting is essential.

Normal clotting is complex, involving many factors. When a blood vessel gets hurt, it first narrows to slow blood flow. Then, platelets stick to the injury, making a plug.
Clotting factors then kick in, making a fibrin clot. This clot stabilizes the plug. The clotting process is a series of chemical reactions. Any problem, like a missing clotting factor, can cause a coagulation disease of blood or bleeding disorder.
| Clotting Factor | Function |
| Fibrinogen | Forms fibrin clot |
| Prothrombin | Converted to thrombin to facilitate clot formation |
| Factor VIII | Essential for the clotting cascade; deficiencies lead to Hemophilia A |
Understanding the mechanics of blood clotting is essential. It helps us understand bleeding disorders and the challenges they bring.
Hemophilia: The Most Well-Known Bleeding Disorder
Hemophilia is a major bleeding disorder that affects how blood clots. It’s a genetic issue that makes it hard for the body to form blood clots. Clotting is key to stopping bleeding.
What is Hemophilia?
Hemophilia happens when there’s not enough clotting factors in the blood. Clotting factors are proteins that help blood clot. Without enough, bleeding can go on for too long or start on its own.
Types of Hemophilia
There are two main types of hemophilia: Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B. Hemophilia A is when there’s not enough clotting factor VIII. Hemophilia B is when there’s not enough clotting factor IX. Both are passed down through genes.
- Hemophilia A: Also known as classic hemophilia, it’s the most common form.
- Hemophilia B: Sometimes called Christmas disease, it’s less common than Hemophilia A.
Genetic Factors in Hemophilia
Hemophilia is mainly caused by genetic mutations. These mutations affect genes that make clotting factors. They can be passed down from parents. Because of this, hemophilia is more common in males, who have only one X chromosome.
Females can carry the mutated gene. In rare cases, they can also have the condition if they get two mutated X chromosomes. Understanding genetic factors in hemophilia is key for diagnosis and family planning. Genetic counseling is often suggested for families with a history of hemophilia.
Other Common Bleeding Disorders
Hemophilia is well-known, but Von Willebrand Disease and platelet function disorders also affect many. These conditions disrupt blood clotting, causing health issues.
Von Willebrand Disease
Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. It affects both males and females. It’s caused by a lack or problem with the von Willebrand factor (VWF), a key clotting protein.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe. They include easy bruising, nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual bleeding. The National Hemophilia Foundation says “VWD affects up to 1% of the general population, though many cases go undiagnosed.”
To diagnose, doctors look at medical history, physical exams, and lab tests. These tests check VWF levels and function. Treatment might include desmopressin to release VWF or VWF concentrates.
Platelet Function Disorders
Platelet function disorders mean platelets don’t clot blood right. These can be inherited or acquired. Symptoms include prolonged bleeding, easy bruising, and petechiae (small spots on the skin due to bleeding).
To diagnose, doctors use platelet function tests. Treatment might include platelet transfusions or medicines to help platelets work better.
“Platelet disorders can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, necessitating a thorough management plan.”
Rare Clotting Factor Deficiencies
Rare clotting factor deficiencies are disorders where clotting factors other than VIII or IX are missing. These can cause bleeding problems. Treatment usually involves replacing the missing clotting factor.
It can be on-demand for acute bleeds or prophylactically to prevent them.
Knowing about these bleeding disorders is key to helping those affected. By understanding each condition’s unique traits and treatments, healthcare providers can better care for patients.
Symptom1: Excessive Bleeding from Minor Cuts or Injuries
Bleeding disorders often show up as too much bleeding from small cuts or injuries. This is a sign that needs medical help right away. It’s a clue that your body might not be clotting blood right.
What Constitutes “Excessive” Bleeding
What’s considered “excessive” bleeding can differ for everyone. But, some signs can help spot when it’s not normal. For example, if a cut or injury keeps bleeding for over 10-15 minutes, it’s likely too much. Also, if it bleeds again after stopping, or if you need to change bandages a lot, it might mean clotting issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help for too much bleeding is key. If you or someone else has any of these signs, you should see a doctor:
- Bleeding that doesn’t stop after 10-15 minutes of pressure
- Frequent or recurrent nosebleeds
- Bleeding into joints or muscles
- A family history of bleeding disorders
Getting a diagnosis and treatment early can really help. A doctor will check your medical history and run tests to find out why you’re bleeding too much.
| Signs of Excessive Bleeding | Action to Take |
| Bleeding lasts more than 10-15 minutes | Apply pressure and seek medical help if it doesn’t stop |
| Recurring bleeding after initial stoppage | Monitor closely and consult a healthcare provider |
| Significant blood loss or large bruises | Seek immediate medical attention |
Symptom2: Easy Bruising
Easy bruising can be a sign of a bleeding disorder. It happens when blood vessels get damaged, letting blood spill into the tissue. While some bruising is normal, too much or unexplained bruising might mean a clotting problem.
Difference Between Normal and Abnormal Bruising
Normal bruising comes from minor injuries and is small. But, abnormal bruising can happen without injury or be much bigger. People with bleeding disorders often get these big bruises, which is a big worry.
Knowing the difference between normal and abnormal bruising is key. If you bruise easily or without reason, it’s time to check it out.
Bruising Patterns in Bleeding Disorders
Bleeding disorders can cause specific bruising patterns. For example, people with hemophilia or von Willebrand disease might get big, painful bruises. The pattern and how bad the bruising is can tell a lot about the condition.
It’s important to understand these patterns to diagnose and treat bleeding disorders right. Doctors look for these signs to figure out if someone has a bleeding disorder.
Symptom3: Joint Bleeding and Pain
Joint bleeding and pain are major issues for people with bleeding disorders like hemophilia. These symptoms can really hurt someone’s quality of life.
How Joint Bleeding Occurs
Joint bleeding, or hemarthrosis, happens when blood leaks into the joint space. This is because of a lack of clotting factors. Normally, a little injury might cause some bleeding, but it gets cleaned up fast.
But for those with bleeding disorders, the lack of clotting factor means a lot of bleeding. A small injury or strain can start the bleeding. This is because the blood vessels in the joint break, leading to bleeding.
With each bleeding episode, the joint gets more and more damaged. This can cause chronic inflammation and harm to the joint.
Long-term Joint Damage
Repeated bleeding in the joints can lead to long-term joint damage. This damage includes chronic pain, swelling, and less mobility. The joint might even become deformed, and the muscles around it can weaken.
This damage can make daily life very hard. Getting diagnosed and treated early is key to avoiding these problems. Treatment, like clotting factor replacement, can help prevent joint damage.
People with bleeding disorders need to work closely with their doctors. This way, they can manage their condition well and avoid long-term joint damage.
Symptom4: Prolonged Nosebleeds
Prolonged nosebleeds can be a worrying sign of a bleeding disorder. Nosebleeds, or epistaxis, are common. But if they last a long time or are hard to stop, it might mean your body can’t clot blood right.
Normal vs. Abnormal Nosebleed Duration
A nosebleed that lasts under 15 minutes is usually okay. But if they last longer or are very heavy, it could mean you have a bleeding disorder. Knowing how long and how often nosebleeds happen is key to figuring out if you need to see a doctor.
Key factors to consider include:
- The length of time the nosebleed lasts
- The frequency of nosebleeds
- The difficulty in controlling the bleeding
Managing Recurrent Nosebleeds
Handling recurrent nosebleeds needs quick action to stop the bleeding and long-term plans to avoid future ones. For people with bleeding disorders, special treatments might be suggested to help with clotting and prevent long nosebleeds.
Immediate steps to manage a nosebleed include:
- Sitting upright and leaning forward to prevent blood from flowing down the back of the throat
- Pinching the nostrils shut for 5-10 minutes to apply direct pressure
- Avoiding blowing the nose or straining, which can dislodge the clot and cause bleeding to resume
If you’re having a lot of nosebleeds or they last a long time, you should see a doctor. They can help you manage the condition and might suggest treatments to control the bleeding.
Symptom5: Blood in Urine or Stool
Blood in urine or stool is a symptom that should not be ignored. It can indicate an underlying bleeding disorder. The presence of blood in these bodily secretions can be alarming and is often associated with various health concerns.
Potential Causes and Concerns
The appearance of blood in urine or stool can result from several factors. These include infections, inflammation, or trauma to the urinary or gastrointestinal tract. In individuals with bleeding disorders, this symptom can be very concerning. It may indicate a more severe underlying condition.
Key concerns include the risk of significant blood loss. There’s also the presence of an underlying condition such as a tumor or ulcer. And the risk of complications if left untreated.
Diagnostic Approach
Diagnosing the cause of blood in urine or stool involves a thorough medical evaluation. This includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Tests such as urinalysis or stool tests are common.
- Urinalysis to check for infections or abnormalities in the urine.
- Stool tests to detect blood or pathogens in the stool.
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans to visualize the urinary or gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding the cause of this symptom is key for proper management and treatment. Individuals experiencing blood in their urine or stool should seek medical attention promptly. This ensures timely intervention.
Symptom6: Prolonged Bleeding After Surgery or Dental Work
Prolonged bleeding after surgery or dental work is a big worry for those with bleeding disorders. It can cause serious problems if not handled right.
Preventive Measures Before Procedures
To lower the chance of bleeding too much, there are steps you can take before surgery or dental work. Preoperative assessment is key. It includes a detailed medical history and lab tests to figure out the bleeding risk.
- Telling healthcare providers about your bleeding disorder
- Changing medications that might affect clotting
- Getting clotting factor replacement therapy if needed
These steps help cut down the risk of bleeding problems during and after the procedure.
Post-Procedure Monitoring
After surgery or dental work, it’s important to watch closely for any bleeding issues. Post-procedure care means looking out for signs of bleeding, like swelling, pain, or oozing from the area.
| Monitoring Aspect | Description | Action if Complication Arises |
| Bleeding Signs | Watching for swelling, pain, or oozing | Apply pressure or seek immediate medical attention |
| Clotting Factor Levels | Checking clotting factor levels after the procedure | Give more clotting factor replacement if needed |
| Pain Management | Keeping pain under control without affecting clotting | Change pain management plan if needed |
Good monitoring after the procedure helps catch any problems early. This makes sure patients do better.
Symptom7: Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy menstrual bleeding is a symptom linked to bleeding disorders. It affects a woman’s quality of life deeply. It means bleeding more or longer than usual, causing discomfort and disrupting daily life.
Identifying Abnormal Menstrual Bleeding
Abnormal menstrual bleeding shows up in different ways. For example:
- Prolonged menstrual periods lasting more than 7 days
- Heavy bleeding that requires changing sanitary products every hour or two
- Passing large blood clots during menstruation
- Experiencing significant discomfort or pain during menstruation
Women should track their menstrual cycles and bleeding patterns. Keeping a menstrual diary helps monitor bleeding duration and intensity.
Impact on Quality of Life
Heavy menstrual bleeding affects a woman’s life in many ways. It impacts:
- Physical health: Leading to anemia, fatigue, and other complications
- Emotional well-being: Causing stress, anxiety, and emotional distress
- Social and work life: Limiting participation in social activities and affecting work productivity
Effective management of heavy menstrual bleeding is key to improve quality of life. This may involve medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and support from healthcare providers.
A healthcare professional noted, “Recognizing and addressing heavy menstrual bleeding is vital for improving the overall well-being of women with bleeding disorders.”
“Women with bleeding disorders often experience heavy menstrual bleeding, which can be a significant challenge. Proper diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve their quality of life.”
Symptom8: Bleeding Into Muscles
Bleeding into muscles is a key symptom of bleeding disorders. It’s painful and can really limit your movement. This happens when the body can’t clot properly, causing blood to leak into muscle tissue. It’s most common in people with hemophilia and other clotting issues.
Recognizing Muscle Bleeds
Spotting muscle bleeds can be tricky. Symptoms depend on how bad the bleed is and where it is. You might notice pain and swelling in the area, limited mobility, or a noticeable lump. Severe cases can cause a lot of pain and swelling, leading to compartment syndrome.
It’s important to catch muscle bleeds early. People with bleeding disorders should watch for these signs. Quick action can prevent serious problems and improve recovery.
Treatment and Recovery
Treating muscle bleeds means replacing the missing clotting factor. The treatment plan depends on the disorder and how bad the bleed is. For minor bleeds, clotting factor concentrates might be enough. But serious cases might need hospital care to manage pain and prevent more issues.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Recovery Time |
| Clotting Factor Replacement | Administering clotting factor concentrates to stop the bleeding. | Several days to weeks |
| Pain Management | Using medications to manage pain and discomfort. | Varies based on severity |
| Physical Therapy | Rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and mobility. | Several weeks to months |
Getting better from muscle bleeds also means physical therapy to build back muscle strength and mobility. It’s also key to prevent bleeds by staying active and avoiding injuries.
Symptom9: Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage is a serious symptom of bleeding disorders. It can cause severe brain damage or even death if not treated fast. This condition means bleeding inside the brain.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to know the warning signs of intracranial hemorrhage. Symptoms include severe headache, often called “the worst headache of my life.” You might also feel nausea and vomiting, get confused, or have trouble speaking.
Other signs are weakness or numbness in parts of your body, vision changes, and trouble with coordination. In bad cases, you might have seizures or become unresponsive.
Emergency Response
If you think someone has intracranial hemorrhage, act fast. Call emergency services right away if you see symptoms. Try to keep the person calm and comfortable while waiting.
Emergency responders will start treatment and take the person to a hospital. Quick medical help can greatly improve their chances of recovery.
Diagnosing Bleeding Disorders
To find out if someone has a bleeding disorder, doctors use several steps. They look at the person’s medical history, do a physical check, and run lab tests. This way, they can make sure they know exactly what’s going on and how to treat it.
Initial Evaluation and Medical History
The first step in figuring out bleeding disorders is very important. Doctors ask a lot of questions to see if there’s a pattern of bleeding or bruising. They want to know how often and how badly the bleeding happens, and if anyone in the family has similar issues.
Knowing the medical history is key. For example, if someone bleeds a lot from their nose or takes a long time to stop bleeding after surgery, it might mean they have a bleeding disorder.
Laboratory Tests
Lab tests are a big part of finding out about bleeding disorders. These tests check how well the blood clots and if there are any missing clotting factors.
| Test | Description | Purpose |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Measures various components of blood, including platelets. | To assess overall blood health and detect any abnormalities. |
| Prothrombin Time (PT) | Measures the time it takes for blood to clot. | To evaluate the extrinsic clotting pathway. |
| Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) | Measures the time it takes for blood to clot via the intrinsic pathway. | To assess the intrinsic clotting pathway. |
| Fibrinogen Test | Measures the level of fibrinogen in the blood. | To diagnose fibrinogen deficiencies. |
Genetic Testing
Genetic tests are very useful for diagnosing bleeding disorders like hemophilia A and B. They look for specific genetic changes that cause these disorders.
These tests not only confirm the diagnosis but also help with family planning. They show the risk of passing the disorder to future generations.
Treatment Options for Bleeding Disorders
Bleeding disorders need a treatment plan that fits each person. This might include clotting factor replacement, clotting medications, and new treatments. The right treatment depends on the disorder, its severity, and the patient’s health.
Clotting Factor Replacement Therapy
Clotting factor replacement is key for managing bleeding disorders like hemophilia A and B. It involves giving a missing clotting factor to help blood clot normally.
Benefits of Clotting Factor Replacement Therapy:
- Reduces bleeding episodes
- Improves life quality by letting people do more
- Can be used to prevent or treat bleeding
Medications to Promote Clotting
Other medications help with clotting or keeping clots stable. These include antifibrinolytics and desmopressin.
| Medication | Use | Benefits |
| Antifibrinolytics | Prevent clot breakdown | Good for mild bleeding, like dental work |
| Desmopressin | Boosts factor VIII and von Willebrand factor | Helps with mild hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease, given as a spray or injection |
Emerging Treatments and Research
New treatments for bleeding disorders are being explored. This includes gene therapy, new clotting factors, and other innovative methods. These could lead to better treatments in the future.
New treatments aim to be more effective, easier to use, and less likely to cause immune reactions. They could change how we manage bleeding disorders.
Bleeding Disorders in Children
Bleeding disorders can greatly affect children’s lives. They need careful management to prevent problems and keep them healthy.
Special Considerations for Pediatric Patients
Children with bleeding disorders need tailored treatment plans. These plans must change as they grow. Regular checks and treatment adjustments are key.
Parents and caregivers must work with doctors to create a detailed care plan. This plan should cover how to handle bleeding, prevent it, and when to get medical help.
School and Activity Guidelines
Children with bleeding disorders can join in school and activities, but with caution. Schools need to know about their condition to help.
Important things to consider include:
- Creating an emergency plan for bleeding episodes.
- Changing physical activities to lower injury risk.
- Ensuring the child has needed medicines or treatments at school.
By following these steps, kids with bleeding disorders can stay active and safe.
Living with a Bleeding Disorder
Living with a bleeding disorder can be tough, but it’s possible to live a full life. Getting a diagnosis affects not just the person but their family too. It’s important to manage it well.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making lifestyle adjustments is key for those with bleeding disorders. It’s important to be careful with physical activities to avoid injuries. Keeping a healthy weight helps reduce stress on joints. And, it’s best to avoid certain medicines that can make bleeding worse.
For example, people with bleeding disorders might choose low-impact sports like swimming or cycling. High-impact activities can lead to injuries. Wearing protective gear during activities also helps prevent bleeds.
Support Resources
Having support resources is vital for managing a bleeding disorder. This includes doctors who specialize in bleeding disorders, support groups, and educational materials.
Support groups, whether online or in-person, offer a community for sharing experiences. They provide emotional support and learning opportunities. Educational resources, like workshops and online courses, help individuals understand and manage their condition better.
Psychological Impact
The psychological impact of living with a bleeding disorder is significant. Chronic conditions can cause anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation. It’s important to have access to mental health professionals.
Counseling and therapy can help individuals deal with the emotional side of their condition. They can improve their quality of life and learn to manage stress and anxiety related to their bleeding disorder.
In conclusion, managing a bleeding disorder requires a holistic approach. This includes making lifestyle changes, using support resources, and addressing the psychological impact. By doing these things, individuals can better manage their condition and improve their overall well-being.
Conclusion
It’s important to understand bleeding disorders to manage them well. Symptoms like excessive bleeding and joint pain are signs of conditions like hemophilia. These signs are key to getting the right treatment.
Spotting these symptoms early can make a big difference. There are many ways to treat bleeding disorders, like clotting factor therapy. Making lifestyle changes and using support resources also helps a lot.
Managing bleeding disorders needs a full approach. This includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and support for the mind. Knowing the symptoms and treatments helps people live better with these conditions. It leads to better management of bleeding disorders like hemophilia.
FAQ
What is hemophilia?
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder that makes it hard for the body to form blood clots. Clots are needed to stop bleeding. It happens when the blood lacks certain clotting factors, causing prolonged or spontaneous bleeding.
What are the symptoms of bleeding disorders?
Symptoms include bleeding a lot from small cuts or injuries, easy bruising, and joint pain. Other signs are prolonged nosebleeds, blood in urine or stool, and heavy menstrual bleeding. Also, bleeding into muscles and intracranial hemorrhage can occur.
What is the difference between Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B?
Hemophilia A is caused by a lack of clotting factor VIII. Hemophilia B is due to a lack of clotting factor IX. Both lead to bleeding issues but have different causes.
How are bleeding disorders diagnosed?
Diagnosing bleeding disorders starts with an initial evaluation and medical history. Then, lab tests check clotting factor levels. Genetic testing identifies specific genetic mutations.
What is Von Willebrand Disease?
Von Willebrand Disease is a bleeding disorder caused by a lack or mutation of von Willebrand factor. This protein is key for blood clotting. Symptoms include easy bruising, heavy menstrual bleeding, and prolonged bleeding after injuries or surgeries.
How is heavy menstrual bleeding related to bleeding disorders?
Heavy menstrual bleeding can be a sign of a bleeding disorder like Von Willebrand Disease or a clotting factor deficiency. Women with heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding should get checked for bleeding disorders.
What are the treatment options for bleeding disorders?
Treatments include clotting factor replacement therapy and medications that help clotting. Other supportive measures are also used. New treatments and research aim to improve management.
Can bleeding disorders be managed in daily life?
Yes, with the right management and lifestyle changes, people with bleeding disorders can live active lives. It’s important to know the risks of bleeding, take preventive steps, and have a plan for managing bleeding episodes.
Are bleeding disorders inherited?
Many bleeding disorders, like hemophilia and Von Willebrand Disease, are inherited. Knowing the genetic factors helps in diagnosing and managing these conditions.
What is the importance of recognizing the symptoms of bleeding disorders?
Recognizing symptoms early is key for timely diagnosis and management. It helps prevent complications, reduces severe bleeding risks, and improves life quality for those with these conditions.
What is a blood clotting disorder?
A blood clotting disorder, or coagulopathy, affects blood clotting. It can cause either too much bleeding or inappropriate clotting.
What are clotting disorders?
Clotting disorders are conditions that disrupt normal blood clotting. They increase the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
What is factor eight deficiency?
Factor eight deficiency, or Hemophilia A, is when the blood lacks enough clotting factor VIII. This leads to bleeding complications.
References
Alonso-Menchén, D., et al. (2022). Unresolved issues in the epidemiology and diagnosis of bacteremia. Revista Española de Quimioterapia. Retrieved from
Kern, W. V. (2020). Burden of bacterial bloodstream infection”a brief update. Swiss Medical Weekly. Retrieved from


































