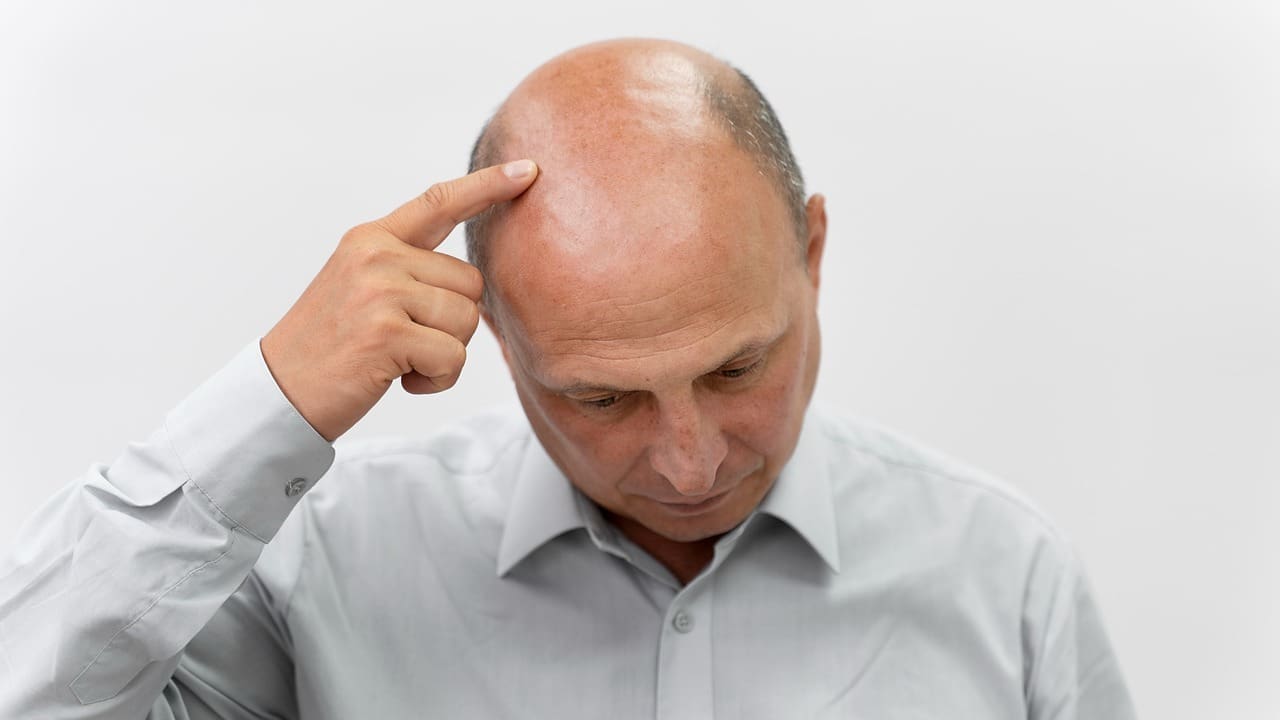
At Liv Hospital, we know how tough it is to deal with symptoms like hair loss and facial changes from brain and pituitary gland tumors. Brain tumors themselves don’t usually cause hair loss. But, treatments like chemotherapy or radiation can harm hair follicles, making hair fall out.
Pituitary gland tumors can mess with hormones, leading to thinner or lost hair and changes in the face. Our team is here to help you understand these effects and what treatment options are available.
Key Takeaways
- Brain tumors rarely cause hair loss directly, but treatments can lead to hair loss.
- Pituitary gland tumors can cause hormonal imbalances, resulting in hair loss and facial changes.
- Liv Hospital provides world-class healthcare with complete support for international patients.
- Our experts utilize innovative and evidence-based care pathways for brain and pituitary conditions.
- We offer expert support and guidance for patients facing hair loss and facial changes.
The Connection Between Brain Health and Physical Appearance

The link between brain health and physical appearance is complex. Neurological conditions often show up in unexpected ways. Our brain health greatly affects our overall well-being, including how we look.
How Neurological Conditions Manifest Externally
Neurological conditions can lead to symptoms like hair loss and facial changes. For example, some brain tumors can cause hormonal imbalances. This affects hair growth and facial features.
As a medical expert says, “The physical signs of neurological conditions can be as upsetting as the condition itself.”
“The physical manifestations of neurological conditions can be just as distressing as the underlying condition itself.”
The Psychological Impact of Appearance Changes
These changes deeply affect patients’ self-esteem and quality of life. We understand the need to address these changes in care. By knowing the connection between brain health and physical appearance, we can help patients manage these symptoms better.
Does Brain Tumor Cause Hair Loss? Understanding the Relationship
Brain tumors themselves don’t usually cause hair loss. But, the treatments for them can really affect hair health. The link between brain tumors and hair loss is complex, with many factors playing a role.
Direct vs. Indirect Effects of Brain Tumors on Hair
Brain tumors can lead to hair loss indirectly, through treatments. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can harm hair follicles, causing hair to fall out. How much hair is lost depends on the treatment type, dosage, and the patient’s health.
Differentiating Tumor-Related Hair Loss from Other Causes
It’s key to tell apart hair loss from brain tumor treatments and other reasons. Hormonal imbalances, lack of nutrients, and stress can also cause hair loss. Knowing the real cause helps in managing hair loss better.
| Treatment Type | Effect on Hair Loss | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Significant hair loss due to damage to hair follicles | Often reversible after treatment completion |
| Radiation Therapy | Hair loss in the irradiated area, potentially permanent | May be reversible, depending on dosage and area treated |
Understanding how brain tumors, their treatments, and hair loss are connected helps patients. They can then manage their hair loss better and look for ways to lessen it.
Treatment-Related Hair Loss in Brain Tumor Patients
Brain tumor treatments save lives but can change how a person looks, like hair loss. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy harm hair follicles, causing different types of hair loss.
Chemotherapy and Its Effects on Hair Follicles
Chemotherapy fights cancer by targeting fast-growing cells, including hair follicles. This leads to hair loss all over the body, not just on the scalp. The amount of hair lost depends on the chemotherapy drugs used.
Radiation Therapy and Patterns of Hair Loss
Radiation therapy, aimed at the head, can cause hair loss in that area. How much hair is lost and if it grows back depends on the radiation dose and how it’s given.
External Beam Radiation and Scalp Damage
External beam radiation can harm the scalp and hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss at high doses. The scalp might also get red, flaky, and even die in severe cases.
Temporary vs. Permanent Hair Loss After Treatment
Hair loss after brain tumor treatment can be temporary or permanent. Some people’s hair grows back after treatment ends. Others might lose hair permanently, based on the treatment’s strength and how they react.
Talking about hair loss with doctors can help patients get ready for this part of their treatment.
The Pituitary Gland: Function and Location
It’s important to know how the pituitary gland works and where it is. This gland is small and sits at the brain’s base. It helps control many body functions.
Anatomy of the Pituitary and Its Position in the Brain
The pituitary gland is in a bony space called the sella turcica, below the hypothalamus. It’s linked to the hypothalamus by a stalk called the infundibulum. This spot lets the pituitary get signals from the hypothalamus, which controls its hormone making.
The Role of the Pituitary as the “Master Gland”
The pituitary gland is called the “master gland” because it controls many other glands. It makes hormones that help or stop other glands from making theirs. For example, it makes TSH to help the thyroid gland work right.
How Pituitary Hormones Affect Hair Growth and Facial Features
Pituitary hormones greatly affect hair growth and facial looks. Growth hormone (GH) helps with growth, including hair. Prolactin, another hormone, can change hair growth patterns. Problems like tumors can cause hair and facial changes, like in acromegaly or Cushing’s disease.
Types and Characteristics of Pituitary Gland Tumors
Pituitary gland tumors can be broadly classified based on their size and hormone-secreting capabilities. This classification greatly affects their symptoms and treatment. We will look at the different types and characteristics of these tumors, focusing on their size and hormone production.
Functioning vs. Non-Functioning Pituitary Adenomas
Pituitary adenomas are tumors in the pituitary gland. They are divided into functioning and non-functioning types. Functioning adenomas produce too much hormone, causing endocrine disorders. On the other hand, non-functioning adenomas don’t make hormones but can cause problems due to their size and pressure.
Size Classifications: Microadenomas and Macroadenomas
Pituitary adenomas are also sized differently. Microadenomas are small, under 10 mm, while macroadenomas are larger, over 10 mm. The size of the tumor is important because it affects symptoms and treatment. Larger tumors can cause more symptoms due to their size and pressure.
Common Hormone-Secreting Tumor Types
Some common functioning pituitary adenomas include:
- Prolactinomas: These tumors secrete prolactin, leading to hormonal imbalances.
- Growth hormone-secreting adenomas: These cause acromegaly, a condition characterized by excessive growth.
- ACTH-secreting adenomas: These lead to Cushing’s disease, resulting from excess cortisol production.
Understanding these different types and characteristics is key for diagnosing and treating pituitary gland tumors effectively.
Hormonal Imbalances and Their Effect on Hair Growth
Pituitary gland tumors can cause hormonal imbalances. These imbalances affect hair growth and texture. The tumor disrupts hormone production, which controls hair growth.
Prolactin-Secreting Tumors and Hair Thinning
Prolactin-secreting tumors, or prolactinomas, lead to too much prolactin. This causes hair to thin. High prolactin levels mess up the hair growth cycle, causing more hair loss.
Growth Hormone Disorders and Hair Texture Changes
Growth hormone disorders, like acromegaly, change hair texture. Too much growth hormone makes hair coarse and thick. Not enough makes it thin and brittle.
Thyroid Hormone Disruption and Hair Loss Patterns
Thyroid hormone issues, linked to pituitary gland tumors, cause specific hair loss patterns. Hypothyroidism makes hair dry and brittle. Hyperthyroidism makes it fine and fragile.
| Hormonal Imbalance | Hair Growth Effect |
|---|---|
| Prolactin-Secreting Tumors | Hair Thinning |
| Growth Hormone Disorders | Changes in Hair Texture |
| Thyroid Hormone Disruption | Distinct Hair Loss Patterns |
It’s important to understand how hormonal imbalances affect hair growth. This knowledge helps in creating effective treatments. Healthcare providers can address these issues to improve hair growth and overall health.
Facial Changes Associated with Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary tumors can cause facial changes due to hormonal imbalances. These changes vary based on the tumor type and affected hormones.
Acromegaly: Progressive Facial Feature Enlargement
Acromegaly, caused by a growth hormone-secreting tumor, enlarges facial features. This leads to a larger nose, jaw, and tongue. The face looks coarse.
Cushing’s Disease and Characteristic Facial Rounding
Cushing’s disease, from an ACTH-producing tumor, causes facial rounding. This is known as a “moon face.” It also brings weight gain and skin changes.
Hypopituitarism and Its Effects on Facial Appearance
Hypopituitarism, or underproduction of hormones, changes the face. It can cause pale skin, fine wrinkles, and loss of facial hair.
Skin Changes and Premature Aging
Hormonal imbalances from pituitary tumors affect the skin. They can make it thin, dry, and age early. This impacts a patient’s look.
Facial Hair Distribution Abnormalities
Hormonal changes from tumors can alter facial hair. Some grow too much, while others lose hair.
Knowing these facial changes is key for diagnosing and treating pituitary tumors. Healthcare providers can then offer the right treatment.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Pituitary Tumors
Diagnosing pituitary tumors needs a mix of clinical checks, advanced imaging, and hormone tests. We’ll look at the tools and methods for spotting these tumors.
Clinical Signs That Suggest a Pituitary Disorder
Signs like unexplained hair loss, facial changes, and hormonal imbalances hint at pituitary issues. These signs are key when checking for tumors.
Imaging Studies and Hormone Level Testing
MRI scans are vital for spotting pituitary tumors. Hormone tests also show how the tumor affects hormone levels.
Differential Diagnosis for Hair Loss and Facial Changes
It’s important to figure out why hair loss and facial changes happen. We need to look at other conditions that might look like or be linked to pituitary tumors.
Treatment Options for Tumor on Pituitary Gland
The treatment for pituitary tumors depends on several things. This includes the type of tumor and the patient’s health. At Liv Hospital, we use a team approach to find the best treatment for each patient.
Medical Management of Hormone-Secreting Tumors
For tumors that make too many hormones, we often start with medicine. Medications can control hormone levels, easing symptoms and shrinking the tumor. We choose the right medicine based on the tumor type.
Surgical Approaches: Transsphenoidal and Transcranial Methods
Surgery is key for many pituitary tumors. Transsphenoidal surgery is usually the first choice for tumors in the sella. But for bigger or more complex tumors, a transcranial surgery might be needed. Our neurosurgeons and endocrinologists work together for the best care.
Radiation Therapy for Residual or Recurrent Tumors
For tumors left behind after surgery or that come back, we use radiation. Stereotactic radiosurgery gives precise radiation, protecting nearby tissues. We use the latest radiation methods for better results.
Recovery Timeline After Pituitary Surgery
Recovery times after surgery vary. Patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days. It can take weeks to months to fully recover, with close monitoring of hormone levels and symptoms.
Liv Hospital’s Innovative Approach to Pituitary Tumor Treatment
At Liv Hospital, we focus on innovative, evidence-based care for pituitary tumors. Our team creates personalized treatment plans. This ensures the best results for our patients.
Conclusion: Managing Physical Changes and Long-Term Outlook
It’s important to know how brain tumors and pituitary gland tumors affect hair and face. At Liv Hospital, we offer detailed and caring support for these patients. We use the latest and most proven treatments.
Dealing with hair loss and face changes needs a team effort. Our experts create special plans for each patient. This way, we tackle the root causes and help patients feel better.
The future looks good for those with pituitary gland tumors. It depends on the tumor’s type and size, and how well treatment works. With the right care, many patients see big improvements in their life quality. We’re dedicated to top-notch healthcare for all, making sure international patients get the best care.
Can a brain tumor directly cause hair loss?
Brain tumors usually don’t cause hair loss directly. But, treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can harm hair follicles. This can lead to hair loss.
How do pituitary gland tumors affect hair growth?
Pituitary gland tumors can mess with hormone balances. This can change hair texture and growth patterns. For example, tumors that release prolactin can cause hair to thin.
What facial changes are associated with pituitary tumors?
Pituitary tumors can cause facial changes. These include bigger facial features (acromegaly), rounded face (Cushing’s disease), and skin changes.
How are pituitary tumors diagnosed?
Finding pituitary tumors involves several steps. These include a clinical check-up, imaging studies (like MRI), and hormone tests.
What are the treatment options for pituitary gland tumors?
Treatments for pituitary gland tumors include medicine, surgery (like transsphenoidal surgery), and radiation therapy.
Can hair loss caused by brain tumor treatment be permanent?
Hair loss from brain tumor treatment varies. It depends on the treatment and its strength. Sometimes, hair loss is temporary, but it can also be permanent.
Where is the pituitary gland located, and how does it affect the body?
The pituitary gland is at the brain’s base. It’s key for controlling the body’s functions, like hormone production.
What are the different types of pituitary gland tumors?
Pituitary gland tumors are classified as functioning or non-functioning. They can be small (microadenomas) or large (macroadenomas). Common types include tumors that release prolactin or growth hormone.
How do hormonal imbalances caused by pituitary tumors affect facial features?
Hormonal imbalances from pituitary tumors can change facial features. This includes acromegaly, Cushing’s disease, and hypopituitarism.
What is the prognosis for patients with pituitary gland tumors?
The outlook for patients with pituitary gland tumors depends on the tumor’s type and size. It also depends on how well treatment works.
References
- PMC – PubMed Central : https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3876007


































