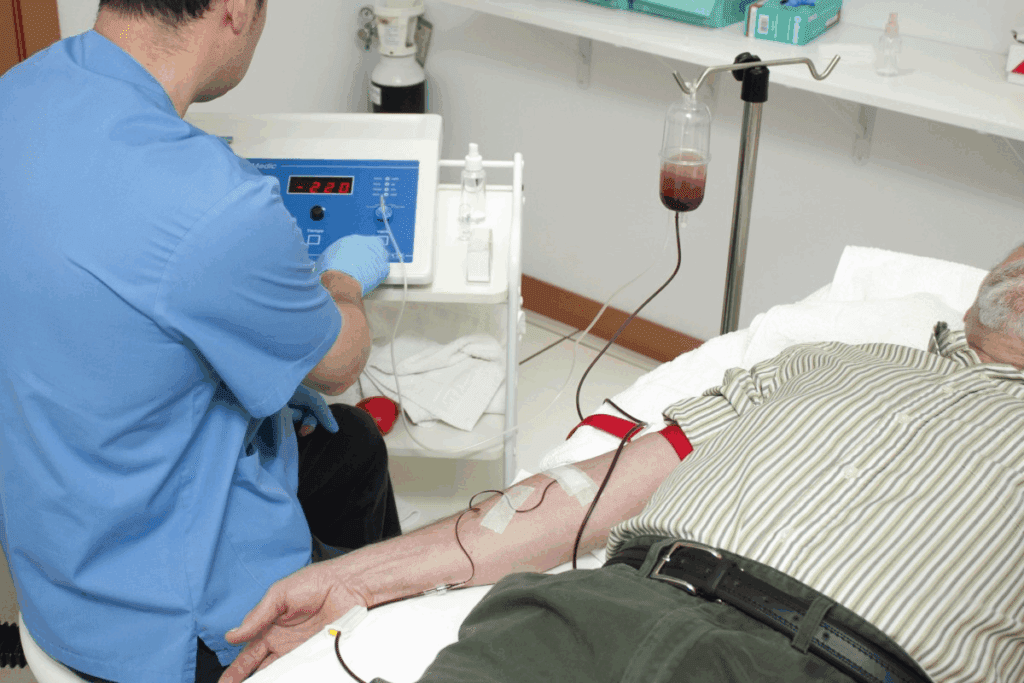
At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch bone marrow transplant care for those with blood cancers and serious diseases. This procedure replaces damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. These cells come from a relative or a donor who matches well.
A bone marrow transplant puts healthy stem cells into your body. This helps replace bone marrow that’s not making enough healthy blood cells. We give our patients the best care and support during the transplant. This ensures they get the best results.
Key Takeaways
- Bone marrow transplant is a medical procedure that replaces damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
- The procedure involves infusing healthy blood-forming stem cells into the body.
- Liv Hospital provides internationally benchmarked, patient-centered care for BMT patients.
- Comprehensive care and support are provided throughout the transplant process.
- Healthy stem cells are often collected from a close relative or compatible donor.
Understanding Bone Marrow and Its Function
Bone marrow is key to our body’s health. It makes blood cells in the spongy tissue of bones like hips and thighbones. This tissue is vital for our overall health.
The Role of Bone Marrow in the Human Body
Bone marrow is vital for making blood cells. It creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infections, and platelets help blood clot.
Without bone marrow, our bodies can’t make these essential blood cells. This would severely harm our health.
How Bone Marrow Produces Blood Cells
Blood cell production, or hematopoiesis, happens in the bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cells turn into different blood cells. This process is controlled by growth factors and cytokines.
We need this system to keep the right balance of blood cells. It’s essential for our health.
When Bone Marrow Fails: Conditions Requiring Transplantation
When bone marrow fails, it can be life-threatening. This can happen due to diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and aplastic anemia. In these cases, a bone marrow transplant is needed.
This transplant helps restore the body’s ability to make healthy blood cells. We will look into these conditions and how bone marrow transplantation helps treat them.
BMT Medical Terminology Explained

The world of bone marrow transplantation is filled with specific medical terms. Patients should know these terms to understand BMT better.
What is BMT in Medical Terms?
BMT stands for “bone marrow transplant.” It’s a procedure that replaces a patient’s bone marrow with healthy stem cells. This is also called a stem cell transplant.
Common Abbreviations and Terms in Transplant Medicine
In transplant medicine, many abbreviations and terms are used. For example, allo-BMT means an allogeneic bone marrow transplant. This is when a donor, often a relative or an unrelated match, donates their stem cells.
Auto-BMT is when a patient uses their own stem cells. Other key terms include graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and engraftment. GVHD is a complication after an allogeneic transplant. Engraftment is when the new stem cells start making blood cells.
| Term | Definition |
| BMT | Bone Marrow Transplant |
| Allo-BMT | Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant |
| Auto-BMT | Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant |
| GVHD | Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
Evolution of Terminology: From Bone Marrow to Stem Cell Transplants
The terms used in bone marrow transplantation have changed over time. At first, it was just called a “bone marrow transplant.” But as stem cell understanding grew, “stem cell transplant” became more common.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplants
There are many types of bone marrow transplants, each with its own benefits. The main difference is where the stem cells come from.
Autologous Transplants: Using Your Own Cells
Autologous bone marrow transplants use your own stem cells. They are often used for certain cancers like lymphoma or multiple myeloma. First, your stem cells are taken out and stored. Then, they are put back in after a special treatment.
Advantages of Autologous Transplants:
- No risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
- Faster engraftment
- Lower risk of complications related to donor cells
Allogeneic Transplants: Donor-Derived Cells
Allogeneic transplants use stem cells from a donor. This donor can be a sibling, an unrelated donor, or a cord blood unit. They are often used for patients with leukemia or other blood disorders.
Key Considerations for Allogeneic Transplants:
- The donor’s human leukocyte antigen (HLA) type must be compatible with the patient’s.
- There is a risk of GVHD, which can be acute or chronic.
- The graft-versus-tumor (GVT) effect can be beneficial in fighting cancer.
As noted by a leading expert:
“The success of allogeneic transplants depends significantly on the degree of HLA matching between the donor and the recipient.”
Haploidentical and Cord Blood Transplants
Haploidentical transplants use stem cells from a family member who is only half-matched HLA-wise. Cord blood transplants use stem cells from the umbilical cord blood of newborns. Both offer options when a fully matched donor is not available.
| Transplant Type | Donor Source | HLA Matching Requirement |
| Autologous | Patient’s own cells | N/A |
| Allogeneic | Matched donor | High |
| Haploidentical | Half-matched family member | Partial |
| Cord Blood | Umbilical cord blood | Lower |
Knowing about the different bone marrow transplants is key to finding the right treatment. Each type has its own benefits and things to consider. The choice depends on the patient’s condition, age, and if a suitable donor is available.
How Does a Bone Marrow Transplant Work? The Complete Process
At Liv Hospital, we help our patients through every step of the bone marrow transplant process. This includes from the first check-up to aftercare. A bone marrow transplant replaces a patient’s bone marrow with healthy stem cells. It’s key for treating serious diseases like some cancers and blood disorders.
Initial Assessment and Compatibility Testing
The first step is a detailed check-up. Our team does many tests to see how healthy the patient is and their condition. These tests include blood work, imaging, and more to see if a transplant is right.
Then, we do tests to find a good match for the transplant. This could be the patient themselves or a donor. HLA typing is a big part of finding a match.
| Test Type | Purpose | Significance in BMT |
| Blood Tests | Evaluate overall health and condition status | Crucial for assessing patient’s suitability for BMT |
| HLA Typing | Determine compatibility between donor and recipient | Essential for reducing risk of graft-versus-host disease |
| Imaging Studies | Assess organ function and detect any abnormalities | Helps in planning conditioning regimen and assessing risks |
Stem Cell Collection Methods
After finding a good match, we collect stem cells. There are two main ways to do this: from blood or bone marrow.
- Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Collection: This is the most common method. It collects stem cells from the donor’s blood after using growth factors.
- Bone Marrow Harvest: This method surgically takes bone marrow from the donor’s hip bone under anesthesia.
Processing and Storage of Stem Cells
After collecting, we process and store the stem cells for later use. The processing separates the stem cells from other blood parts and freezes them. Keeping the stem cells in the right conditions is key until they’re given to the patient.
At Liv Hospital, we follow strict rules for processing and storing stem cells. Our modern facilities have the latest tech to keep stem cells safe and effective.
Patient Preparation for BMT
Preparing for a bone marrow transplant is essential for success. It involves several key steps to improve health and transplant chances.
Conditioning Regimens: Chemotherapy and Radiation
Patients get chemotherapy and radiation before the transplant. These treatments kill cancer cells and weaken the immune system. This makes it easier for the new bone marrow to take hold.
The treatment plan is made just for each patient. It’s tough, both in body and mind. But it’s a necessary step towards healing.
Central Venous Catheter Placement
Getting a central venous catheter (CVC) is also part of preparation. This catheter is used for stem cell infusion and other treatments.
The CVC is placed in a chest vein. It’s a minor surgery. Our team makes sure it’s done safely and with little pain.
Physical and Psychological Preparation
Medical treatments are just part of the story. Physical and psychological preparation are also key. This includes nutrition advice, physical therapy, and mental support.
We create a care plan for each patient. It’s tailored to their needs, making them as ready as possible for the transplant.
The Transplantation Procedure
On the day of the transplant, our team infuses stem cells into the patient’s bloodstream. This is a key step in their treatment. It comes after a lot of preparation and planning.
Is BMT Painful? What to Expect During Infusion
Many patients wonder if the bone marrow transplant hurts. The stem cell infusion itself is usually painless. But, some patients might feel discomfort from the treatment they had before.
Our team works hard to manage any pain or discomfort. We want the process to be as easy as possible for the patient.
During the infusion, we keep a close eye on the patient’s health. We watch for any bad reactions. The stem cells are given through a central venous catheter, which takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
The Day of Transplant: Step by Step
The transplant day is a big moment for the patient. Here’s what happens:
- The patient gets comfortable, and we access the central venous catheter.
- We thaw and prepare the stem cells for infusion.
- The infusion starts, and we watch the patient’s vital signs closely.
- After it’s done, we flush the catheter and keep an eye on the patient for a bit.
Our medical team is always there to help with any issues or worries.
Immediate Post-Transplant Monitoring
Right after the infusion, we watch for any quick reactions or problems. This includes looking out for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), infections, or other issues. We focus on keeping the patient comfortable and safe.
Watching the patient closely right after the transplant is very important. We use the latest tools and methods to check their health. This way, we can quickly adjust their care if needed.
Recovery and Aftercare for BMT Patients
Recovering from a bone marrow transplant is a long and complex journey. It requires careful aftercare to help patients get better. After the transplant, patients start the engraftment phase. This is when new stem cells start making blood cells.
Managing side effects and complications is key during this time. Long-term follow-up care is also vital. It helps monitor the patient’s health and address any problems quickly.
Engraftment: The Critical First Phase
Engraftment is the first and most important phase of recovery. It’s when the new stem cells start making blood cells. Monitoring engraftment closely is vital to see if the transplant is working and if the bone marrow is functioning right.
Managing Side Effects and Complications
Managing side effects and complications is a big part of BMT aftercare. Patients might face issues like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), infections, and organ damage. We focus on creating a care plan that meets each patient’s needs. This helps reduce risks and improve their quality of life during recovery.
For more information on managing complications after a transplant, patients can check out UCLA Health’s guide on recovery after bone marrow. It offers detailed insights into what to expect and how to navigate the recovery journey.
Long-term Follow-up Care
Long-term follow-up care is a key part of the BMT recovery process. It includes regular check-ups and monitoring to keep an eye on the patient’s health. We emphasize the importance of sticking to follow-up care schedules. This helps ensure the best outcomes and quality of life for patients.
BMT Care in Cancer Treatment: Advances and Outcomes
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) has changed how we treat cancer, giving hope to patients everywhere. At our institution, we focus on giving full and caring care to those getting BMT.
Success Rates for Different Conditions
The success of BMT depends on the cancer type. For example, some leukemia and lymphoma patients see big improvements in survival after BMT.
| Condition | Success Rate |
| Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) | 60-80% |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | 50-70% |
| Multiple Myeloma | 40-60% |
These numbers show how important BMT is for treating blood cancers. Our team helps decide the best treatment for each patient based on their condition and medical history.
Quality of Life After Bone Marrow Cure
Many patients find BMT not only cures their cancer but also improves their quality of life. We focus on post-transplant care to help patients easily get back to their daily lives.
Key factors influencing quality of life post-BMT include:
- Effective management of side effects
- Comprehensive follow-up care
- Emotional and psychological support
Multidisciplinary Approach to BMT Care
Our BMT care is a team effort, with experts like hematologists, oncologists, nurses, and support staff. This team approach covers all aspects of care, from the first visit to recovery after BMT.
We use the latest medical knowledge and tailor care to each patient. Our goal is to get the best results for our patients. Our dedication to BMT care is shown in our detailed treatment plans and ongoing support for patients.
Conclusion: The Future of Bone Marrow Transplantation
The field of bone marrow transplantation is changing fast. This is thanks to new research and better treatment options. At Liv Hospital, we aim to lead in BMT research and care, giving our patients the best treatment.
Scientists are always looking to make bone marrow transplants better. They’re finding new ways to help patients. Thanks to these advances, more people are living better lives after their transplants.
Looking ahead, we need to keep investing in BMT research. New treatments and better care will help more people. This will save more lives and improve the quality of life for those needing transplants.
We’re dedicated to top-notch healthcare and helping international patients. Our goal is to make a big difference in the lives of those needing bone marrow transplants.
FAQ
What is BMT in medical terms?
BMT stands for Bone Marrow Transplant. It’s a procedure that replaces damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
What is the role of bone marrow in the human body?
Bone marrow is key in making blood cells. It produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What are the different types of bone marrow transplants?
There are several types. These include autologous transplants (using the patient’s own stem cells), allogeneic transplants (using cells from a donor), haploidentical transplants, and cord blood transplants.
Is BMT painful?
The transplant procedure itself isn’t painful. Patients get medication to manage any discomfort during the stem cell infusion.
What is the process of a bone marrow transplant?
The process starts with assessment and compatibility testing. Then, stem cells are collected and processed. Next, conditioning regimens are done to prepare the body. This is followed by central venous catheter placement and the transplant itself.
What is conditioning regimen in BMT?
Conditioning regimens use chemotherapy and/or radiation. They prepare the body for the transplant by eradicating diseased cells and suppressing the immune system.
What is engraftment in BMT?
Engraftment is the first phase after a transplant. It’s when new stem cells start producing blood cells, beginning the recovery process.
What is the success rate of bone marrow transplants for different conditions?
Success rates vary. They depend on the condition, donor compatibility, and patient health. Our team will discuss specific success rates and outcomes for individual cases.
How is bone marrow collected from a close relative?
Bone marrow is collected from a donor through a surgical procedure. This is usually done under general anesthesia, where stem cells are extracted from the donor’s bone marrow.
What is the importance of central venous catheter placement in BMT?
Central venous catheter placement is key. It allows for administering medications, transfusions, and stem cells during the transplant. This reduces the need for multiple needle sticks.
What is the role of a multidisciplinary team in BMT care?
A multidisciplinary team, including hematologists, oncologists, nurses, and support staff, work together. They provide complete care to BMT patients, aiming for the best outcomes.
What is the future of bone marrow transplantation?
Ongoing research and advances in BMT are continually improving treatment options and patient outcomes. We remain committed to staying at the forefront of BMT research and treatment.
References:
- American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT). (2023). Practice Guidelines.https://www.astct.org/Education/Practice-Guidelines




































