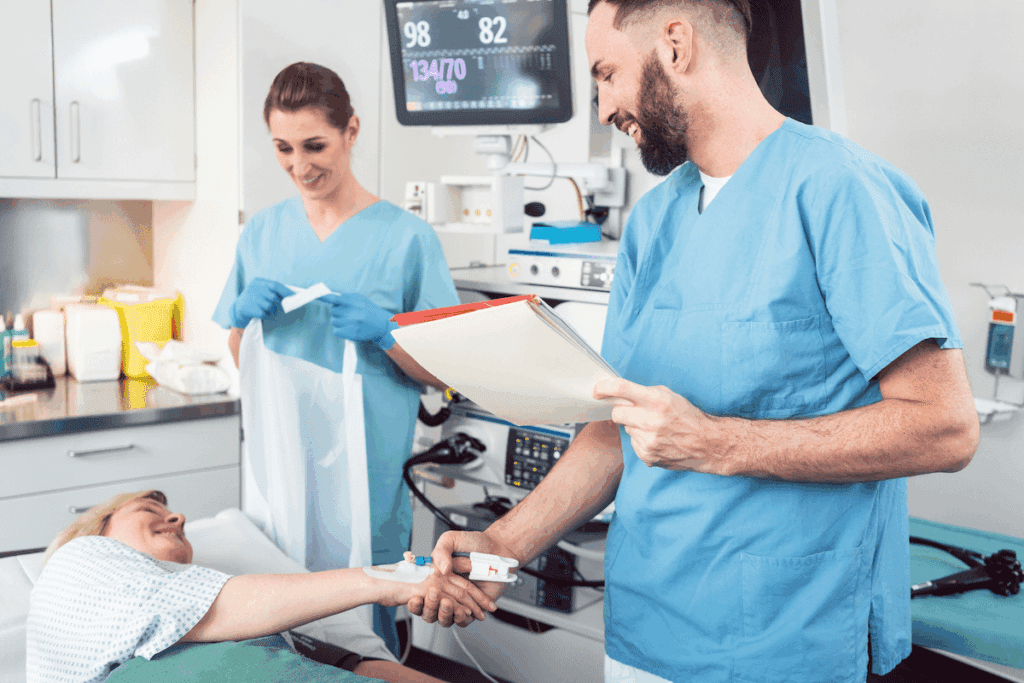
For those who need a colonoscopy, knowing what to expect can ease worries. At LivHospital, we focus on your comfort and safety. Our team of skilled gastroenterologists and advanced technology make sure you’re well cared for. Wondering “how is a colonoscopy performed?” This ultimate, step-by-step guide explains the prep, the procedure, and what to expect.
A colonoscopy checks the large intestine with a special tool called a colonoscope. This flexible tube has a camera and light, letting doctors see inside the colon and rectum. The whole process usually takes 15 to 30 minutes.
Key Takeaways
- Colonoscopy is a key tool for finding and stopping colorectal cancer early.
- The test uses a colonoscope to look inside the colon through the rectum.
- LivHospital uses the latest tech and expert gastroenterologists for these tests.
- The whole procedure usually lasts 15 to 30 minutes.
- Your comfort and safety are our main goals during the test.
What Is a Colonoscopy?
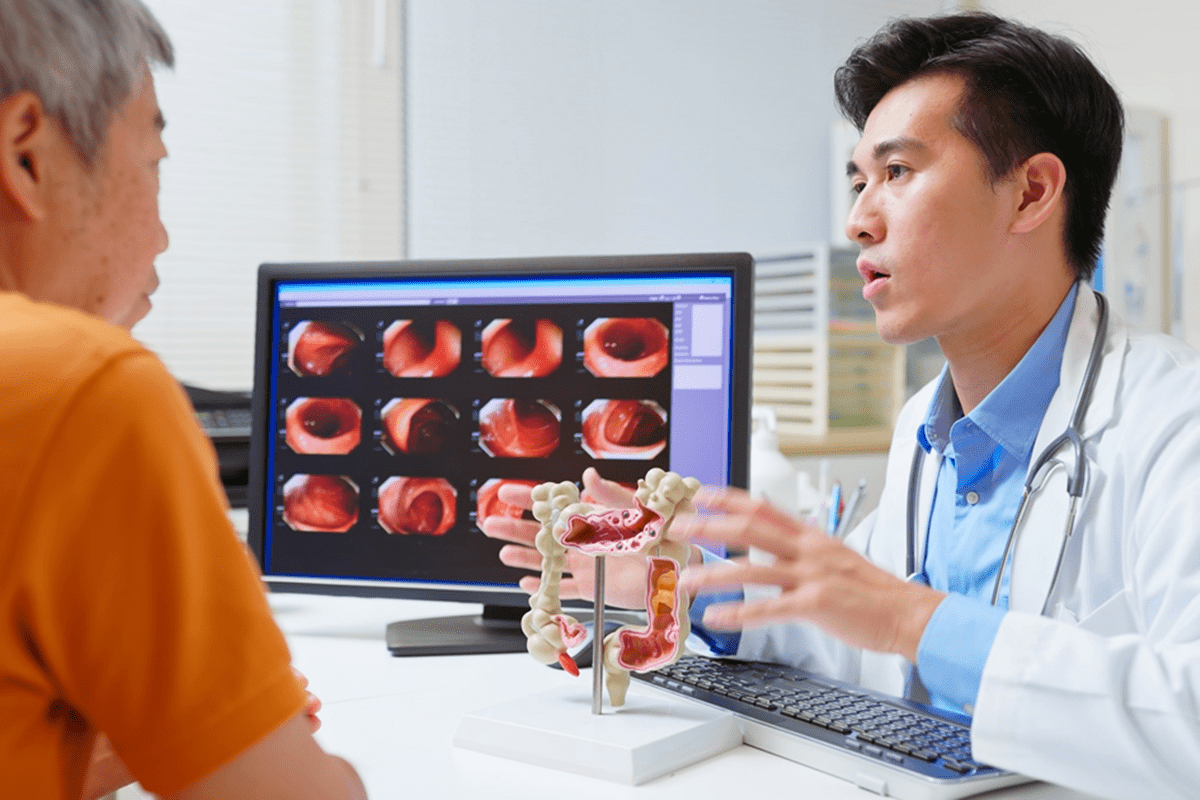
A colonoscopy is a key test for finding and stopping colorectal cancer early. It lets doctors see inside the colon and rectum for polyps, cancer, and other issues. Knowing about colonoscopies is important for those who need to get one.
Definition and Medical Purpose
A colonoscopy lets doctors see inside the colon with a special tube and camera. It helps find and sometimes treat problems like cancer and polyps. This test is used for many colon and rectum issues.
The camera on the colonoscope shows the colon’s lining clearly. This helps doctors spot problems that other tests can’t find.
When Is a Colonoscopy Recommended?
Colonoscopies are suggested for those with a family history of colorectal cancer. They’re also for people with symptoms like bleeding or changes in bowel habits. Adults over 45 are screened for early cancer detection.
The need for a colonoscopy depends on several things. This includes polyps or a history of cancer.
The following table summarizes the common indications for a colonoscopy:
Indication | Description |
Family History | Individuals with a first-degree relative diagnosed with colorectal cancer |
Symptoms | Rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, or abdominal pain |
Screening | Adults over 45 years old for early detection of colorectal cancer |
In summary, a colonoscopy is a vital tool for checking the colon and rectum. It’s needed for screening, symptoms, and family history. Understanding its purpose helps patients prepare and see its importance for health.
Preparing for Your Colonoscopy

Getting ready for a colonoscopy is key to a successful procedure. This includes changing your diet and cleaning your bowel. We know it might seem hard, but with the right help, you can make it through smoothly.
Dietary Restrictions Before the Procedure
Before your colonoscopy, you need to eat a special diet. This diet is called a clear liquid diet and lasts from one to three days. It includes:
- Clear broths
- Plain gelatin
- Water
- Clear juices (like apple or white grape)
- Black coffee or tea (without cream or sugar)
It’s also important to avoid certain foods. Stay away from:
- Red or purple liquids
- Dairy products
- Solid foods
“A clear liquid diet is essential for a successful colonoscopy. It helps ensure that the colon is free from any debris, allowing for a more accurate examination.”
A leading gastroenterologist
Bowel Preparation Process
Bowel prep is a big part of getting ready for your colonoscopy. You’ll take a laxative preparation to clean your bowel. Your doctor will pick the best one for you.
The prep starts the day before your colonoscopy. You’ll mix the solution with water and drink it as told. It’s important to follow the instructions well to clean your bowel right.
Bowel Prep Type | Description | Potential Side Effects |
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) | A non-absorbable solution that flushes out the colon | Bloating, nausea |
Magnesium Citrate | A saline laxative that helps cleanse the bowel | Electrolyte imbalance, abdominal cramps |
Sodium Phosphate | A saline laxative that induces bowel movements | Dehydration, electrolyte disturbances |
Drink lots of clear liquids during prep to stay hydrated. If you have bad side effects or worries, call your doctor.
The Day of Your Colonoscopy
Getting ready for your colonoscopy? Knowing what to expect can make you feel more at ease. Arrive 30 minutes early to get through the check-in smoothly.
What to Bring to Your Appointment
Here’s what you should bring to make your visit easy:
- Insurance cards and identification: Bring your insurance cards and a valid ID to confirm your details.
- A driver or companion: You’ll be sedated, so having someone to drive you home is key.
- Any relevant medical documents: Bring any medical records or lists of medications you have.
- Comfortable clothing: Wear loose, comfy clothes to relax during the procedure.
Pre-Procedure Check-In Process
Our friendly staff will welcome you and help with the check-in. They’ll verify your identity, review your medical history, and confirm your procedure details. They’ll also answer any questions you might have.
Meeting With Your Healthcare Team
You’ll meet your healthcare team before the procedure. This includes the doctor and the nursing staff. It’s a chance to:
- Discuss any last-minute concerns: Share any worries or questions you have about the procedure.
- Review the procedure details: Your healthcare team will explain what to expect and how you’ll be sedated.
- Sign consent forms: You’ll need to sign consent forms before the procedure starts.
Being prepared and knowing what to expect can make your colonoscopy day smoother. Our team is here to provide the best care and support every step of the way.
How Is a Colonoscopy Performed: The Procedure Explained
Learning about the colonoscopy process can ease anxiety for those about to have it done. We’ll cover the main steps, from how you’ll be positioned to the examination itself.
Patient Positioning: Which Side Do You Lay On
During a colonoscopy, you’ll usually lie on your left side. This makes it easier for the doctor to move the colonoscope through your colon. Medical Expert, a gastroenterologist, says, “The left lateral decubitus position is best because it makes it simpler to enter the rectum and move through the sigmoid colon.”
Sedation Administration and Monitoring
To keep you comfortable, sedation is given during the procedure. The kind and amount of sedation depends on your health and the doctor’s choice. Our team watches your vital signs closely and adjusts the sedation to keep you comfortable.
The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) says, “sedation is key during a colonoscopy. It helps reduce discomfort and anxiety for the patient.”
Duration and Stages of the Examination
The colonoscopy usually takes 30 to 60 minutes. It goes through several stages:
- Insertion of the colonoscope through the rectum
- Advancement of the colonoscope through the colon, checking the mucosa
- Looking for polyps, diverticula, or other issues in the colon
- Doing any needed treatments, like removing polyps or taking biopsies
- Removing the colonoscope and checking the colon again
Our team makes sure you’re comfortable and the exam is done well and quickly.
Tools and Equipment Used During a Colonoscopy
The success of a colonoscopy relies on the tools and equipment used. We use advanced medical devices for accurate diagnoses and treatments.
The Colonoscope: Structure and Function
The colonoscope is a flexible tube, about 1/3 inch thick and up to 6 feet long. It can reach the entire colon. It has a high-definition camera and light source for clear views inside the colon.
Its flexibility lets it bend and move through the colon’s twists and turns.
Camera and Visualization Technology
The camera at the colonoscope’s tip captures high-resolution images of the colon’s lining. These images are shown on a monitor for the team to examine. This tech helps spot issues like polyps, ulcers, or inflammation.
Advanced techniques, like narrow-band imaging, make some features easier to see.
Instruments for Biopsies and Polyp Removal
Various instruments can be used through the colonoscope for biopsies or polyp removal. These include biopsy forceps and snares. They are designed to be precise and safe, reducing risks.
Using these tools, we can diagnose and treat in one go. This makes colonoscopies accurate and safe, giving patients reliable diagnoses and treatments.
Anatomical Journey Through the Colon
Exploring the colon during a colonoscopy is a detailed process. We examine several key areas as we move the colonoscope. Each section of the colon has its own features and challenges.
The Ascending Colon Examination
The journey starts in the ascending colon, the first part of the large intestine. Careful examination is key here because it absorbs water and salts. We look closely for any issues.
Navigating the Transverse and Descending Colon
Next, we navigate the transverse colon, which has a bend. The transverse colon is vital for spotting polyps or other problems. Then, we examine the descending colon for signs of disease.
Examining the Sigmoid Colon and Rectum
The sigmoid colon, with its S-shaped curve, is another challenge. We inspect this area and the rectum for any issues, like polyps or cancer. The rectum is important because of its close location to the anus and the risk of bleeding.
Therapeutic Interventions During Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is more than just a test; it’s a chance to treat problems in the colon too. During a colonoscopy, doctors can do several things to help patients. These treatments can make a big difference in how well someone feels.
Polyp Removal Techniques
Removing polyps is a key part of colonoscopy. Polyps are growths that could turn into cancer. Doctors use different methods to take them out, like:
- Snare polypectomy: Using a wire loop to cut off the polyp.
- Hot biopsy forceps: Removing the polyp with electrical current.
- Cold snare polypectomy: Removing the polyp without electrical current.
Biopsy Collection Process
Another important part is taking biopsies. Doctors take tissue samples from areas that look suspicious. This helps figure out if there’s cancer. The samples are then checked in a lab.
Biopsy Type | Description | Clinical Use |
Forceps Biopsy | Tissue samples taken with forceps | Diagnosing lesions and abnormalities |
Needle Biopsy | Samples taken with a needle | Assessing submucosal lesions |
Other Therapeutic Applications
Colonoscopy can also treat other issues. For example:
- Stricture dilation: Widening narrowed sections of the colon.
- Bleeding control: Managing bleeding lesions within the colon.
- Foreign body removal: Retrieving objects that have been swallowed or are in the colon.
These treatments show how important colonoscopy is. It helps doctors both find and fix problems in the gut. This way, doctors can give patients better care and improve their lives.
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care
The recovery after a colonoscopy is very important. You need to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. This helps you recover safely and smoothly.
Immediate Recovery Room Experience
After your colonoscopy, you’ll go to the recovery room. Our team will watch over you as the sedation fades. This is a key time to see if you have any reactions to the procedure or sedation.
Monitoring in the recovery room typically includes:
- Checking vital signs such as blood pressure and heart rate
- Observing for any adverse reactions to the sedation
- Ensuring you are comfortable and managing any discomfort
You might feel a bit drowsy or confused because of the sedation. Our team will make sure you’re comfortable and let you know when it’s time to go home.
Going Home: Discharge Instructions
Before you leave, we’ll give you detailed instructions for home care. It’s best to have someone with you because you might not feel fully awake yet.
Discharge instructions typically cover:
Care Aspect | Instructions |
Rest and Activity | Rest at home for the remainder of the day. Avoid strenuous activities. |
Diet | Resume your normal diet unless instructed not to. Stay hydrated. |
Medication | Follow any medication instructions provided by your healthcare team. |
One of our patients said, “The clear instructions from the healthcare team really helped my recovery.”
“The care and clarity provided post-procedure were outstanding. I felt supported throughout the recovery.”
Potential Side Effects and When to Seek Help
Even though complications are rare, it’s good to know about possible side effects. Common ones are bloating, gas, or mild stomach cramps. These usually go away on their own.
But, you should get medical help right away if you have:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Heavy rectal bleeding
- Fever or chills
We’re dedicated to your care and safety during recovery. If you have any questions or concerns, please contact your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
A colonoscopy is key for catching colorectal cancer early and preventing it. It also helps diagnose and treat other colon and rectum issues. This summary shows how important it is for our gut health.
The guide we shared explains the whole process of a colonoscopy. It covers everything from getting ready to recovering afterwards. Each step is made to keep patients safe and comfortable.
During a colonoscopy, doctors can remove polyps and take biopsies. This makes it a powerful tool for both diagnosing and treating. Knowing how a colonoscopy works helps patients see its value in fighting gut diseases.
To wrap it up, a colonoscopy is vital in the battle against colorectal cancer and other gut problems. We hope this detailed look at the colonoscopy process has made its importance clear. It’s a big part of keeping us healthy.
FAQ
What is a colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a test to look inside the colon and rectum. A colonoscope is inserted through the rectum. It helps find and sometimes treat problems.
What is the purpose of a colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is used to find and treat issues in the colon and rectum. This includes finding cancer, polyps, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Which side do you lay on for a colonoscopy?
Patients usually lie on their left side. This makes it easier to use the colonoscope.
What is the colonoscope?
The colonoscope is a flexible tube with a camera and light. It lets doctors see inside the colon.
Is a colonoscopy a surgical procedure?
No, a colonoscopy is not surgery. It’s a minimally invasive test that can also treat some issues.
How long does a colonoscopy take?
A colonoscopy usually takes 15 to 30 minutes. More time might be needed if polyps are removed.
What kind of sedation is used during a colonoscopy?
Sedation is used to keep patients comfortable. The type and amount depend on the patient and doctor.
What are the possible side effects of a colonoscopy?
Side effects can include bloating and discomfort. Reactions to sedation are also possible. Patients are told how to handle these and when to get help.
Can polyps be removed during a colonoscopy?
Yes, polyps can be removed during a colonoscopy. Special tools like snares are used.
What is the bowel preparation process for a colonoscopy?
Before the procedure, patients follow a clear liquid diet for a day or two. They may also take laxatives to clean their bowel.
What happens during the recovery phase after a colonoscopy?
After the procedure, patients are watched for sedation reactions. They then get instructions on managing side effects and when to seek help.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559274/



































