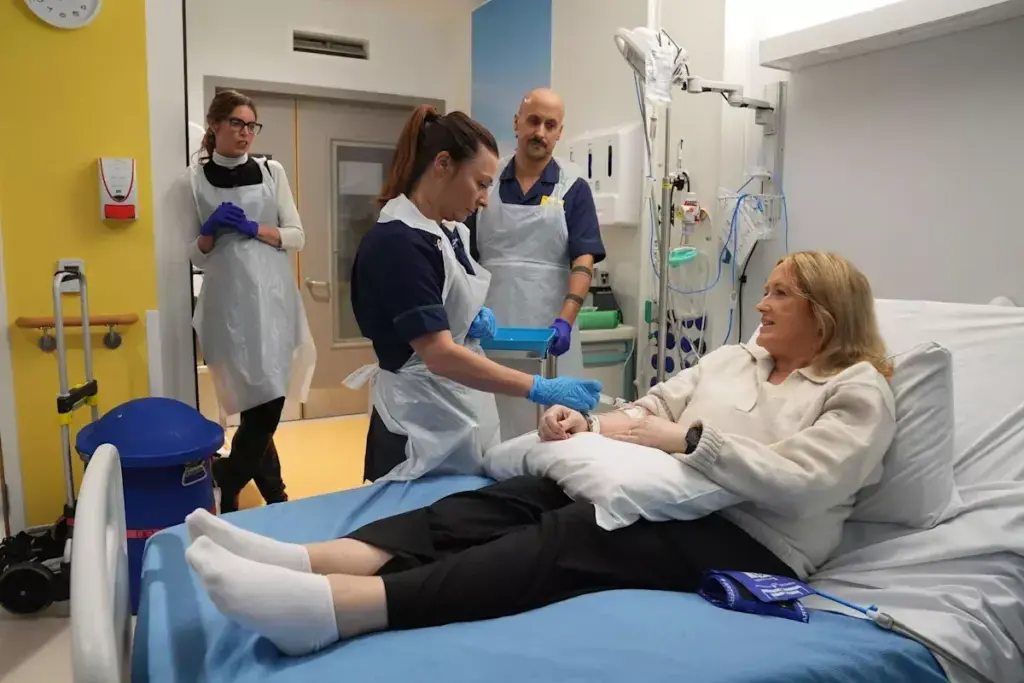
Dealing with blood disorders like anemia can be scary. Knowing how bone marrow removal works can help. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch care that meets international standards.
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are key for diagnosing blood issues. These tests take bone marrow from inside your bones.
We’ll look at the bone marrow removal process. We’ll cover why it’s done and the possible risks. Knowing about bone marrow aspiration and biopsy helps patients get ready for what’s ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are diagnostic procedures to collect and examine bone marrow.
- These procedures help diagnose and monitor various blood disorders and conditions.
- The process involves extracting the liquid portion (aspiration) and collecting a small core of the solid marrow (biopsy).
- Understanding the reasons and risks associated with bone marrow removal can help patients prepare.
- Liv Hospital provides complete care and advice during the bone marrow removal process.
Understanding Bone Marrow and Its Function
Bone marrow is vital for our body’s blood cell production and health. It’s the soft, fatty tissue inside our breastbone and pelvic bones. It plays a key role in our hematopoietic system.
What Is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow is a spongy tissue inside our bones. It’s a complex organ that helps us survive. It produces blood cells that flow through our body.
The marrow has blood vessels, nerves, and cells, including stem cells. These stem cells turn into blood cells.
The Role of Bone Marrow in Blood Production
Bone marrow’s main job is to make blood cells through hematopoiesis. It turns stem cells into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight off infections, and platelets help blood clot.
Without bone marrow, our bodies can’t make blood cells. This leads to health problems.
Types of Bone Marrow: Red vs. Yellow
There are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow. Red bone marrow makes blood cells and is found in bones like hips and spine.
Yellow bone marrow is mostly fat and doesn’t make blood cells. But it can turn into red marrow when needed.
In kids, red marrow is more common. In adults, yellow marrow takes over. Knowing about these types helps us understand bone marrow’s role in health.
Types of Bone Marrow Removal Procedures
Bone marrow removal procedures vary, showing the complexity of the conditions they diagnose. These procedures help us get samples to understand blood-related disorders.
Aspiration Explained
Bone marrow aspiration removes a liquid sample from the bone marrow. It’s done to check the marrow’s cells and find any problems.
Key aspects of bone marrow aspiration include:
- Use of a specialized needle to access the marrow
- Extraction of a liquid sample for laboratory analysis
- Often performed in conjunction with other procedures
Biopsy Process
A bone marrow biopsy takes a small bone tissue sample with the marrow inside. It gives a detailed look at the marrow’s structure and cells.
The biopsy process is key for:
- Checking the bone marrow’s health
- Finding conditions that affect the marrow’s structure
- Seeing if treatments are working
Combined Aspiration and Biopsy Procedures
Often, both aspiration and biopsy are done together. This way, we get a detailed look at the bone marrow, with both cell and structure information.
The benefits of combined procedures are:
- More detailed diagnostic info
- Less need for repeat tests
- Better accuracy in diagnosis and treatment plans
Knowing about the different bone marrow removal procedures helps patients prepare for their diagnostic journey.
Common Reasons for Bone Marrow Biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is often done to diagnose and monitor blood disorders. It gives doctors valuable info about the bone marrow’s health. This helps them find conditions that affect blood cell production.
Diagnosing Blood Disorders
Blood disorders affect blood cell production and function. A bone marrow biopsy is key for diagnosing these disorders. Doctors can see how blood cells are made and find any problems.
Common blood disorders diagnosed with bone marrow biopsy include:
- Anemia
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Aplastic anemia
Bone Marrow Test for Anemia Investigation
Anemia is when there’s not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. While blood tests can diagnose many cases, a bone marrow biopsy is needed for severe or ongoing anemia. It helps find the cause.
The bone marrow test can show:
- Inadequate red blood cell production
- Abnormal red blood cell development
- Bone marrow infiltration by cancer or other diseases
Confirming Leukemia and Lymphoma
Leukemia and lymphoma are cancers that affect the blood and lymphatic system. A bone marrow biopsy is used to confirm these diagnoses and see how far the disease has spread.
| Disease | Bone Marrow Biopsy Findings |
| Leukemia | Presence of leukemic cells, abnormal cell morphology |
| Lymphoma | Involvement of lymphoma cells in the bone marrow |
Evaluating Unexplained Cytopenias
Cytopenias are low counts of blood cells. This includes anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia. When the cause is unknown, a bone marrow biopsy can find problems like bone marrow failure or disease infiltration.
Doctors can learn about blood cell production and development. This helps diagnose conditions that other tests can’t show.
Preparing for a Bone Marrow Procedure
To get ready for a bone marrow procedure, patients must do some medical checks and lifestyle changes. This is key to reduce risks and make sure the procedure goes well.
Required Medical Evaluations
Before a bone marrow procedure, patients need some medical tests. These include:
- Blood tests to check clotting and health
- Imaging studies to see any special body parts
- A look at the patient’s medical history for risks
These tests help doctors understand the patient’s health. They make smart choices for the procedure.
Medication and Supplement Considerations
Patients often need to change their medicines and supplements before the procedure. Telling your doctor about all medicines and supplements is very important. Some might need to stop or change to avoid bleeding or other problems.
“Patients should talk to their doctor about their medicines before the procedure.”
Some medicines that might need to be changed include:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Antiplatelet drugs
- Certain herbal supplements
Physical Preparation and Logistics
Getting ready physically for a bone marrow procedure is important. Patients might be told to:
- Not eat for a while before the procedure
- Have someone drive them home because of sedation
- Wear comfy, loose clothes
Following your doctor’s advice on after-care is also key. This includes wound care and what activities to avoid.
By following these steps and listening to your doctor, patients can prepare well for their bone marrow procedure. This helps reduce risks and improves results.
How Is Bone Marrow Removed: The Aspiration Procedure
Learning about bone marrow aspiration can ease anxiety. We’ll guide you through the steps, from preparation to getting the bone marrow sample.
Step 1: Patient Positioning and Site Selection
The first step is to position the patient correctly. They usually lie on their stomach or side. The posterior superior iliac crest, a hip bone part, is often chosen. It’s safe and easy to access.
Step 2: Sterilization and Anesthesia Administration
The site is cleaned and sterilized first to prevent infection. Local anesthesia is given to numb the area. This makes sure the patient doesn’t feel pain when the needle is inserted.
“The use of local anesthesia has significantly reduced patient discomfort during bone marrow aspiration procedures.”
Dr. Jane Smith, Hematologist
Step 3: Needle Insertion Process
With the area numbed, a special needle is inserted. It goes through the skin and into the bone marrow. This step needs precision to avoid problems.
Step 4: Liquid Marrow Extraction Technique
After the needle is in, a syringe is attached. A small amount of bone marrow is taken out. This marrow is then analyzed in a lab. The whole process usually takes 10-15 minutes, but preparation and recovery can take longer.
Here’s a quick summary of the bone marrow aspiration steps:
| Step | Description |
| 1 | Patient positioning and site selection |
| 2 | Sterilization and anesthesia administration |
| 3 | Needle insertion into the bone marrow |
| 4 | Liquid marrow extraction |
Knowing these steps helps patients prepare for the procedure. It’s a quick and safe process when done by skilled healthcare professionals.
The Bone Marrow Biopsy Procedure Step-by-Step
A bone marrow biopsy is a key test that removes a small bone piece and its marrow. It’s vital for diagnosing blood disorders and cancers. This helps doctors understand what’s going on inside the body.
Step 1: Selecting the Biopsy Site (Usually Hip Bone)
The first step is picking the right spot for the biopsy. Most often, the hip bone (pelvis) is chosen because it’s easy to reach and has lots of marrow. The patient lies on their stomach or side to make it easier to get to the hip bone.
Step 2: Local Anesthesia Application
To make the procedure painless, local anesthesia is given at the site. This numbs the area, so the patient won’t feel pain. The anesthesia is injected with a fine needle into the skin and deeper tissues.
“The use of local anesthesia has significantly improved patient comfort during bone marrow biopsy procedures.”
Source: Medical Journal
Step 3: Making the Incision
Once the area is numb, a small incision is made in the skin. This incision is about 1-2 mm long. It’s big enough for the biopsy needle to go through.
Step 4: Core Sample Extraction with Specialized Needle
The biopsy needle is then inserted through the incision into the bone. A specialized needle is used to get a core sample of bone marrow. This sample is then examined to help diagnose diseases.
| Step | Description |
| 1 | Selecting the biopsy site, usually the hip bone |
| 2 | Administering local anesthesia to numb the area |
| 3 | Making a small incision at the biopsy site |
| 4 | Extracting a core sample using a specialized needle |
The bone marrow biopsy is a precise and quick process. It gives doctors important information. Knowing the steps helps patients prepare and understand what to expect.
What to Expect During Recovery
Knowing what happens after a bone marrow procedure can ease worries. It helps make the healing process smoother. We’ll guide you through what to expect, so you can manage your recovery well.
Immediate Post-Procedure Monitoring
Right after the procedure, patients are watched closely for any issues. This happens in the clinic or hospital where the procedure took place.
Medical staff will keep an eye on your vital signs and look for any bad reactions. This close watch is key to keeping you safe and solving any problems quickly.
Pain Management Strategies
Handling pain is a big part of getting better. Stick to the pain plan your doctor gives you. This might include pain relievers you can buy or prescription drugs.
It’s important to take the right amount of medicine and tell your doctor if the pain is bad or lasts too long. Also, using ice on the sore area can help with pain and swelling.
Activity Restrictions and Wound Care
It’s important to follow the activity limits your doctor sets. This means avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or hard work for a while.
Good wound care is also key to avoid infection and help it heal. Make sure the dressing stays clean and dry. Follow your healthcare team’s advice on changing the dressing and checking the wound.
Normal vs. Abnormal Recovery Symptoms
Knowing the difference between normal and abnormal symptoms is important. After a bone marrow procedure, you might feel some tenderness, bruising, or swelling at the site.
But, if you have severe pain, a lot of bleeding, signs of infection (like fever, redness, or swelling), or any other worries, tell your doctor right away. Knowing about these issues helps get the right help fast.
Being informed and ready can make you feel more confident during recovery. If you have questions or concerns, always ask your healthcare provider for help and advice.
Bone Marrow Biopsy Risks and Complications
Bone marrow biopsy is usually safe, but it’s important to know the possible risks and complications. Knowing these helps patients get ready and deal with any problems that might come up.
Common Side Effects from Bone Marrow Biopsy
Most people feel some discomfort during or after the test. You might feel pain, bruising, or swelling at the site. These symptoms are usually mild and go away in a few days.
Potential Bleeding Complications
Bleeding is a serious risk with bone marrow biopsy. It can be from just a little oozing to a lot of bleeding. People with bleeding problems or on blood thinners are at higher risk.
Infection Risks and Prevention
There’s a chance of infection with bone marrow biopsy, but it’s rare. Using clean tools and taking care of the wound helps prevent it. Watch the biopsy site for signs of infection like redness or fever. Tell your doctor if you notice anything.
Rare but Serious Bone Marrow Extraction Risks
Even though it’s rare, serious problems can happen. These include big bleeding, infection spreading, or damage to nearby areas. In very rare cases, the needle might break a bone or hurt nerves or blood vessels. Talk to your doctor about these risks to understand your specific situation.
Bone Marrow Analysis for Anemia and Other Conditions
Bone marrow analysis is key for diagnosing blood disorders like anemia. When a sample is taken, it’s sent to a lab for detailed analysis. This helps find out if the bone marrow makes enough healthy blood cells and spots any odd cells.
The process of analyzing bone marrow includes several steps. These steps are important for both patients and doctors to make informed decisions. Understanding these steps helps everyone involved.
Laboratory Processing of Samples
When the bone marrow sample reaches the lab, it goes through several steps. The sample is stained with special dyes to help see different cell types under a microscope.
The lab processing includes:
- Fixation to keep the sample intact
- Dehydration to remove water
- Embedding in a medium for thin sectioning
- Sectioning into thin slices for microscopic examination
Specific Tests in Bone Marrow Analysis
Several tests are done on the bone marrow sample. Cytogenetic testing checks the chromosomes of cells for genetic issues.
Some tests in bone marrow analysis include:
- Morphological examination to check cell structure
- Flow cytometry to count different cell types
- Molecular testing to find specific genetic mutations
Timeline for Results Availability
The time to get bone marrow analysis results varies. Simple tests might take a few days, while complex ones take longer.
It’s important for patients to talk to their doctor about when they’ll get their results. This way, they know what to expect next.
Understanding Your Bone Marrow Pathology Report
A bone marrow pathology report gives detailed info about the analysis. The report will include details on cellularity, abnormal cells, and test results.
Patients should go over their report with their doctor. This helps understand the findings and how they affect treatment.
Conclusion
Bone marrow removal is key in diagnosing and treating blood-related issues. Through bone marrow harvesting, doctors collect stem cells. This helps treat diseases like leukemia and lymphoma.
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are important for diagnosis. They help doctors check the bone marrow’s health. This leads to accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Understanding bone marrow removal is essential. It plays a big role in managing blood disorders. Its importance in modern medicine is clear.
FAQ
What is bone marrow, and what is its function?
Bone marrow is key to our body’s blood-making system. It creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Why is a bone marrow biopsy performed?
Doctors use a bone marrow biopsy to check for blood-related issues. This includes anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma. It also helps with unexplained low blood counts.
What is the difference between bone marrow aspiration and biopsy?
Bone marrow aspiration takes out liquid marrow. A biopsy takes out solid tissue. Both are used together for a full diagnosis.
How is bone marrow removed during an aspiration procedure?
A needle is inserted into the bone marrow. Then, a syringe pulls out the liquid marrow.
What are the common side effects of a bone marrow biopsy?
Side effects include pain, bruising, and bleeding at the site. You might also feel tired and uncomfortable.
How can I prepare for a bone marrow procedure?
First, get any needed medical checks. Tell your doctor about your medications. Follow their instructions for getting ready physically and logistically.
What are the possible risks and complications of bone marrow biopsy?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and nerve damage, but they’re rare. Common side effects are usually mild and short-lived.
How long does it take to get the results of a bone marrow analysis?
Results time varies based on the tests and lab work. Your doctor will tell you when to expect them.
What is involved in the laboratory processing of bone marrow samples?
Samples are examined under a microscope and tested. The results help diagnose and monitor blood conditions.
How can I manage pain and discomfort after a bone marrow procedure?
Use medication, rest, and ice to manage pain. Your doctor will guide you on how to handle discomfort.
What are the signs of abnormal recovery symptoms after a bone marrow procedure?
Look out for severe pain, too much bleeding, or signs of infection. These include redness, swelling, or fever. Seek medical help if you notice these.
References:
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2024). Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/bone-marrow-aspiration-biopsy