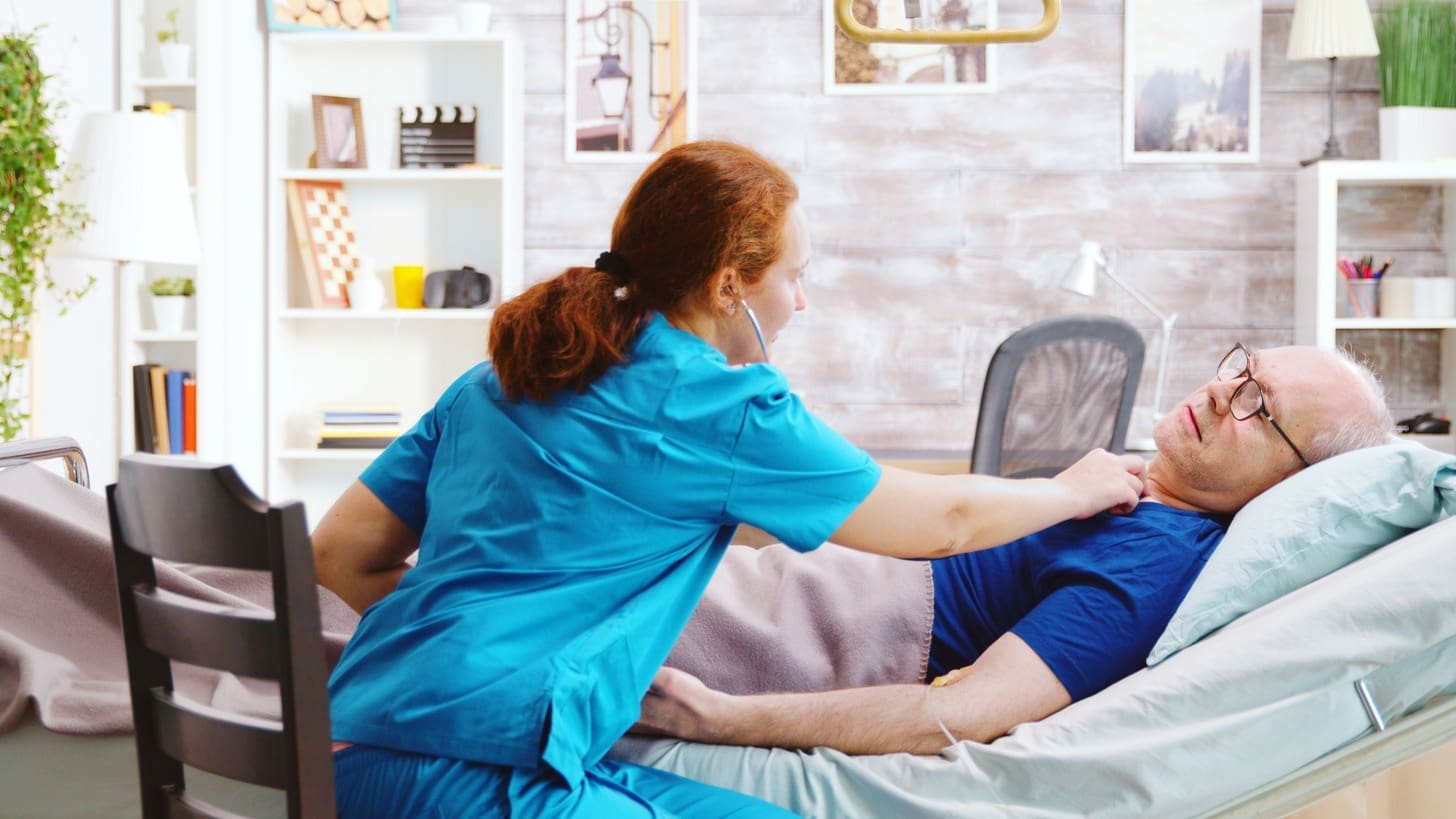
Dealing with a brain blood clot is urgent. At Liv Hospital, we use mechanical thrombectomy to quickly remove clots. This helps restore blood flow to the brain.
The American Stroke Association says stroke is the No. 5 cause of death in the U.S. It’s also the leading cause of disability. Our surgeons use stent retrievers or direct aspiration to remove clots. This greatly improves patient outcomes after an ischemic stroke.
Removing a blood clot from the brain is complex and delicate. Our team is dedicated to top-notch care. We aim for the best outcomes for our patients.
Key Takeaways
- Mechanical thrombectomy is a highly effective procedure for removing blood clots from the brain.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced techniques to restore blood flow and improve patient outcomes.
- Our skilled surgeons employ modern methods like stent retrievers and direct aspiration.
- Prompt treatment is key in addressing ischemic stroke and reducing disability.
- At Liv Hospital, we are committed to providing world-class healthcare with full support.
Understanding Brain Blood Clots and Their Impact
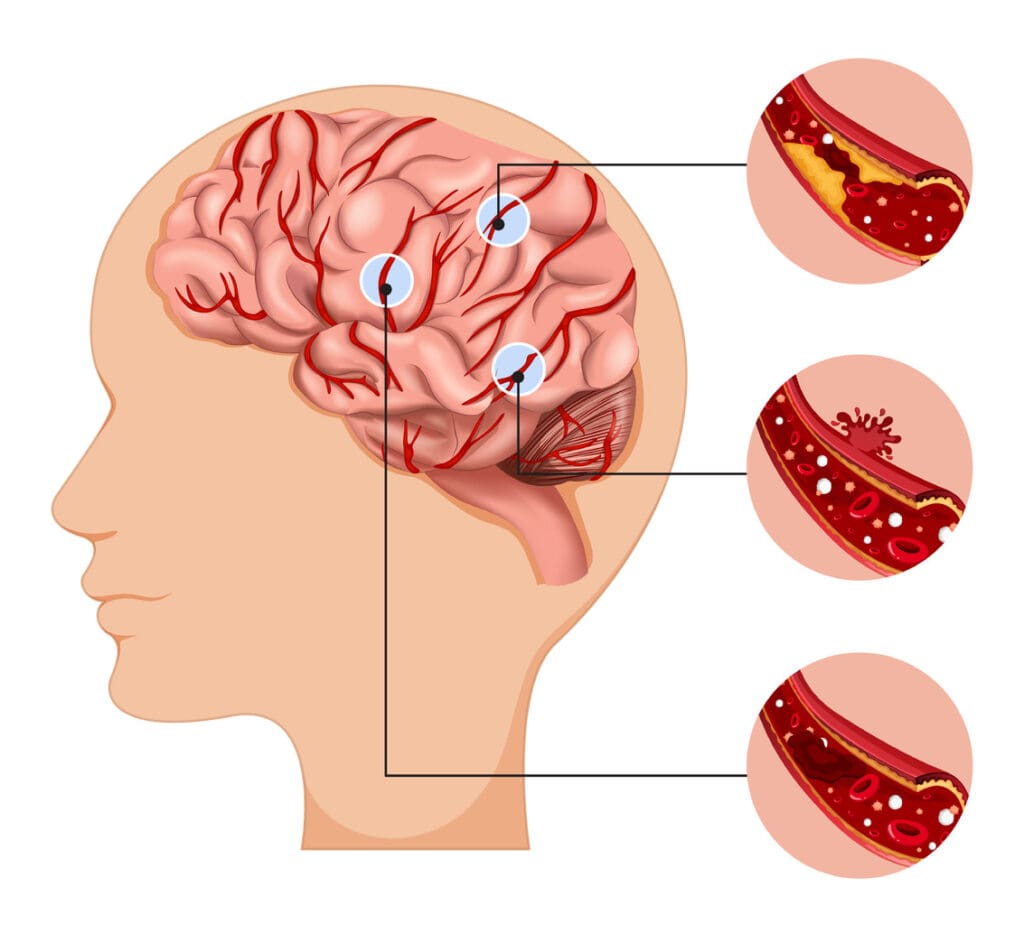
It’s important to understand brain blood clots to help patients. These clots, or cerebral thrombosis, block blood and oxygen to the brain. This can harm vital areas.
Types of Brain Blood Clots
Brain blood clots are divided into two main types. They differ by where they form and what they’re made of.
- Thrombotic Clots: These form right in the brain’s blood vessels.
- Embolic Clots: These start elsewhere and travel to the brain, causing a blockage.
Causes and Risk Factors
Many things can lead to brain blood clots. These include:
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can damage blood vessel walls, making them more likely to clot.
- High Cholesterol: Too much bad cholesterol can cause plaque in arteries, raising clotting risk.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can harm blood vessels and affect how blood clots.
- Atrial Fibrillation: An irregular heartbeat can cause clots in the heart, which can travel to the brain.
Other risk factors include being overweight, smoking, and having a family history of strokes or blood clots.
Signs and Symptoms of Brain Blood Clots
The symptoms of brain blood clots vary. They depend on where and how severe the clot is. Common signs include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden vision changes
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Severe headache
It’s key to spot these symptoms early for quick medical help.
Diagnosing Blood Clots in the Brain
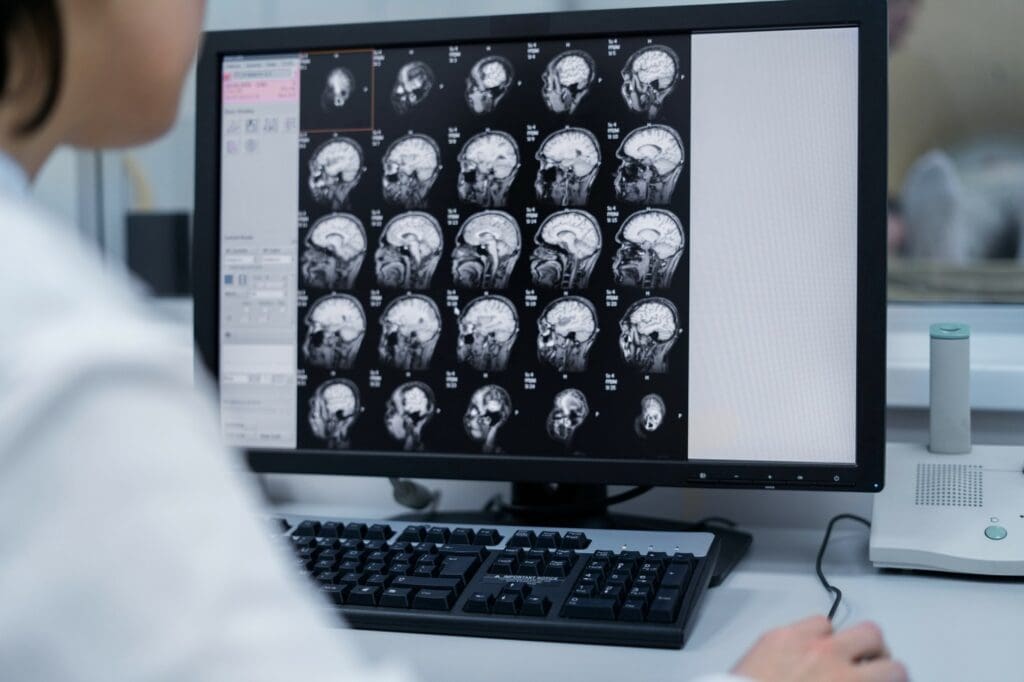
Diagnosing blood clots in the brain is a detailed process. It includes an initial check, a neurological exam, and advanced imaging. We know that quick diagnosis is key to treating brain blood clots well.
Initial Assessment and Neurological Examination
When a patient arrives at the hospital, they get checked right away. We look at their medical history and symptoms. We also do a neurological exam to see how bad the condition is.
We check for signs like weakness, numbness, or trouble speaking. We also look at vision and coordination. This helps us understand the damage and where the clot is.
The neurological exam is very important. It helps us see how much damage there is. It also helps us decide the best treatment.
Imaging Techniques for Blood Clot Detection
Imaging is key in finding blood clots in the brain. We use CT (Computed Tomography) scans and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) to see the brain. These help us find the clot.
| Imaging Technique | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| CT Scan | Uses X-rays to create detailed images of the brain | Quick, widely available, sensitive to acute hemorrhage |
| MRI | Uses magnetic fields to create detailed images of brain tissue | High sensitivity for detecting ischemia, detailed soft tissue imaging |
These methods not only confirm the clot but also show how much damage there is. This info is key for treatment decisions.
Time-Critical Nature of Diagnosis
Diagnosing blood clots in the brain quickly is very important. Waiting too long can cause serious damage or even death. Quick treatment can help reduce damage in many cases.
Our team works fast to diagnose and treat. The sooner we act, the better the patient’s chances of recovery.
The Critical Time Window for Effective Treatment
The time to treat brain blood clots is short. Quick action is key. When a stroke hits, the brain misses out on oxygen and nutrients, causing cells to die fast. The sooner treatment starts, the less damage there is, and the better the patient’s chances.
Understanding the “Golden Hour”
The “Golden Hour” is a big deal in emergency care, mainly for strokes. It’s the first hour after a stroke when fast treatment can really help. Thrombolytic therapy given in this time can almost double the chance of getting better. It’s vital to spot stroke signs fast and get medical help right away to use this critical time well.
Recent studies show how urgent it is to act fast. For example, a study found that those who got thrombectomy quickly after a stroke did much better than those who waited.
Extended Treatment Windows for Select Patients
While the “Golden Hour” is key, not everyone can get treated in time. New tech and treatment methods have opened up extended treatment windows for some patients. New imaging tools can spot who might benefit from treatment even after the first hour, sometimes up to 24 hours later.
- Advanced imaging techniques help identify eligible patients.
- Some patients may benefit from treatment up to 24 hours after stroke onset.
- Individual assessment is key to find the best treatment.
Impact of Treatment Timing on Recovery Outcomes
How fast treatment is given really matters for recovery. Waiting too long can lead to big problems or even death. But, acting quickly can mean better results and a better life. We’ve seen patients get back to their lives with little lasting effect thanks to fast treatment.
“Time is brain” is a saying in stroke treatment. It shows how urgent it is to act fast to save brain function and improve outcomes.
In short, the time to treat brain blood clots is complex. It involves knowing the “Golden Hour,” finding who can get extended treatment, and seeing how fast treatment affects recovery. Quick action and smart decisions can make a big difference in saving lives and improving outcomes.
Mechanical Thrombectomy: The Gold Standard for Removing Blood Clot from Brain
Mechanical thrombectomy is the top choice for treating acute ischemic strokes. It’s a minimally invasive way to remove blood clots from the brain. This method has greatly improved how we treat strokes, leading to better results for patients.
How Mechanical Thrombectomy Works
This procedure starts with a catheter inserted through an artery in the groin. It’s then guided to the brain’s blockage. Our skilled surgeons use advanced methods to clear the clot and get blood flowing again. It’s a key treatment for acute ischemic strokes.
The first step is to reach the blocked artery with a catheter. Once the clot is found, the surgeon uses stent retriever technology and direct aspiration techniques to remove it.
Stent Retriever Technology
Stent retriever technology uses a stent-like device to catch the clot. This allows for safe removal. It’s proven to be very effective in getting blood flowing again and improving patient results.
- High success rates in recanalization
- Minimally invasive with reduced risk of complications
- Effective in treating complex clots
Direct Aspiration Techniques
Direct aspiration techniques use a catheter to suck out the clot. It’s great for certain types of clots and can be used with other methods.
- A catheter is guided to the clot location
- A suction force is applied to remove the clot
- Blood flow is restored, improving patient outcomes
By using these advanced methods, we can effectively clear blood clots from the brain. This greatly improves patient outcomes after an ischemic stroke. Mechanical thrombectomy keeps getting better, giving new hope to those with this condition.
Step-by-Step Process of Brain Blood Clot Surgery
Our medical team takes a careful step-by-step approach to remove brain blood clots. This ensures the best results for our patients.
Anesthesia and Patient Preparation
The first step is getting the patient ready for surgery. We use anesthesia to keep them comfortable and safe. Our team watches the patient’s vital signs and brain activity closely during this time.
Catheter Insertion and Navigation
Next, we insert a catheter through an artery in the groin. We then guide it to the brain blockage. Advanced imaging helps us place it accurately. Our skilled doctors use the latest imaging to guide the catheter through the blood vessels.
Clot Engagement and Removal
When we reach the clot, we use special techniques to remove it. These can include stent retrievers or direct aspiration, based on the clot’s type and location. Our goal is to quickly and safely get blood flowing again.
Post-Procedure Imaging
After removing the clot, we do imaging to check if it’s gone and blood flow is restored. This step is key to seeing if the surgery worked and planning further care.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Anesthesia and Patient Preparation | Administering anesthesia and preparing the patient for surgery | Monitoring vital signs and neurological status |
| Catheter Insertion and Navigation | Inserting a catheter and navigating it to the clot | Precise imaging guidance for accurate placement |
| Clot Engagement and Removal | Using advanced techniques to remove the clot | Choosing between stent retriever and direct aspiration techniques |
| Post-Procedure Imaging | Confirming clot removal and assessing blood flow restoration | Evaluating procedure success and planning next stages of care |
The Multidisciplinary Team Behind Brain Clot Removal
Removing brain clots requires a team of experts. A group of specialists from different fields is key for good care. They work together to help patients with this complex procedure.
Roles of Interventional Neuroradiologists
Interventional neuroradiologists are vital in removing brain clots. They use a procedure called mechanical thrombectomy. This involves safely taking out the clot from the brain.
Key Responsibilities:
- Performing mechanical thrombectomy procedures
- Navigating complex brain vasculature
- Collaborating with other specialists to ensure complete care
Neurosurgeons and Neurologists
Neurosurgeons and neurologists are also important. Neurosurgeons handle surgeries, while neurologists manage brain conditions. They work with neuroradiologists to create treatment plans that fit each patient.
| Specialist | Role | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Interventional Neuroradiologists | Perform mechanical thrombectomy | Clot removal, vascular navigation |
| Neurosurgeons | Provide surgical expertise | Surgical interventions, patient care |
| Neurologists | Diagnose and manage neurological conditions | Diagnosis, treatment planning, patient management |
Specialized Nursing and Support Staff
Our nursing and support staff are essential. They give critical care to patients before, during, and after the procedure. This ensures the best care for our patients.
Our team works together to offer care that meets each patient’s needs. This approach helps patients get the best results from brain clot removal.
Alternative Surgical Approaches for Brain Clot Removal
Removing brain clots often needs a custom plan. There are many surgical options. The right method depends on the clot’s location, size, and the patient’s health.
Craniotomy for Hemorrhagic Stroke
A craniotomy is a surgery that removes part of the skull. It’s used for hemorrhagic strokes with a lot of bleeding. This helps relieve pressure on the brain.
Key aspects of craniotomy include:
- Relieving pressure on the brain by removing part of the skull
- Evacuating the hematoma to prevent further brain damage
- Repairing any damaged blood vessels
Endovascular Coiling
Endovascular coiling is a less invasive way to treat aneurysms or vascular malformations. It uses a catheter to reach the affected area through blood vessels.
The process of endovascular coiling includes:
- Inserting a catheter through a major artery
- Navigating the catheter to the aneurysm or malformation
- Deploying coils to fill the aneurysm and prevent further bleeding
Surgical Clipping
Surgical clipping is a method to treat aneurysms or vascular abnormalities. It involves surgery to directly access the aneurysm. A clip is then applied to stop bleeding.
Advantages of surgical clipping include:
- Immediate exclusion of the aneurysm from circulation
- Potential for complete obliteration of the aneurysm
- Direct visualization of the aneurysm and surrounding structures
In conclusion, there are many surgical options for brain clot removal. Each method is tailored to the patient’s needs. Knowing these options is key to giving the best care for brain clot patients.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Brain Blood Clots
Medical technology has grown, giving us more non-surgical ways to treat brain blood clots. We find that some patients do well with non-surgical treatments. This is a good option for those who might not need surgery.
Thrombolytic Therapy (tPA)
Thrombolytic therapy, like tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), breaks down blood clots. It helps blood flow back to the brain. This treatment works best when given quickly after symptoms start. We check each patient to see if tPA is right for them.
Anticoagulation Medications
Anticoagulation medications stop new clots from forming. They help prevent more strokes or problems. It’s important to watch patients on these medications closely to avoid bleeding.
When Non-Surgical Approaches Are Preferred
We look at each patient’s situation to decide on non-surgical treatments. We consider the clot’s location, size, and the patient’s health. Non-surgical treatments are often best for those at high risk for surgery or with hard-to-reach clots.
By using the right non-surgical treatments, we help patients with brain blood clots. This improves their recovery chances and lowers the risk of complications.
Recovery and Outcomes After Brain Clot Removal
Recovering from brain clot removal surgery is a detailed process. It includes immediate care after surgery and a thorough rehabilitation program. This helps patients regain their strength and abilities.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Patients are watched closely in the ICU after surgery. We focus on monitoring them to ensure a smooth recovery. This care is key to quickly address any issues.
“The care right after surgery greatly affects how well a patient recovers,” says a top neurosurgeon. “Our team works hard to provide the best care during this critical time.”
Rehabilitation Process
The rehab process is made for each patient’s needs. It involves a team of experts like physical, occupational, and speech therapists. Our programs aim to help patients regain lost abilities and adjust to any lasting changes.
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and strength
- Occupational therapy to assist with daily activities
- Speech therapy to address communication challenges
Success Rates and Outcome Statistics
We track success rates and outcomes to improve our care. Research shows timely treatment greatly improves patient results. Our data shows a strong link between quick treatment and better recovery rates.
| Treatment Timing | Recovery Rate |
|---|---|
| Within 6 hours | 80% |
| Within 12 hours | 60% |
Factors Affecting Recovery Prognosis
Several things can affect how well a patient recovers. These include the clot’s severity, how quickly treatment starts, and the patient’s health. Knowing these factors helps us tailor our care to each patient’s needs.
“The key to successful recovery is timely treatment, skilled care, and thorough rehab,” says a neurologist. “By meeting each patient’s unique needs, we can improve their chances for a good outcome.”
By focusing on these key recovery aspects, we can greatly improve patient outcomes and quality of life after brain clot removal.
Potential Risks and Complications of Blood Clot Brain Surgery
Surgery for brain blood clots carries risks. It’s important for patients and doctors to know these risks. Removing a blood clot from the brain can greatly improve a patient’s health if done right. But, like any surgery, it has risks and complications that need careful management.
Procedure-Related Complications
Complications can happen during or right after surgery. These might include:
- Bleeding or hemorrhage at the surgical site
- Infection, as with any invasive procedure
- Damage to surrounding brain tissue
- Reaction to anesthesia
We do everything we can to avoid these risks. This includes choosing patients carefully, using precise techniques, and providing detailed care after surgery.
Long-Term Risks
After surgery, there are risks like cognitive or motor problems. These risks depend on the clot’s size and location, and the patient’s health.
| Long-Term Risk | Description | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Impairment | Difficulty with memory, concentration, or decision-making | Cognitive rehabilitation therapy |
| Motor Impairment | Weakness or paralysis in parts of the body | Physical therapy and rehabilitation |
Monitoring and Managing Complications
We watch our patients closely for any signs of problems. This is during their hospital stay and after they go home. Managing these issues involves a team of doctors, including neurologists and neurosurgeons.
Key to managing complications: Finding problems early, planning care fully, and teaching patients.
Knowing the risks of blood clot brain surgery helps us prepare patients better. Our goal is to give top-notch care, not just during surgery but also during recovery. This includes support every step of the way.
Conclusion: Advances and Future Directions in Brain Blood Clot Treatment
Medical innovation is pushing us forward, changing how we treat brain blood clots. New research and technology are making treatments better. This means we can help more people affected by these clots.
We’re always looking to improve, using the newest research and tech. The future of treating brain blood clots looks bright. We’re talking about new, less invasive methods and treatments tailored to each person.
We’re combining the latest tech with our skills and care to help our patients. We’re excited for what’s next in treating brain blood clots. It’s all thanks to the progress in medical science and our growing understanding of this condition.
FAQ
What is a brain blood clot and how is it formed?
A brain blood clot is a clump of blood in the brain. It can happen due to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or obesity. Diabetes, atrial fibrillation, or past strokes also raise the risk.
What are the signs and symptoms of a brain blood clot?
The symptoms of a brain blood clot vary. They can include sudden weakness, numbness, or paralysis. This depends on where and how big the clot is.
How is a brain blood clot diagnosed?
To diagnose a brain blood clot, a quick and accurate check is needed. This includes a detailed neurological exam and scans like CT or MRI.
What is mechanical thrombectomy and how does it work?
Mechanical thrombectomy is a procedure to remove brain clots. It uses a catheter to reach the clot. Then, it uses stent retriever technology or direct aspiration to clear it out.
What is the “golden hour” in treating a brain blood clot?
The “golden hour” is the first hour after a stroke. Quick treatment during this time can greatly improve outcomes.
What are the alternative surgical approaches for brain clot removal?
Other surgical options include craniotomy, endovascular coiling, and surgical clipping. These might be needed for some patients.
What are the non-surgical treatments for brain blood clots?
Non-surgical treatments include thrombolytic therapy, like tPA, and anticoagulation medications. These might be better for some patients.
What is the recovery process like after brain clot removal?
Recovery starts with immediate care after surgery. Then, a detailed rehabilitation program helps patients regain strength and abilities.
What are the possible risks and complications of blood clot brain surgery?
Risks include bleeding or infection during the procedure. Long-term risks include cognitive or motor impairments.
How is the success of brain clot removal measured?
Success rates are tracked to improve care. Factors affecting recovery include the clot’s severity, treatment timing, and the patient’s health.
What is the role of interventional neuroradiologists in brain clot removal?
Interventional neuroradiologists are key in performing mechanical thrombectomy.
How do neurosurgeons and neurologists contribute to brain clot removal?
Neurosurgeons and neurologists are vital in providing care and support during treatment.
What is the importance of timely treatment for brain blood clots?
Quick treatment is critical to reduce brain damage and improve outcomes.
FAQ
What is a brain blood clot and how is it formed?
A brain blood clot is a clump of blood in the brain. It can happen due to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or obesity. Diabetes, atrial fibrillation, or past strokes also raise the risk.
What are the signs and symptoms of a brain blood clot?
The symptoms of a brain blood clot vary. They can include sudden weakness, numbness, or paralysis. This depends on where and how big the clot is.
How is a brain blood clot diagnosed?
To diagnose a brain blood clot, a quick and accurate check is needed. This includes a detailed neurological exam and scans like CT or MRI.
What is mechanical thrombectomy and how does it work?
Mechanical thrombectomy is a procedure to remove brain clots. It uses a catheter to reach the clot. Then, it uses stent retriever technology or direct aspiration to clear it out.
What is the “golden hour” in treating a brain blood clot?
The “golden hour” is the first hour after a stroke. Quick treatment during this time can greatly improve outcomes.
What are the alternative surgical approaches for brain clot removal?
Other surgical options include craniotomy, endovascular coiling, and surgical clipping. These might be needed for some patients.
What are the non-surgical treatments for brain blood clots?
Non-surgical treatments include thrombolytic therapy, like tPA, and anticoagulation medications. These might be better for some patients.
What is the recovery process like after brain clot removal?
Recovery starts with immediate care after surgery. Then, a detailed rehabilitation program helps patients regain strength and abilities.
What are the possible risks and complications of blood clot brain surgery?
Risks include bleeding or infection during the procedure. Long-term risks include cognitive or motor impairments.
How is the success of brain clot removal measured?
Success rates are tracked to improve care. Factors affecting recovery include the clot’s severity, treatment timing, and the patient’s health.
What is the role of interventional neuroradiologists in brain clot removal?
Interventional neuroradiologists are key in performing mechanical thrombectomy.
How do neurosurgeons and neurologists contribute to brain clot removal?
Neurosurgeons and neurologists are vital in providing care and support during treatment.
What is the importance of timely treatment for brain blood clots?
Quick treatment is critical to reduce brain damage and improve outcomes.
References
- Blood Clot in Brain: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Retrieved from: https://www.yashodahospitals.com/blog/blood-clot-in-brain/
- Blood Clot in Brain: Reason, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment. Retrieved from: https://psrihospital.com/causes-symptoms-treatment-of-blood-clot-in-brain/
- Ischemic Strokes. Retrieved from: https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/types-of-stroke/ischemic-stroke-clots


































