Millions of people worldwide deal with thyroid problems. These problems can be hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to tell these conditions apart for the right treatment.
Understanding the differences between hypothyroid vs hyperthyroid conditions is key. It helps find the cause of symptoms. This is the first step to the right treatment and care.
We will look at five main differences between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. This will help people understand their thyroid health better. We want to give them the knowledge to take care of their thyroid.
Key Takeaways
- Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are two opposite thyroid conditions.
- Understanding their differences is key for effective management.
- Early detection is key to managing thyroid dysfunction.
- Accurate diagnosis is essential for the right treatment.
- Liv Hospital is committed to providing complete care for thyroid disorders.
Understanding Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism

The thyroid gland is key to many body functions. Its problems can cause hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Knowing about these conditions helps us understand their impact on health.
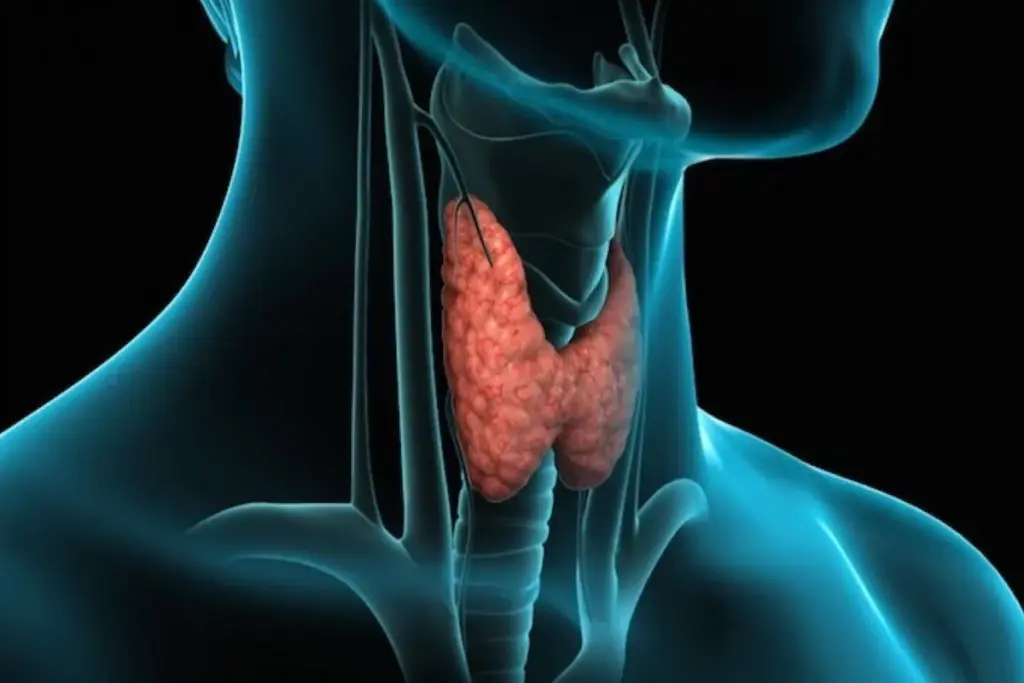
The Thyroid Gland and Its Function
The thyroid gland makes hormones that control many body systems. These include heart rate and energy levels to body temperature and brain health. Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are essential for keeping the body balanced and healthy.
Prevalence of Thyroid Disorders in the United States
Thyroid problems are a big health issue in the U.S., affecting about 20 million people. Hypothyroidism is more common than hyperthyroidism, with women more likely to get it. Knowing about these conditions helps in getting the right treatment.
Thyroid health is vital for our overall well-being. Learning about hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism helps us find the right medical care.
Key Differences in Causes and Symptoms
When we look at hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, we see big differences. These thyroid disorders affect millions, each with its own causes and symptoms.
Difference #1: Underlying Causes
Hypothyroidism happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough hormones. This is often due to Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, where the immune system attacks the thyroid. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism is when the thyroid makes too many hormones. This is usually because of Graves’ disease, another autoimmune issue that makes the thyroid overactive.
Difference #2: Symptom Presentation
The symptoms of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are quite different. Hyperthyroidism brings symptoms like anxiety, weight loss, and rapid heartbeat. Hypothyroidism, on the other hand, causes fatigue, weight gain, and cold sensitivity. Knowing these differences helps doctors diagnose and treat these conditions right.
Diagnostic and Treatment Differences
Distinguishing between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism is key for diagnosis and treatment. It greatly affects patient outcomes. Lab tests play a big role in making this distinction.
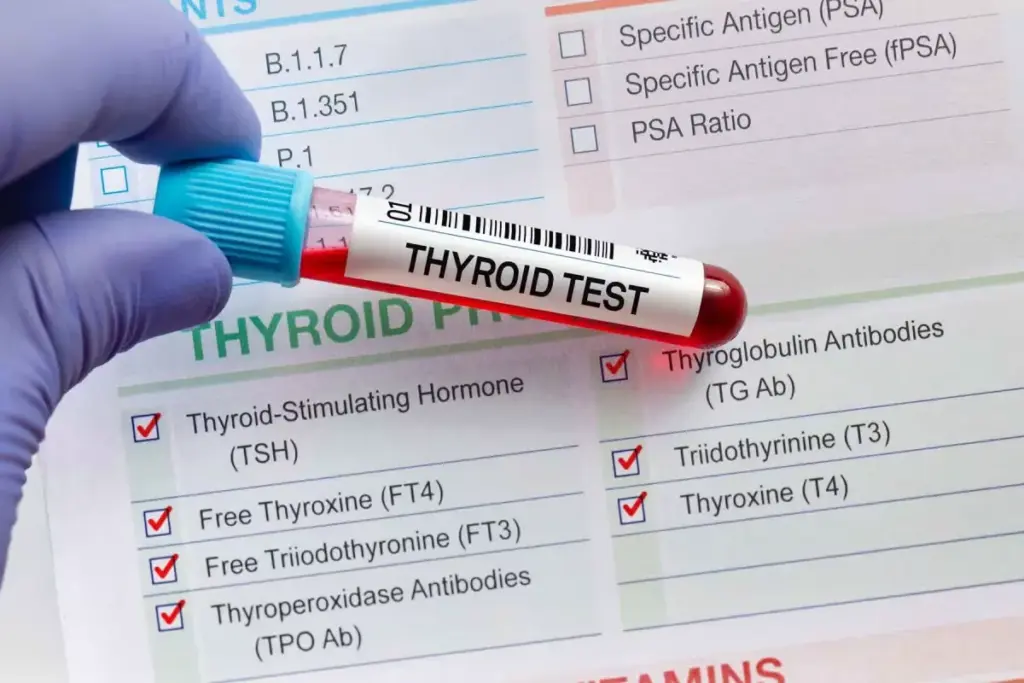
Laboratory Findings
Lab tests, like Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels, are essential for diagnosing thyroid disorders. Hypothyroidism is often seen with high TSH levels. This shows the pituitary gland is trying to get the thyroid to make more hormones.
In contrast, hyperthyroidism is marked by low TSH levels. This means the thyroid is making too many hormones, stopping the pituitary gland from releasing TSH.
Other tests, like free thyroxine (FT4) and free triiodothyronine (FT3) levels, are also important. In hypothyroidism, these levels are low. In hyperthyroidism, they are high. Knowing these lab results is vital for diagnosing and treating thyroid issues.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism is different because of their opposite nature. Hypothyroidism is usually treated with thyroid hormone replacement. This involves taking synthetic hormones to replace what’s missing.
For hyperthyroidism, the goal is to lower hormone production. Treatment options include medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery. The best treatment depends on the cause, severity, and the patient’s health.
Long-term Health Implications
The long-term effects of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism differ. This highlights the need for proper management. Untreated hypothyroidism can lead to heart disease. Untreated hyperthyroidism can cause osteoporosis or atrial fibrillation.
Managing both conditions well can greatly improve life quality and prevent serious problems. Regular check-ups and adjusting treatment as needed are key to keeping the thyroid in balance and maintaining overall health.
Conclusion
It’s key to know the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism for good care. These two conditions have big differences in how they are treated and affect your health.
Hyper v hypo thyroid conditions have different causes and symptoms. Getting the right diagnosis is important. This helps in choosing the right treatment for each condition.
Functional medicine is a good way to deal with thyroid problems. It looks at the causes, not just the symptoms. This approach helps people with thyroid issues feel better overall.
In short, knowing the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism is critical. We stress the need for thorough diagnosis and treatment plans. These plans should fit each condition’s unique needs.
FAQ
What is the main difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Hypothyroidism means the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough hormones. Hyperthyroidism means it makes too many.
What are the common causes of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis often causes hypothyroidism. Graves’ disease usually causes hyperthyroidism.
How do the symptoms of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism differ?
Hypothyroidism symptoms include feeling tired, gaining weight, and being cold. Hyperthyroidism symptoms are losing weight, having a fast heart, and feeling hot.
How are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism diagnosed?
Doctors use lab tests, like TSH levels, to tell them apart. High TSH levels mean hypothyroidism. Low TSH levels mean hyperthyroidism.
What are the treatment approaches for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is treated with hormone replacement medicine. For hyperthyroidism, doctors might use medicine, radioactive iodine, or surgery.
What are the long-term health implications of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Untreated hypothyroidism can lead to heart disease. Untreated hyperthyroidism can cause weak bones and heart problems.
Can functional medicine help address thyroid health?
Yes, functional medicine can help by finding and fixing thyroid problems. It looks at nutrition and toxins.
What is the role of TSH levels in diagnosing thyroid disorders?
TSH levels are key in diagnosing thyroid issues. They show if the thyroid is working right.
How do hypo and hyperthyroidism affect the body differently?
Hypothyroidism slows down metabolism, causing weight gain and tiredness. Hyperthyroidism speeds up metabolism, leading to weight loss and more energy.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.thyroid.org/hypothyroidism/