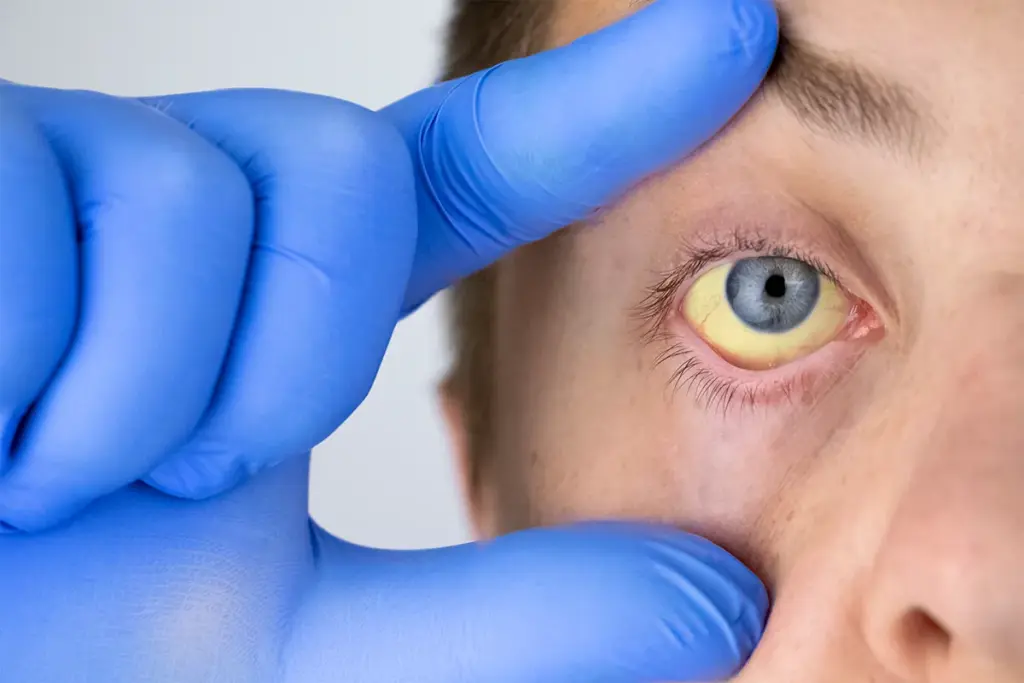
Chronic hepatitis B is a big health problem worldwide, affecting millions. It’s important to diagnose and code it right for good patient care. The ICD-10 code B18.1 is for chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent. This helps doctors document this serious condition well.
At Liv Hospital, we know how key it is to follow the latest health guidelines and offer top-notch care. Using the B18.1 diagnosis code right is key to managing chronic viral hepatitis B well. In this article, we’ll dive into what ICD-10 code B18.1 means, its importance, and how to document it for treatment.
Key Takeaways
- ICD-10 code B18.1 is used for chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent.
- Accurate coding is key for good patient care and management.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to providing high-quality, ethical healthcare services.
- Right documentation of B18.1 is vital for diagnosis and treatment.
- Using B18.1 correctly helps doctors manage chronic viral hepatitis B well.
Understanding Chronic Hepatitis B ICD-10 Code B18.1
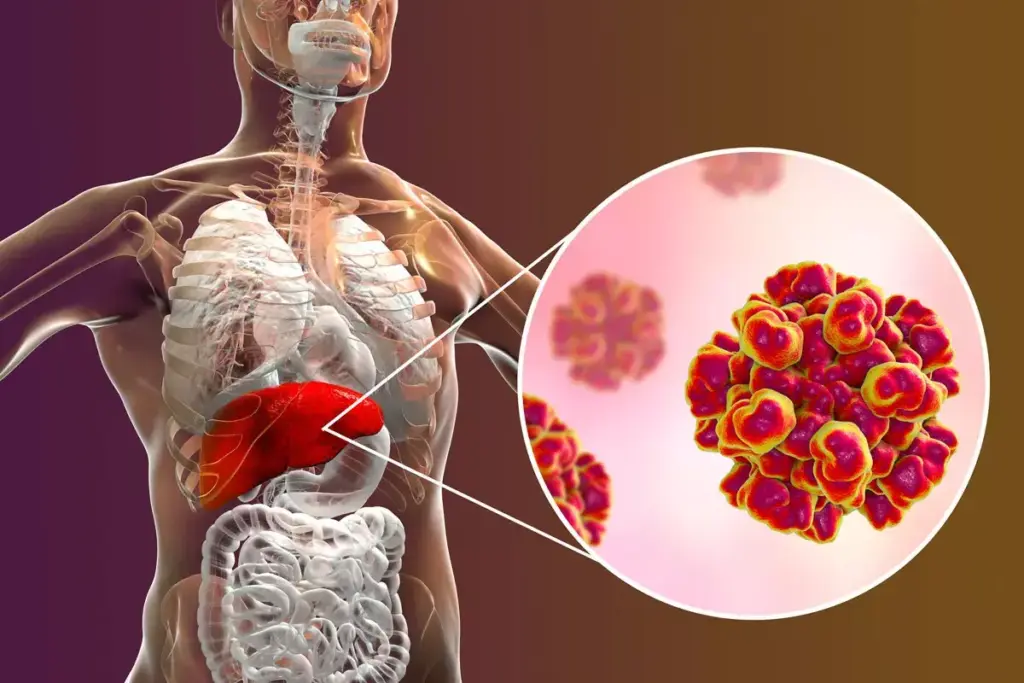
Healthcare professionals need to know about ICD-10 code B18.1 to treat chronic hepatitis B well. This liver infection is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Accurate coding helps in patient care and tracking the disease.
Definition and Classification
Chronic hepatitis B lasts more than six months. The ICD-10 code B18.1 is for chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent. This is key because having the hepatitis D virus (delta-agent) needs different treatment.
Knowing if hepatitis B is acute or chronic is vital. Chronic hepatitis B means a long-term infection. It can cause serious liver damage if not managed right.
Difference Between Acute and Chronic Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B is a short-term infection that usually heals in six months. On the other hand, chronic hepatitis B lasts more than six months. It can cause chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
- Acute hepatitis B is often symptomatic and may need supportive care.
- Chronic hepatitis B can be silent for years, making regular check-ups and management key.
The ICD-10 code B18.1 is for chronic hepatitis B. It shows the importance of correct diagnosis and differentiating it from acute hepatitis B, which has its own code.
Key differences between acute and chronic hepatitis B include:
- Duration of infection: Acute hepatitis B is short-term, while chronic hepatitis B is long-term.
- Clinical implications: Chronic hepatitis B has more severe long-term consequences.
- Coding: Acute and chronic hepatitis B have different ICD-10 codes.
Epidemiology and Transmission of Chronic Hepatitis B
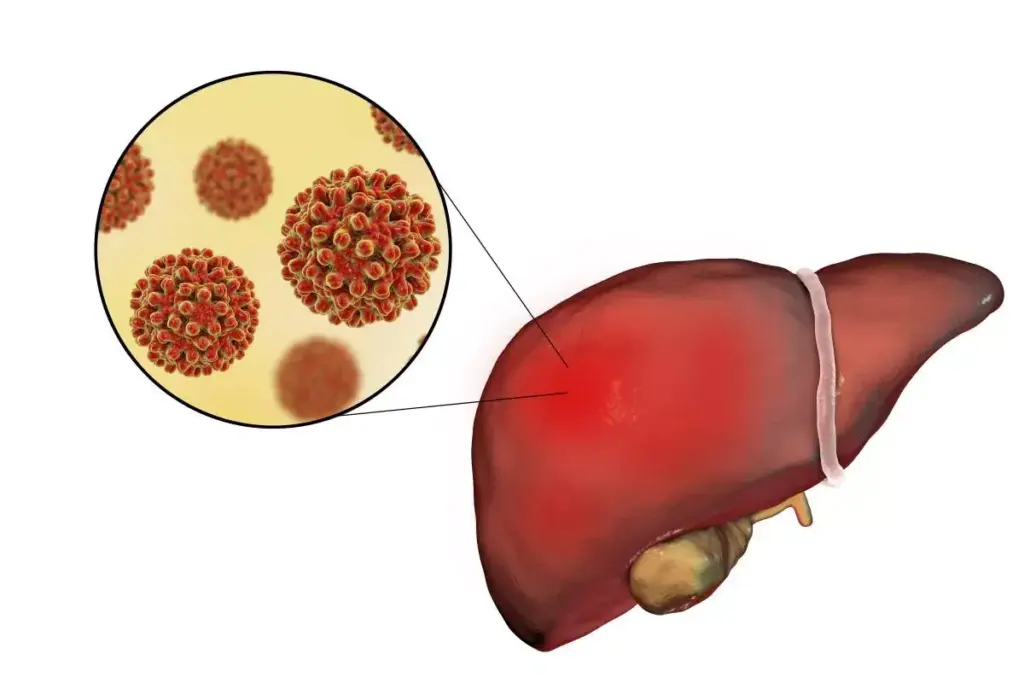
About 2 million Americans have chronic hepatitis B. It’s a big public health problem in the U.S. Knowing how it spreads helps us prevent and manage it.
Prevalence in the United States
Two million people in the U.S. live with chronic hepatitis B. But, about two-thirds don’t know they have it. We need to screen more people to find and treat those infected.
Some groups, like immigrants from high-risk areas, get hepatitis B more often. Knowing who’s at risk helps us target our health efforts.
| Population Group | Prevalence Rate | Estimated Number Infected |
| General U.S. Population | 0.3% | 2 million |
| Asian/Pacific Islanders | 3-5% | 1.2 million |
| Non-Hispanic Blacks | 1.2% | 300,000 |
Modes of Transmission
Hepatitis B spreads mainly through blood and bodily fluids. This can happen during birth, through sex, or by sharing needles. Knowing how it spreads helps us prevent it.
Key Modes of Hepatitis B Transmission:
- Vertical transmission from mother to child during birth
- Sexual contact with an infected individual
- Sharing needles or syringes
- Less commonly, through tattooing or acupuncture with contaminated equipment
Preventing hepatitis B is key. Vaccination and safe practices can help. By understanding how it spreads, we can fight it better.
Clinical Significance and Health Risks
Chronic hepatitis B is very serious because of its health risks. It affects millions around the world, including many in the United States. We will look at the long-term problems it can cause and the death and illness rates.
Long-term Complications
People with chronic hepatitis B face serious long-term health issues. Some major risks include:
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver that can lead to liver failure.
- Liver Cancer: Chronic hepatitis B is a major risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Liver Failure: Advanced liver disease can result in liver failure, necessitating transplantation.
About 15 to 40 percent of those with chronic hepatitis B may get these serious problems. This shows why managing and treating it is so important.
Mortality and Morbidity Statistics
The death and illness rates for chronic hepatitis B are very high. It can cause early death from cirrhosis and liver cancer. It’s estimated that 15 to 25 percent of those with it may die early from these issues.
Knowing these numbers shows we need to find it early and treat it well. Using the right ICD-10 codes and effective treatments are key. We must manage chronic hepatitis B to avoid long-term health problems and lower death rates.
Proper Documentation and Coding for Chronic Hepatitis B
Managing chronic hepatitis B well needs good documentation and coding. Using the ICD-10 code B18.1 correctly is key. It helps patients get the right care and ensures doctors get paid right.
Documentation Requirements
Healthcare providers must document chronic hepatitis B diagnosis clearly. They should note the patient’s medical history, lab results, and symptoms. The CDC guidelines say to document HBsAg positivity for over six months.
Key documentation elements include:
- Patient’s medical history
- Laboratory results confirming HBsAg positivity
- Relevant symptoms and clinical findings
Common Coding Errors and Tips
Mistakes in coding can cause claims to be denied and slow down payments. Common errors include mixing up acute and chronic hepatitis B codes. Also, not documenting the diagnosis well enough.
| Coding Error | Correct Coding Practice |
| Using ICD-10 code B18.1 for acute hepatitis B | Use B16.9 for acute hepatitis B; B18.1 is for chronic hepatitis B |
| Insufficient documentation | Ensure documentation includes HBsAg positivity for more than six months |
By sticking to these guidelines and avoiding common mistakes, healthcare providers can code and bill for chronic hepatitis B correctly. This means using the ICD-10 code B18.1 properly.
Conclusion
Knowing the ICD-10 code B18.1 is key for diagnosing and treating chronic hepatitis B. We’ve talked about how important it is to use the right icd 10 chronic hepatitis b code. This helps identify people with this condition.
Using the right coding, like ≥2 outpatient codes or ≥1 inpatient codes, is important. It helps doctors diagnose chronic hepatitis B better. This way, healthcare providers can give the best care to those with chronic hepatitis B.
The study shows we need to be precise with our coding and documentation. This leads to better patient care. As we deal with chronic hepatitis B, knowing ICD-10 code B18.1 is essential. It helps doctors make the right decisions and care for their patients well.
FAQ
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic hepatitis B?
The ICD-10 code for chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent is B18.1.
What is the difference between acute and chronic hepatitis B?
Acute hepatitis B is a short-term infection. Chronic hepatitis B is a long-term infection that can cause serious health problems. The ICD-10 code B18.1 is for chronic infections.
How is chronic hepatitis B transmitted?
Chronic hepatitis B spreads through bodily fluids like blood and semen. It can also pass from mother to child during birth.
What are the long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B?
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to serious problems like cirrhosis and liver cancer.
What is the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B in the United States?
Chronic hepatitis B affects many people in the United States. The rate varies among different groups.
What are the documentation requirements for using the ICD-10 code B18.1?
To use the ICD-10 code B18.1, you need to document chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent. This includes lab results and clinical findings.
What are common coding errors for chronic hepatitis B?
Common mistakes include coding acute hepatitis B wrong, not documenting delta-agent status, and using the wrong codes.
Why is accurate coding important for chronic hepatitis B management?
Accurate coding is key for proper care and management of chronic hepatitis B. It also ensures correct billing and reimbursement.
What is the significance of the ICD-10 code B18.1 in healthcare?
The ICD-10 code B18.1 is vital for diagnosing and managing chronic hepatitis B. It helps healthcare providers document and manage the condition accurately.
How can healthcare providers ensure accurate coding for chronic hepatitis B?
Healthcare providers can ensure accurate coding by keeping up with coding guidelines, documenting well, and avoiding common mistakes.
References:
World Health Organization. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en#/B18.1









