Infectious diseases are caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites, spreading through contact or air and often requiring early diagnosis and proper treatment.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Following the ingestion of the Hepatitis A virus, there is a distinct biological interval known as the incubation period. This phase represents the time required for the virus to traverse the gastrointestinal tract, enter the bloodstream, travel to the liver, and replicate to numbers sufficient to trigger a systemic response. Current clinical data indicate that this period typically ranges from 14 to 28 days, though it can extend to 50 days in some individuals. During this time, the infected individual remains clinically well and unaware of the biological invasion occurring within their body.
A critical aspect of Hepatitis A transmission dynamics is the phenomenon of pre-symptomatic viral shedding. The virus begins to be excreted in stool at high concentrations approximately 1 to 2 weeks before the onset of clinical symptoms. This biological reality is the primary driver of community transmission. An individual becomes maximally infectious precisely when they feel healthy and are continuing their daily routines—working, preparing food, and interacting with family. By the time the first symptoms of jaundice or malaise appear, the peak period of infectivity has often passed, meaning the virus has likely already been transmitted to close contacts. This silent dissemination poses a significant challenge for outbreak control.

The clinical illness typically manifests abruptly, with a prodromal phase characterized by nonspecific systemic symptoms. This phase reflects the initial robust immune response to the viral replication in the liver. Patients often report a sudden onset of low-grade fever, accompanied by profound fatigue and malaise that feels disproportionate to their exertion levels.
Gastrointestinal symptoms are prominent during the prodrome. Anorexia, or a complete loss of appetite, is a hallmark sign; the mere sight or smell of food may induce nausea. Vomiting and vague abdominal discomfort, particularly in the right upper quadrant where the liver resides, are common. This pain is caused by the stretching of the Glisson’s capsule (the fibrous layer covering the liver) due to hepatic inflammation and swelling. In addition, patients may experience myalgia (muscle pain) and arthralgia (joint pain), mimicking a severe case of influenza. Because these symptoms are non-specific, the condition is frequently misdiagnosed as viral gastroenteritis or flu during this early stage.
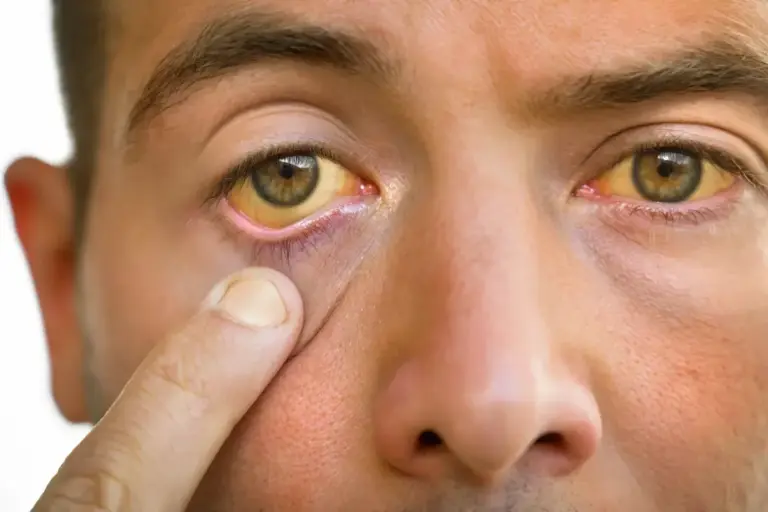
As the disease progresses, usually within a week of symptom onset, the icteric phase begins. “Icterus” refers to the yellow pigmentation of the skin and sclera (the whites of the eyes) known as jaundice. This occurs due to the accumulation of bilirubin, a yellow byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. In a healthy state, the liver processes bilirubin and excretes it into bile. In Hepatitis A, the inflamed and damaged hepatocytes lose the capacity to transport bilirubin effectively, causing it to back up into the bloodstream and deposit in body tissues.
The onset of jaundice is often heralded by the darkening of the urine, which may resemble the color of strong tea or cola. This “bilirubinuria” occurs because the kidneys attempt to filter the excess conjugated bilirubin from the blood. Conversely, the stool may become pale, gray, or clay-colored (acholic) because the bilirubin pigment that usually gives stool its brown color is blocked from entering the intestine. Pruritus, or generalized itching, can be severe and distressing and result from the deposition of bile salts in the skin. Paradoxically, as jaundice appears, the systemic symptoms of fever and nausea may begin to subside, although fatigue often persists.
The transmission of Hepatitis A is governed almost exclusively by the fecal-oral route. This mechanism describes the passage of the virus from the stool of an infected individual to the mouth of a susceptible host. Because the virus is non-enveloped and highly stable, it can survive the transit through the environment and the acidic barrier of the human stomach.
Waterborne Transmission: Ingestion of water contaminated with sewage is a primary route of transmission in areas with compromised sanitation infrastructure. This applies not only to drinking water but also to water used for washing produce or making ice.

Specific environmental vectors are notoriously associated with Hepatitis A due to the virus’s physical properties.
Frozen Foods: The virus’s ability to withstand freezing temperatures means that contaminated frozen berries or other produce can serve as vectors months or even years after harvest, facilitating international transmission.
The severity and presentation of symptoms are strongly correlated with the patient’s age.
Adult Presentation: In contrast, symptomatic illness is the norm for older children and adults. The severity of the disease, including the depth of jaundice and the duration of illness, tends to increase with age. Older adults and individuals with pre-existing liver conditions are at higher risk for severe complications, including acute liver failure.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Pre-symptomatic shedding means an infected person excretes the virus in their stool and remains highly contagious for 1 to 2 weeks before they actually feel sick or show any symptoms. This makes it very difficult to stop the spread, as people are transmitting the virus while going about their everyday lives, unaware they are infected.
The urine turns dark because of a buildup of bilirubin in the blood. When the liver is inflamed and cannot properly process bilirubin, the yellow pigment leaks into the bloodstream. The kidneys filter excess water-soluble bilirubin from the blood and excrete it in the urine, giving it a dark, tea-colored appearance.
No, Hepatitis A is not a respiratory virus. It is not spread through droplets from coughing or sneezing. It is strictly transmitted via the fecal-oral route, meaning the virus must be ingested. However, close contact with an infected person can facilitate transmission if hygiene is poor.
Yes, it is possible to contract Hepatitis A by swimming in water contaminated with sewage. If contaminated water is accidentally swallowed while swimming, the virus can enter the digestive system and cause infection. This is more common in freshwater bodies or coastal areas near sewage outlets.
The duration of illness varies. For most healthy people, symptoms last a few weeks, and full recovery takes about 2 to 3 months. However, in some cases, symptoms can last up to 6 months, or patients may experience a “relapsing” course in which symptoms disappear and then return before finally resolving.


Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)