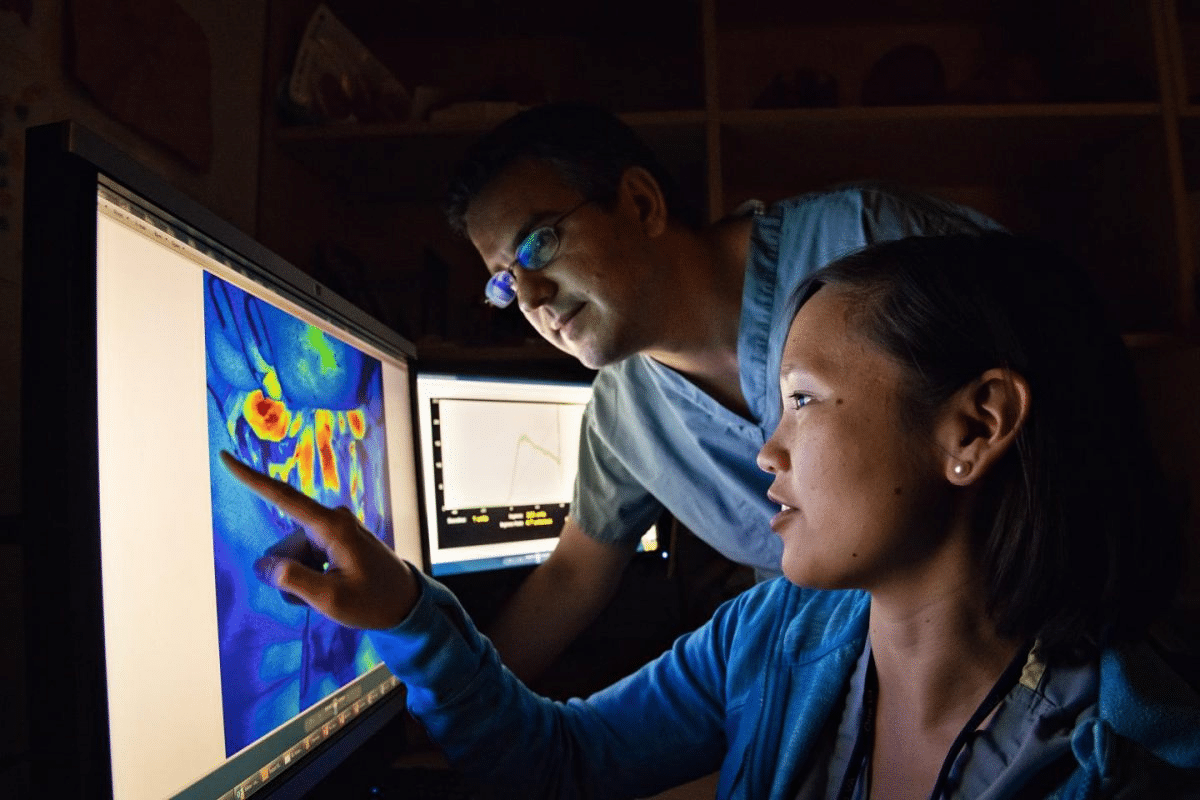
As the U.S. population ages, surgeries get more complex. This makes intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) key in avoiding neurological harm. Learn what is the difference between intraoperative neuromonitoring vs EEG. Understand the distinct uses of both techniques clearly.
IONM checks the nervous system during surgery in real-time. It greatly lowers the chance of problems. But, a big question is: does Medicare cover this important service? Knowing Medicare’s coverage for IONM is essential for both patients and doctors.
We will dive into Medicare’s IONM coverage. We’ll look at its importance, what’s covered, and who qualifies. This will clear up any confusion on this complex topic.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the role of IONM in surgical procedures.
- Overview of Medicare coverage for IONM.
- Eligibility criteria for IONM coverage under Medicare.
- The significance of IONM in preventing neurological damage.
- How Medicare coverage impacts patient care and surgical outcomes.
Understanding Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM)
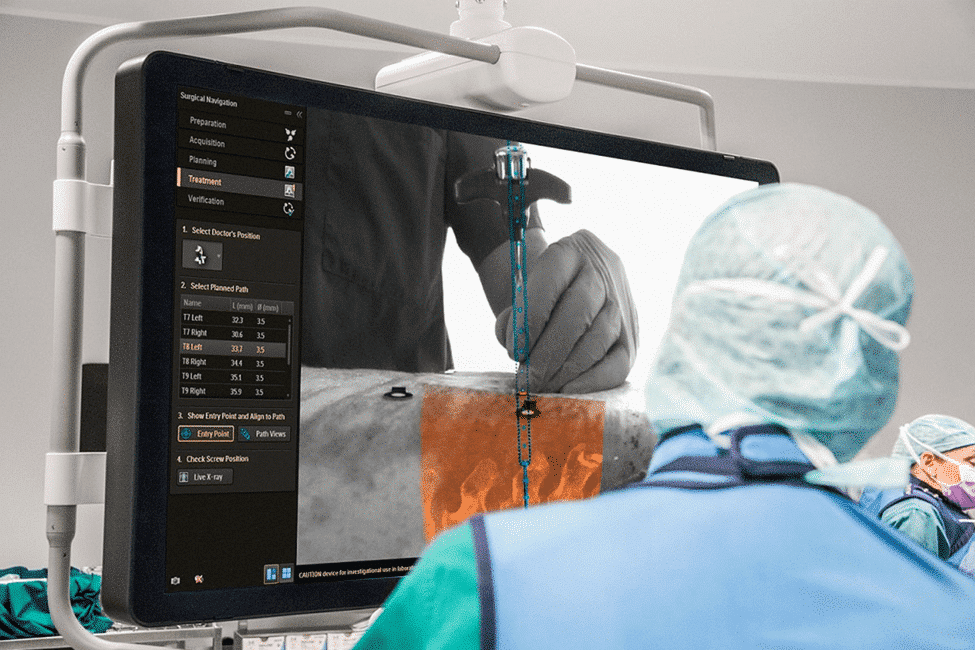
Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) is key in many surgeries. It uses special techniques to check if nerves are okay during surgery. This helps avoid nerve damage and makes surgeries better.
Definition and Purpose of IONM
IONM uses special monitoring during surgery. It checks if nerves are working right. This way, surgeons can act fast to avoid nerve problems.
Research shows IONM lowers the chance of nerve issues in surgeries. This is true for spine, brain, and blood vessel surgeries. It does this by watching nerve functions closely and acting quickly if needed.
Types of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring Techniques
There are many ways to do IONM, including:
- Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEP): checks sensory pathways.
- Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP): looks at motor pathways.
- Electromyography (EMG): watches muscle activity and nerve issues.
- Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potentials (BAEP): monitors hearing pathways.
Doctors pick the right method based on the surgery and nerves involved.
Common Surgical Procedures Utilizing IONM
IONM is used in:
- Spine surgeries: to keep the spinal cord safe during operations like fixing scoliosis.
- Brain surgeries: to watch brain function during tumor removals or clipping aneurysms.
- Vascular surgeries: to check blood flow in the brain during carotid endarterectomy.
Using IONM in these surgeries helps by lowering the risk of nerve problems.
The Importance of Neuromonitoring in Surgical Procedures
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is key in many surgeries. It makes patients safer and improves their results. As surgery gets better, neuromonitoring’s role in avoiding problems and better outcomes is vital.
Reducing Neurological Complications
IONM helps lower the risk of brain problems during surgery. It watches neural structures in real time. This lets surgeons act fast to avoid serious damage.
Studies show IONM cuts down on brain problems after surgery. This leads to better health for patients.
Improving Surgical Outcomes
IONM makes surgeries better in many ways. It gives feedback on brain function. This helps surgeons be more precise.
Being precise means better surgeries. This leads to better health for patients. IONM has helped many surgeries be successful.
Cost-Effectiveness of Preventive Monitoring
At first, IONM seems expensive. But it saves money in the long run. It cuts down on brain problems.
This means shorter hospital stays and less need for rehab. It also saves on healthcare costs. Plus, happy patients and fewer legal issues are benefits.
Patient Safety Benefits
IONM’s biggest plus is making patients safer. It watches brain function in real time. This lets surgeons prevent brain damage.
This is very important in complex surgeries. As surgical procedures advance, the importance of IONM in safeguarding patient health will continue to increase.
Medicare Coverage Intraoperative Neuromonitoring: An Overview
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is key in today’s surgery. Knowing Medicare’s coverage is important for doctors. It’s vital to understand the current IONM coverage rules.
Medicare’s General Stance on IONM
Medicare sees IONM as a covered service when it’s needed. Medical necessity depends on the patient’s health and the surgery. IONM helps lower risks of nerve problems during surgery.
Evolution of Medicare IONM Coverage Policies
Medicare’s IONM coverage has changed over time. At first, IONM was new and experimental. But as its benefits grew, so did Medicare’s coverage.
Now, IONM is widely recognized for improving surgery results. This shift shows the medical world’s growing trust in IONM.
Current Coverage Framework
Medicare’s IONM coverage is based on several rules. It uses national and local coverage rules. National coverage determinations set the standard nationwide. Local coverage determinations allow for local adjustments.
|
Coverage Aspect |
Description |
Medicare Policy |
|---|---|---|
|
Medical Necessity |
Determination based on patient condition and surgical procedure |
Covered when deemed medically necessary |
|
National Coverage Determinations (NCDs) |
Baseline for medical necessity nationwide |
Provides national standards |
|
Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) |
Regional flexibility for coverage |
Allows for local adjustments |
Knowing these Medicare rules is key for doctors. It helps them ensure patients get the care they need.
Medicare Part A and IONM Coverage
It’s important for healthcare providers to know about Medicare Part A’s IONM coverage. Medicare Part A helps cover hospital inpatient services, like IONM. This is used to watch the nervous system during complex surgeries.
Hospital Inpatient Coverage Details
Medicare Part A covers IONM services during inpatient hospital stays. This is key for making sure patients get the right care during complex surgeries. The IONM service must be needed and done by the right people to qualify for coverage.
Key aspects of hospital inpatient coverage include:
- The IONM service must be provided in an inpatient setting.
- The service must be ordered by a physician and documented in the patient’s medical record.
- The IONM procedure must be performed by qualified healthcare professionals.
Bundled Payment Considerations
IONM services might be part of bundled payments for surgeries. This means the cost of IONM is bundled with other services in one payment. It’s important for healthcare providers to understand these payments to manage costs and follow Medicare rules.
Bundled payment considerations include:
- Identifying which services are included in the bundled payment.
- Understanding how IONM services are reimbursed within the bundled payment structure.
- Ensuring that all necessary documentation is maintained to support the billing of bundled services.
Facility Responsibility for IONM Services
Hospitals and healthcare facilities must make sure IONM services are done by the right people. They also need to document and bill these services correctly. Facilities must follow Medicare’s IONM coverage rules, including keeping accurate records and proving the service is needed.
Facility responsibilities include:
- Ensuring that IONM services are performed by qualified professionals.
- Maintaining accurate and detailed records of IONM procedures.
- Complying with Medicare’s billing and reimbursement guidelines for IONM services.
Medicare Part B and IONM Coverage
It’s important for healthcare providers and patients to know about Medicare Part B’s IONM coverage. Medicare Part B covers the professional and technical parts of IONM in outpatient settings. This ensures patients get full care during surgeries.
Outpatient Coverage Specifications
Medicare Part B covers IONM in outpatient settings like hospital outpatient departments and ambulatory surgical centers. This is key for patients having surgeries in these places to get the neuromonitoring they need.
Key aspects of outpatient IONM coverage under Medicare Part B include:
- Coverage for IONM services during surgical procedures that require neuromonitoring.
- Requirement for healthcare providers to follow Medicare guidelines for IONM coverage.
- Importance of accurate billing and documentation for IONM services.
Professional Component Coverage
The professional component of IONM is when doctors interpret neuromonitoring data. Medicare Part B covers this, seeing the doctor’s role as vital for patient safety during surgeries.
The professional component includes:
- Physician interpretation of IONM data.
- Documentation of findings and recommendations.
- Billing for professional services rendered.
Technical Component Coverage
The technical component of IONM is the actual neuromonitoring during surgeries. Medicare Part B also covers this, making sure the technical side of IONM is paid for.
Technical component coverage includes:
- The performance of IONM during surgical procedures.
- The use of necessary equipment and personnel for IONM.
- Billing for technical services rendered.
Knowing about the coverage for both the professional and technical parts of IONM under Medicare Part B helps healthcare providers. It ensures patients get the care they need.
Medicare-Approved Procedures for Neuromonitoring
Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) is a key tool in many surgeries approved by Medicare. We will look at the different surgeries where Medicare covers IONM.
IONM helps in complex surgeries by checking the nervous system in real-time. This reduces the chance of nerve damage. Medicare covers IONM based on medical need and the surgery type.
Spine Surgeries
Spine surgeries often use IONM. Medicare covers IONM for spine surgeries that risk the spinal cord or nerve roots. This includes complex fusions, correcting deformities, and removing tumors.
Brain Surgeries
Brain surgeries, which risk important areas for brain function, also use IONM. Medicare approves IONM for brain surgeries with a high risk to neural structures.
Vascular Procedures
Vascular procedures, like aneurysm clipping and AVM surgery, also use IONM. Medicare covers IONM for these when it’s needed to avoid neurological problems.
Other Approved Surgical Interventions
Medicare also covers IONM for other surgeries at risk for neurological damage. This includes peripheral nerve surgeries and some ear, nose, and throat procedures.
|
Surgical Category |
Examples of Procedures |
Medicare Coverage for IONM |
|---|---|---|
|
Spine Surgeries |
Complex fusions, deformity corrections, tumor resections |
Covered when medically necessary |
|
Brain Surgeries |
Tumor resections, aneurysm clipping, AVM surgery |
Covered for high-risk procedures |
|
Vascular Procedures |
Aneurysm clipping, AVM surgery |
Covered when medically necessary |
|
Other Surgeries |
Peripheral nerve surgeries, certain otolaryngological procedures |
Covered on a case-by-case basis |
Medicare Eligibility Requirements for IONM Coverage
To get Medicare to cover IONM, there are many rules to follow. These rules cover who can get the service, what procedures are covered, and who can perform them. Knowing these rules is key for patients to get the care they need.
Patient Eligibility Criteria
Patients must meet certain criteria to get Medicare to cover IONM. These include:
- Being enrolled in Medicare Part A and/or Part B
- Having a medical condition that requires a surgical procedure where IONM is deemed medically necessary
- Receiving treatment from a Medicare-approved healthcare provider
Healthcare providers must check if a patient is eligible before doing IONM services. This ensures the services are covered.
Procedure-Specific Requirements
Not every surgery can get Medicare to cover IONM. The surgery must be:
- A Medicare-approved surgical intervention
- Deemed medically necessary for the patient’s condition
- Performed by a qualified healthcare provider
Examples of surgeries that are covered include some spine, brain, and vascular surgeries.
|
Procedure Type |
Medicare Coverage Status |
Additional Requirements |
|---|---|---|
|
Spine Surgeries |
Covered |
Must be performed by a qualified specialist |
|
Brain Surgeries |
Covered |
Requires pre-operative assessment |
|
Vascular Procedures |
Covered |
Must be medically necessary |
Provider Qualification Requirements
Providers doing and reading IONM tests must meet certain standards. These include:
- Having the necessary training and experience in IONM
- Being licensed to practice in their state
- Being credentialed by their healthcare organization
It’s important for providers to meet these standards. This ensures quality care and Medicare coverage.
By following these rules, healthcare providers can make sure patients get the IONM services they need. These services are covered by Medicare.
Regional Variations in Medicare IONM Coverage
It’s key for healthcare providers and patients to know about Medicare IONM coverage differences. Medicare’s IONM coverage changes a lot from one area to another. This is because of local policies and guidelines.
Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs)
Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) are made by Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs). They decide if certain medical services, like IONM, are covered in their areas. These decisions are based on if the service is medically necessary.
LCDs can differ between MAC areas, leading to coverage changes. For example, one MAC might cover IONM for some spinal surgeries, but another might not. Knowing your area’s LCDs is very important.
Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) Policies
MACs are key in giving out Medicare benefits, including deciding on coverage. Their rules can affect IONM service coverage. They check if IONM is needed for different surgeries and make guidelines.
Healthcare providers need to keep up with MAC policies in their area. This helps them follow rules and tell patients about IONM coverage chances.
State-by-State Coverage Differences
IONM coverage can change a lot from state to state. This is because of different LCDs and MAC policies. For instance, some states might cover IONM more during certain surgeries than others.
“The variability in Medicare coverage for IONM across states highlights the need for healthcare providers to be well-versed in local regulations and policies to navigate these differences effectively.” –
A healthcare professional
How to Research Local Coverage Rules
To deal with Medicare IONM coverage complexities, healthcare providers can do a few things:
- Check the relevant MAC’s website for LCDs and policies.
- Look at Medicare’s national coverage determinations (NCDs) for help.
- Keep up with LCD and MAC policy updates.
- Join professional groups that share coverage policy news.
By following these steps, healthcare providers can understand Medicare IONM coverage differences. This helps them give the best care to their patients.
Medicare Reimbursement for Intraoperative Monitoring
Medicare’s payment for IONM services is complex. It depends on many factors and payment types. Knowing these details helps healthcare providers manage their billing well.
Current Reimbursement Rates
Medicare pays different rates for IONM services, depending on where they are done. For example, rates change for inpatient or outpatient procedures. Medicare has set rates for various CPT codes for IONM.
The rate for CPT code 95940 changes every year. Providers need to keep up with these changes for accurate billing.
|
CPT Code |
Description |
Reimbursement Rate |
|---|---|---|
|
95940 |
Continuous intraoperative neurophysiology monitoring |
$200 – $300 |
|
95941 |
Continuous intraoperative neurophysiology monitoring, requiring personnel outside the operating room |
$300 – $400 |
Factors Affecting Reimbursement
Many things can change how much Medicare pays for IONM services. These include the surgery type, where it’s done, and the CPT codes used.
Setting: Rates are different for inpatient and outpatient settings because of different payment rules.
Geographic Location: Rates can also change based on where you are. This is because of local rules and policies.
Payment Models and Structures
Medicare uses different ways to pay for IONM services. These include fee-for-service and bundled payments. Knowing these helps providers get the most from their payments.
Fee-for-Service: Medicare pays for each service separately, based on the CPT code and rate.
Bundled Payments: Some surgeries are paid for in one bundle. This includes the cost of IONM services.
Understanding these rates, factors, and payment models helps providers manage Medicare’s complex IONM reimbursement better.
IONM Medicare Billing Codes and Guidelines
Understanding IONM Medicare billing can be easier with the right codes and practices. It’s key for healthcare providers to bill correctly for IONM services. This ensures they get paid and follow Medicare rules.
CPT Codes for Neuromonitoring Services
To bill Medicare for IONM services, providers need specific CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes. These codes describe the neuromonitoring done during surgeries. Common CPT codes for IONM include:
- 95940: Continuous intraoperative neurophysiology monitoring, from outside the operating room (remote monitoring).
- 95941: Continuous intraoperative neurophysiology monitoring, from outside the operating room (remote monitoring), with a separate technician or physician.
Choosing the right CPT code is important. It depends on the services and where the monitoring is done.
Proper Billing Practices
For IONM services under Medicare, follow these steps:
- Make sure the IONM service is needed and documented well in the patient’s record.
- Use the correct CPT codes for the services given.
- Follow Medicare’s rules for billing IONM services, including technical and professional components.
- Keep detailed and accurate records of the services given.
Common Billing Errors to Avoid
Healthcare providers should watch out for common billing mistakes. These can cause claims to be denied or lead to audits. Mistakes include:
- Using wrong or old CPT codes.
- Not documenting the need for the IONM service.
- Not following Medicare’s rules for IONM services.
Avoiding these errors can make billing more accurate. It also reduces the chance of payment problems.
Modifier Usage for IONM Services
Modifiers add extra details to CPT codes for IONM services. For example, the -26 modifier shows the professional part of a service. The -TC modifier shows the technical part.
A medical billing expert says, “Using the right modifiers is key for correct billing and payment. It clarifies the services and follows Medicare rules.”
“The right modifiers are vital for IONM billing success. It’s not just about the CPT code. It’s also about the context given by modifiers.” – Medical Billing Expert
Documentation Requirements for Medicare IONM Claims
When we submit Medicare claims for Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) services, we need to have all the right documents. This is key for getting our claims approved and paid. We’ll go over what documents are needed for successful claims.
Required Medical Records
We must keep detailed medical records to prove IONM services are needed. These records should have:
- Patient history: Medical history that shows why IONM is needed.
- Preoperative diagnosis: A clear diagnosis that makes IONM during surgery necessary.
- Surgical plan: Details about the surgery, like the type and expected results.
Physician Orders and Medical Necessity
Physician orders are key to show IONM services are medically necessary. We need to make sure these orders are:
- Clear and specific: Orders should clearly state why IONM is needed and what kind is required.
- Documented in the patient’s medical record: Orders must be documented well to support the claim.
Technical Reports and Interpretations
Technical reports and interpretations are very important for IONM claims. These reports should have:
- Monitoring techniques used: A description of the IONM methods used during surgery.
- Findings and interpretations: Detailed findings and interpretations of the IONM data.
- Clinical correlation: How the IONM findings relate to the surgery and patient outcomes.
Baseline and Intraoperative Documentation
Keeping accurate baseline and intraoperative documentation is very important. This includes:
- Baseline measurements: Records of IONM measurements before surgery.
- Intraoperative data: Continuous records of IONM data during surgery.
- Significant events: Notes on any important events or changes in IONM data during the procedure.
By keeping detailed and accurate records, we can make sure Medicare claims for IONM services are successful. This helps us provide the best care to our patients.
Medicare Medical Necessity Criteria for Neuromonitoring
It’s key for healthcare providers to know Medicare’s rules for Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM). Medicare says IONM must be needed for the patient’s health and the surgery’s complexity. We’ll look at how Medicare decides if IONM is needed.
Defining Medical Necessity for IONM
IONM is needed when surgery might harm nerves or the spinal cord. We’ll talk about what makes a surgery risky for these areas.
Risk Assessment Considerations
When checking if IONM is needed, we look at the patient’s past health, the surgery type, and other important details. For example, people having spine surgery might need IONM if they already have nerve problems.
|
Risk Factor |
Description |
IONM Necessity |
|---|---|---|
|
Pre-existing neurological conditions |
Patients with prior neurological deficits |
High |
|
Type of surgical procedure |
Surgeries involving the spine or brain |
High |
|
Surgical complexity |
Procedures with multiple stages or high-risk maneuvers |
High |
Documentation of Necessity
It’s important to document why IONM is needed. This includes the patient’s history, the surgery plan, and why IONM is used.
Surgical Complexity Factors
The surgery’s complexity is a big factor in needing IONM. More complex surgeries or those near important nerves often need IONM.
In summary, Medicare’s rules for IONM cover risk, documentation, and surgery complexity. Healthcare providers need to grasp these to use IONM correctly and get it covered.
Patient Costs and Financial Considerations
It’s important for Medicare beneficiaries to know about the costs of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM). We need to look at the expenses that come with IONM services. This helps us understand what we might have to pay out of pocket.
Medicare Beneficiary Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Medicare beneficiaries might have to pay for IONM services themselves. This includes deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. The amount you pay can change based on your Medicare plan and the surgery type. It’s key to know your Medicare benefits and what IONM might cost you.
For example, Medicare Part B usually covers 80% of IONM costs. You’ll pay the other 20% and any deductible. Check your Medicare Summary Notice (MSN) to see your exact costs.
Supplemental Insurance Coverage
Supplemental insurance, or Medigap, can help with IONM costs. With supplemental insurance, you might not have to pay coinsurance, copayments, or deductibles. Make sure to check your policy to see what it covers.
“Having supplemental insurance can significantly reduce the financial burden of IONM services for Medicare beneficiaries.”
Advance Beneficiary Notice Requirements
In some cases, Medicare won’t cover IONM for certain procedures. If this happens, you’ll get an Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN). It tells you Medicare might not pay and estimates the cost. Read the ABN carefully and think about your options before getting IONM services.
Financial Assistance Options
If IONM costs are too high, there are ways to get help. Some might qualify for Medicaid, which can cover IONM. There are also patient assistance programs from non-profits or drug companies.
Understanding the financial side of IONM is key for Medicare beneficiaries. Knowing what help is out there can make managing costs easier.
Medicare Coverage Limitations and Exclusions for IONM
It’s important for healthcare providers and patients to know about Medicare’s rules for Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM). IONM helps lower the risk of brain problems during surgery. But, Medicare has rules on what it covers and what it doesn’t.
Non-Covered Procedures
Not every surgery can use IONM, and Medicare won’t cover it for all. Medicare usually doesn’t pay for IONM if it’s not needed or is new and untested. For example, some cosmetic surgeries or low-risk procedures might not be covered.
Frequency Limitations
Medicare also has rules on how often IONM can be used. Using IONM too many times might need extra checks to see if it’s really needed. Medicare might ask for more information to approve it for more surgeries.
Service Provider Restrictions
Medicare is very strict about who can do IONM. Only certain doctors and professionals can do and bill for IONM. This makes sure the care is top-notch and really needed.
Experimental Monitoring Techniques
Medicare doesn’t pay for new or untested IONM methods. New monitoring ways need to be tested and approved before Medicare will cover them. This helps make sure patients get the best, proven care.
Knowing these rules helps doctors and patients deal with Medicare’s IONM coverage. It makes sure patients get the care they need and avoids denied claims.
Appealing Denied Medicare IONM Claims
When Medicare denies IONM claims, knowing how to appeal is key. We’ll show you how to effectively appeal denied Medicare IONM claims.
Understanding Denial Reasons
To appeal a denied Medicare IONM claim, first find out why it was denied. Reasons include lack of medical need, wrong coding, and not enough proof. Knowing the exact reason is key to a strong appeal.
It’s wise to check the denial notice against the patient’s medical and billing records. This helps spot any mistakes or areas to improve.
The Five Levels of Medicare Appeals
The Medicare appeals process has five levels. First, you ask for a redetermination from the Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC). If that fails, you can ask for a reconsideration by a Qualified Independent Contractor (QIC).
- Level 1: Redetermination – Requested to the MAC.
- Level 2: Reconsideration – Conducted by a QIC.
- Level 3: Hearing – Conducted by an Administrative Law Judge (ALJ).
- Level 4: Review – Conducted by the Medicare Appeals Council.
- Level 5: Judicial Review – Conducted by a federal district court.
Each level needs careful preparation and the right documents to support your appeal.
Tips for Successful Appeals
To boost your appeal’s success, provide detailed records and explain why IONM services are needed. Make sure all info is right and complete.
Also, keep a record of all your communications and submissions during the appeal process.
Conclusion
Medicare coverage for intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is key to patient safety in surgeries. It’s important for healthcare providers and patients to understand this coverage well.
Medicare covers IONM for specific surgeries like spine, brain, and vascular ones. Patients must meet certain criteria to qualify. Providers must follow Medicare’s rules and billing practices.
Local coverage decisions and Medicare Administrative Contractors play big roles in coverage policies. This affects how IONM is used in surgeries.
To fully grasp Medicare’s IONM coverage, knowing eligibility, limits, and appeal processes is essential. This helps ensure patients get the monitoring they need. It improves surgical results and care overall.
In summary, understanding Medicare’s IONM coverage is critical. It helps plan for complex surgeries and ensures patients get the right care.
FAQ
What is intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM), and why is it important during surgeries?
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is a tool used in surgeries. It checks the nervous system’s function. This helps prevent damage to the nerves.
It’s key for keeping patients safe during complex surgeries.
Does Medicare cover intraoperative neuromonitoring services?
Yes, Medicare covers IONM for some surgeries. But, you must meet certain criteria.
What are the different types of intraoperative neuromonitoring techniques?
IONM uses many techniques. These include EEG, EMG, and SSEP. They help monitor different parts of the nervous system.
For which surgical procedures does Medicare approve IONM?
Medicare approves IONM for many surgeries. This includes spine, brain, and vascular surgeries. It’s also used for other high-risk procedures.
What are the eligibility requirements for Medicare coverage of IONM?
To be eligible, you must meet certain criteria. This includes specific requirements for the procedure and the healthcare provider.
How does Medicare Part A cover IONM services for hospital inpatients?
Medicare Part A covers IONM for hospital inpatients. It considers bundled payments and the hospital’s role in providing the service.
What are the specifics of Medicare Part B coverage for IONM in outpatient settings?
Medicare Part B covers IONM in outpatient settings. It has specific guidelines for coverage and payment.
How do regional variations affect Medicare coverage for IONM?
Regional variations can impact coverage. This includes Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) and Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) policies.
What are the current Medicare reimbursement rates for IONM services?
Reimbursement rates for IONM vary. They depend on the procedure, location, and provider qualifications. Rates can change over time.
What are the appropriate CPT codes for billing IONM services under Medicare?
Specific CPT codes are used for IONM services. Proper billing, including correct modifier usage, is needed for payment.
What documentation is required for submitting Medicare claims for IONM services?
You need detailed medical records and physician orders. Technical reports and interpretations are also required. They support the need for IONM.
How does Medicare determine medical necessity for IONM?
Medicare looks at risk, surgical complexity, and documentation. This helps decide if IONM is needed during a procedure.
What are the financial considerations for Medicare beneficiaries undergoing IONM?
Beneficiaries should know about out-of-pocket costs. They should also understand supplemental insurance, Advance Beneficiary Notice, and financial help options.
Are there limitations or exclusions to Medicare coverage for IONM?
Yes, Medicare has limits and exclusions. This includes non-covered procedures, frequency limits, provider restrictions, and exclusions for new techniques.
How can denied Medicare IONM claims be appealed?
To appeal, understand the denial reasons. Then, navigate the five levels of Medicare appeals. Follow tips for successful appeals to get reimbursement.
What is the role of supplemental insurance in covering costs associated with IONM?
Supplemental insurance can help with IONM costs. It reduces the financial burden on Medicare beneficiaries.
How can healthcare providers ensure compliance with Medicare guidelines for IONM?
Providers must stay updated on coverage policies and billing guidelines. They also need to know about eligibility and documentation requirements. This ensures compliance and successful reimbursement.
References
JAMA Network. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2778477



































