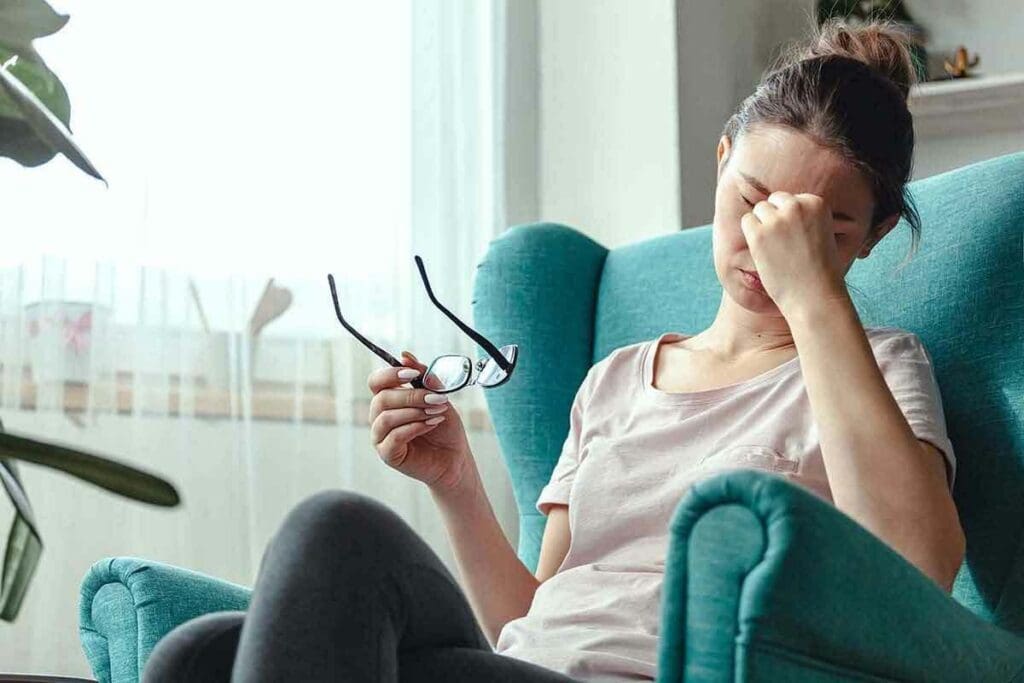
Do you often feel tired or lightheaded? You might wonder if low iron levels are the reason. Iron deficiency anemia affects millions, happening when the body doesn’t have enough iron for hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.Learn iron deficiency symptoms like fatigue and dizziness, plus how to detect low iron early.
It’s important to know the signs and symptoms of iron deficiency to get help quickly. Liv Hospital’s patient-focused care can help you find the right treatment.
Knowing how iron is key for health can help you see when you need a doctor. If you’re always tired or have other symptoms, see a doctor.
Key Takeaways
- Iron deficiency anemia is a widespread condition globally.
- Recognizing its symptoms is key for early diagnosis.
- Liv Hospital offers expert care for patients with iron deficiency.
- Understanding iron’s role in the body is vital for health.
- Consulting a healthcare professional is necessary for persistent symptoms.
Understanding Iron Deficiency and Its Impact on Health

Iron deficiency is a big problem worldwide. It affects many people and has serious health effects. It happens when the body doesn’t have enough iron to make hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
What Is Iron Deficiency?
Iron deficiency means the body has less iron. This leads to less hemoglobin being made. It can be caused by not eating enough iron, needing more iron, or losing blood too often. Key factors contributing to iron deficiency include:
- Inadequate dietary iron intake
- Poor absorption of iron from the diet
- Chronic blood loss due to menstruation, internal bleeding, or frequent donations
- Increased iron requirements during pregnancy or rapid growth periods
Why Iron Is Essential for Your Body
Iron is key for making hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is needed to carry oxygen to the body’s tissues. Without enough iron, tissues and organs don’t get the oxygen they need. This can cause many health problems.
- Supporting the production of healthy red blood cells
- Facilitating the transport of oxygen throughout the body
- Contributing to the proper functioning of muscles and the nervous system
Knowing how important iron is and recognizing its deficiency can help. People can take steps to keep their health good and avoid problems from low iron.
Recognizing Iron Deficiency Symptoms: The Complete Picture
Iron deficiency symptoms can be hard to spot, but it’s important to know them. When iron levels go down, the body can’t make enough hemoglobin. This leads to symptoms that can get worse over time.
How Symptoms Develop as Iron Stores Deplete
At first, the body uses stored iron to keep things running smoothly. But when these stores run out, symptoms start to show up. You might feel fatigue or weakness at first.
As the problem gets worse, symptoms get more serious. You might start to feel shortness of breath and dizziness.
Doctors say iron deficiency is a slow process. Symptoms can be different for everyone, making it hard to diagnose without tests. Knowing these symptoms is key to catching it early.
Why Symptoms Alone Can Be Misleading
Finding out if you have iron deficiency can be tricky. Symptoms like fatigue can mean many things, not just iron deficiency. This can lead to wrong or late diagnoses.
Knowing the specific signs of iron deficiency, like pale skin and cold hands and feet, helps doctors make better guesses. It’s also vital for people to know these signs to get checked by a doctor if they don’t go away.
Understanding all the symptoms of iron deficiency helps people spot the problem sooner. This means they can get help faster.
Fatigue and Weakness: Primary Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Persistent fatigue and weakness are signs you should check your iron levels. These aren’t just feelings of tiredness after a long day. They mean you’re constantly lacking energy, making it hard to do everyday things.
Why Iron Deficiency Causes Persistent Tiredness
Iron is key for making hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. It carries oxygen to your body’s parts. Low iron means less hemoglobin, less oxygen to your cells and organs.
This lack of oxygen makes you feel tired and weak. Your body’s cells can’t work right without enough oxygen.
Health experts say, “Fatigue is a big problem for people with iron deficiency anemia. It really affects their life quality.” This shows why we need to fix iron deficiency fast.
Distinguishing Iron-Related Fatigue from Other Causes
Fatigue from iron deficiency is different from other kinds. It’s a deep tiredness that doesn’t go away with rest. It’s not just feeling tired after hard work. Iron deficiency fatigue lasts all day, no matter what you do.
- Feeling weak and tired all the time
- Experiencing shortness of breath during normal activities
- Noticing a lack of energy that interferes with daily tasks
To see if fatigue is from iron deficiency, look at other symptoms and get tested. Spotting iron deficiency signs early helps fix your health faster.
Pale Skin and Mucous Membranes: Visual Indicators
A lack of iron can make your skin look pale. This isn’t just about the skin; mucous membranes can also be affected. The reason is simple: less hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, means less oxygen for your body.
The Science Behind Pallor in Iron Deficiency
Hemoglobin is key to keeping your skin its normal color. With low iron, your body makes less hemoglobin. This means less oxygen gets to your tissues, making your skin look pale.
This is really common in people with iron deficiency anemia. Here, iron is so low that hemoglobin production drops way down.
Understanding how hemoglobin and iron work together is important. Hemoglobin needs iron to carry oxygen. Without enough iron, it can’t do its job, causing paleness and other iron deficiency symptoms.
Areas of the Body Where Paleness Is Most Noticeable
Paleness from iron deficiency shows up in specific places. These include:
- The face, specially around the eyes and mouth
- The inner lining of the lower eyelids
- The mucous membranes inside the mouth
- The nail beds
Looking at these spots can help spot iron deficiency. Doctors often check these areas during physical exams to find signs of anemia and other issues.
Shortness of Breath and Heart Palpitations During Activity
Iron deficiency anemia can cause shortness of breath and heart palpitations when you’re active. This happens because your body can’t carry enough oxygen to its tissues. This is due to less hemoglobin being made.
How Iron Deficiency Affects Oxygen Transport
Iron is key for making hemoglobin, which carries oxygen. With less iron, your body makes less hemoglobin. This means less oxygen gets to your tissues and organs.
Your heart has to work harder to get enough oxygen. This can lead to heart palpitations and shortness of breath, even when you’re just doing light activities.
- Reduced hemoglobin levels lead to decreased oxygen delivery.
- The heart works harder, potentially causing palpitations.
- Shortness of breath occurs due to inadequate oxygen supply.
When to Be Concerned About Breathing Difficulties
It’s normal to feel a bit out of breath when you’re really active. But if you have iron deficiency anemia, you might feel it even when you’re just walking. You should worry if:
- Shortness of breath gets worse or lasts longer.
- Heart palpitations happen often or are very strong.
- You feel dizzy or faint when you’re having trouble breathing.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, see a doctor right away. They can figure out why you’re feeling this way and help you get better.
Headaches and Dizziness: Neurological Effects of Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency anemia can cause headaches and dizziness. This is because it lowers hemoglobin production. Hemoglobin is key for oxygen to reach the brain, affecting its function.
The Connection Between Brain Function and Iron Levels
Iron is vital for brain health. It helps make hemoglobin, which carries oxygen. Without enough iron, the brain gets less oxygen, causing symptoms.
Key aspects of how iron deficiency affects brain function include:
- Reduced oxygen delivery to brain tissues
- Impaired neurotransmitter synthesis and function
- Increased oxidative stress and inflammation
These factors lead to headaches and dizziness in those with iron deficiency anemia.
Patterns of Headaches Associated with Low Iron
Headaches from iron deficiency can be different. They might be:
- Persistent headaches that don’t get better with usual treatments
- Morning headaches that are worse because of dehydration after sleep
- Headaches with dizziness or lightheadedness, showing less oxygen to the brain
Knowing these patterns helps find iron deficiency as the headache cause.
It’s important to understand iron deficiency’s link to brain symptoms. If you have ongoing headaches and dizziness, see a doctor. They can find the real reason.
Cold Hands and Feet: Circulatory Signs of Low Iron
Feeling cold in your hands and feet might be a sign of iron deficiency. This symptom is linked to how low iron affects your blood flow.
Why Iron Deficiency Affects Body Temperature Regulation
Iron is key for making hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in your blood. With less iron, your body makes less hemoglobin. This means less oxygen gets to your tissues and organs.
This lack of oxygen makes it hard for your body to keep a steady temperature. You might feel cold, mostly in your hands and feet.
Distinguishing Between Iron-Related Cold Sensitivity and Other Causes
Cold hands and feet can have many causes, like poor blood flow or diabetes. To know if it’s due to iron deficiency, look for other signs and get tested.
| Cause | Common Symptoms | Distinguishing Features |
| Iron Deficiency | Cold hands and feet, fatigue, pale skin | Presence of other iron deficiency symptoms like brittle nails or hair loss |
| Poor Circulation | Cold hands and feet, pain in legs when walking | Often associated with cardiovascular disease or smoking |
| Diabetes | Cold hands and feet, increased thirst, frequent urination | High blood sugar levels and presence of diabetes-related complications |
Knowing why you feel cold in your hands and feet is important. If you think it might be iron deficiency, see a doctor for a check-up and treatment plan.
Low Iron in Women Symptoms: Gender-Specific Considerations
Iron deficiency affects women in many ways, mainly because of menstrual cycles and pregnancy. These factors make women more likely to have iron deficiency. This can lead to health problems if not treated.
Menstruation and Iron Loss
Menstruation plays a big role in iron deficiency in women. The blood lost each month depletes iron stores. This can cause iron deficiency anemia over time.
Women with heavy periods are at higher risk of iron deficiency.
Key Statistics on Menstruation and Iron Loss:
| Condition | Average Iron Loss | Risk of Iron Deficiency |
| Normal Menstruation | 20-30 mg per cycle | Moderate |
| Heavy Menstrual Bleeding | 50-100 mg per cycle | High |
Pregnancy and Increased Iron Requirements
Pregnancy raises iron needs due to increased blood volume and fetal development. Pregnant women need more iron for their health and the baby’s.
Iron needs during pregnancy are not just about the mother’s health; they are also vital for the baby’s development.
How Symptoms May Present Differently in Women
Iron deficiency symptoms in women can differ from men. They are often linked to menstruation and pregnancy. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. But, they can also include other concerns specific to women.
It’s important to understand these gender-specific factors for early detection and treatment of iron deficiency in women. Healthcare providers need to consider these when diagnosing and treating iron deficiency anemia in female patients.
Unusual Cravings and Pica: Strange Signs of Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency can cause pica, a condition where people crave non-food items. Pica is more than just odd eating habits. It’s a sign of nutritional issues, like iron deficiency.
What Is Pica and How It Relates to Iron Levels
Pica is when people eat non-food items like ice, dirt, or clay. It’s not just odd eating. It’s linked to iron deficiency anemia. The body might crave these items because it lacks essential nutrients.
Key Facts About Pica:
- Cravings for non-food items like ice, dirt, or clay
- Often associated with iron deficiency anemia
- Can be a sign of other nutritional deficiencies
Common Non-Food Items Craved During Iron Deficiency
People with iron deficiency might crave non-food items. Some common ones include:
| Non-Food Item | Description |
| Ice | Pagophagia, or ice eating, is a common manifestation of pica in iron-deficient individuals. |
| Dirt or Clay | Geophagy involves eating earth or clay and is often reported in cases of iron deficiency. |
| Other Items | Some people may crave paper, chalk, or other non-food substances. |
It’s important to understand and address these cravings. Eating non-food items can harm your health. Seeing pica as a sign of iron deficiency can lead to getting medical help.
Physical Changes: Brittle Nails, Hair Loss, and Skin Issues
Iron deficiency often shows up in our nails, hair, and skin. It affects their health and strength.
How Iron Affects Nail and Hair Structure
Iron helps make hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to our cells. This includes those that help our nails and hair grow.
Brittle Nails: Low iron can make nails weak and easy to break. This is because iron helps make keratin, a key nail protein.
Hair Loss: Iron deficiency can also cause hair loss. Without enough iron, hair follicles stop growing, leading to more hair falling out.
| Physical Change | Description | Relation to Iron Deficiency |
| Brittle Nails | Nails become fragile and prone to breaking | Lack of iron affects keratin production |
| Hair Loss | Excessive hair shedding | Iron deficiency pushes hair follicles into resting phase |
| Skin Issues | Skin becomes pale, dry, and itchy | Reduced hemoglobin levels affect skin health |
Skin Manifestations of Iron Deficiency
Skin problems are common with iron deficiency. Low iron can make the skin pale. It can also make the skin dry and itchy.
In conclusion, iron deficiency can cause big changes like brittle nails, hair loss, and skin problems. Spotting these signs early can help treat iron deficiency.
Lab Findings for Iron Deficiency Anemia: How Diagnosis Works
Lab tests are key in finding iron deficiency anemia and its causes. Finding iron deficiency anemia involves several steps. These include checking your health history and doing lab tests.
Key Blood Tests for IDA Diagnosis
Several blood tests are important for diagnosing iron deficiency anemia. These include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checks the levels of different blood cells.
- Iron Level Tests: Measures the iron in your blood.
- Ferritin Test: Looks at the iron storage protein levels.
- Transferrin Saturation Test: Shows how much iron is available for making red blood cells.
| Blood Test | Normal Range | Indications for IDA |
| Hemoglobin (Hb) | 13.5-17.5 g/dL (men), 12-16 g/dL (women) | Low levels indicate anemia |
| Ferritin | 20-250 ng/mL (men), 10-120 ng/mL (women) | Low levels indicate depleted iron stores |
| Transferrin Saturation | 20-50% | Low percentage indicates insufficient iron for erythropoiesis |
Understanding Your Test Results
It’s important to understand your blood test results for iron deficiency anemia. For example, low ferritin levels mean you have less iron. Low transferrin saturation shows you don’t have enough iron for making red blood cells.
When to Seek Medical Evaluation
If you have symptoms like fatigue or weakness, see a doctor. Early treatment can make a big difference.
Healthcare providers use both your medical history and lab tests to diagnose iron deficiency anemia. This helps them create a good treatment plan for you.
Conclusion: Addressing Iron Deficiency Effectively
Iron deficiency is a big health issue that needs quick action. Knowing why it happens, its signs, and how to find it is key. This helps people take steps to stop and fix it.
Seeing signs like tiredness, pale skin, and hard breathing means it’s time to see a doctor. They can help with the right treatment.
Acting fast to deal with iron deficiency can make you feel better. It stops serious problems and keeps you healthy. Knowing the risks and signs is the first step to getting better.
FAQ
What are the signs and symptoms of iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency can cause fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. You might also feel short of breath, have headaches, or feel dizzy. Women might experience heavy menstrual bleeding and pregnancy issues.
How can you tell if you are low in iron?
Look out for tiredness, weakness, or shortness of breath. Pale skin, headaches, and dizziness are also signs. A blood test is the only way to confirm.
What are the effects of iron deficiency on overall health?
Iron deficiency can cause anemia and affect your brain. It can also lead to brittle nails, hair loss, and skin problems.
How is iron deficiency anemia diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests to check for iron deficiency anemia. They look at hemoglobin, hematocrit, and iron levels. A complete blood count (CBC) and iron studies are key.
What are the causes of iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency can come from not eating enough iron or losing blood too much. Pregnancy and certain health issues can also cause it.
How does iron deficiency affect oxygen transport in the body?
Iron helps make hemoglobin, which carries oxygen. Without enough iron, you might feel short of breath. This is because your body can’t transport oxygen well.
Can iron deficiency cause neurological symptoms?
Yes, it can. You might get headaches, feel dizzy, or have restless leg syndrome. It can also make it hard to focus and think clearly.
How does iron deficiency affect women differently?
Women are more likely to have iron deficiency because of menstrual blood loss and pregnancy needs. Heavy periods are a common cause.
What is pica, and how is it related to iron deficiency?
Pica is when you crave non-food items. It’s often linked to iron deficiency. Eating non-foods can be a sign of iron deficiency.
How can iron deficiency be treated?
Treatment includes iron supplements and eating more iron-rich foods. You should also address why you’re losing iron. Always follow a doctor’s advice.
What are the key blood tests used to diagnose iron deficiency anemia?
Important tests are a complete blood count (CBC), serum iron, and ferritin levels. These help find iron deficiency anemia and how severe it is.
How can iron deficiency be prevented?
Eat a diet full of iron, avoid too much tea or coffee, and manage menstrual blood loss. Pregnant women might need iron supplements.
References
- World Health Organization. (2025, February 9). Anaemia. WHO. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/anaemia This fact sheet reports that about 30% of women aged 15-49 and 40% of children under 5 worldwide are affected by anemia, with iron deficiency being the leading cause.




































