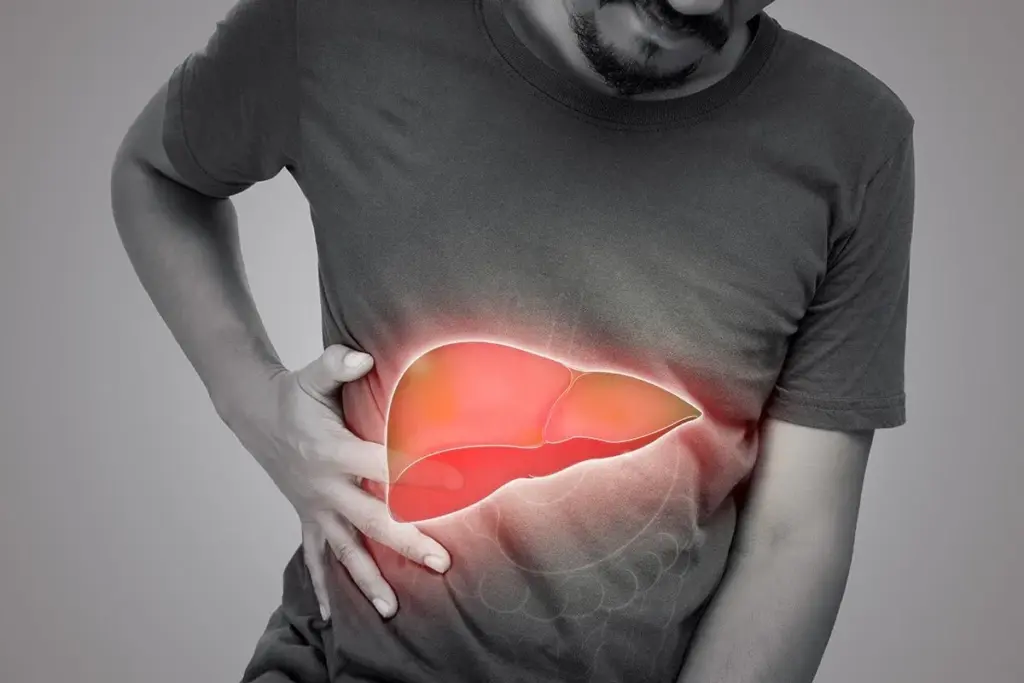
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease. It happens when the immune system attacks liver cells. This can cause inflammation and damage. If not treated, it can lead to serious health issues like cirrhosis and liver failure. But, with early treatment, many people can manage it and live longer.
There’s no cure for autoimmune liver hepatitis. But, long-term treatment can control the disease. This helps many patients go into remission. Managing autoimmune disease hepatitis needs a full plan. This includes knowing the different autoimmune hepatitis types and their symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic condition that can lead to serious liver damage if untreated.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition and improve life expectancy.
- Long-term immunosuppressive treatment can suppress the disease and lead to remission.
- Understanding the different types of autoimmune hepatitis is key for effective management.
- Comprehensive care includes treatment, patient support, and education.
Understanding Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is a condition where the immune system attacks the liver. This leads to inflammation and damage. It’s a chronic liver disease that needs a deep understanding to manage well.
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis?
Autoimmune hepatitis happens when the immune system sees liver cells as enemies. It attacks them, causing inflammation and damage. This leads to a chronic condition that can get worse if not treated.
Key aspects of autoimmune hepatitis include:
- The immune system’s mistaken attack on liver cells
- Chronic inflammation and possible liver damage
- The risk of cirrhosis or liver failure without treatment
Dr. [Last Name] says, “Autoimmune hepatitis is a big health challenge. It needs quick diagnosis and treatment to avoid long-term liver damage.”
This condition shows how important it is to understand the immune system’s role in health and disease.
How Autoimmune Hepatitis Affects the Liver
The liver is key for metabolism, detoxification, and making important proteins. When autoimmune hepatitis attacks, it can harm these functions. This leads to various health problems.
The effects of autoimmune hepatitis on the liver include:
- Increased inflammation, which can cause scarring
- Impaired liver function, affecting metabolism and detoxification
- Potential progression to cirrhosis or liver failure if not managed well
Knowing how autoimmune hepatitis affects the liver is key. It shows why early treatment and ongoing care are so important.
Types and Causes of Autoimmune Hepatitis
It’s important to know about the different types and causes of autoimmune hepatitis. This knowledge helps in managing the condition effectively. Autoimmune hepatitis is mainly divided into two types, based on certain antibodies and symptoms.
Type 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis
Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common, making up about 80% of cases. It can happen to anyone but often affects young or middle-aged women. People with this type have antinuclear antibodies (ANA) or anti-smooth muscle antibodies (SMA) in their blood.
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent liver damage.
Type 2 Autoimmune Hepatitis
Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is less common and mostly affects children or teenagers. It’s identified by liver/kidney microsomal type 1 (LKM-1) antibodies or anti-liver cytosol type 1 (LC1) antibodies. This type can get worse quickly if not treated right away.
Risk Factors and Possible Causes
The exact cause of autoimmune hepatitis is not known. But, some risk factors and triggers have been found. Genetics play a big role, with certain genes making it more likely to get the disease. Viral infections or certain drugs might also trigger it in some people.
According to the Medical organization, knowing these risk factors is key for early detection and treatment.
We know autoimmune hepatitis is complex, influenced by genetics, environment, and the immune system. More research is needed to understand it better and find better treatments.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Autoimmune hepatitis can show different symptoms in different people. This makes it hard to diagnose. The symptoms can be vague, adding to the challenge.
Common Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis vary. Here are some common ones:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort
- Aching joints
- Itching
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes)
- Enlarged liver
- Nausea
- Spider-like angiomas (blood vessels) on the skin
At first, symptoms might be mild or not there at all. But as the disease gets worse, symptoms can get stronger. This can really affect a person’s life.
“The diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis is based on a combination of clinical, laboratory, and histological findings.”
Source: Expert Opinion in Hepatology
Diagnostic Process and Tests
To diagnose autoimmune hepatitis, doctors use a detailed approach. They run several tests to rule out other liver diseases. The process includes:
- Blood tests to check liver function and find autoantibodies
- Imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI to see liver damage
- Liver biopsy to look at liver tissue for inflammation and damage
Laboratory Tests are key in diagnosing autoimmune hepatitis. These tests find specific autoantibodies and check liver inflammation levels.
| Test | Purpose | Expected Findings in Autoimmune Hepatitis |
| Liver Function Tests | Assess liver damage | Elevated liver enzymes |
| Autoantibody Tests | Detect specific autoantibodies | Presence of ANA, SMA, or LKM antibodies |
| Liver Biopsy | Examine liver tissue | Interface hepatitis, plasma cell infiltration |
Getting a diagnosis early and starting treatment can greatly improve outcomes. A thorough diagnostic process is vital for effective management.
Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Curable? Treatment Options
Knowing about treatment options for autoimmune hepatitis is key for patients. It helps them manage their condition and improve their life quality. While there’s no cure, long-term treatment can control the disease and help many patients get better.
Corticosteroid and Immunosuppressant Therapy
The main goal is to stop the body’s attack on itself. This is done by suppressing the immune system. Corticosteroids like prednisone and azathioprine are used together. This combo helps reduce liver inflammation and slow disease growth.
Achieving and Maintaining Remission
Getting into remission is a big goal in treating autoimmune hepatitis. Remission means the disease is controlled, and liver inflammation is low. To get there, it’s important to keep an eye on liver function and adjust meds as needed. Keeping the disease in check often means taking lower doses of medication.
| Treatment Phase | Primary Goal | Common Medications |
| Induction | Reduce liver inflammation | Prednisone, Azathioprine |
| Maintenance | Prevent relapse | Azathioprine, Low-dose Prednisone |
Living with Autoimmune Hepatitis
Living with autoimmune hepatitis means ongoing management and lifestyle changes. Patients should eat well and exercise regularly to help their liver. It’s also important to see healthcare providers regularly to keep an eye on the disease and adjust treatment if needed.
By understanding treatment options and working with healthcare providers, patients can live active and meaningful lives. It’s about managing the condition well and making choices that support overall health.
Conclusion
Autoimmune hepatitis is a serious condition that needs quick diagnosis and treatment. This is to prevent long-term liver damage. We’ve talked about the different types of autoimmune hepatitis, like Type 1 and Type 2, and their unique features.
It’s important to know the symptoms and how doctors diagnose it. This helps people get medical help early. With the right treatment, like corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, most people can manage their condition well.
Managing autoimmune liver hepatitis well lets people live active lives. It’s key to keep an eye on the disease and stick to the treatment plan. This helps prevent the disease from getting worse and ensures the best results.
Learning about autoimmune hepatitis and its treatments helps us support those affected. It also improves their quality of life.
FAQ
What is autoimmune hepatitis?
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease. It happens when the body’s immune system attacks liver cells. This leads to inflammation and damage.
What are the types of autoimmune hepatitis?
There are two main types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 is common and can happen at any age. Type 2 is less common and often affects children and young adults.
What are the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis?
Symptoms include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Some people may not show symptoms early on.
How is autoimmune hepatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging studies, and liver biopsy. Blood tests check liver function and look for specific antibodies.
Is autoimmune hepatitis curable?
There’s no cure, but treatment can manage the disease. Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants can induce remission and prevent damage.
What are the treatment options for autoimmune hepatitis?
Treatment includes corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and immunosuppressants to stop the immune system’s attack. The goal is to achieve and maintain remission.
Can autoimmune hepatitis go away?
With treatment, autoimmune hepatitis can go into remission. This means the disease is no longer active. But, ongoing management is needed to keep it in remission.
What lifestyle adjustments are necessary for managing autoimmune hepatitis?
A healthy lifestyle is key. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding too much alcohol. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are also important.
What causes autoimmune hepatitis?
The exact cause is unknown. It’s thought to be a mix of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers that make the immune system attack the liver.
Is hepatitis an autoimmune disease?
Autoimmune hepatitis is a specific type of hepatitis caused by an autoimmune response. Not all hepatitis is autoimmune; it can also be caused by viruses or toxins.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11155538/