
It’s important for patients to know the risks of brain blood clot surgery. At Liv Hospital, we offer clear and caring help to those with brain clots.
Brain clots can harm brain function a lot. Surgery is often needed to remove the clot and get blood flowing again. Our team explains the risks and treatment options for blood clot removal from brain procedures. We make sure patients get the safest and most effective care for their needs.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the risks of brain blood clot surgery is essential for patients.
- Brain clots can significantly impact brain function and require immediate attention.
- Surgical intervention is often necessary to remove the clot and restore blood flow.
- Liv Hospital provides internationally recognized, patient-focused care.
- Advanced surgical techniques and post-operative care have improved outcomes for patients undergoing brain clot surgery.
Understanding Brain Blood Clots and Their Impact
Brain blood clots, also known as intracranial hematomas, are a serious threat to brain health. They can form from trauma, aneurysms, or other medical issues.
We will look at the different types of brain blood clots and their effects. We will also discuss when surgery is needed.
Types of Brain Blood Clots
Brain blood clots are classified by their location and cause. The main types are:
- Epidural hematoma: Clot formation between the skull and the outer layer of the brain.
- Subdural hematoma: Clot formation between the outer and inner layers of the brain.
- Intracerebral hematoma: Clot formation within the brain tissue itself.
Each type has its own characteristics and treatment needs.
How Blood Clots Affect Brain Function
Blood clots in the brain can damage brain cells by applying pressure. This can lead to symptoms like:
- Headaches
- Confusion
- Weakness or paralysis
- Seizures
The severity of symptoms depends on the clot’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
When Surgical Intervention Becomes Necessary
Surgery is often needed for large clots or those in critical areas. The decision to operate depends on several factors, including the patient’s age, health, and the clot’s characteristics.
We will explore what influences the decision to go for surgery.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Surgery Decision |
|---|---|---|
| Clot Size | Large clots are more likely to cause significant brain damage. | Large clots often require surgical removal. |
| Clot Location | Clots in critical areas can cause severe neurological deficits. | Location can dictate the necessity and approach for surgery. |
| Patient’s Health Status | Underlying health conditions can affect surgical risks. | Health status is a key factor in deciding whether to operate. |
Is Brain Blood Clot Surgery Dangerous? Examining the Risks
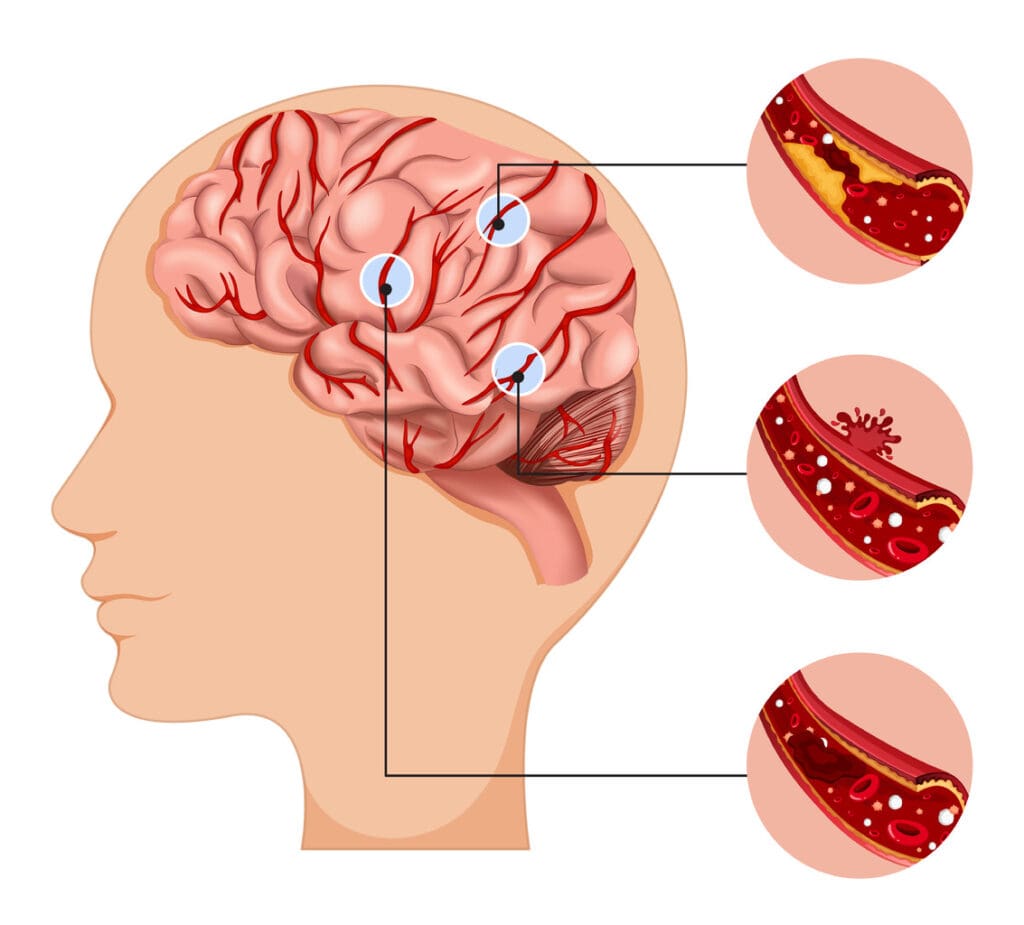
It’s important for patients and doctors to know the risks of brain blood clot surgery. This surgery can save lives but comes with big risks. These risks need to be thought about carefully.
Immediate Surgical Complications
Brain blood clot surgery can cause serious problems right away. These include:
- Bleeding or hemorrhage during or after surgery, which can be life-threatening.
- Infection at the surgical site, which requires prompt treatment.
- Stroke or cerebral vasospasm, which can result from the surgery itself or as a reaction to the surgical intervention.
These immediate complications show why skilled neurosurgical teams and good postoperative care are so important.
Potential Long-Term Complications
Brain blood clot surgery can also lead to long-term problems. These include:
- Neurological deficits, such as weakness, numbness, or cognitive impairments, depending on the area of the brain affected.
- Seizures, which may occur as a result of the surgery or the underlying condition that led to the blood clot.
- Cognitive and behavioral changes, which can impact the patient’s quality of life and require ongoing rehabilitation.
Mortality and Severe Outcome Rates
The death rates from brain blood clot surgery depend on many things. These include the patient’s health, the clot’s location and size, and the surgery method. Research shows that while risks are high, many patients have successful surgeries and see big improvements.
We stress that brain blood clot surgery is risky but sometimes necessary. It can prevent more brain damage or death. Deciding to have surgery should be done after weighing the benefits and risks with a qualified neurosurgeon.
Surgical Techniques for Brain Blood Clot Removal
Neurosurgery has made big strides in removing brain blood clots. Each method is designed for different patients. The choice depends on the clot’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
Traditional Craniotomy Procedure
A traditional craniotomy removes part of the skull to reach the brain. This lets surgeons see and remove the clot. Craniotomy for blood clot removal is best for big clots or hard-to-reach areas.
We watch the patient’s vital signs and brain activity closely during the surgery. Craniotomy works well but takes longer to recover from than newer methods.
Burr Hole Drainage Method
The burr hole method is less invasive. It makes small holes in the skull to drain the clot. This is good for clots near the brain’s surface and can be done with a small cut.
Burr hole drainage is done under local anesthesia. This lowers the risk of general anesthesia and leads to less damage and quicker recovery than craniotomy.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Approaches
Minimally invasive surgery for brain blood clots is becoming more common. It aims to reduce recovery time and damage. These methods use advanced imaging and special tools for smaller cuts.
We’re always improving these techniques to help our patients more. By using minimally invasive surgery and the latest diagnostic tools, we can treat brain blood clots more effectively.
Factors Affecting Blood Clot Removal Effectiveness
When we look at how well brain blood clot removal works, many things matter. The success of this surgery depends on several key factors. We must carefully look at these to get the best results for our patients.
Clot Location and Accessibility
Where the blood clot is in the brain is very important. Clots in easier-to-reach spots are simpler to remove. We use special imaging to find the clot and plan the best surgery.
But, clots in harder-to-reach areas are tougher to deal with. We have to think hard about the risks and benefits of surgery. Sometimes, other treatments might be better.
Size and Age of the Blood Clot
The size and how long the clot has been there also matter a lot. Bigger clots need bigger surgeries, which can be riskier. Older clots stick to the brain more, making them harder to remove.
Acting fast is often key to removing clots successfully. The sooner we treat a clot, the better the patient’s chances of doing well.
Patient-Specific Considerations
Every patient is different, and that affects how well clot removal works. The patient’s health, including any other health issues, plays a big role. We look at age, other health problems, and how well the brain is working at surgery time.
By thinking about these things, we can make surgery and care after surgery fit each patient’s needs. This helps improve their chances of a good outcome.
Causes of Blood Clots During and After Brain Surgery
Brain surgery is lifesaving but comes with risks. Blood clots can form during and after the surgery. We’ll look at why this happens, focusing on surgical trauma, immobility after surgery, and health conditions.
Surgical Trauma and Inflammation
Surgical trauma in brain surgery can cause inflammation. This increases the risk of blood clots. The body’s response to injury includes chemicals that help clots form. This natural defense can cause problems in brain surgery.
The surgical site itself can be a source of clot formation. This is true if there’s a lot of tissue damage or if the surgery is in areas with lots of blood vessels. Knowing this helps doctors prevent problems.
Prolonged Immobility Following Surgery
After brain surgery, patients often can’t move much. Prolonged immobility increases the risk of blood clots. This is because blood doesn’t circulate well when patients are less active.
To lower this risk, doctors encourage patients to move early. They might also use devices to help blood flow in the legs.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Patients with brain surgery often have health issues that raise blood clot risk. Conditions like cancer, heart disease, and obesity can increase this risk.
| Underlying Condition | Risk Factor for Blood Clots |
|---|---|
| Cancer | High |
| Heart Disease | Moderate to High |
| Obesity | Moderate |
Knowing these risk factors helps in managing and preventing blood clots. By identifying high-risk patients, doctors can take steps to lower the chance of blood clots during and after brain surgery.
Post-Surgical Treatment and Rehabilitation
After brain blood clot surgery, the right treatment is key. It includes rehabilitation and watching for any problems. We make sure the recovery is thorough for the best results.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Right after surgery, it’s important to watch for any issues. Patients often need to stay in an ICU to catch problems early.
We work hard to keep the patient stable, manage pain, and prevent infections. This early care is vital for a good recovery.
Long-Term Rehabilitation Strategies
Rehab plans are made just for each patient. They aim to bring back lost skills and improve life quality. Physical, occupational, and speech therapy are big parts of this.
Our team creates a rehab plan that fits each person. This helps them become independent again and adjust to any lasting changes.
Monitoring for Recurring Clots
Watching for new clots is a big part of care after surgery. We teach patients about severe headache, confusion, or weakness signs. We stress the need to get help right away if these happen.
We also have regular check-ups and scans. These help catch any new clots or problems early, so we can act fast.
Preventing Blood Clots in Brain Surgery Patients
Preventing blood clots is key for brain surgery patients. We use many strategies to lower the risk of blood clots and other complications.
Pharmacological Prevention Methods
Medicine is a big part of preventing blood clots. Anticoagulant medications help a lot. We often use low molecular weight heparin or unfractionated heparin because they work well.
| Anticoagulant Medication | Dosing Frequency | Monitoring Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Low Molecular Weight Heparin | Once or twice daily | Periodic anti-Xa levels |
| Unfractionated Heparin | Two to three times daily | Regular aPTT monitoring |
Non-Pharmacological Prevention Strategies
There are also non-medical ways to prevent blood clots. Early mobilization helps blood flow and reduces clot risk. We also use compression devices like IPC to help.
Other non-medical strategies include wearing compression stockings and staying hydrated. We take a full approach that includes medicine and non-medical methods to prevent blood clots in brain surgery patients.
Advances in Brain Blood Clot Treatment and Research
Medical technology and research are making big strides in treating brain blood clots. These changes are key to better patient care and lower surgery risks. We’re seeing big improvements in surgery, medicine, and care plans.
Emerging Surgical Technologies
Neurosurgery is getting a boost from new tech. Now, we have minimally invasive surgery and endovascular procedures. These methods are less invasive and help patients recover faster.
- Minimally invasive surgery causes less damage and helps patients heal quicker.
- Endovascular procedures treat blood clots without needing open surgery.
- Advanced imaging makes surgeries more precise.
Research on Early Heparin Administration
Studies on early heparin use are showing great promise. They suggest that starting anticoagulation therapy early can prevent blood clots in at-risk patients.
“Early heparin administration has been shown to be effective in preventing venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing major surgery.”
We’re exploring the best time and amount of heparin to use. This aims to boost its benefits while lowering risks.
International Treatment Standards and Protocols
Using international care standards is vital for quality patient care. These standards help make treatment more consistent and effective worldwide.
By sticking to these protocols, doctors can provide better, more consistent care. This leads to better results for patients.
In summary, treating brain blood clots is getting better thanks to new surgery tech, medicine research, and global care standards. These advances are improving patient care and giving hope to those with brain blood clots.
Conclusion: Weighing the Risks and Benefits of Brain Blood Clot Surgery
Deciding on brain blood clot surgery needs careful thought. This article has covered the details of brain blood clots, the risks of surgery, and how treatments have gotten better. These improvements have helped patients more than ever before.
Choosing to have surgery should be a well-thought-out decision. It’s important to consider your own situation and the latest medical findings. Knowing the risks and benefits helps patients make the right choice for their care.
As medical technology and treatments keep getting better, so does the chance of success for surgery. It’s key to talk to doctors to find the best treatment plan. This way, you can understand the risks and benefits of surgery clearly.
FAQ
What are the risks associated with brain blood clot surgery?
Brain blood clot surgery can lead to immediate issues like bleeding or infection. It can also cause long-term problems, such as neurological deficits. Yet, many patients see big improvements after the surgery.
How are brain blood clots typically treated?
Doctors often use surgery to remove brain blood clots. This helps restore blood flow to the brain. The type of surgery depends on the clot and the patient’s health.
What are the different surgical techniques used for brain blood clot removal?
There are several ways to remove brain blood clots. These include traditional craniotomy, burr hole drainage, and minimally invasive methods. The choice depends on the clot’s location, size, and the patient’s health.
How can blood clots be prevented during or after brain surgery?
To prevent blood clots, doctors use medicine and other strategies. Anticoagulants are one option. Early movement and mechanical devices are also used.
What is the importance of post-surgical treatment and rehabilitation?
After surgery, treatment and rehab are key. They help manage complications, regain lost functions, and watch for clot return.
What are the latest developments in the treatment of brain blood clots?
New technologies and research are changing how we treat brain blood clots. Early heparin use and international standards are among the advancements.
How do underlying medical conditions affect the risk of blood clots during or after brain surgery?
Certain health conditions can increase the risk of blood clots after brain surgery. This shows why each patient’s situation needs careful attention.
What factors affect the success of brain blood clot removal?
Success depends on several things. These include the clot’s location, size, and age, as well as the patient’s specific situation.
How do surgical trauma and inflammation contribute to clot formation?
Surgery can cause trauma and inflammation. This disrupts blood flow and clotting, leading to clot formation.
What is the role of prolonged immobility in clotting risk after brain surgery?
Staying immobile for too long after surgery increases clot risk. Early movement is key to preventing this.
How is the decision made to perform surgery for a brain blood clot?
Deciding on surgery involves many factors. These include the clot’s location, size, and the patient’s health. The risks and benefits of surgery are weighed carefully.
FAQ
What are the risks associated with brain blood clot surgery?
Brain blood clot surgery can lead to immediate issues like bleeding or infection. It can also cause long-term problems, such as neurological deficits. Yet, many patients see big improvements after the surgery.
How are brain blood clots typically treated?
Doctors often use surgery to remove brain blood clots. This helps restore blood flow to the brain. The type of surgery depends on the clot and the patient’s health.
What are the different surgical techniques used for brain blood clot removal?
There are several ways to remove brain blood clots. These include traditional craniotomy, burr hole drainage, and minimally invasive methods. The choice depends on the clot’s location, size, and the patient’s health.
How can blood clots be prevented during or after brain surgery?
To prevent blood clots, doctors use medicine and other strategies. Anticoagulants are one option. Early movement and mechanical devices are also used.
What is the importance of post-surgical treatment and rehabilitation?
After surgery, treatment and rehab are key. They help manage complications, regain lost functions, and watch for clot return.
What are the latest developments in the treatment of brain blood clots?
New technologies and research are changing how we treat brain blood clots. Early heparin use and international standards are among the advancements.
How do underlying medical conditions affect the risk of blood clots during or after brain surgery?
Certain health conditions can increase the risk of blood clots after brain surgery. This shows why each patient’s situation needs careful attention.
What factors affect the success of brain blood clot removal?
Success depends on several things. These include the clot’s location, size, and age, as well as the patient’s specific situation.
How do surgical trauma and inflammation contribute to clot formation?
Surgery can cause trauma and inflammation. This disrupts blood flow and clotting, leading to clot formation.
What is the role of prolonged immobility in clotting risk after brain surgery?
Staying immobile for too long after surgery increases clot risk. Early movement is key to preventing this.
How is the decision made to perform surgery for a brain blood clot?
Deciding on surgery involves many factors. These include the clot’s location, size, and the patient’s health. The risks and benefits of surgery are weighed carefully.
References
- What you can expect from your brain blood clot surgery recovery. Retrieved from: https://jhawarneuro.com/what-you-can-expect-from-your-brain-blood-clot-surgery-recovery/
- Craniotomy Recovery Time: What to Expect Week by Week. Retrieved from: https://drgurneetsawhney.com/blog/craniotomy-recovery-time-what-to-expect-week-by-week/
- Brain Clot Recovery Time: What to Expect. Retrieved from: https://www.starhealth.in/answers/what-is-the-recovery-time-for-a-brain-clot/























