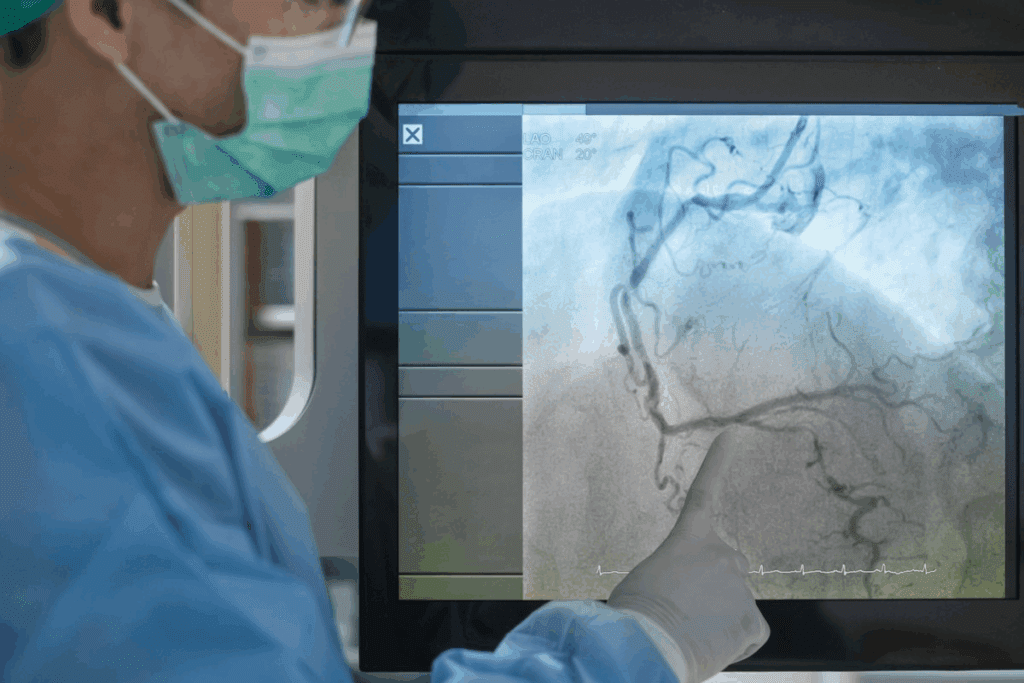
Laser ablation equipment has changed how we treat many medical issues. It’s a less invasive option compared to old surgeries. Over 100,000 procedures have been done worldwide, showing its growing popularity. Get the definitive answer: is laser ablation FDA approved? Understand the regulation of the laser ablation equipment clearly.
Looking into laser ablation, it’s key to know about the rules for these medical tools. The FDA’s approval process is vital. It makes sure laser ablation equipment, like Visualase, is safe and works well.
We’ll dive into why FDA approval matters for laser ablation equipment. We’ll see how it affects both patients and doctors.
Key Takeaways
- FDA approval is key for the safety and success of laser ablation equipment.
- Visualase is a top example of FDA-approved laser ablation tech.
- Knowing the rules is important for everyone involved in healthcare.
- Laser ablation is a new, less invasive way to treat diseases.
- More and more people around the world want this technology.
What Is Laser Ablation and How Does It Work?
Laser ablation is a new medical technology that changes how we treat some diseases. It uses a laser to remove bad tissue safely, without the need for big surgeries.
Definition and Basic Principles
Laser ablation uses a strong laser beam to heat and kill bad tissue. It’s done under MRI watch to make sure it’s done right. The laser goes through a thin probe, making it safe and less invasive.
The laser works by heating the bad tissue only. This way, it can destroy the bad tissue without harming the good tissue around it. This is why it’s great for treating sensitive areas, like the brain.
Types of Medical Laser Ablation Procedures
There are many laser ablation procedures for different health issues. Some common ones include:
- Laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) for brain tumors and epilepsy
- Treatment of certain cardiac arrhythmias through laser ablation of abnormal electrical pathways
- Dermatological procedures for skin lesions and cosmetic treatments
- Gynecological and urological applications for various conditions
Each procedure is customized for the patient’s needs. The right laser and settings are chosen for each case.
Evolution of Laser Technology in Medicine
Laser technology in medicine has grown a lot in recent years. Old lasers were big and not very good. But now, laser systems are much better, with:
- Better laser precision and control
- Improved real-time imaging and monitoring
- Smaller, less invasive delivery systems
- Better treatment planning and dosimetry
These improvements mean more people can be treated with laser ablation. It’s safer and works better. As technology gets even better, we’ll see more uses for laser ablation in medicine.
The FDA Approval Process for Medical Devices

The FDA oversees medical devices through a detailed approval process. This ensures devices are safe and work well. It’s key for keeping people healthy and giving doctors good treatment options.
Classification of Medical Devices
The FDA sorts medical devices into three groups based on risk. Class I devices are the least risky and follow basic rules. Class II devices are a bit riskier and need more rules. Class III devices, like implants, are the most risky and face the toughest rules.
| Device Class | Risk Level | Regulatory Controls |
| Class I | Low | General Controls |
| Class II | Moderate | General and Special Controls |
| Class III | High | Premarket Approval (PMA) |
Premarket Approval vs. 510(k) Clearance
Devices need either Premarket Approval (PMA) or 510(k) clearance to be sold in the U.S. Premarket Approval is strict and needed for Class III devices. It requires showing the device is safe and works well through clinical data.
510(k) clearance is for devices similar to ones already approved. It needs less data but ensures the device meets safety and performance standards.
“The 510(k) clearance process allows for the marketing of devices that are substantially equivalent to predicate devices, facilitating innovation while ensuring safety and effectiveness.”
— FDA Statement
Clinical Trial Requirements for Laser Systems
Laser systems, often Class II or III, might need clinical trials for approval. These trials check if the device is safe and works well in real use. The FDA makes sure these trials are done right, under an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE).
Knowing the FDA approval process helps manufacturers and doctors. It ensures devices are safe and effective, helping everyone get better care.
Current FDA Status of Laser Ablation Equipment
It’s key for healthcare providers and patients to know the FDA status of laser ablation equipment. The FDA makes sure these devices are safe and work well.
Fully Approved Applications
Some laser ablation devices are fully approved by the FDA for certain uses. For example, Medtronic’s Visualase system is okay for MRI-guided laser therapy in the brain. This approval comes from solid clinical data showing it’s safe and effective.
Other uses that are fully approved include:
- Treating certain heart rhythm problems
- Removing unwanted hair and skin spots
- Helping with heavy menstrual bleeding
These approvals mean the FDA has checked the evidence for laser ablation in these areas.
Conditionally Approved Applications
Some laser ablation devices have conditional approval. This is through the FDA’s 510(k) clearance or IDEs for trials. For example, some lasers for tumor treatment are conditionally approved because they’re similar to other devices.
These conditionally approved uses need more data after they’re on the market. We should remember that:
| Device | Condition | FDA Status |
| Visualase | Brain tumors | Fully Approved |
| Cardiac Laser System | Cardiac arrhythmias | Conditionally Approved |
| Dermatological Laser | Unwanted hair removal | Fully Approved |
Investigational Device Exemptions
Laser ablation devices in trials have an IDE. This lets makers get data for future FDA approval.
“The IDE process is key for laser ablation tech, helping get vital data on new uses and improvements.” –
FDA Guidelines
Devices with IDEs face strict checks and reports to keep patients safe.
Medtronic Visualase: FDA Approval Journey and Applications
Medtronic Visualase is revolutionizing neurological treatments with its advanced technology. This system offers precise, minimally invasive treatments for many neurological issues.
System Components and Technology
The Medtronic Visualase system has several key parts. They work together for accurate and effective treatments. These include:
- A laser ablation catheter
- A cooling system to prevent overheating
- Advanced MRI-compatible hardware
- Sophisticated software for real-time temperature monitoring
This tech allows for real-time monitoring of the ablation process. This means doctors can control and adjust the treatment as needed.
FDA Clearance Timeline and Process
Medtronic Visualase went through a strict FDA evaluation. This process showed its safety and effectiveness. The FDA clearance timeline included:
- Pre-submission meetings with the FDA
- Submission of a De Novo classification request
- Clinical trials to gather data on safety and effectiveness
- FDA review and clearance
The FDA clearance was based on clinical data. This data showed the device’s safety and effectiveness in treating certain conditions.
Approved Medical Indications
Medtronic Visualase is cleared for treating specific neurological conditions. These include:
| Condition | Description |
| Epilepsy | Laser ablation for epileptogenic foci |
| Brain Tumors | Laser interstitial thermal therapy for certain tumor types |
These approved uses show the Medtronic Visualase system’s versatility. It can treat complex neurological conditions with minimally invasive procedures.
Laser Ablation as an Alternative to Traditional Craniotomy
Laser ablation is becoming a new option for some brain surgeries. It’s less invasive than traditional craniotomy. This could mean faster recovery times and less damage to tissues.
Comparing Invasiveness and Recovery
Traditional craniotomy requires removing part of the skull. This can cause a lot of damage and lead to longer recovery times. Laser ablation, on the other hand, uses a small probe through a tiny hole. This makes the procedure less invasive.
Key differences in invasiveness and recovery:
| Procedure | Invasiveness Level | Typical Recovery Time |
| Traditional Craniotomy | High | Several weeks to months |
| Laser Ablation | Low | A few days to a few weeks |
Patient Selection Criteria
Not every patient is right for laser ablation. The choice depends on several factors. These include the type and location of the lesion, the patient’s health, and any previous treatments.
Careful patient selection is key for laser ablation success. The size and location of the lesion, along with the patient’s medical history, are important in deciding if this procedure is suitable.
Clinical Outcomes and Success Rates
Research shows laser ablation can work well for some conditions. This includes epilepsy and brain tumors. It has success rates similar to traditional surgery in certain cases.
Clinical outcomes comparison:
| Condition | Success Rate with Laser Ablation | Success Rate with Traditional Craniotomy |
| Epilepsy | 70-80% | 60-80% |
| Brain Tumors | 80-90% | 70-90% |
As technology improves, we’ll see more uses for laser ablation in brain surgery.
FDA-Approved Laser Ablation for Epilepsy Treatment
In the world of epilepsy treatment, laser ablation is a big deal. It’s FDA-approved and works well without being too invasive. We’ll look into how it works, its benefits, and how it stacks up against other treatments.
Targeting Epileptogenic Foci
Laser ablation for epilepsy involves finding and treating the brain areas that cause seizures. It uses MRI to pinpoint these areas. This makes it a good choice for those who don’t respond to drugs.
Patient Selection Guidelines
Choosing the right patients is key for laser ablation to work. It’s best for those with hard-to-treat epilepsy. Doctors use tests and scans to see if it’s right for someone.
Effectiveness Compared coordin to Resective Surgery
Laser ablation can be as good as surgery for some patients. It causes less damage and might have fewer side effects. But, it depends on the patient and their epilepsy.
| Treatment Aspect | Laser Ablation | Resective Surgery |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | More invasive |
| Seizure Outcome | Comparable in selected cases | Variable, depending on the case |
| Recovery Time | Generally shorter | Often longer |
Laser ablation is a big step forward in treating epilepsy. It shows how technology can help patients. Doctors can now offer better choices to their patients.
Laser Ablation for Brain Tumor Treatment
Laser ablation is a new way to treat brain tumors. It’s less invasive than old surgery methods. This method uses lasers to kill tumor cells without harming the brain around them.
Types of Tumors Approved for Laser Treatment
Laser ablation works best on glioblastomas and hypothalamic hamartomas. These tumors are hard to reach with regular surgery. Laser ablation is precise, making it a good choice for these cases.
Procedural Overview and Imaging Guidance
The laser ablation process uses MRI-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT). It lets doctors watch the treatment in real-time. This ensures the tumor is targeted right, while keeping the brain safe.
First, a laser probe is put into the tumor. Then, laser energy heats and kills the tumor cells.
Clinical Evidence and Long-term Outcomes
Many studies show laser ablation works well for brain tumors. It helps control tumors, reduces symptoms, and improves life quality. Long-term results are promising, showing laser ablation’s value in treating some brain tumors.
Types of FDA-Approved Laser Ablation Equipment
Laser ablation technology has grown a lot. Now, there are many FDA-approved tools for medical use. These tools help treat many health issues more accurately and safely.
MRI-Guided Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy Systems
MRI-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) systems are a big step forward. They use MRI to guide lasers to the right spot. The Visualase system by Medtronic is a great example. It’s used for treating brain tumors and epilepsy in a less invasive way.
These systems can watch the temperature in real-time. This makes the treatment safer and more effective. It’s very useful in brain surgery, where being precise is key.
Stereotactic Laser Ablation Systems
Stereotactic laser ablation systems mix stereotactic surgery with laser tech. They’re made for precise treatments, like removing deep brain lesions.
The SLA (Stereotactic Laser Ablation) system is a good example. It’s a less invasive option compared to old surgery methods. It uses stereotactic guidance to hit the right spot with less damage to nearby tissue.
Comparative Analysis of Available Technologies
When we look at MRI-guided LITT systems and stereotactic laser ablation systems, we see some differences. MRI-guided systems let doctors watch the temperature in real-time, which is important for some treatments. Stereotactic systems, on the other hand, are very accurate for finding specific spots in the body.
Choosing between these depends on the treatment needed, the type of tissue, and the doctor’s choice. Both are important tools for treating different health issues.
Laser ablation tech is getting better all the time. We’ll see more precise, safer, and better treatments. New systems and better versions of old ones will help treat more conditions and improve care for patients.
Other FDA-Approved Applications of Laser Ablation
Laser ablation is used in many medical fields, thanks to its versatility. It’s not just for the brain; it’s also used in other areas of medicine.
Cardiac Arrhythmia Treatment
Laser ablation helps treat heart rhythm problems like atrial fibrillation. It uses laser energy to make precise cuts in the heart. This helps get the heart back to a normal beat.
Using laser ablation for heart problems has many benefits. It’s less invasive, which means less recovery time. It also targets the problem areas more accurately than older methods.
Dermatological Procedures
In dermatology, laser ablation is used for both beauty and health treatments. It can resurface the skin, remove hair, treat blood vessel problems, and more. The laser’s settings can be adjusted to protect the skin around the treated area.
Some common uses of laser ablation in skin care include:
- Removing benign skin growths
- Improving skin texture and appearance
- Getting rid of unwanted hair
Gynecological and Urological Applications
Laser ablation is also used in gynecology and urology. In gynecology, it treats endometriosis and chronic pain. In urology, it’s used for BPH and other urinary issues.
Using laser ablation in these areas has many benefits. It leads to less pain and quicker recovery. It can also improve treatment results in some cases.
As laser technology gets better, we’ll see it used in even more medical areas. This could lead to new treatments and options for patients.
Benefits and Advantages of FDA-Approved Laser Ablation
FDA-approved laser ablation has changed medical treatment a lot. It offers a safer and more effective way to treat many medical conditions. This is different from old surgical methods.
Minimally Invasive Nature and Reduced Scarring
Laser ablation is minimally invasive, which means it’s safer and heals faster. It doesn’t need big cuts like old surgeries. This is great for areas where looks matter a lot.
- Smaller cuts mean less chance of infection
- Less pain after the treatment
- Less scarring, making things look better
Shorter Hospital Stays and Recovery Times
Laser ablation means you can leave the hospital and get back to life faster. It’s less harsh on the body than old surgeries. This makes recovery quicker.
- Get back to daily life sooner
- Save money on hospital costs
- Less chance of getting sick in the hospital
Precision Targeting and Real-time Monitoring
This technology lets doctors target the right area with precision. It also lets them watch and adjust the treatment live. This makes the treatment safer and more effective.
As medical tech gets better, laser ablation will help more people. Knowing its benefits helps patients and doctors choose the best treatments.
Potential Risks and Complications of Laser Ablation
It’s key for healthcare providers and patients to know about the risks of laser ablation. This treatment has changed how we handle many health issues. But, we must also deal with the risks it brings.
FDA-Documented Adverse Events
The FDA has listed several bad outcomes from laser ablation. These include:
- Infection at the treatment site
- Bleeding or hemorrhage
- Nerve damage or neurological deficits
- Thermal injury to surrounding tissues
These issues show why it’s vital to choose the right patients, use the right techniques, and care for them well after treatment.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Healthcare providers use many ways to lower the risks of laser ablation. These include:
- Comprehensive Patient Evaluation: Checking if a patient is right for laser ablation, looking at their health history and current condition.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Using MRI or other imaging to guide the treatment and watch it in real-time.
- Precise Treatment Planning: Planning carefully to hit the right spot and avoid important areas.
By using these methods, doctors can greatly cut down the chance of problems.
Patient Monitoring Requirements
Watching patients closely before, during, and after laser ablation is very important. This means:
- Keeping an eye on vital signs during the treatment
- Using real-time imaging to see how the treatment is going and spot any problems
- Watching for signs of trouble after the treatment
Having a team of doctors from different fields helps a lot in taking care of patients before, during, and after laser ablation. This way, we can make sure patients get the best care.
Insurance Coverage and Cost Considerations
Many patients worry about the cost of laser ablation, including insurance coverage. As this treatment grows in popularity, it’s key to know the costs and insurance policies. This knowledge is vital for those thinking about this option.
Medicare and Medicaid Coverage Policies
Medicare and Medicaid’s coverage for laser ablation changes based on the procedure and patient’s health. Medicare often covers FDA-approved treatments, including some laser ablation, if it’s needed. Patients should check their Medicare or Medicaid plan for details.
“Medic are Part B (Medical Insurance) covers certain FDA-approved procedures, including some laser ablation treatments, when medically necessary.”Medicare.gov
To get the latest on coverage, patients should talk to their insurance and healthcare team.
Private Insurance Reimbursement
Private insurance for laser ablation varies a lot. Some plans cover it fully, while others might need copays, deductibles, or pre-approval. Patients should look at their policy or call their insurance to know what’s covered.
| Insurance Type | Typical Coverage | Patient Responsibility |
| Medicare | Generally covers FDA-approved procedures | May include copays, deductibles |
| Medicaid | Varies by state and planmen | Often minimal to no out-of-pocket |
| Private Insurance | Varies widely by policy and provider | Can include copays, deduct Eraibles, coinsurance |
Patient Assistance Programs
For those struggling financially, help is available. Manufacturers, non-profits, and government programs offer assistance. Patients can ask their healthcare provider or contact the manufacturers for more information.
Knowing about insurance and aid programs can help with the cost of laser ablation. We suggest patients look into these options. This way, they can get the care they need without financial stress.
Future Developments in Laser Ablation Technology
The future of laser ablation technology looks bright. Ongoing research aims to make it safer and more effective. This technology is leading the way in medical innovation.
Advancements in Clinical Trials
Many laser ablation systems are being tested in clinical trials. These tests check their safety and how well they work. They help us treat more conditions and improve patient care.
Notable trials include:
- Studies on using laser ablation for some cancers
- Research on treating neurological disorders with laser ablation
- Trials on using laser ablation for heart diseases
Expanding Applications Seeking FDA Approval
New uses for laser ablation are being researched and sent to the FDA. These new uses could make laser ablation even more useful in medicine.
“The growth of laser ablation into new areas is a big step towards better, less invasive treatments for patients.”
Technological Innovations on the Horizon
New technology is also on the way for laser ablation. These advancements will make procedures more precise and safer. They promise better results for patients.
Some of these innovations include:
- Better imaging for guiding laser ablation
- New laser tech for more accurate targeting
- Software for real-time monitoring and adjusting laser settings
Advanced imaging and laser tech will change minimally invasive surgery.
The future of medicine is about precision and less invasiveness. Laser ablation is leading this change.
We’re excited about the future of laser ablation technology. It has the power to change patient care. As these advancements grow, we’ll keep you updated on this fast-changing field.
Conclusion
Laser ablation is a cutting-edge medical technology that has won FDA approval for many uses. We’ve looked into what laser ablation is, how it works, and the FDA’s approval process. We’ve also talked about the current state of laser ablation equipment. This technology is known for being minimally invasive, precise, and allowing for real-time monitoring. These benefits make it a good choice compared to old-school surgeries. But, we’ve also talked about the possible downsides of laser ablation. Laser ablation is getting better, and we’ll see more uses and improvements soon. Knowing about FDA approval and what laser ablation means is key for patients and doctors. It helps them make smart choices about treatments.
In short, laser ablation is a big step forward in medicine. It offers precise and less invasive ways to treat many health issues. We hope this guide has helped everyone understand laser ablation and its FDA status. This knowledge will help patients and doctors use this technology wisely.
FAQ
What is laser ablation, and how does it work?
Laser ablation is a minimally invasive procedure. It uses a laser to remove damaged tissue. The laser delivers heat to the area, guided by MRI images.
Is Medtronic Visualase FDA approved for epilepsy treatment?
Yes, Medtronic Visualase is FDA approved for treating epilepsy. It’s used for laser therapy in patients with hard-to-treat epilepsy.
Is laser ablation a viable alternative to traditional craniotomy?
Yes, laser ablation can be a good alternative to traditional craniotomy for some patients. It’s less invasive and may lead to quicker recovery.
What are the benefits of FDA-approved laser ablation?
FDA-approved laser ablation is minimally invasive. It causes less scarring and has shorter hospital stays. It also targets areas precisely and can be monitored in real-time.Q: What are the possible risks and complications of laser ablation? Laser ablation may have risks like cerebral edema, infection, and damage to brain tissue. It’s important to review FDA reports on these issues.
Is craniectomyомен craniotomy the same as impuls laser ablation?
No, craniotomy and laser ablation are different. Craniotomy involves removing part of the skull to access the brain. Laser ablation is a less invasive procedure that uses a laser to remove abnormal tissue.
Does insurance cover laser content ablation procedures?
Insurance coverage for laser ablation varies. It depends on the procedure, patient, and insurance provider. Check Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance policies for details.
What is the difference between MRI-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy systems and stereotactic laser ablation systems?
MRI-guided and stereotactic laser ablation systems are used for different purposes. MRI-guided systems use MRI images for real-time guidance. Stereotactic systems use a frame to target areas.
Are there any new developments in laser ablation technology?
Yes, new laser ablation systems are in clinical trials. There are also new applications seeking FDA approval. Advances in imaging and laser technology are expected.


































