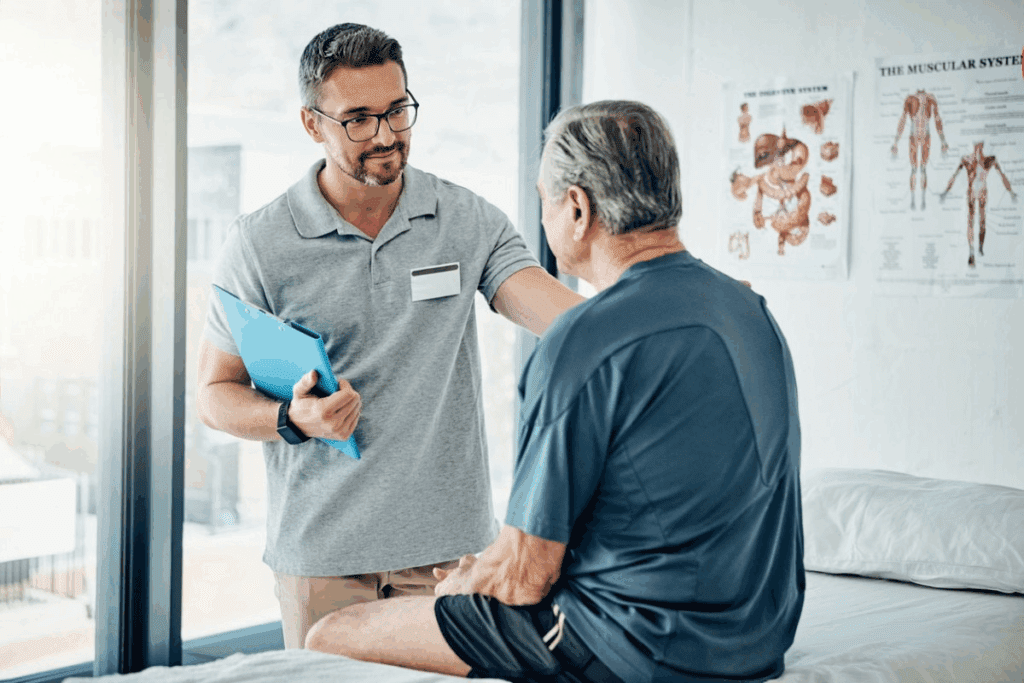
neuro critical care fellowship
Life-threatening neurological conditions affect thousands of people worldwide each year. Neurocritical Care has emerged as a vital medical specialty to manage these complex cases.
We are a team of specialists from Neurology, Neurosurgery, Neuroradiology, and Critical Care. We work together to provide comprehensive care to patients with severe neurological illnesses or injuries.
Our goal is to improve patient outcomes by providing timely and effective interventions. A Neuro Critical Care Fellowship plays a crucial role in advancing patient care. It equips healthcare professionals with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Key Takeaways
- Neurocritical Care is a multidisciplinary approach to managing life-threatening neurological conditions.
- A team of specialists works together to provide comprehensive care.
- The goal is to improve patient outcomes through timely interventions.
- A Neuro Critical Care Fellowship is essential for advancing patient care.
- It equips healthcare professionals with necessary skills and knowledge.
The Definition and Scope of Neurocritical Care
A team of medical professionals gathered around a patient in a neurocritical care unit. In the foreground, a doctor in a white coat examines the patient’s vital signs on a monitor, while nurses in scrubs administer medications and adjust life support equipment. In the middle ground, additional medical staff confer and review charts, their expressions focused and determined. The background is dimly lit, with subtle lighting illuminating the scene, conveying the gravity and intensity of the situation. The overall atmosphere is one of clinical professionalism and unwavering dedication to the patient’s care.
Neurocritical care is a team effort to treat severe brain disorders. It combines neurology, neurosurgery, and critical care. This approach ensures patients get the best care possible.
It’s not just about treating the illness. It’s also about the patient’s and their family’s needs. Our department focuses on training future doctors to give top-notch care.
Historical Development of Neurocritical Care
Neurocritical care has grown a lot in recent decades. It started as a need for specialized care for brain conditions. Advances in technology and medicine have shaped it.
Key milestones include the creation of neuro ICUs and new monitoring tools. Also, training programs for neurointensivists have been set up.
Year | Milestone | Description |
1980s | Emergence of Neuro ICUs | The first dedicated neuro ICUs were established, marking the beginning of specialized care for neurological patients. |
1990s | Advancements in Neuromonitoring | Technologies such as intracranial pressure monitoring became more prevalent, improving patient care. |
2000s | Specialized Training Programs | The first neurocritical care fellowship programs were established, formalizing training for neurointensivists. |
The Multidisciplinary Nature of Neurointensive Care
Neurocritical care brings together many healthcare experts. This team includes neurointensivists, neurologists, and nurses. They all work together to care for patients.
- Neurointensivists: Specialized physicians trained in both neurology and critical care medicine.
- Critical Care Nurses: Nurses with expertise in caring for critically ill neurological patients.
- Rehabilitation Specialists: Professionals who help patients regain functional abilities.
The complexity of neurocritical care requires teamwork. Our team works together to care for patients from start to finish.
Primary Goals of Neurocritical Care
A high-tech medical facility with state-of-the-art equipment and monitoring systems. In the foreground, an intensive care unit bed with advanced life support technology, including ventilators, IV drips, and vital sign monitors. Surrounding the bed, medical professionals in sterile white coats and scrubs, focused on providing specialized care. In the middle ground, a panoramic view of the neurocritical care ward, with rows of beds and medical staff tending to patients. The background showcases a clean, well-lit environment with a calming, clinical atmosphere, emphasizing the specialized nature of the neurocritical care unit. Lighting is bright and even, creating a sense of professionalism and attention to detail.
Preventing Secondary Brain Injury
Stopping secondary brain injury is key in Neurocritical Care. We use meticulous monitoring and management of body functions to avoid more brain damage. Tools like intracranial pressure monitoring are vital in this effort.
Optimizing Neurological Recovery
Improving neurological recovery is another main goal. We use tailored therapeutic interventions to meet each patient’s needs. This includes medicines and rehabilitation to help patients recover as much as possible.
Managing Life-Threatening Neurological Conditions
Handling life-threatening neurological conditions is also a main goal. This work needs a team effort from neurointensivists, nurses, and other experts. Our team gets advanced training and follows neuro ICU fellowship programs to tackle tough cases well.
The Neurocritical Care Team Composition
A team of medical professionals, dressed in scrubs, gathered around a hospital bed in a well-lit neurocritical care unit. In the foreground, a neurosurgeon and a critical care nurse examine the patient’s chart, their expressions focused and attentive. In the middle ground, a respiratory therapist adjusts the ventilator, while a pharmacist consults a medication list. In the background, a neurologist and a neuropsychologist discuss the patient’s condition, their postures conveying deep concentration. The scene is captured with a wide-angle lens, creating a sense of depth and emphasizing the collaborative nature of the neurocritical care team.
Neurocritical care works best with a team of experts. This team is key for taking care of patients with serious brain issues.
Neurointensivists and Their Role
Neurointensivists are doctors who focus on brain care. They lead the team, make big decisions, and ensure top care for patients.
They handle many brain problems, like strokes and brain injuries. They also deal with seizures and muscle disorders.
Specialized Nursing in Neuro ICU
Neuro ICU nurses are vital, working all day and night. They watch patients closely and act fast if needed.
They manage important treatments and spot early signs of problems.
Allied Health Professionals in Neurocritical Care
Physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists play big roles. They help patients get better and live better lives.
They help patients move again, do daily tasks, and talk better. This helps patients reach their best outcomes.
Team Member | Role |
Neurointensivists | Lead the neurocritical care team, making critical decisions, and ensuring the best possible care. |
Specialized Nurses | Provide around-the-clock patient care, monitoring neurological status, and responding to changes. |
Physiotherapists | Assist in physical rehabilitation, helping patients regain mobility. |
Occupational Therapists | Help patients regain daily functioning and independence. |
Speech Therapists | Aid in recovering communication skills, improving patients’ ability to interact. |
The neurocritical care team works together. They give complete care to patients with serious brain issues.
Common Neurological Conditions Requiring Critical Care
A high-contrast, photorealistic image of a neurosurgeon performing a complex procedure to manage a traumatic brain injury. The foreground shows the surgeon’s steady hands and precision instruments working on an open cranial cavity, surrounded by state-of-the-art medical equipment. The middle ground depicts a team of critical care specialists closely monitoring vital signs and administering treatments. The background reveals the sterile, well-lit operating theater with advanced imaging technology providing real-time data. The scene conveys the gravity and intensity of delivering expert neurocritical care to stabilize and treat a patient suffering from a devastating head trauma.
The field of neurocritical care deals with acute neurological conditions. We know that neurological emergencies need quick and effective treatment. Here, we’ll look at common neurological conditions that need critical care.
Traumatic Brain Injury Management
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of illness and death worldwide. Effective management of TBI requires a team effort from neurosurgeons, neurointensivists, and rehab specialists. We use advanced monitoring, like intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring, to make treatment decisions.
The management of TBI includes:
- Initial stabilization and resuscitation
- Monitoring and management of ICP
- Cerebral perfusion pressure optimization
- Neuroprotective strategies
Stroke Care in the Neuro ICU
Stroke is a critical condition that needs quick and specialized care. Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes need different treatments, and our team is ready for both. We provide close monitoring and supportive care to improve patient outcomes.
Key aspects of stroke care include:
- Rapid diagnosis and thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke
- Blood pressure management
- Monitoring for complications such as cerebral edema
Status Epilepticus and Seizure Management
Status epilepticus is a life-threatening condition with prolonged or recurrent seizures. Prompt treatment is key to prevent neurological damage and other complications. We use various antiepileptic medications and interventions to manage status epilepticus.
“The timely management of status epilepticus is crucial to prevent long-term neurological sequelae.” –
A leading neurocritical care expert
Neuromuscular Disorders in Critical Care
Neuromuscular disorders, like Guillain-Barré Syndrome and myasthenia gravis, can cause respiratory failure and need critical care. We offer supportive care, including mechanical ventilation, and manage the underlying condition to aid recovery.
The management of neuromuscular disorders involves:
Disorder | Key Management Strategies |
Guillain-Barré Syndrome | Plasmapheresis, IVIG, supportive care |
Myasthenia Gravis | Immunomodulatory therapy, thymectomy |
Advanced Monitoring Techniques in Neurocritical Care
A high-resolution, hyper-realistic image of an advanced neurocritical care monitoring station. The foreground features a sleek, state-of-the-art medical display console with a variety of real-time data visualizations, including brain wave patterns, intracranial pressure readings, and oxygen saturation levels. In the middle ground, a team of medical professionals in scrubs and lab coats closely observe the displays, discussing the patient’s condition. The background depicts a sterile, well-lit hospital room with high-tech medical equipment, creating a sense of cutting-edge medical technology and expertise dedicated to the patient’s care.
In neurocritical care, advanced monitoring is key. It helps guide treatments for critically ill patients. This is crucial for improving their outcomes.
Intracranial Pressure Monitoring
Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring is vital, especially for those with brain injuries. It helps spot high pressure early, allowing for quick action to avoid more damage.
We use different methods for ICP monitoring. These include intraventricular catheters and intraparenchymal monitors. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the situation.
Brain Tissue Oxygenation
Monitoring brain tissue oxygen levels is another advanced technique. It shows how well the brain is working. This is key for patients with severe brain injuries, helping ensure they get enough oxygen.
Continuous EEG Monitoring
Continuous EEG (cEEG) monitoring is a big help in the neuro ICU. It watches brain activity in real-time. It’s great for catching seizures and checking how deep a patient is under sedation. cEEG helps spot when a patient’s condition is getting worse, so we can act fast.
Cerebral Blood Flow Assessment
Checking cerebral blood flow (CBF) is important in neurocritical care. It tells us if the brain is getting enough blood. We use methods like transcranial Doppler ultrasonography and CT perfusion to check CBF. Knowing about CBF is crucial for stroke or vasospasm patients, helping us make better treatment choices.
Monitoring Technique | Clinical Application | Benefits |
Intracranial Pressure Monitoring | Traumatic brain injury, elevated ICP | Early detection of increased ICP, guiding interventions |
Brain Tissue Oxygenation | Severe brain injuries | Optimizing oxygen delivery, reducing secondary brain injury |
Continuous EEG Monitoring | Seizure detection, sedation monitoring | Early detection of neurological deterioration |
Cerebral Blood Flow Assessment | Stroke, vasospasm | Guiding therapeutic decisions to optimize cerebral perfusion |
Therapeutic Interventions in Neurocritical Care
A vibrant scene of a neurocritical care unit, lit by the soft glow of medical equipment. In the foreground, a team of healthcare professionals intently monitors a patient, their faces etched with concern as they administer essential interventions. The middle ground showcases advanced monitoring devices, their screens displaying vital signs and diagnostic data. In the background, a serene window overlooking a peaceful landscape, offering a calming contrast to the intense, life-saving procedures unfolding. The scene conveys a sense of urgency, precision, and the unwavering commitment of the medical team to provide the best possible care for their critically ill patient.
Therapeutic interventions are key in neurocritical care. They help improve patient outcomes. In the ICU, specialists use many treatments for serious brain conditions.
Pharmacological Management Strategies
Medications are crucial in neurocritical care. They help prevent brain damage, manage seizures, and control pressure inside the skull. We use sedatives, anticonvulsants, and other drugs to care for patients.
Key pharmacological strategies include:
- Administration of antiepileptic drugs to prevent and treat seizures
- Use of sedatives to reduce agitation and promote comfort
- Management of blood pressure to ensure adequate cerebral perfusion
Surgical Interventions in Neuroemergencies
Surgery is vital in neurocritical care, especially for emergencies like brain injuries or bleeding in the brain. We team up with neurosurgeons for quick and effective surgery.
Surgical options may include:
- Decompressive craniectomy to relieve intracranial pressure
- Clipping or coiling of aneurysms to prevent rebleeding
- Evacuation of hematomas to reduce mass effect
Temperature Management and Neuroprotection
Keeping the body temperature normal is critical in neurocritical care. High body temperature can make brain injuries worse. We use methods to keep the body cool and sometimes warm it up to protect the brain.
Temperature management strategies include:
- Use of cooling devices to achieve target temperature
- Administration of antipyretic medications to control fever
- Monitoring of core temperature to guide therapy
Neuro Critical Care Fellowship: Pathway to Specialization
A vibrant, photorealistic image of a modern neurocritical care fellowship program. In the foreground, a group of medical professionals in scrubs and lab coats huddle around a patient’s bedside, intently studying vital signs and discussing treatment options. The middle ground features state-of-the-art medical equipment, including an advanced life support system and high-resolution imaging monitors. In the background, a panoramic view of a well-equipped, high-tech hospital ward, with clean lines, ample natural lighting, and a calming, professional atmosphere. The lighting is warm and even, creating a sense of focused intensity and critical care. The overall scene conveys the specialized skills, dedicated teamwork, and cutting-edge technology required for effective neurocritical care.
Healthcare professionals can advance their skills in neurocritical care through a fellowship program. A Neuro Critical Care Fellowship offers specialized training for critically ill neurological patients. This training helps fellows provide top-notch care.
Prerequisites and Application Process
To apply for a Neuro Critical Care Fellowship, you need a medical degree and residency training in neurology, neurosurgery, or anesthesiology. The application includes your academic and clinical achievements, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement. This statement should explain why you want to pursue this career path.
Core Curriculum and Clinical Rotations
The fellowship’s core curriculum covers managing traumatic brain injury, stroke, and status epilepticus. Fellows also get hands-on experience in the neuro ICU. They work under the guidance of experienced neurointensivists.
Research Requirements and Scholarly Activities
Fellows must participate in research and scholarly activities. They contribute to neurocritical care through clinical research, case reports, or quality improvement projects. This part of the fellowship helps develop critical thinking and research skills.
Here’s an overview of a Neuro Critical Care Fellowship program:
Component | Description | Duration |
Clinical Rotations | Hands-on experience in neuro ICU | 12 months |
Research Projects | Clinical research or quality improvement | 6 months |
Core Curriculum | Theoretical foundation in neurocritical care | Throughout the fellowship |
Neuro Critical Care Fellowship programs combine clinical training with scholarly activities. This prepares healthcare professionals for the challenges of caring for critically ill neurological patients. After completing the fellowship, they are ready to provide high-quality care and contribute to the field’s advancement.
Neurocritical Care Fellowship Programs Across the United States
In the U.S., there are many Neurocritical Care Fellowship programs for healthcare professionals. These programs offer advanced training in managing complex neurological conditions. They provide a comprehensive education and hands-on experience.
Top-Ranked Programs and Their Unique Features
Some Neurocritical Care Fellowship programs are known for their excellence. They offer specialized tracks in traumatic brain injury and stroke care. These programs have distinguished faculty who are experts in neurointensive care.
These programs use cutting-edge technology and focus on multidisciplinary team training. They emphasize teamwork between neurosurgery, neurology, and critical care medicine.
Program Accreditation and Standards
Accreditation is key for Neurocritical Care Fellowship programs. It ensures they meet high standards set by accrediting bodies. Programs are checked on their curriculum, clinical training, and research opportunities.
The accreditation process reviews the program’s structure, faculty, and educational resources. It helps keep the quality of fellowship programs consistent.
Fellowship Duration and Structure Variations
Neurocritical Care Fellowship programs vary in length and structure. Some are one-year fellowships, while others are two-year tracks with more research or administrative training. The focus can be on clinical training, research, or both.
Fellows have a mix of clinical duties, educational seminars, and research projects. The program structure is flexible, allowing fellows to focus on their career goals.
The Journal of Neurocritical Care: Advancing the Field
The Journal of Neurocritical Care is key in moving neurocritical care forward. It’s a top spot for experts to share their work. This journal is vital for the future of neurocritical care.
It covers many topics, like traumatic brain injury management, stroke care, and neuromuscular disorders. It publishes top-notch research. This helps doctors and nurses give the best care to their patients.
Key Research Areas and Trending Topics
Important topics in The Journal of Neurocritical Care include intracranial pressure monitoring and brain tissue oxygenation. These are key for understanding and treating neurocritical care. There’s also a big interest in neuroprotection and personalized medicine.
It also talks about advanced imaging techniques and therapeutic hypothermia. These could change how we treat patients and improve their outcomes.
Impact on Clinical Practice Guidelines
The Journal of Neurocritical Care’s research shapes clinical practice guidelines. It offers evidence-based advice for doctors. This helps them make better choices for their patients.
For example, studies on intracranial pressure management have updated brain injury treatment guidelines. Research on stroke care has led to new acute stroke management protocols.
Contribution to Evidence-Based Neurocritical Care
The Journal of Neurocritical Care supports evidence-based neurocritical care. It publishes solid studies and reviews. This helps create guidelines and protocols based on the latest evidence.
Its focus on translational research connects basic science to clinical practice. This lets doctors apply new research to solve real-world problems. It improves patient care.
Comparing Neurocritical Care to General Critical Care Medicine
Neurocritical care is a unique part of critical care medicine. It needs special knowledge and skills. General critical care medicine deals with many serious conditions. But neurocritical care focuses on severe brain illnesses that need careful management.
Neurological conditions are complex. They require understanding how the brain reacts to injury or illness. This knowledge helps in creating treatments that are different from general critical care.
Specialized Knowledge and Skill Requirements
Neurocritical care needs a mix of brain and critical care skills. Doctors in this field handle serious brain injuries, strokes, and seizures. They need advanced training, like a critical care medicine fellowship with a neurocritical care focus.
- Advanced monitoring techniques, including intracranial pressure monitoring and continuous EEG monitoring
- Specialized therapeutic interventions, such as pharmacological management strategies and surgical interventions for neuroemergencies
- Expertise in managing life-threatening neurological conditions, including traumatic brain injury and stroke
The advanced critical care training from a neurocritical care fellowship program is crucial. It teaches healthcare professionals to handle the complexities of neurological critical care. This training is key to better patient care in the neuro ICU.
Unique Challenges in Neurological Critical Care
One big challenge in neurocritical care is balancing prevention of secondary brain injury and improving neurological recovery. This requires deep knowledge of neurological conditions and quick, informed decisions.
“The care of patients with acute neurological illnesses requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating the expertise of neurointensivists, neurosurgeons, neurologists, and rehabilitation specialists.”
— Guidelines for Neurocritical Care
Dealing with these challenges needs specialized knowledge and teamwork. The neuro ICU training prepares practitioners for these challenges.
Overlap with Other Critical Care Subspecialties
Neurocritical care is unique but shares some areas with other critical care subspecialties. For example, managing blood flow and breathing is similar. But in neurocritical care, these are tailored for brain patients.
It’s important to understand neurocritical care and its connection to other critical care areas. This knowledge helps in providing top-notch care to critically ill patients. Specialized training, like through a critical care medicine fellowship, is vital for advancing in critical care medicine.
Career Paths After Completing a Neurointensive Care Fellowship
A Neurointensive Care Fellowship opens doors to many careers in neurology and critical care. After finishing this training, doctors can find jobs that match their skills and interests. These jobs can be very rewarding.
Academic Medicine Opportunities
Doctors can find jobs in academic medicine. They can help the field by doing research, teaching, and seeing patients. Some roles include:
- Faculty positions at medical schools
- Principal investigators in research studies
- Authors of scholarly articles and textbooks
- Presenters at conferences and symposia
These jobs help grow neurocritical care. They also give doctors a chance to teach and guide new professionals.
Private Practice in Neurocritical Care
Private practice is another good option. It lets neurointensivists focus on patient care in a personal way. They can:
- Start or join a private practice group
- Work with hospitals and healthcare systems
- Offer consultation services
- Help with community health projects
Working in private practice needs strong clinical skills, good communication, and business knowledge.
Research and Leadership Roles
For those interested in research and leadership, there are big opportunities. They can:
- Lead research teams on neurocritical care projects
- Take on leadership roles in professional groups
- Help create clinical guidelines
- Work on policy changes for better care
These jobs need a deep understanding of the field. They also require strong leadership and communication skills.
The Future of Neurocritical Care Education
The future of neurocritical care education will blend new tech, simulation learning, and global teamwork. As we grow in neurocritical care, our teaching methods must change to fit new healthcare needs.
Emerging Technologies in Training
New tech is changing how we train neurocritical care experts. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) offer immersive learning. They let trainees practice complex tasks safely.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also making a big impact. It tailors learning, gives instant feedback, and spots where extra help is needed.
Simulation-Based Learning Approaches
Simulation learning is key in neurocritical care education. It mimics real scenarios, helping professionals hone their skills safely.
It’s great for team training on rare but crucial events. For example, it prepares for managing seizures or acute strokes.
Simulation Scenario | Learning Objectives | Key Skills Developed |
Status Epilepticus Management | Recognize and manage seizures effectively | Critical thinking, teamwork |
Acute Stroke Response | Rapidly assess and treat stroke patients | Time management, decision-making |
Traumatic Brain Injury Care | Understand the principles of TBI management | Prioritization, communication |
International Educational Initiatives
Global teamwork is vital for neurocritical care education. Conferences, online courses, and research projects share best practices worldwide.
These efforts also let experts from different places share knowledge. This helps improve care for patients everywhere.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Neurocritical Care
In neurocritical care, healthcare providers face many challenges. They need both technical skills and ethical understanding. These challenges include making end-of-life decisions and deciding how to use resources. Ensuring patients get the right care is key.
End-of-Life Decision Making
Deciding when to stop life-saving treatments is tough. Healthcare providers must be sensitive and compassionate in these situations. They have to balance saving lives with respecting patient wishes and dignity.
One big challenge is figuring out what the patient wants. This is hard when patients can’t talk because of their condition.
Key Considerations in End-of-Life Decision Making:
- Patient autonomy and advance directives
- Family involvement and support
- Prognosis and likelihood of recovery
- Quality of life considerations
Resource Allocation in High-Acuity Neurological Care
Managing resources is a big challenge in neurocritical care. ICUs are very resource-intensive. It’s important to allocate resources well to make sure patients get the care they need.
Resource | Description | Allocation Considerations |
ICU Beds | Specialized beds for critically ill patients | Availability, patient acuity |
Monitoring Equipment | Advanced equipment for continuous monitoring | Technical capabilities, maintenance |
Specialized Staff | Trained healthcare professionals | Staffing ratios, expertise |
Balancing Aggressive Treatment and Quality of Life
It’s important to balance aggressive treatment with the patient’s quality of life. Healthcare providers must think about the patient’s values and prognosis. This helps ensure care is focused on the patient’s needs.
By tackling these challenges, healthcare providers can give patients the best care. This care respects the patient’s autonomy and dignity.
Patient Outcomes and Quality Metrics in Neurocritical Care
The success of neurocritical care is seen in patient outcomes and quality metrics. As we improve in neurocritical care education and training for doctors, it’s key to see how these changes help patients.
Measuring Success in Neurological Recovery
Success in neurological recovery is about how well patients get better and their quality of life. We use scales like the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) to check on patients. These tools help us see if our treatments are working and guide better training in neuro ICU fellowship.
Long-term Functional Outcomes
Long-term outcomes are key to knowing if neurocritical care is working. We follow up with patients to see how they’re doing in terms of thinking, moving, and daily functions. This helps us make our care better and improve patient results in neurocritical care.
Quality Improvement Initiatives
Improving quality is vital for better care in neurocritical care units. We use proven practices, watch outcomes, and change our plans as needed. By focusing on quality, we aim to help patients recover better and have better long-term outcomes.
With fellowship for neurocritical care physicians, we make sure doctors have the newest knowledge and skills. Ongoing learning and training are crucial for moving forward and getting better results for patients.
The Global Perspective on Neurocritical Care
Neurocritical care varies a lot around the world. This is due to local healthcare setups, availability of training programs, and guidelines for ICU care.
International Variations in Practice
Countries have their own ways of handling neurocritical care. This is influenced by their healthcare systems, culture, and resources. Some have advanced units, while others struggle to provide basic care.
International efforts help bridge these gaps. They promote best practices and offer training. This standardizes care and improves outcomes worldwide.
- Variability in neurocritical care practices
- Impact of local healthcare infrastructure
- Role of international educational initiatives
Resource Disparities and Solutions
Resource gaps are a big issue in neurocritical care. Some areas lack essential tools, trained staff, or both. To tackle this, we need creative solutions like telemedicine and research partnerships.
Telemedicine connects experts with those in need. It improves care quality. Research partnerships find affordable solutions and best practices for various settings.
Key strategies to address resource disparities include:
- Implementing telemedicine programs
- Promoting collaborative research
- Developing context-appropriate guidelines
Collaborative International Initiatives
Global collaborations are key to advancing neurocritical care. They share knowledge, resources, and expertise. This improves patient care worldwide.
Examples include international conferences, joint research, and global health partnerships. These efforts boost clinical practice and support training programs.
Together, we can tackle common challenges. We can reduce disparities and enhance care quality for all patients globally.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of Neurocritical Care in Modern Medicine
Neurocritical Care is growing in importance in today’s medicine. Our understanding of brain conditions is getting better. This shows how vital specialized care in ICUs is.
Education and fellowship programs are key in training neurointensivists. They help shape the future of this field.
Advanced training lets doctors give top-notch care to brain patients in critical condition. The field is seeing big steps forward in treatments and monitoring. This leads to better patient results and care quality.
We see Neurocritical Care as a crucial part of healthcare. Its growth is vital for better care of brain patients. By focusing on education and fellowship, we can keep improving care for those who need it most.
FAQ
What is Neurocritical Care, and why is it important?
Neurocritical Care is a special field of medicine. It deals with patients who have severe brain problems. It’s key because it helps patients with serious brain illnesses or injuries get better care.
What are the primary goals of Neurocritical Care?
The main goals are to stop further brain damage, help patients recover, and manage serious brain conditions.
What is a Neuro Critical Care Fellowship, and what does it entail?
A Neuro Critical Care Fellowship is a training program. It teaches healthcare professionals how to care for very sick brain patients. It includes hands-on training, research, and learning activities.
What are the prerequisites for applying to a Neuro Critical Care Fellowship program?
To apply, you need to finish a residency in Neurology, Neurosurgery, or Critical Care Medicine. You also need to meet specific program needs.
How do I choose the right Neurocritical Care Fellowship program?
Look at the program’s accreditation, what it teaches, and the chances for clinical and research work. Also, check the skills of the teachers.
What are the career paths available after completing a Neurointensive Care Fellowship?
After finishing, you can work in teaching, private practice, research, or leadership roles.
How does Neurocritical Care differ from general Critical Care Medicine?
Neurocritical Care needs special knowledge and skills. It faces unique challenges and works closely with other critical care areas.
What are the emerging trends and technologies in Neurocritical Care education?
New trends include using simulation and international programs. Also, new technologies are being used in training.
What are the challenges and ethical considerations in Neurocritical Care?
Challenges include making end-of-life decisions and deciding how to use resources. It’s about treating aggressively while considering quality of life.
How is patient outcome measured in Neurocritical Care?
Outcomes are measured by how well patients recover, their long-term function, and quality improvement efforts.
What is the role of the Journal of Neurocritical Care in advancing the field?
The Journal publishes important research and trends. It helps shape clinical practices and guidelines.
What are the international variations in Neurocritical Care practice?
Practices vary due to differences in resources, guidelines, and culture. These factors affect how care is given.
What are the requirements for becoming a neurointensivist?
To be a neurointensivist, you need to finish a Neuro Critical Care Fellowship. You must also gain expertise in caring for critically ill brain patients.
What is the significance of advanced monitoring techniques in Neurocritical Care?
Techniques like monitoring brain pressure and EEG are crucial. They help manage patients and guide treatments.
How does Neurocritical Care contribute to improving patient outcomes?
Neurocritical Care improves outcomes by providing specialized care. It prevents further brain damage and helps patients recover better.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Neurocritical Care Management of Life-Threatening Neurological Conditions. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557766/


































