ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) is a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) is a rare, devastating, and rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease that directly attacks the nerve cells, called motor neurons, responsible for controlling all voluntary muscles. When these motor neurons die, the brain loses its ability to initiate and control movement.
The condition is widely known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, named after the famous American baseball player who was diagnosed in 1939.
While there is currently no cure, treatment and specialized, aggressive care focuses on managing its aggressive progression and improving the patient’s quality of life.
ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) affects two important types of nerve cells: upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem. Damage to both leads to a mix of stiffness and weakness, which is the main feature of the disease.
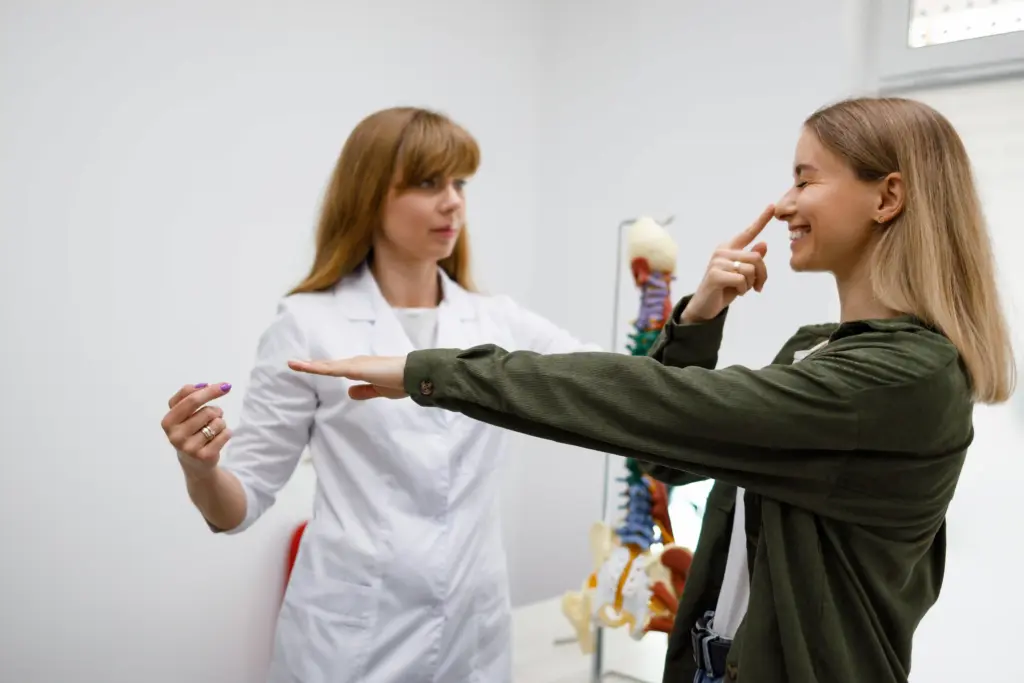

Upper Motor Neurons (UMN):
Lower Motor Neurons (LMN):
It’s important to tell ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) apart from other nerve and muscle diseases, because some of the early signs like muscle weakness can look similar. But ALS is different because it damages both upper and lower motor neurons and gets worse over time in a clear, predictable way. Knowing this helps patients get the right diagnosis and care as early as possible.
How ALS is different from other conditions:
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

All forms of ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) lead to the same functional decline, but the way the disease begins influences initial care needs. The disease is categorized based on whether it is inherited and the body region where symptoms first appear.
These distinctions help specialized clinics provide precise projections for care needs, such as early respiratory or nutritional support.
While ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) is a neurological disease, its devastating impact is felt by multiple organ systems that rely on voluntary muscle control. The core management strategy centers on supporting the function of these failing systems.
The long-term care of ALS patients requires continuous collaboration between specialists focused on these critical functions.

The complex, rapidly progressing nature of ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) demands a continuous, coordinated effort from a variety of medical and therapeutic specialists. Neurologists lead this multidisciplinary care model, coordinating treatment across the entire spectrum of functional loss.
This specialized, team-based approach has been scientifically proven to extend survival time and significantly improve the daily comfort and quality of life for patients.
The study of ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) is paramount in medicine due to the clinical complexity required to manage rapid functional decline and the immense potential for research breakthroughs. ALS research provides vital clues into the fundamental mechanisms of other major neurodegenerative processes.
Early and accurate diagnosis is exceptionally important for ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis). A proper assessment helps quickly exclude other treatable conditions that may mimic the initial signs of motor neuron disease, such as severe vitamin deficiencies or nerve compression.
Crucially, an early diagnosis allows patients to immediately begin treatments that can slow the disease’s functional progression and provides valuable time for essential advanced care planning.
ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease where motor neurons die, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis. A neurologist diagnoses the condition and manages the medical aspects of care, coordinating a multidisciplinary treatment team
ALS does not treat conditions; rather, it is the condition. The specialist care team treats the associated symptoms, which include muscle spasticity, difficulty breathing, problems swallowing, and impaired speech.
The main categories are Sporadic ALS (most common, without a known family link) and Familial ALS (inherited). It is also categorized by its onset: Limb Onset (starts in arms/legs) or Bulbar Onset (starts in speech/swallowing muscles).
You should see a neurologist immediately if you experience unexplained, persistent muscle weakness, visible muscle twitching (fasciculations), or worsening difficulty swallowing or speaking without a clear cause.
ALS is a progressive, fatal disease involving the direct death of motor neurons. MS is an autoimmune disease where the nerve coating is attacked, causing inflammation and episodic symptoms that may improve or stabilize over time.

A recent study in the Radiation Oncology journal found that 13% of patients died within 30 days after getting palliative radiotherapy for bone metastases. Another
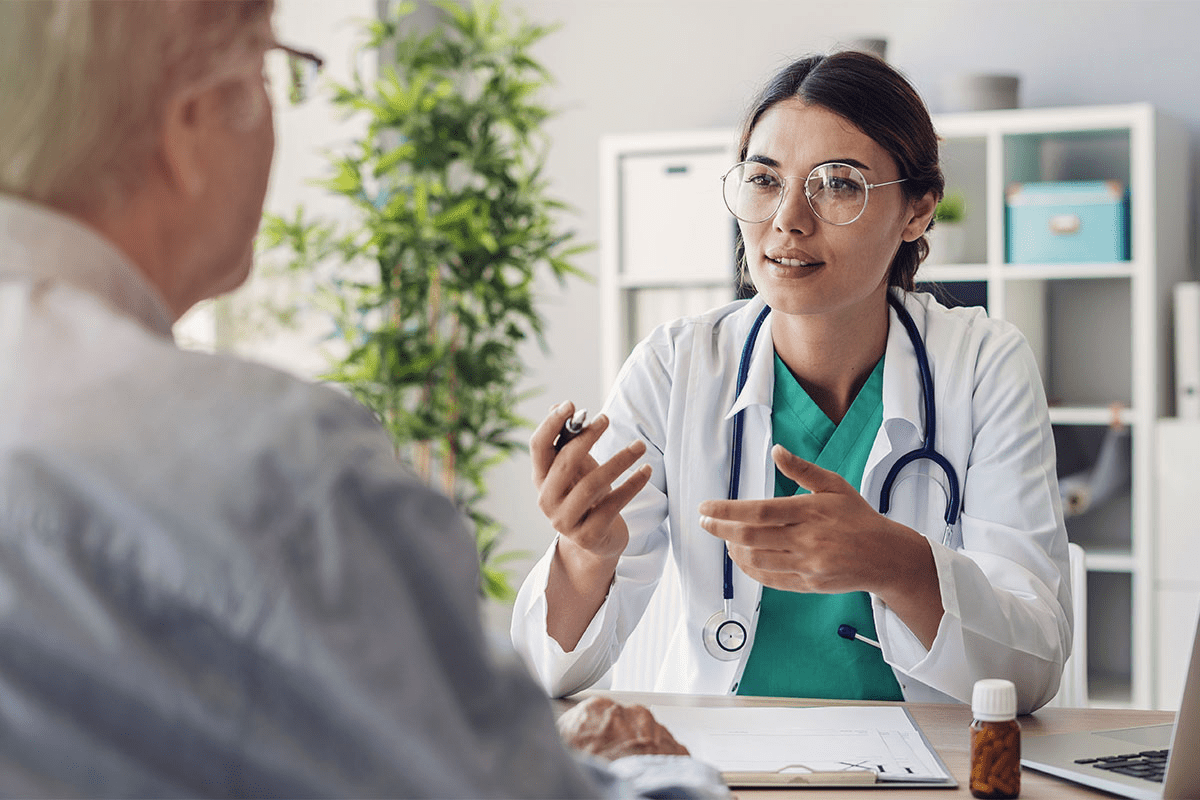

Choosing to have a carotid endarterectomy is a big decision. It’s important to know what to expect during recovery. Did you know that almost 100,000
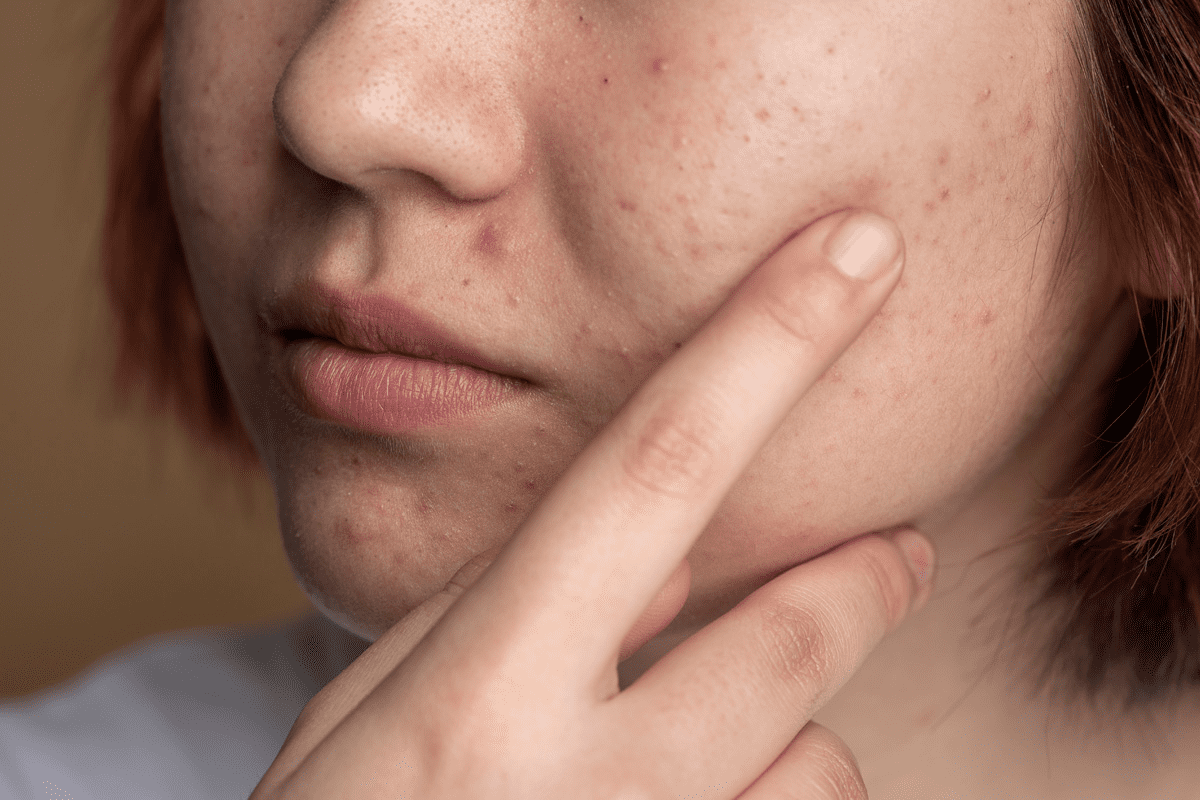

Finding a lump inside your cheek can be scary. But knowing what it might be and when to see a doctor can help. At Liv
When serious bone damage happens, like from fractures or disease, our body might not heal on its own. That’s when a bone graft operation is
Cadaver bone grafts have changed orthopedic surgery a lot. They help patients who need bone replacement because of injuries, diseases, or surgery problems. Johns Hopkins

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)