Explore Stroke Medicine treatments including clot busters and thrombectomy. Learn about rehabilitation therapies like physical and speech therapy for recovery.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
Stroke Medicine treatment depends entirely on the type of stroke. For ischemic stroke, the goal is to restore blood flow to the brain as quickly as possible. This is often done using medication or a mechanical procedure to remove the clot. The phrase “time is brain” emphasizes that every minute matters; roughly 2 million brain cells die every minute during a stroke.
For hemorrhagic stroke, the goal is to control the bleeding and reduce pressure in the brain. This may involve medications to lower blood pressure, stopping any blood thinners the patient is taking, and surgery to repair the ruptured vessel. Supportive care involves maintaining oxygen levels, managing blood sugar, and preventing complications like fever.
Anyone experiencing the symptoms of a stroke needs immediate treatment. There is no “wait and see” with a stroke. Even if symptoms disappear (suggesting a TIA), treatment is needed to prevent a major stroke. The specific type of treatment is determined by the neurologist based on the time elapsed since symptoms began.
Certain treatments, like clot busting drugs, can only be given within a specific time window, usually up to 4.5 hours after symptom onset. Mechanical clot removal has a longer window, sometimes up to 24 hours. Therefore, identifying the “last known well” time is the critical factor in deciding who receives which treatment.

The gold standard medical treatment for ischemic stroke is an intravenous thrombolytic drug, often called a “clot buster.” This medication dissolves the blood clot that is blocking blood flow to the brain. It significantly improves the chances of recovering fully, but it must be given quickly.
Before administering this drug, doctors must be absolutely certain there is no bleeding in the brain, as the drug would make bleeding worse. This is why the initial CT scan is so important. Patients are monitored closely in the ICU during and after the infusion.
For strokes caused by a blockage in a large artery, medication alone may not be enough. In these cases, a procedure called mechanical thrombectomy is performed. A specialized doctor inserts a catheter into an artery in the groin or wrist and guides it up to the blocked blood vessel in the brain.
A stent retriever or suction device is used to physically grab and pull the clot out of the body. This procedure can be a game changer, reversing severe paralysis if done in time. It is often used in combination with clot busting medication.
Treatment for bleeding strokes focuses on stopping the bleeding and relieving pressure. If the patient is on blood thinners, they are given drugs to reverse the effect. Blood pressure is lowered carefully to prevent more bleeding but maintain flow to the rest of the brain.
Surgical treatments may include:
Managing blood pressure is critical in both types of stroke. In ischemic stroke, doctors may allow blood pressure to run slightly high initially to help push blood through collateral vessels to the brain. However, it must be kept below a certain limit if clot busting drugs are used.
In hemorrhagic stroke, strict blood pressure control is vital to prevent the hematoma from growing. Long term, controlling blood pressure is the most effective way to prevent a second stroke. This involves lifestyle changes and daily medication.
Rehabilitation usually begins as soon as 24 to 48 hours after the stroke, once the patient is stable. Physical therapy focuses on restoring movement and balance. Strokes often cause weakness or paralysis on one side of the body (hemiparesis).
Therapists use exercises to strengthen muscles and retrain the brain. They work on gait training to help the patient walk again. They may use assistive devices like walkers or canes. The concept of neuroplasticity is central here; repetitive practice helps the healthy parts of the brain take over functions from the damaged parts.
Stroke often affects the ability to speak and understand language, a condition called aphasia. It can also cause muscle weakness in the mouth, leading to slurred speech (dysarthria) and difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
Speech therapists work with patients to relearn language skills. This might involve practicing sounds, matching words to pictures, or learning alternative communication methods. They also evaluate swallowing safety and recommend diet changes, such as thickened liquids, to prevent choking and pneumonia.
Occupational therapy focuses on the activities of daily living. The goal is to help the stroke survivor become as independent as possible. This involves relearning skills like dressing, bathing, eating, and writing.
Occupational therapists teach compensatory strategies. For example, they might teach a patient how to dress using only one hand. They also assess the patient’s home environment and recommend modifications like grab bars or shower chairs to ensure safety upon discharge.
Stroke care is expensive due to the intensity of acute treatment and the duration of rehabilitation. Costs vary globally but generally include emergency transport, ICU stay, imaging, surgery, and long term therapy.
In many developed healthcare systems, the cost of an acute stroke admission can range from ten thousand to over fifty thousand dollars depending on the interventions. Long term care and loss of productivity add significantly to the global economic burden. Rehabilitation centers and nursing home care are major components of the long term financial impact.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
All brain procedures carry risk but thrombectomy is a minimally invasive standard procedure with high success rates for large clots.
It varies for everyone recovery is fastest in the first 3 months but improvements can continue for years with dedicated practice.
Dead brain cells do not grow back but the brain can reorganize itself neuroplasticity to allow other cells to take over functions.
It is a condition where muscles become stiff and tight after a stroke limiting movement physical therapy helps manage it.
Post stroke weakness can cause food to go into the lungs aspiration leading to pneumonia a leading cause of death after stroke.

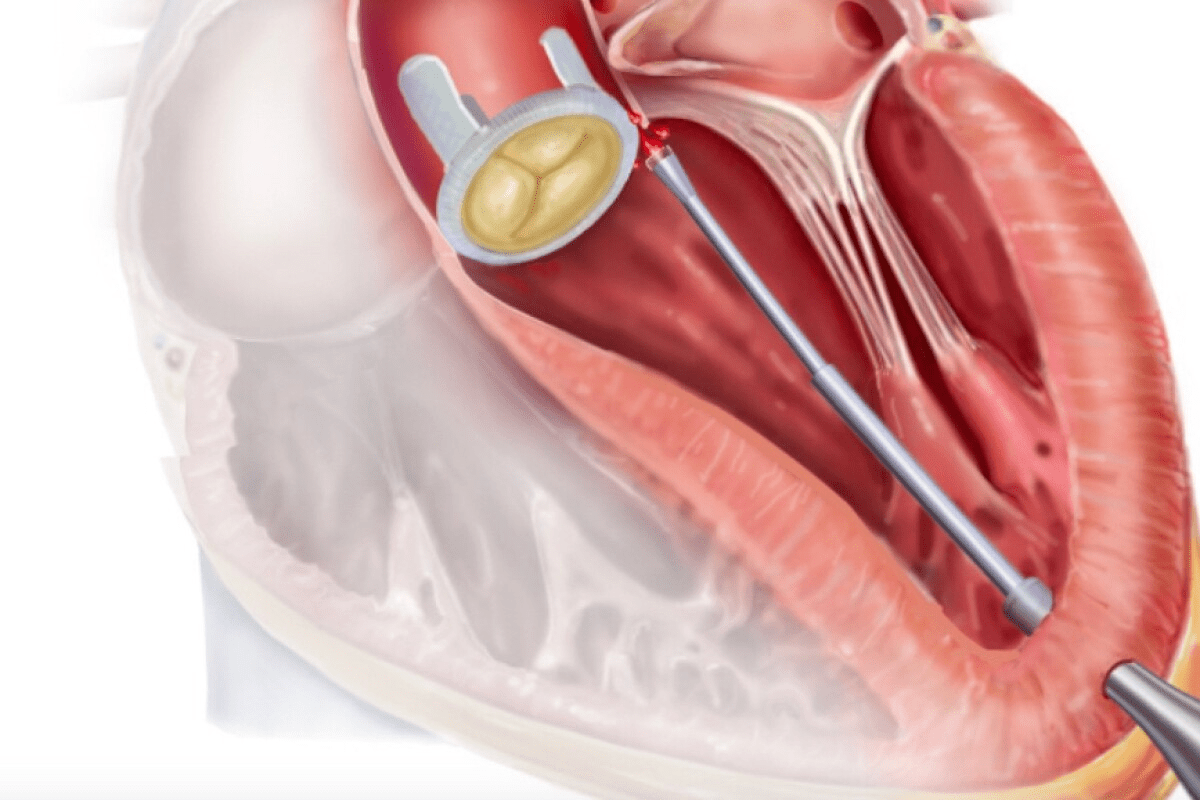
Cardiac ablation is a procedure to treat irregular heartbeats. It’s generally safe but comes with risks, like stroke. A study found that the risk of

Nearly 90,000 carotid endarterectomy procedures are done every year in the United States. This shows how important it is to know about the recovery process

Having a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), also known as a mini stroke, is a serious warning. It’s a short-term issue that doesn’t cause lasting harm.
Research shows that strokes are most likely to occur in the early morning hours, around 6:30 am. This timing is not a coincidence. Our circadian
Find the right stroke ICD codes for cerebrovascular disease. This is the essential guide for medical billing and coding professionals. Cerebrovascular disease is a significant

About 75% of strokes happen to people aged 65 and older. This makes it a big health issue for seniors. Knowing how to help them

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)