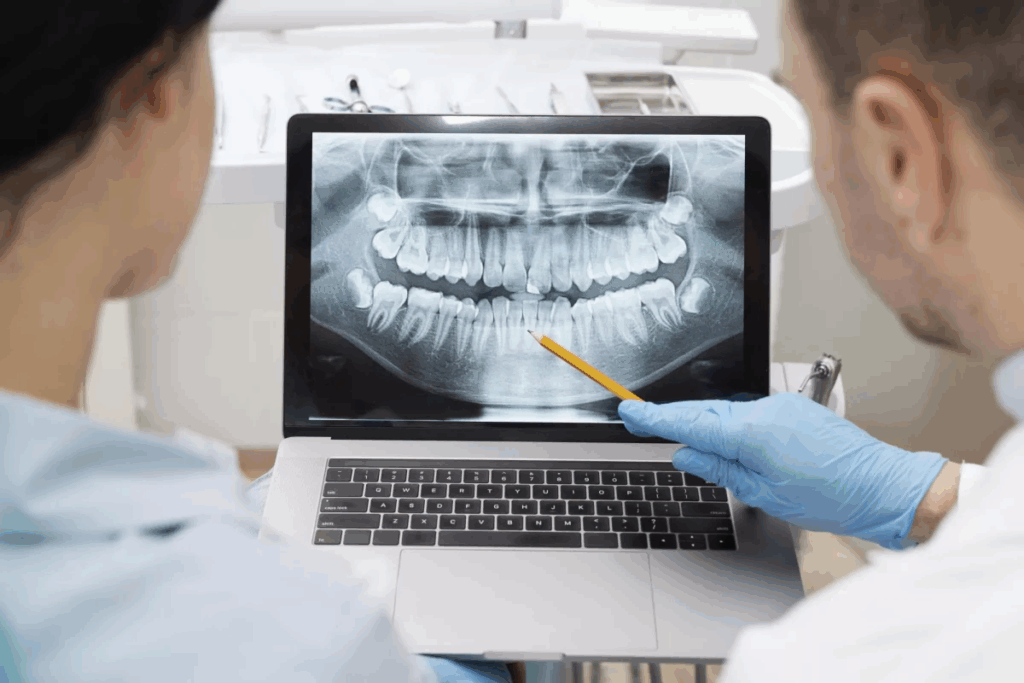
Oral radiology is key in today’s dentistry. It helps us make accurate decisions. This technology ensures better patient care.
The dental imaging market is growing fast. It was worth USD 3.14 billion in 2024. This shows how important it is to keep up with oral radiology advancements.
In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of radiology. We’ll look at its history and its role in dentistry today. We’ll also talk about different imaging tools and how they help diagnose and treat dental issues.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the importance of oral radiology in modern dentistry
- Exploring the latest advancements in dental imaging technologies
- Learning how to apply radiology in clinical decision-making
- Discovering the role of imaging technologies in diagnosing dental conditions
- Mastering the skills needed to deliver superior diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes
The Cornerstone of Modern Dental Diagnosis
Oral radiology is key in today’s dental world. It helps dentists diagnose and treat patients better. This field is essential for modern dental care.
Historical Development of Dental Imaging
Dental imaging has a long history. A big step was Medical Expert’s cephalometric analysis in 1931. It changed how orthodontists plan treatments.
Over time, dental imaging has grown. New technologies have made it more accurate. This has helped dentists a lot.
Intraoral radiology is a big part of dental care today. It’s expected to make a lot of money in 2023. This equipment gives dentists clear images. They can see cavities and jawbone health better.
Impact on Clinical Decision-Making
Oral radiology changes how dentists make decisions. It gives them clear images for better diagnosis. Dentists can spot problems early and plan treatments well.
New imaging tech has also improved patient care. Dentists can now see how bad dental diseases are. This helps them create treatments that fit each patient’s needs.
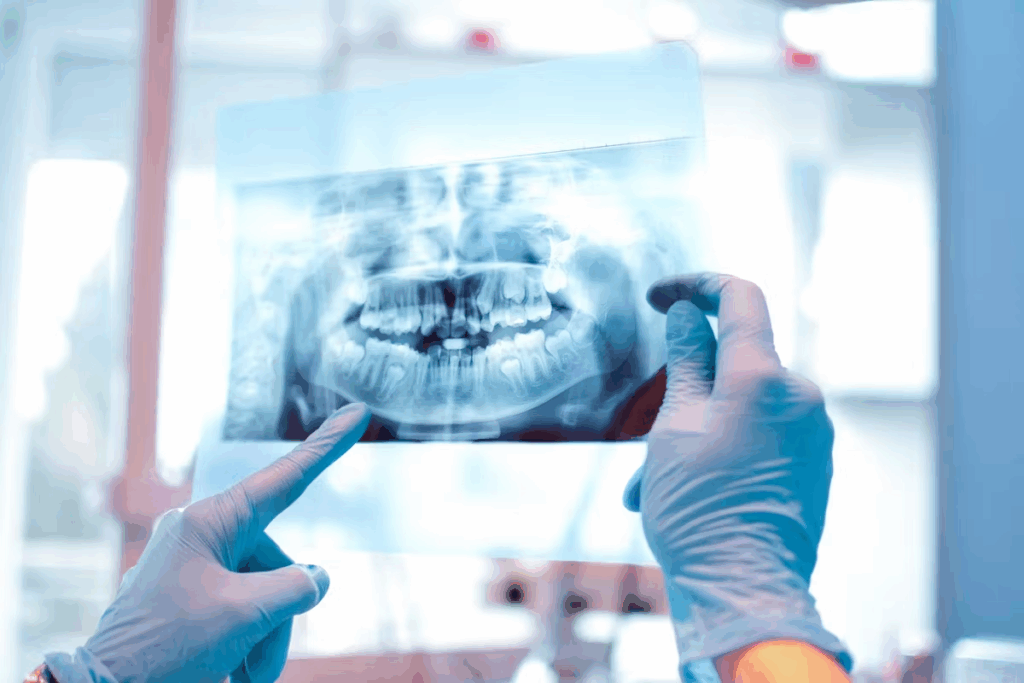
Fundamentals of Oral Radiology Physics
Understanding oral radiology starts with knowing the physics behind it. This includes X-ray generation and keeping radiation safe. The quality of dental X-rays depends on these principles.
X-ray Generation and Tissue Interaction
X-rays are key in oral radiology. They are made when high-energy electrons hit a metal target, like tungsten, in the X-ray tube. These X-rays then interact with dental tissues, showing us the inside of teeth and bones.
When X-rays hit tissues, they can be absorbed, scattered, or passed through. The density of the tissue affects how much X-rays are absorbed. This is why denser materials like enamel and metal show up white, while softer tissues appear darker.
As Medical Expert, a renowned expert in oral radiology, notes,
“The key to high-quality radiographic images lies in understanding the physics of X-ray generation and tissue interaction.”
Radiation Protection Standards
Keeping radiation safe is vital in oral radiology. The ALARA principle guides us to use the least amount of radiation needed. Digital radiography and CBCT have lowered radiation while improving images.
Dental professionals must follow strict safety rules. This includes shielding the X-ray tube and using protective gear for patients. Regular checks on radiography equipment are also key for safety.
As digital radiography gets better, so does patient safety. “Modern digital cephalometric systems offer enhanced image quality, reduced radiation exposure, and seamless integration with computer-aided diagnostic tools,” showing the progress in oral radiology.
Essential Equipment in Oral Radiology Practice
The heart of good oral radiology is using the right imaging tools. We use different types of imaging to help diagnose and treat our patients.
Intraoral Imaging Systems are key in our work. They take detailed pictures of teeth and the areas around them. We use intraoral X-rays to get clear images for diagnosing dental issues.
Intraoral Imaging Systems
Intraoral systems give us high-quality images and detailed views of teeth. We use them to spot cavities, check bone health, and see how dental work is doing.
Switching to digital intraoral imaging has improved our work a lot. Digital systems let us get images fast, use less radiation, and even enhance pictures for better diagnosis.
Extraoral Imaging Devices
Extraoral devices help us see bigger parts of the mouth and face. They’re vital for many dental fields, like orthodontics and oral surgery.
Cephalometric X-rays give us detailed skull and soft tissue images. We use them for orthodontic planning and to study facial structure.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is another big tool. It makes 3D images of teeth, soft tissues, nerves, and bones in one scan. We use CBCT for complex tasks like planning implants and checking for diseases.
In short, choosing the right imaging tools is key in oral radiology. Knowing how to use intraoral and extraoral systems helps us give better care to our patients.
Mastering Intraoral Radiographic Techniques
Intraoral radiography has changed dental diagnostics, giving us deep insights into oral health. Dental professionals use these methods for accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Periapical Radiography Methods
Periapical radiography gives a full view of a tooth, from crown to the periapical area. It’s key for checking the tooth’s health and the bone around it.
The paralleling technique is the most used in periapical radiography. It positions the X-ray beam straight to the dental film or sensor. This reduces distortion and shows the tooth and structures clearly.
Bitewing Radiography Applications
Bitewing X-rays show the crowns of upper and lower teeth. They’re the best for finding cavities between teeth. This method is great for spotting interproximal caries and checking restoration margins.
Key Applications of Bitewing Radiography:
- Detection of interproximal caries
- Assessment of marginal integrity of restorations
- Evaluation of alveolar bone levels
Radiography Technique | Primary Use | Key Benefits |
Periapical | Assessing entire tooth and surrounding bone | Accurate diagnosis of periapical pathology |
Bitewing | Detecting interproximal caries and assessing restorations | Early detection of caries, evaluation of restoration margins |
Occlusal | Examining larger areas of the jaw, locating impacted teeth | Comprehensive view of jaw anatomy, localization of impacted teeth |
Occlusal Radiography Implementation
Occlusal radiography shows a larger jaw area in two dimensions. It’s good for looking at the mouth floor, finding impacted teeth, and checking lesion sizes.
To use occlusal radiography well, dental pros need to place the X-ray beam and receptor right. They must know dental anatomy and radiography well.
Advances in dental radiology, like artificial intelligence, are promising. Surveys show 88.47 percent of dental pros think AI can improve diagnosis. This shows AI’s future in intraoral radiography.
Advanced 3D Imaging with CBCT Technology
CBCT has changed oral radiology with its 3D imaging. Now, we can see oral structures in great detail. This has changed how we diagnose and plan treatments in dentistry.
Technical Principles of Volumetric Imaging
CBCT uses a cone-shaped X-ray beam for a wide view in one rotation. This volumetric imaging makes 3D images from 2D projections. The images show unparalleled detail of teeth, bone, nerves, and soft tissues, helping with complex cases.
The tech behind CBCT uses advanced algorithms to make 3D datasets from raw data. These datasets can be viewed in different ways, giving a full view of the mouth.
Clinical Applications in Implantology
In implantology, CBCT is key for pre-surgical planning. It checks bone volume, density, and shape, vital for implant placement. The 3D images show how implants fit with nearby structures like nerves or sinuses.
CBCT also helps with bone grafting and implant integration checks. This boosts the success of implants.
Orthodontic and Surgical Case Planning
CBCT is also vital for orthodontic treatment planning. It lets us see tooth positions, root shapes, and bone. This is key for complex orthodontic cases, helping find the best anchor points and checking treatment results.
In surgery planning, CBCT gives 3D models for complex surgeries like orthognathic surgery or impacted tooth removal. Seeing the surgical site in 3D helps surgeons understand anatomy better and work more precisely.
Digital Radiography Revolution in Dental Practice
Digital radiography has changed oral radiology a lot. It offers many benefits over old systems. Now, digital radiography is key for diagnosing and planning treatments in dental offices.
The move from old to new systems has brought big advantages. These include getting images right away, better image quality, and less radiation. These changes have made patient care better and made dental work smoother.
Transitioning from Analog to Digital Systems
Switching from old to new systems means using digital sensors or phosphor plates instead of film. This change has made dental work more efficient and accurate.
Digital systems let dentists see images right away. This quick view helps in diagnosing and planning treatments faster.
Image Enhancement Techniques
Digital radiography lets dentists improve image quality with software tools. These tools help adjust brightness, contrast, and size. This makes diagnosing easier.
These techniques also let dentists use filters and algorithms. This highlights important details or problems in images. It makes radiographic images even more useful for diagnosis.
PACS and Digital Storage Solutions
The use of digital radiography has led to the use of PACS for image storage. PACS is a secure system for storing and sharing images. It makes images easy to access and share.
PACS has made it easier for dental professionals to work together. It has also improved patient care by making information more accessible.
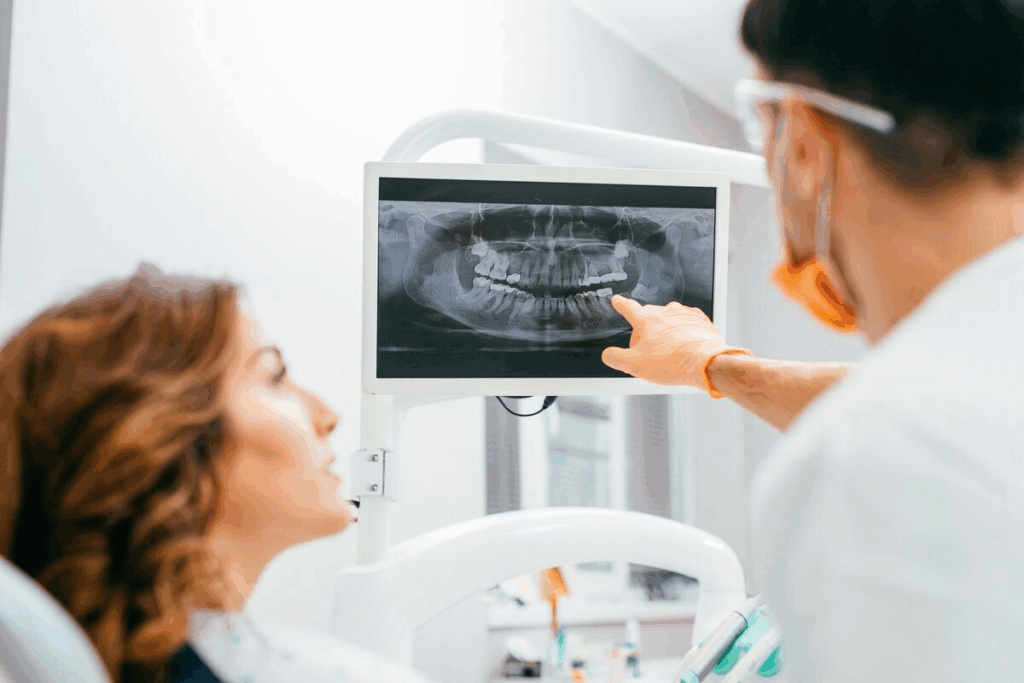
Developing Expert Radiographic Interpretation Skills
Being good at reading radiographs is key for top-notch patient care. Dental pros use these images to spot and plan treatments for many dental issues. It takes knowledge, skill, and practice to get it right.
Systematic Analysis Framework
Using a systematic way to read radiographs is vital. It helps us make sure we don’t miss anything important. We follow a set of steps to check the image quality, look at the body parts, and find any problems.
Here’s a simple guide for reading radiographs:
Step | Description |
1. Image Quality Assessment | Check how clear, contrasty, and good the radiograph looks. |
2. Anatomical Structure Assessment | Spot and check the normal body parts and structures seen on the radiograph. |
3. Pathology Identification | Find signs of disease, like cavities, bone loss, or other issues. |
4. Correlation with Clinical Findings | Match what we see on the radiograph with the patient’s symptoms and history. |
Normal Anatomical Landmark Recognition
Knowing what normal body parts look like is essential. Dental pros need to recognize things like the maxillary sinuses, nasal cavity, and mandibular canal.
For example, when looking at cephalometric X-rays, dentists and orthodontists find and measure specific body landmarks. This helps them understand the patient’s face and jaw structure. It’s important for planning treatments in orthodontics and oral surgery.
Pathology Identification and Differentiation
Spotting and telling apart different diseases is a big challenge. It needs a deep understanding of dental diseases and how to read radiographs. We must be able to tell apart cysts, tumors, and inflammation.
By using a systematic method and having a solid base in radiographic interpretation, we can give accurate diagnoses and plan effective treatments. As oral radiologists, we are key in diagnosing and managing dental diseases. Our skills are vital for the best patient outcomes.
Clinical Applications of Oral Radiology in Specialty Practice
Oral radiology is key in dental specialties. It boosts diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. We use it in endodontics, periodontics, and orthodontics for full patient care.
Endodontic Diagnosis and Treatment
In endodontics, oral radiology is vital for complex root canal anatomy diagnosis and treatment. CBCT imaging lets us see the root canal system in 3D. This helps us spot apical periodontitis and other issues better.
- Accurate diagnosis of root canal anatomy
- Detection of periapical lesions
- Guidance for endodontic surgery
We depend on radiographic evidence to check if endodontic treatment worked. This helps us decide on further steps.
Periodontal Disease Documentation
Oral radiology is essential in periodontics for disease extent assessment. We use radiographs to check alveolar bone loss and spot periodontal defects.
- Assessment of alveolar bone density
- Measurement of periodontal pocket depths
- Monitoring of disease progression
By studying radiographic images, we craft specific treatment plans for periodontal disease.
Orthodontic Analysis Techniques
In orthodontics, oral radiology aids in treatment planning and tracking. Cephalometric X-rays help us check jaw and tooth alignment. This allows for precise orthodontic analysis.
We use radiographic images to track treatment progress. This ensures the best results for our patients.
Research Trends in Oral Radiology Literature
The field of oral radiology is always changing. This is thanks to new research and technology. Original studies lead the way, focusing on how to apply research in real life.
Bibliometric Analysis of Current Research
Recent studies have shown us what’s new in oral radiology. They found that clinical uses are a big part of the research. This is driving better ways to diagnose and treat patients.
Some key points from these studies are:
- More papers are coming out on advanced imaging.
- There’s a big push to use oral radiology in different dental areas.
- New areas like using artificial intelligence in imaging are starting to appear.
Evidence-Based Approaches to Radiographic Diagnosis
Using evidence-based practice is key in oral radiology. It makes sure treatments are based on solid research. This helps patients and moves the field forward.
Some main evidence-based methods are:
- Systematic reviews help combine research to guide practice.
- Guidelines are made from the latest research to help doctors.
- Putting patients at the center of diagnosis and treatment is important.
Translating Research into Clinical Practice
Turning research into practice is vital for oral radiology. It means sharing findings and using them to improve care.
To make research useful in practice, we need:
- Researchers and doctors working together to make research relevant.
- Ways to help adopt new technologies and methods.
- Training to keep doctors up-to-date with new discoveries.
By keeping up with the latest in oral radiology research, we can improve patient care. As the field grows, staying focused on evidence-based practice and practical applications is essential.
Artificial Intelligence Integration in Diagnostic Imaging
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostic imaging is changing oral radiology. It’s important for oral radiologists to keep up with these changes to offer top care.
Current AI Applications in Dental Radiology
AI is making dental radiology better by improving diagnosis accuracy. For example, AI can spot caries, periodontal disease, and other issues in X-rays. A survey found 88.47 percent of dental pros believe AI boosts diagnosis.
Key Applications of AI in Dental Radiology:
- Automated detection of dental caries
- Analysis of periodontal bone loss
- Identification of periapical lesions
- Detection of oral cancers
Machine Learning for Image Interpretation
Machine learning, a part of AI, is key for image analysis. It looks at lots of X-ray data to find patterns and oddities. This helps oral radiologists make better diagnoses.
“The future of dental radiology lies in the synergy between human expertise and AI capabilities.”
Professional Attitudes and Adoption Rates
Dental pros are excited about AI but have concerns about using it in practice. They worry about data privacy, algorithm trustworthiness, and training needs. These issues are being worked on to make AI more accepted.
Aspect | Current Status | Future Direction |
AI Adoption | Increasing | Widespread |
Professional Training | Limited | Comprehensive |
Data Privacy | Concerns exist | Enhanced security |
As we look ahead, teamwork between AI creators and oral radiologists will shape diagnostic imaging’s future. For more info, a detailed dental radiology book is a great resource.
Conclusion: Achieving Excellence in Oral Radiology
To excel in oral radiology, you need to know a lot about imaging, how to interpret images, and how to use them in practice. Using the latest imaging tech and keeping up with new research helps dental pros give top-notch care.
We’ve looked at the basics of oral radiology. This includes how dental imaging has evolved and the newest 3D imaging and AI. Knowing these well is key for making accurate diagnoses and planning treatments.
Keeping up with new education and training is vital for staying at the top in oral radiology. Dental pros must learn about new tech like digital radiography and AI in image reading. This ensures they can give the best care to their patients.
By combining technical skills with a strong grasp of how to apply them in practice, we can raise the bar in oral radiology. This helps improve patient care and outcomes.
FAQ
What is oral radiology, and why is it important in dentistry?
Oral radiology uses X-rays to help diagnose and treat dental problems. It’s key for quality dental care. Dentists can see inside teeth and make precise diagnoses thanks to it.
What are the different types of imaging technologies used in oral radiology?
There are many imaging tools, like digital radiography and CBCT. Each has its own uses and benefits for dental care.
How has digital radiography changed dental practice?
Digital radiography has made dental care faster and safer. It offers better image quality and helps in diagnosing and treating patients.
What is CBCT technology, and how is it used in dentistry?
CBCT gives 3D images of teeth. It’s used for implants, orthodontics, and planning surgeries. It helps in making accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
How do oral radiologists interpret radiographic images?
They use a systematic approach to analyze images. They look for normal structures and any problems. This skill is vital for correct diagnoses and treatment.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in oral radiology?
AI helps in interpreting images and planning treatments. It improves accuracy and makes dental care more efficient.
What are the benefits of mastering oral radiology for dental professionals?
Knowing oral radiology helps dental professionals give better care. They can make accurate diagnoses and plan treatments effectively. It boosts their skills in using imaging technologies.
What is the importance of radiation protection standards in oral radiology?
Following radiation protection standards is vital. It keeps patients and dental staff safe from radiation. It ensures safe dental practices.
How does oral radiology contribute to different dental specialties?
Oral radiology is important for many dental fields, like endodontics and orthodontics. It helps in diagnosing and planning treatments. It improves patient care in these areas.
References
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37876387



































