Did you know over 1 million pacemakers are put in worldwide each year? This shows how much we rely on these devices. But, many wonder: is there an age limit for getting a pacemaker?pacemaker age limitAtrial Fibrillation Pacemaker: Key Facts
Many think there’s a strict age limit for pacemakers. But, it’s not that simple. Doctors look at more than just the patient’s age when deciding. They check the patient’s health, medical history, and how bad their symptoms are.
Key Takeaways
- There is no strict age limit for pacemaker implantation.
- The decision to implant a pacemaker is based on individual patient needs.
- Factors such as overall health and medical history play a critical role.
- Pacemaker eligibility is determined on a case-by-case basis.
- Medical professionals consider multiple criteria when evaluating candidates.
Understanding Pacemakers: Function and Purpose
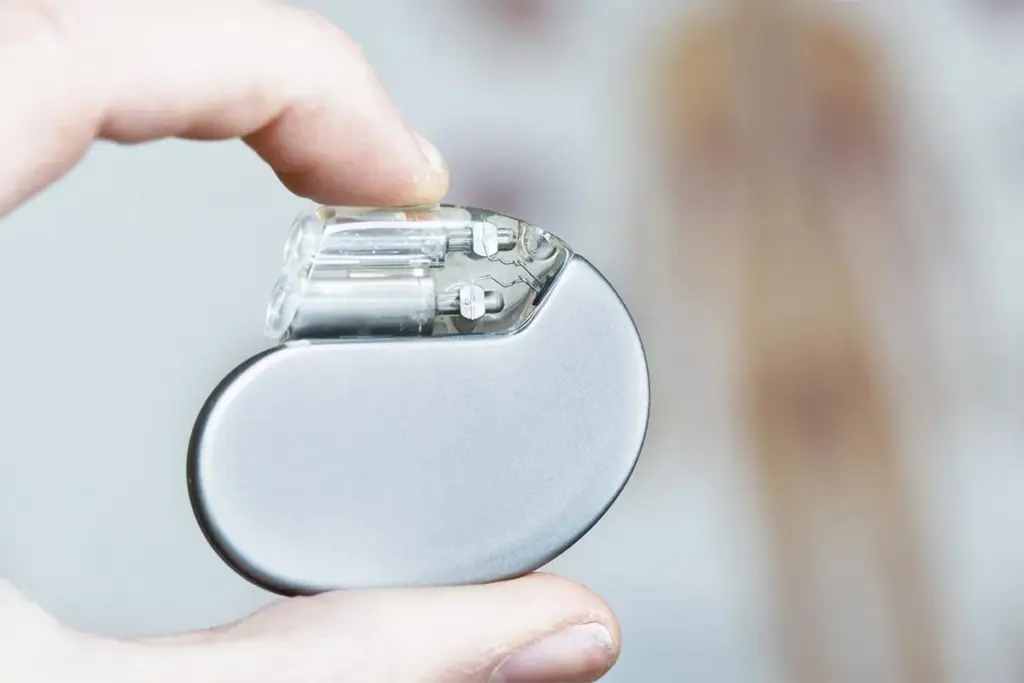

Pacemakers have changed how we manage heart conditions. They are small devices that help the heart beat at the right pace. This makes life better for many people.
How Pacemakers Work
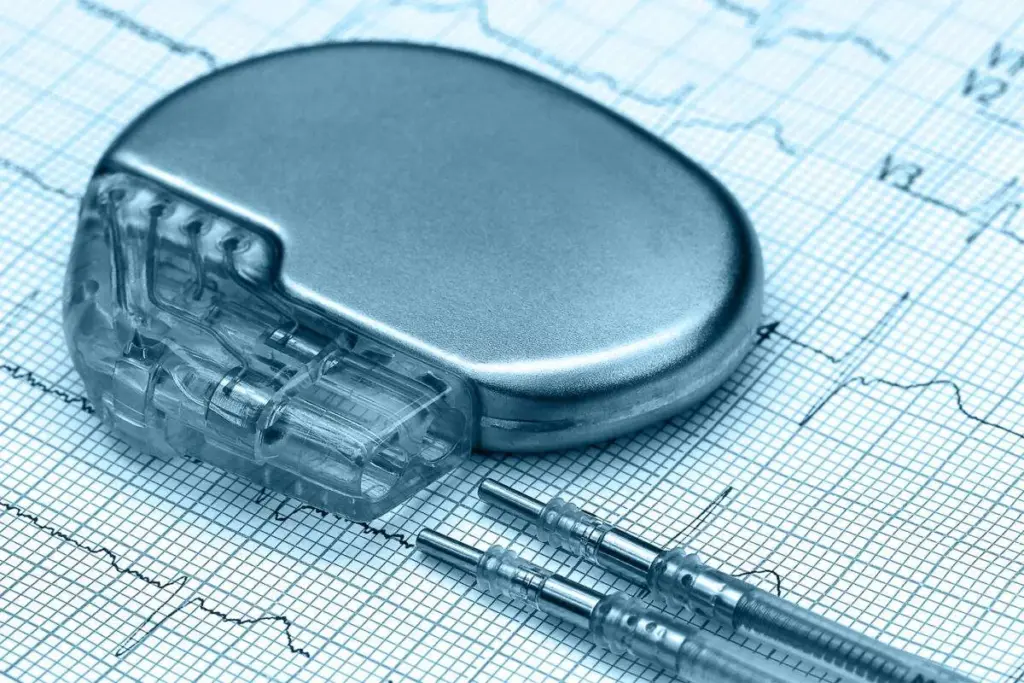
A pacemaker is a device that helps control the heartbeat. It has two main parts: the pulse generator and the leads. The pulse generator is a small metal box with the electronics and battery. The leads are wires that connect the pulse generator to the heart.
The pulse generator watches the heart’s rhythm and sends electrical impulses when needed. This keeps the heart rate normal, even when you’re active or stressed. Today’s pacemakers have sensors that adjust the heart rate based on your activity.
Types of Pacemakers Available Today
There are different pacemakers for various heart issues. The main types are single-chamber, dual-chamber, and biventricular pacemakers. Single-chamber pacemakers have one lead in the heart. Dual-chamber pacemakers have two leads for better pacing.
Biventricular pacemakers, or CRT devices, help with heart failure. They make sure the ventricles beat together. This is great for some heart failure patients.
New pacemaker technology includes MRI-compatible ones. These can be safely scanned during MRI tests. This is a big plus, as it lets patients get needed tests without worrying about their pacemaker.
Medical Conditions That Typically Require Pacemakers
Heart conditions like bradycardia and arrhythmias often need pacemakers. Pacemakers are devices that control the heartbeat. They send electrical impulses to make the heart muscle contract. We’ll look at the main medical conditions that need pacemakers.
Bradycardia and Heart Blocks
Bradycardia means a heart rate that’s slower than normal. It can cause fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Heart blocks disrupt the heart’s electrical signals. Pacemakers help keep the heart rate steady.
To diagnose bradycardia and heart blocks, we use:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to detect abnormal heart rhythms
- Holter monitoring for continuous ECG tracking
- Stress tests to evaluate heart function under exertion
Arrhythmias and Irregular Heart Rhythms
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats that can be too fast, too slow, or irregular. Pacemakers manage certain arrhythmias by keeping the heart rate steady. Atrial fibrillation, a common arrhythmia, may benefit from pacemaker therapy.
To diagnose arrhythmias, we use:
- ECG detection to identify irregular heart rhythms
- Event monitors to track heart activity over time
- Implantable loop recorders for long-term monitoring
Heart Failure and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Heart failure happens when the heart can’t pump enough blood. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is a treatment for heart failure. It uses a special pacemaker to sync the heart’s chambers. CRT can improve symptoms and quality of life for some patients.
- Severe heart failure symptoms
- Left bundle branch block, a condition affecting the heart’s electrical conduction
- Reduced ejection fraction, indicating poor heart function
The Truth About Pacemaker Age Limit: Is There a Cutoff?
Pacemaker age limits are more of a myth than a medical reality. The decision to implant a pacemaker is based on a complex evaluation of a patient’s health status, not solely on their age. We often encounter misconceptions about the age cutoff for pacemaker eligibility, and it’s essential to clarify these misunderstandings.
Medical Guidelines vs. Common Misconceptions
Medical guidelines for pacemaker implantation are based on specific heart conditions, not age. Pacemaker eligibility criteria consider symptoms, medical history, and diagnostic test results like ECGs.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is key in determining pacemaker need. Knowing what a normal ECG looks like and understanding ECG results is important. It helps assess heart function and identify issues that may need a pacemaker.
Factors That Influence Eligibility Beyond Age
Many factors influence pacemaker eligibility beyond age. Symptoms like dizziness, fainting, or shortness of breath matter. So does the underlying heart condition and the patient’s overall health and lifestyle.
The age cutoff for pacemaker is not strict. It’s a decision based on the individual’s medical needs and circumstances. By looking at all these factors, we can decide if a pacemaker is right, regardless of age.
Pacemakers in Elderly Patients (75+)
Pacemakers can greatly improve the lives of seniors aged 75 and older. They help manage heart conditions. As more people live longer, more seniors need pacemakers. We’ll look at the benefits and what to consider.
Benefits and Considerations for Seniors
Seniors encounter distinct challenges related to pacemaker considerations. They might have other health problems or cognitive decline. But, pacemakers can be very helpful for them. They can ease symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath.
Doctors look at many things before deciding on a pacemaker for an elderly patient. They consider the patient’s health, how long they might live, and how the pacemaker will affect their life. Being old doesn’t mean you can’t get a pacemaker.
|
Consideration |
Description |
Impact on Seniors |
|---|---|---|
|
Comorbidities |
Presence of other health conditions |
May complicate surgery or recovery |
|
Cognitive Function |
Ability to understand and manage device |
Requires additional support or simpler devices |
|
Life Expectancy |
Estimated remaining lifespan |
Influences decision-making regarding implantation |
Quality of Life Improvements in Advanced Age
Pacemakers can make a big difference in the lives of elderly people. They help reduce symptoms and improve how well seniors can do things. Research shows that seniors with pacemakers often feel better and can stay independent.
Also, new pacemaker technologies, like rate-responsive pacing, make devices more adaptable. This helps seniors live better lives.
Middle-Aged Adults and Pacemaker Implantation
Choosing to get a pacemaker is a big decision for those between 40 and 75. This age group has to handle work and aging’s physical changes. We’ll look at how pacemakers affect middle-aged adults, focusing on long-term effects and work-life balance.
Long-term Outcomes for Patients 40-75
Pacemakers can greatly improve life for middle-aged adults. They help control heart rhythms and reduce symptoms. Studies show most patients in this age group see their heart function improve and symptoms lessen.
Key factors influencing long-term outcomes include:
- Regular follow-up care to monitor pacemaker function and adjust settings as needed.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as incorporating regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet.
- Adherence to medication regimens and other treatment plans.
Balancing Career and Recovery
For many middle-aged adults, balancing work and family with recovery is tough. It’s key to plan for enough recovery time and talk openly with employers and family about needs during this period.
Efficient recovery strategies include:
- Gradually returning to work and normal activities to avoid overexertion.
- Utilizing EKG monitoring during exercise to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- Seeking support from healthcare providers, family, and friends to manage stress and responsibilities.
Understanding pacemaker implantation’s effects and taking steps for recovery helps middle-aged adults make this big health choice with confidence.
Young Adults and Pacemakers: Special Considerations
Young adults with pacemakers face unique challenges. They must adapt to a new normal and deal with the emotional side of their condition. It’s key to grasp the full impact of living with a pacemaker at a young age.
Lifestyle Adaptations for Younger Patients
Having a pacemaker means big changes for young adults. They need to adjust their exercise routines and watch out for electromagnetic interference. They also have to think about how their condition might affect their future plans, like having kids or choosing a career.
Physical activity is a big part of adapting to life with a pacemaker. While many sports are okay, some might need to be changed or avoided. For example, sports that involve hitting the chest are not recommended.
|
Activity |
Safety Recommendation |
Precautions |
|---|---|---|
|
Running/Jogging |
Generally Safe |
Avoid high-impact activities that may cause lead displacement. |
|
Swimming |
Safe |
Inform your doctor; most pacemakers are waterproof. |
|
Contact Sports (e.g., Football, Rugby) |
Not Recommended |
Risk of lead displacement or pacemaker damage. |
Psychological Impact and Support Systems
The emotional side of having a pacemaker is important, too. Young adults might already be dealing with big life changes. Feeling anxious, depressed, or stressed about the device is common.
Having a strong support system helps a lot. This includes counseling, support groups, and educating family members. Healthcare providers should also offer lots of guidance and reassurance.
Knowing how a pacemaker works and what to watch for can help ease worries. Regular check-ups and monitoring ensure the device is working right. Addressing any fears or myths about pacemakers can also boost well-being.
Pediatric Pacemakers: When Children Need Cardiac Support
Children born with heart conditions may need pacemakers to survive. These devices help manage irregular heartbeats. They ensure the heart works right.
Congenital Heart Conditions and Pacemaker Necessity
Congenital heart defects are heart problems present at birth. Some defects cause abnormal heart rhythms. This might need a pacemaker.
Conditions like bradycardia (slow heart rate) or heart block (delayed electrical signals) can greatly benefit from pacemakers.
says congenital heart defects affect about 1 in 100 births. Not all will need a pacemaker. But, those with certain conditions can greatly benefit.
|
Congenital Heart Condition |
Description |
Pacemaker Benefit |
|---|---|---|
|
Bradycardia |
Slow heart rate that can lead to fatigue and shortness of breath |
Regulates heart rate to improve energy levels and overall health |
|
Heart Block |
Delay or blockage of electrical signals between heart chambers |
Ensures proper timing of heartbeats to prevent complications |
Growth Considerations and Device Adjustments
One challenge with pediatric pacemakers is growing. As kids grow, the pacemaker leads may need adjusting or replacing.
” “Regular follow-ups are vital to monitor and adjust as needed.”
ECG monitoring is critical for managing pediatric pacemaker patients. Regular ECG checks help healthcare providers adjust settings as needed.
Understanding children’s pacemaker needs helps healthcare providers offer tailored care. This ensures these young patients can live active, fulfilling lives.
The Evaluation Process for Pacemaker Candidacy
Checking if someone needs a pacemaker involves many steps. We look at different tests and factors. This helps us decide if a pacemaker is the best choice for a patient.
Diagnostic Tests and Assessments
To see if a pacemaker is right, we use several tests. These include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test shows how the heart’s electrical activity works. It helps find heart rhythm problems.
- Holter Monitoring: This 24-hour ECG test records the heart’s activity. It gives more detailed info about heart rhythms.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound test that looks at the heart’s structure and function. It checks how well the heart pumps and finds any problems.
- Stress Test: This test checks how the heart works under stress. It’s done through exercise or medicine.
These tests are key in finding out if a pacemaker is needed.
The Multidisciplinary Team Approach
A team of doctors, including cardiologists and electrophysiologists, works together. They:
- Look at the patient’s medical history and test results.
- Check the patient’s overall health and decide the best treatment.
- Talk about the benefits and risks of getting a pacemaker.
This team approach means each patient gets a treatment plan made just for them.
With this detailed process, we can tell if a pacemaker is right for someone. Then, we create a treatment plan that works best.
Risks vs. Benefits: Age-Related Considerations
When thinking about getting a pacemaker, it’s important to weigh the risks and benefits. This is even more true as you get older. We look at how well a pacemaker might work for you by checking these things carefully.
Surgical Risks Across Different Age Groups
The risks of getting a pacemaker vary with age. Young people usually face fewer problems, while older adults might have more risks. This is because older people often have other health issues and their bodies might not recover as well.
We’ve noticed that:
- People under 40 usually have fewer surgery-related problems.
- Those between 40 and 75 might face some risks, but these can often be managed with good care before surgery.
- People over 75 are at a higher risk for issues like infections, bleeding, and problems with the device itself.
|
Age Group |
Surgical Risks |
Complication Rate |
|---|---|---|
|
<40 years |
Low |
2% |
|
40-75 years |
Moderate |
5% |
|
>75 years |
High |
8% |
Long-term Outcomes and Life Expectancy
The long-term effects and life span of pacemaker patients depend on several things. These include the heart condition, overall health, and age when the pacemaker is put in.
Important things to think about include:
- The kind of pacemaker used and its features.
- Any other health issues that might affect the heart or overall health.
- Changes in lifestyle and sticking to follow-up care.
Research shows that pacemakers can greatly improve life quality and survival for those who really need them. Ekg monitoring is key in managing these patients and making sure the device works right.
Recovery and Lifestyle After Pacemaker Implantation
After getting a pacemaker, the focus is on recovery and adjusting to life with it. This time can be both a relief and a challenge for patients.
Immediate Post-Procedure Recovery
Right after the procedure, patients stay in a recovery room for a few hours. Our team checks for any immediate issues and makes sure the pacemaker works right. They usually tell patients to rest and avoid hard activities for a few days. We also teach them about wound care and how to spot infection signs.
Long-term Lifestyle Adjustments
As patients get better, they can start doing normal things again, like exercising and working. But, they need to make some lifestyle changes to keep the pacemaker working well and their heart healthy. It’s important to listen to our advice on exercise, as too much can be bad. We also teach them how to manage their pacemaker, including checking its function and when to see a doctor.
Monitoring heart rate during exercise is key when you have a pacemaker. We tell patients what exercises are safe and how to keep an eye on their heart rate. This helps them stay active while keeping their heart safe.
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
Regular check-ups are important for managing the pacemaker. At these visits, we check the device’s battery, adjust settings if needed, and look at the patient’s heart health. These visits help catch any problems early and make sure the pacemaker keeps working well.
We also teach patients about remote monitoring systems. These systems let us check the pacemaker’s status and the patient’s heart rhythm without needing to see them in person. This makes managing the pacemaker safer and more convenient.
Alternative Treatments When Pacemakers Aren’t Suitable
When pacemakers aren’t the right choice, doctors look at other ways to help. This makes sure patients get the best care for their heart issues.
Medication Management Options
For many, taking medicine is a good alternative to getting a pacemaker. Beta-blockers and anti-arrhythmic drugs can help control heart rate and rhythm. This can mean fewer invasive procedures.
Doctors tailor medication plans to each patient. They consider the patient’s health, how serious their heart condition is, and any other medicines they’re on. Regular checks and changes to the medication can make treatment work better.
|
Medication Type |
Primary Use |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Beta-blockers |
Control heart rate |
Reduce symptoms, improve exercise tolerance |
|
Anti-arrhythmic drugs |
Manage irregular heart rhythms |
Improve quality of life, reduce hospitalization |
Emerging Non-Invasive Technologies
New, non-invasive technologies are also helping patients. These include ECG-guided treatments and other new ways to manage heart rhythm issues. They don’t require surgery.
Wearable devices are a promising area. They can track heart activity and give feedback to patients and doctors. This can lead to quicker and better care for heart conditions.
As research keeps moving forward, we’ll see even more new solutions. These will give patients more options than just pacemakers.
Insurance Coverage and Cost Considerations Across Age Groups
Insurance is key to getting pacemakers for those who need them. It’s important to know how insurance works for pacemakers.
Medicare Coverage for Pacemakers
People 65 and older get help from Medicare for pacemaker costs. Medicare Part B sees pacemakers as durable medical equipment. But, the details can change based on your Medicare plan and any extra insurance.
Medicare can be hard to understand. Usually, Medicare pays 80% of the cost for pacemaker implants. You pay the other 20% and any deductibles.
|
Medicare Coverage Aspect |
Description |
Patient Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
|
Pacemaker Implantation |
Covered under Medicare Part B |
20% of Medicare-approved amount |
|
Deductibles |
Vary by Medicare plan |
Applicable deductible amount |
|
Supplemental Insurance |
May cover additional costs |
Varies by supplemental plan |
Private Insurance and Financial Assistance Programs
Those under 65 or with private insurance face different rules for pacemaker coverage. Many plans do cover pacemaker implants. But, how much you pay depends on your plan.
Financial worries are common for pacemaker patients. There are programs to help with costs. These can cover copays, deductibles, and more.
Financial Assistance Options:
- Manufacturer-funded programs
- Non-profit organization assistance
- Government programs for eligible patients
Talking to your doctor about insurance and financial help is important. This way, you can find out what’s available to you.
Conclusion
Choosing to get a pacemaker is a big decision. Age is just one thing to think about. Medical guidelines, overall health, and personal needs also matter a lot.
Tests like ECG and EKG help doctors check the heart’s health. These tests can show if a pacemaker is needed. For people of all ages, pacemakers can greatly improve life and sometimes save lives.
There’s no fixed age limit for getting a pacemaker. A team of doctors needs to evaluate each case carefully. It’s important for patients to talk to their doctors about their specific situation.
Looking at each patient’s unique needs and health is key. This way, those who could really benefit from a pacemaker get the right care. It helps improve heart health and overall well-being for people of all ages.
FAQ
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507823/
What does ECG stand for?
ECG stands for electrocardiogram. It’s a test that checks the heart’s electrical activity.
Can an electrocardiogram detect a heart attack?
Yes, an electrocardiogram can spot a heart attack. It looks for signs like ST-segment elevation or Q-waves.
If EKG is normal, is my heart OK?
A normal EKG is reassuring. But it doesn’t mean your heart is perfectly fine. Some heart issues might not show up on an EKG.
What is a normal ECG result?
A normal ECG shows a regular heartbeat and rate. It also doesn’t show signs of heart problems or other issues.
Can ECG detect heart attack?
Yes, ECG can detect heart attacks. It looks for signs of heart damage.
Is there an age limit for getting a pacemaker?
There’s no strict age limit for pacemakers. The decision depends on your health, medical condition, and symptoms.
What are the benefits of pacemakers for elderly patients?
Pacemakers can greatly improve life for the elderly. They manage heart issues like slow heart rate and reduce symptoms like tiredness and dizziness.
Can pacemakers be used in children?
Yes, pacemakers can help children with heart problems. They need special care, like adjustments for growth and monitoring.
What is the evaluation process for pacemaker candidacy?
To see if you need a pacemaker, you’ll have tests like ECG and echocardiogram. A team of doctors will also assess you.
What are the risks and benefits of pacemaker implantation?
Pacemakers can improve heart function and reduce symptoms. But, there are risks like surgery problems, device failure, and infections.
How does insurance coverage work for pacemakers?
Insurance for pacemakers varies by type, age, and condition. Medicare and private plans might cover the cost and care after implantation.
Can an EKG detect blockages?
An EKG can show signs of heart damage, which might mean blockages. But, it’s not a direct test for blockages.
What is a normal EKG reading?
A normal EKG shows a regular heartbeat and rate. It also doesn’t show heart problems or other issues.
Can a pacemaker improve quality of life?
Yes, a pacemaker can make life better. It manages heart issues and reduces symptoms like tiredness and shortness of breath.
Are there alternative treatments to pacemakers?
Yes, there are other options like medicine and new technologies. These can help manage heart conditions without a pacemaker.









