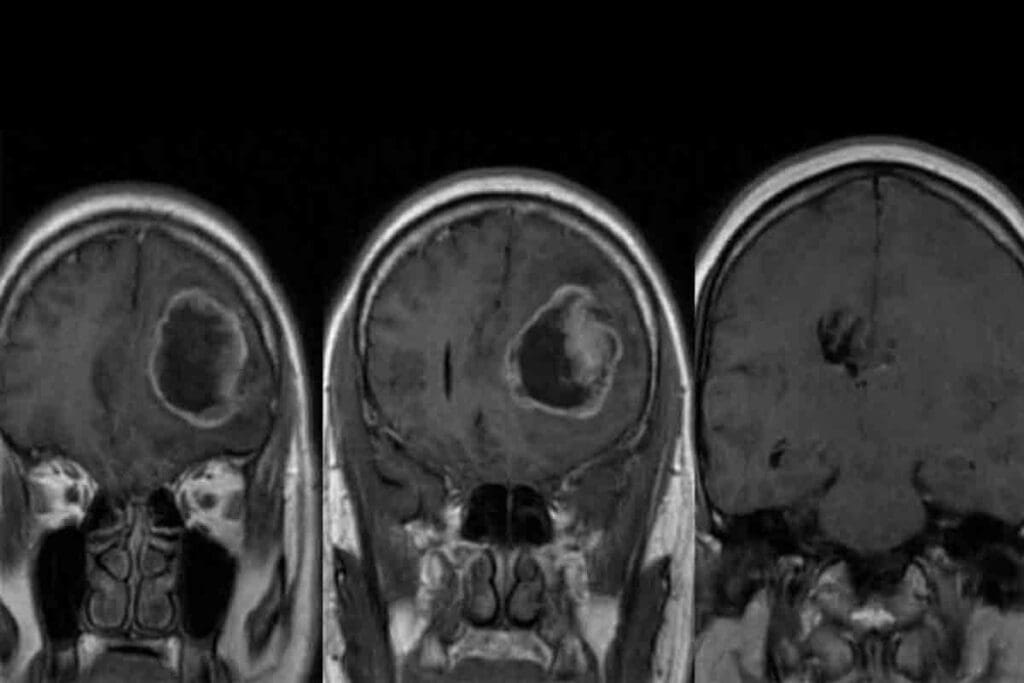
Glioblastoma multiforme is a rare and aggressive brain cancer that affects children, typically between the ages of 8 and 18. It starts in the brain’s astrocytes, which are cells that support nerve cells.
Symptoms can include persistent headaches, memory loss, and sudden behavioral changes. It’s important to understand the causes and treatment options for this condition. At Liv Hospital, we offer expert care and the latest treatment pathways for children diagnosed with this complex condition.
Our approach combines medical authority with empathetic understanding, ensuring complete support for our patients.
Key Takeaways
- Glioblastoma multiforme is a rare and aggressive brain tumor in children.
- Symptoms include headaches, memory loss, and behavioral changes.
- Understanding causes and treatment options is key for patients.
- Liv Hospital offers expert care and the latest treatment pathways.
- Comprehensive support is provided for patients and their families.
Understanding Pediatric Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)
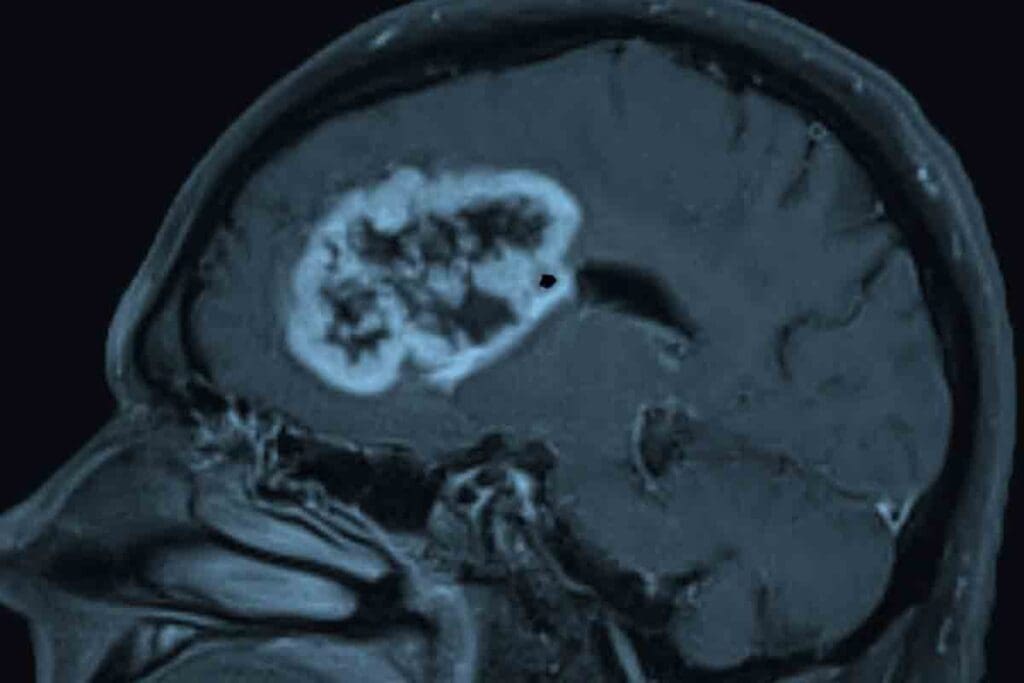
It’s important to understand Pediatric Glioblastoma Multiforme to find better treatments. We’ll explore what it is, how it’s classified, and how common it is. We’ll also see how it differs from GBM in adults.
Definition and Classification of GBM
Glioblastoma Multiforme, or GBM, is a very aggressive brain tumor. It’s classified as a Grade IV astrocytoma by the World Health Organization. This means it grows fast and spreads to other brain areas.
Key characteristics of GBM include:
- High degree of cellular atypia
- Microvascular proliferation
- Presence of necrosis
Incidence and Epidemiology in the United States
In the United States, about 500 kids get glioblastoma each year. While it’s more common in older people, it can happen at any age. The Medical organization says glioblastoma is most common in older adults, but it can affect anyone.
| Age Group | Incidence Rate |
| 0-19 years | 0.7 per 100,000 |
| 20-44 years | 0.9 per 100,000 |
| 45-64 years | 3.4 per 100,000 |
| 65+ years | 5.6 per 100,000 |
How Pediatric GBM Differs from Adult GBM
Pediatric GBM is different from adult GBM in its genetics and biology. Adult GBM comes from many genetic changes over time. But pediatric GBM has its own genetic causes. Knowing these differences helps us create treatments for kids.
The difference between pediatric and adult GBM is more than age. It’s about the biology, which affects treatment and results.
The Biology of Glioblastoma Multiforme in Children
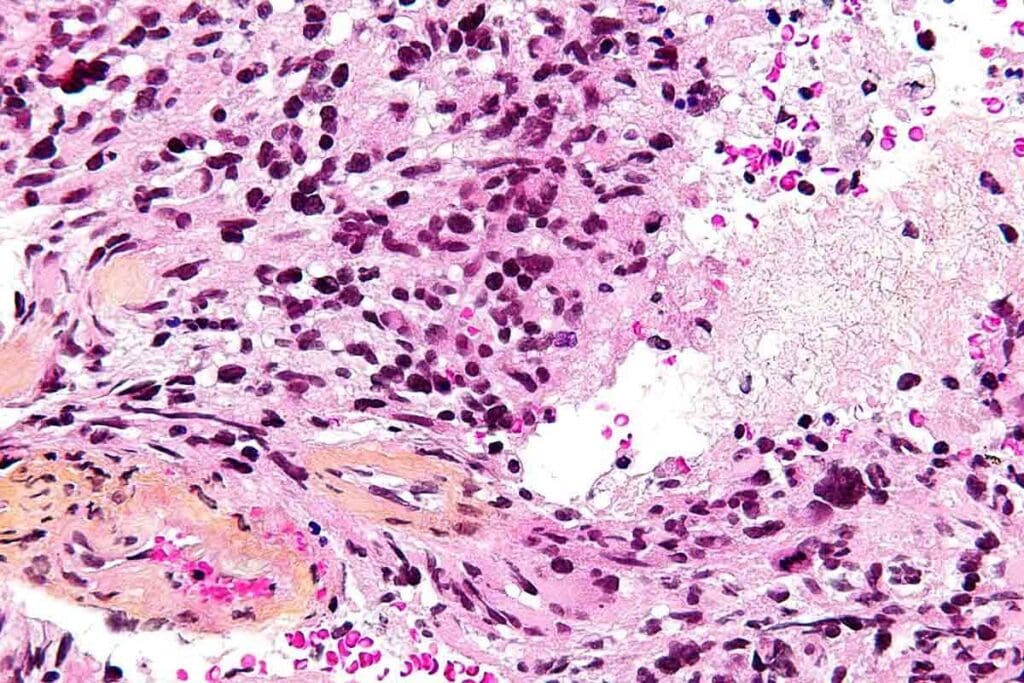
Understanding glioblastoma multiforme in kids is key to better treatments. We’ll look at the tumor’s cells, genes, where it grows, and how it spreads.
Cellular and Molecular Characteristics
Pediatric glioblastoma multiforme grows fast and is very aggressive. It has many cell types, including stem-like cells. These cells help the tumor fight off treatmentsas studies show.
The tumor’s genes and epigenes change a lot. These changes mess with signals that control cell growth and survival. For example, TP53 and PTEN gene mutations are common in GBM, making it very bad.
Common Locations in the Brain
GBM can pop up anywhere in the brain but often shows up in the cerebral hemispheres. It likes the frontal lobe and areas above the tentorium. It can also appear in the brainstem and cerebellum, but that’s less common in kids.
Growth Patterns and Invasiveness
GBMs grow fast and spread into brain tissue. They start in the white matter and can get big before symptoms show. Their ability to spread makes surgery hard, as they can sneak into nearby brain areas.
| Characteristics | Description |
| Cellular Heterogeneity | Presence of various cell types, including stem-like cells |
| Molecular Alterations | Genetic and epigenetic changes affecting signaling pathways |
| Common Locations | Cerebral hemispheres, frontal lobe, supratentorial regions |
| Growth Patterns | Rapid growth, invasive nature, formation in cerebral white matter |
Signs and Symptoms of Pediatric Glioblastoma Multiforme
It’s important to know the signs of pediatric glioblastoma multiforme early. This brain tumor is aggressive and can be hard to spot because its symptoms are similar to those of less serious conditions.
Early Warning Signs
Children with glioblastoma might have headaches, nausea, and vomiting a lot. These are signs of increased pressure in the brain because of the tumor.
Parents and caregivers should watch for these signs. If they don’t go away or get worse, it’s time to see a doctor.
Neurological Symptoms
As the tumor grows, kids might have neurological symptoms like seizures, weakness, or numbness. These happen because the tumor is pressing on the brain.
The symptoms can depend on where the tumor is in the brain. For example, a tumor near the motor cortex might cause weakness in a limb.
Cognitive and Behavioral Changes
Kids with glioblastoma might also have cognitive and behavioral changes. They might have trouble remembering things, act differently, or find it hard to focus or learn new things.
These changes can start small but get bigger as the disease gets worse. It’s key for parents and teachers to keep an eye on these changes.
Age-Specific Symptom Presentation
Symptoms can look different in different age groups. Young kids might seem irritable, tired, or not grow as they should. Older kids and teens might have more specific symptoms like headaches or vision problems.
Doctors need to know these age differences to make the right diagnosis.
| Age Group | Common Symptoms |
| Infants and Toddlers | Irritability, Lethargy, Macrocephaly |
| Children (2-12 years) | Headaches, Nausea, Vomiting, Seizures |
| Adolescents | Headaches, Visual Disturbances, Cognitive Changes, Personality Changes |
Risk Factors and Causes of Glioblastoma in Children
The exact causes of glioblastoma multiforme in kids are not fully known. But, research has found several risk factors. Knowing these helps us find who’s at higher risk and how to prevent it.
Genetic Predisposition and Syndromes
Genetics play a big role in glioblastoma in kids. Some genetic syndromes raise the risk of getting this disease. For example, Li-Fraumeni syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that increases cancer risk, including glioblastoma.
Another condition, neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also raises the risk. NF1 causes many noncancerous tumors and increases cancer risk, including glioblastoma.
“The presence of certain genetic syndromes can significantly increase the risk of developing glioblastoma multiforme, highlighting the importance of genetic screening and counseling for families with a history of such conditions.” – expert opinion
Environmental Risk Factors
Environmental factors also play a part. Ionizing radiation is a known risk for brain tumors, including glioblastoma. Kids exposed to radiation therapy for other conditions are at higher risk.
Other environmental risks are being studied. Research is ongoing into how different exposures might affect glioblastoma risk.
Previous Radiation Exposure
Being exposed to ionizing radiation is a big risk factor. Kids who had radiation therapy, like for cancer, are at higher risk. A Medical organization says radiation exposure is a known risk for glioblastoma.
Knowing the risk factors for glioblastoma is key to early detection and care. By spotting kids at higher risk, doctors can take steps to prevent and manage the disease.
Diagnosis of Pediatric GBM
Diagnosing pediatric GBM is tough. It needs a detailed approach with advanced imaging and molecular tests. Getting it right is key to good treatment plans.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed check-up and physical exam. We look at the child’s health history for signs of a brain tumor. We also check their brain function and motor skills.
Imaging Studies (MRI, CT Scans)
Imaging is vital for diagnosing pediatric GBM. MRI and CT scans help us see the tumor in the brain. MRI gives us clear images of soft tissues, showing the tumor’s size and where it is.
Biopsy and Histopathological Evaluation
A biopsy is key to confirming GBM. We take tissue samples during surgery. Looking at these samples under a microscope helps us spot the tumor’s unique features.
Molecular and Genetic Testing
Molecular and genetic tests give us more info for diagnosis and treatment. We check for genetic mutations and the MGMT promoter’s methylation status. This helps us understand how the tumor might react to treatment.
By using all these methods, we can accurately diagnose pediatric GBM. Then, we can create a treatment plan that fits the child’s needs.
Treatment Options for Pediatric Glioblastoma Multiforme
Treating pediatric glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) needs a team effort. Doctors, nurses, and specialists work together to create a treatment plan. This plan is made just for the child, taking into account their unique situation.
Surgical Approaches
Surgery is often the first step in treating pediatric GBM. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is done carefully to avoid harming the brain.
The surgery method depends on the tumor’s location and size. Modern tools like intraoperative MRI help surgeons remove the tumor more accurately.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is key in treating pediatric GBM. External beam radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. This helps shrink the tumor.
The radiation plan is made to focus on the tumor while protecting the brain. This reduces the chance of long-term side effects and keeps the child healthy.
Chemotherapy Protocols
Chemotherapy is a vital part of treating pediatric GBM. Different chemotherapy plans are used, often with surgery and radiation. Temozolomide, a common drug, is taken by mouth.
| Chemotherapy Agent | Administration Route | Common Side Effects |
| Temozolomide | Oral | Nausea, fatigue, hair loss |
| Carboplatin | Intravenous | Hearing loss, kidney damage, low blood counts |
| Vincristine | Intravenous | Nerve damage, constipation, hair loss |
Chemotherapy plans are customized for each child. Researchers are always looking for better ways to treat pediatric GBM.
Managing Treatment Side Effects and Complications
Managing side effects and complications is key in treating pediatric glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). It’s important for better patient outcomes and quality of life.
Short-term Side Effects
Treatment for pediatric GBM can cause short-term side effects. These include:
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss
- Cognitive impairment
We work with patients and their families to lessen these effects. We use supportive care strategies.
Long-term Complications
Long-term complications can come from treating pediatric GBM. Some are:
- Neurocognitive deficits
- Endocrine dysfunction
- Increased risk of secondary malignancies
It’s vital to monitor and manage these complications. This helps keep the patient’s quality of life good.
Supportive Care Strategies
Supportive care is key in managing side effects and complications. It includes:
- Pain management
- Nutritional support
- Psychological counseling
Rehabilitation Services
Rehabilitation services are a big part of supportive care for pediatric GBM. They may include:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech therapy
Rehabilitation helps patients regain lost functions. It also helps them adapt to any lasting changes.
With complete supportive care, including rehabilitation, we can greatly improve the quality of life for patients with pediatric GBM.
Support Resources for Families Facing Pediatric GBM
Families with pediatric glioblastoma multiforme need a lot of support. The journey from diagnosis to recovery is tough. Having the right resources is key.
Financial Assistance Programs
Financial help is very important for families with pediatric GBM. Many groups offer aid to cover treatment costs. For example, the Glioblastoma Research Organization helps with expenses.
Support Groups and Counseling
Emotional support is essential for families with pediatric GBM. Support groups offer a place to share and get advice. Professional counseling helps manage the emotional impact of diagnosis and treatment.
Educational Resources
Knowledge is power for families with pediatric GBM. There are resources on treatments, clinical trials, and managing side effects. These can be found at reputable cancer organizations and healthcare providers.
Navigating the Healthcare System
Understanding the healthcare system is hard, but important. Families should get help from patient navigators or social workers. They can make care coordination easier and help access resources.
Conclusion: Advances in Research and Hope for the Future
Recent studies have greatly improved our understanding of pediatric glioblastoma multiforme. This offers new hope to patients and their families. Research is ongoing to find new treatments and better outcomes for glioblastoma.
There’s a big increase in clinical trials for new treatments, like targeted therapies and immunotherapy. These new approaches are key to better care and survival rates. The National Cancer Institute and other top research places are leading this effort, bringing hope to gbm patients.
The future looks brighter for kids with pediatric GBM. With more money for research, we’ll see better treatments. This means better chances for these young patients.
The progress in gbm research and treatment shows the strength of teamwork and the medical community’s dedication. We’re committed to top-notch healthcare and support for patients worldwide, including those with pediatric GBM.
FAQ
What is pediatric glioblastoma multiforme?
Pediatric glioblastoma multiforme, or pediatric GBM, is a rare and aggressive brain tumor in kids. It grows quickly and starts in the brain’s glial cells.
What are the common symptoms of pediatric GBM?
Symptoms of pediatric GBM can vary. They include headaches, nausea, vomiting, seizures, and changes in thinking and behavior.
How is pediatric GBM diagnosed?
Doctors use MRI and CT scans to find pediatric GBM. A biopsy confirms the tumor type and grade. They also do molecular and genetic tests.
What are the treatment options for pediatric GBM?
Treatment for pediatric GBM is a team effort. It includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The plan depends on the tumor and the child’s health.
What is the prognosis for children with GBM?
The outlook for kids with GBM varies. It depends on the tumor’s grade, size, and location, and how well the child responds to treatment. Research and new treatments offer hope.
Are there any risk factors associated with pediatric GBM?
Yes, some risk factors for pediatric GBM include genetics, radiation, and certain genetic syndromes. Knowing these can help identify high-risk children.
What kind of support is available for families affected by pediatric GBM?
Families can find many resources. These include financial help, support groups, counseling, and educational materials. These services help families cope with the challenges.
What are the possible long-term effects of pediatric GBM treatment?
Treatment for pediatric GBM can lead to short- and long-term problems. These include cognitive and neurological issues, endocrine disorders, and secondary cancers. Supportive care and rehabilitation can help manage these effects.
How can I access the latest research and clinical trials for pediatric GBM?
Families can find the latest research and trials through trusted sources. These include the National Cancer Institute, pediatric cancer organizations, and research centers.
What is glioblastoma multiforme GBM?
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a brain cancer that starts in the brain’s glial cells. In kids, it’s called pediatric GBM.
What are the causes of glioblastoma multiforme?
The exact causes of glioblastoma multiforme are not known. But risk factors include genetics, radiation, and certain genetic syndromes.
References
- Wu, G., Broniscer, A., McEachron, T. A., Lu, C., Paugh, B. S., Becksfort, J.,… Zhang, J. (2012). Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas. Nature Genetics. https://www.nature.com/articles/ng.1102
- Fangusaro, J. (2012). Pediatric high-grade glioma: a review and update on tumor clinical characteristics and biology. Frontiers in Oncology. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2012.00105/full



































