Alzheimer’s disease is a complex condition. It is marked by the buildup of two abnormal protein structures in the brain. These are amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. They gradually disrupt normal brain function, causing cognitive decline.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the importance of plaques and tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Our patient-centered approach and commitment to the latest medical protocols help us offer complete care. This is for those affected by this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Alzheimer’s disease is marked by the buildup of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain.
- These abnormal protein structures disrupt normal brain function, leading to cognitive decline.
- Understanding plaques and tangles is key for early diagnosis and new treatments.
- Liv Hospital’s patient-centered approach provides complete care for those with Alzheimer’s disease.
- Our commitment to the latest medical protocols ensures world-class healthcare.
The Hallmark Features of Alzheimer’s Disease

Alzheimer’s disease is known for its slow worsening and specific changes in the brain. It’s important to understand these features to find better treatments.
The brain builds up plaques and tangles in areas for learning, memory, and decision-making. This buildup kills nerve cells and reduces brain tissue, affecting many brain functions.
The Progressive Nature of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurological disorder that gets worse over time. It affects people differently, but it usually follows a pattern of cognitive decline.
- Memory loss and confusion
- Difficulty with communication and language
- Impaired problem-solving abilities
- Changes in mood and personality
As the disease gets worse, these symptoms get stronger, making daily life harder.
Overview of Pathological Changes
The changes in Alzheimer’s disease include amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. These changes harm brain function, causing the disease’s symptoms.
- Amyloid plaques form outside neurons, disrupting cell function.
- Neurofibrillary tangles develop inside neurons, causing cellular damage.
Knowing about these changes is key to creating treatments that can slow or stop the disease’s progress.
Plaques and Tangles: The Signature Proteins of Alzheimer’s

At the heart of Alzheimer’s disease are two key protein abnormalities: amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. These features are not just signs of the disease. They also play a big role in how it progresses.
Defining Amyloid Plaques and Tau Tangles
Amyloid plaques are deposits of beta-amyloid protein outside nerve cells. They are thought to harm the function of neurons. This harm leads to the memory loss seen in Alzheimer’s patients.
Neurofibrillary tangles, by contrast, are found inside neurons. They are made of tau protein that has clumped together. These tangles are a key sign of Alzheimer’s disease.
Historical Discovery and Significance
The discovery of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles goes back to the early 1900s. Alois Alzheimer first found them in a patient with dementia. Ever after, scientists have learned more about their role in Alzheimer’s.
Knowing about amyloid plaques and tau tangles is key to finding treatments for Alzheimer’s. Studies on these proteins help us understand the disease better. They also guide the development of new treatments.
Amyloid Plaques: Formation and Structure
Understanding amyloid plaques is key to understanding Alzheimer’s disease. These plaques are a major sign of the disease. They play a big role in how the disease affects the brain.
Beta-Amyloid Protein
Beta-amyloid protein is a main part of amyloid plaques. It comes from the amyloid precursor protein (APP) found in nerve cells’ membranes. When APP is cut by enzymes, beta-amyloid peptides are made. These peptides stick together, forming insoluble fibrils that build up between nerve cells.
This buildup of beta-amyloid protein harms brain function. It’s thought that beta-amyloid starts to build up early in Alzheimer’s disease. This leads to damage to nerve cells and loss of cognitive abilities.
Plaque Formation Process
Plaque formation starts with beta-amyloid peptides being released into the space outside nerve cells. Over time, these peptides clump together, forming small, soluble oligomers. As more peptides join, these oligomers grow into insoluble fibrils that form amyloid plaques.
Many factors can influence how plaques form, like genetics, age, and environment. For example, some genetic mutations can make people more likely to get plaques at a younger age.
Extracellular Location and Distribution
Amyloid plaques mainly form outside nerve cells. They can be found in different parts of the brain, like the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. These areas are important for memory and thinking.
The plaques don’t spread evenly in the brain. They tend to build up in areas that Alzheimer’s disease affects. This is important because it shows how plaques can harm brain function. They can cause inflammation, oxidative stress, and damage to nerve cells, making Alzheimer’s disease worse.
Neurofibrillary Tangles: Development and Composition
Neurofibrillary tangles are a key feature of Alzheimer’s disease. They are made of tau protein inside neurons. This protein clumps into insoluble fibrils due to abnormal phosphorylation. We’ll look into how these tangles form and their impact on neurons and Alzheimer’s disease.
Tau Protein’s Role in Maintaining Neuronal Structure
In healthy neurons, tau protein is vital. It helps keep microtubules stable, which is key for axonal transport and neuron health. Tau protein binds to microtubules, helping transport nutrients and organelles. This is essential for keeping neurons healthy and supporting brain function.
The Process of Neurofibrillary Tangle Formation
Neurofibrillary tangles form when tau protein is abnormally phosphorylated and aggregates. This process is triggered by oxidative stress and inflammation. As tau aggregates, they form tangles that harm normal neuronal function.
Distribution of Neurofibrillary Tangles within Neurons
Neurofibrillary tangles are found in the cell body and proximal dendrites of neurons. Their distribution in the brain matches the severity of Alzheimer’s symptoms. We’ll see how their location affects neurons and contributes to Alzheimer’s progression.
- Neurofibrillary tangles build up in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex, key for memory.
- These tangles disrupt communication between neurons, leading to memory loss.
- As Alzheimer’s worsens, tangles spread to more brain areas, worsening cognitive decline.
How Plaques and Tangles Damage Brain Cells
Plaques and tangles, key proteins in Alzheimer’s, harm brain function in many ways. They block brain cells from working right, causing memory loss and other symptoms.
Disruption of Neural Communication
Plaques and tangles stop brain cells from talking to each other. Amyloid plaques form outside neurons, while tau tangles build up inside. This messes up memory and learning.
Impact on Cellular Transport Systems
Plaques and tangles mess with how neurons move stuff around. Tau tangles, for example, mess up the microtubules needed for moving nutrients. This causes neuronal dysfunction and helps Alzheimer’s get worse.
Neuronal Death and Brain Atrophy
More plaques and tangles mean more neuronal death. Losing neurons leads to brain atrophy, making symptoms worse. The more neurons lost, the worse the symptoms.
|
Pathological Feature |
Effect on Brain Cells |
Consequence |
|---|---|---|
|
Amyloid Plaques |
Disrupt neural communication |
Cognitive decline |
|
Tau Tangles |
Impair cellular transport |
Neuronal dysfunction |
|
Neuronal Loss |
Brain atrophy |
Severe cognitive impairment |
We’ve seen how plaques and tangles harm brain cells, causing Alzheimer’s symptoms. Knowing this helps us find better treatments.
Brain Regions Affected by Pathological Changes
Brain areas linked to memory, learning, and making decisions are hit hard by Alzheimer’s disease. The buildup of plaques and tangles in these spots greatly adds to the cognitive decline seen in patients.
Hippocampal Formation and Memory Functions
The hippocampal formation is key for memory and finding our way around. In Alzheimer’s, this area gets hit first by neurofibrillary tangles. This leads to big problems with memory.
Research shows the hippocampus is very sensitive to Alzheimer’s changes. This results in memory loss and trouble making new memories.
Cerebral Cortex and Higher Cognitive Processes
The cerebral cortex handles things like language, solving problems, and making judgments. As Alzheimer’s gets worse, amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles build up here. This messes with these functions, causing cognitive decline.
The damage to the cerebral cortex is why Alzheimer’s patients show a wide range of symptoms. These include trouble with language, and problems with judgment and decision-making.
Relationship Between Pathology and Cognitive Decline
Recent studies have greatly improved our understanding of Alzheimer’s disease. They show how the buildup of certain proteins leads to cognitive decline. This buildup is key in worsening symptoms.
Tangles vs. Plaques: Correlation with Symptom Severity
Research has found that neurofibrillary tangles are more linked to cognitive problems than amyloid plaques. Studies show that the number of tangles closely matches the level of cognitive impairment. This suggests a strong link between tangles and symptom severity.
On the other hand, amyloid plaques are a big part of Alzheimer’s disease. But, their presence doesn’t as strongly link to cognitive decline. This shows how complex Alzheimer’s disease is and why we need specific treatments.
Progression of Cognitive Impairment Related to Protein Accumulation
The buildup of tau protein in tangles and beta-amyloid in plaques is a major factor in cognitive decline. As these proteins build up, they harm neural communication and lead to neuron death. This results in the cognitive symptoms seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
Understanding how these proteins accumulate is key to finding treatments. By focusing on the causes of cognitive decline, researchers hope to slow or stop Alzheimer’s disease. This could greatly improve the lives of those affected.
Detecting and Treating Plaques and Tangles
Recent breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research have made it easier to detect and treat plaques and tangles. We are getting better at understanding and treating Alzheimer’s disease. This is thanks to new diagnostic and treatment methods.
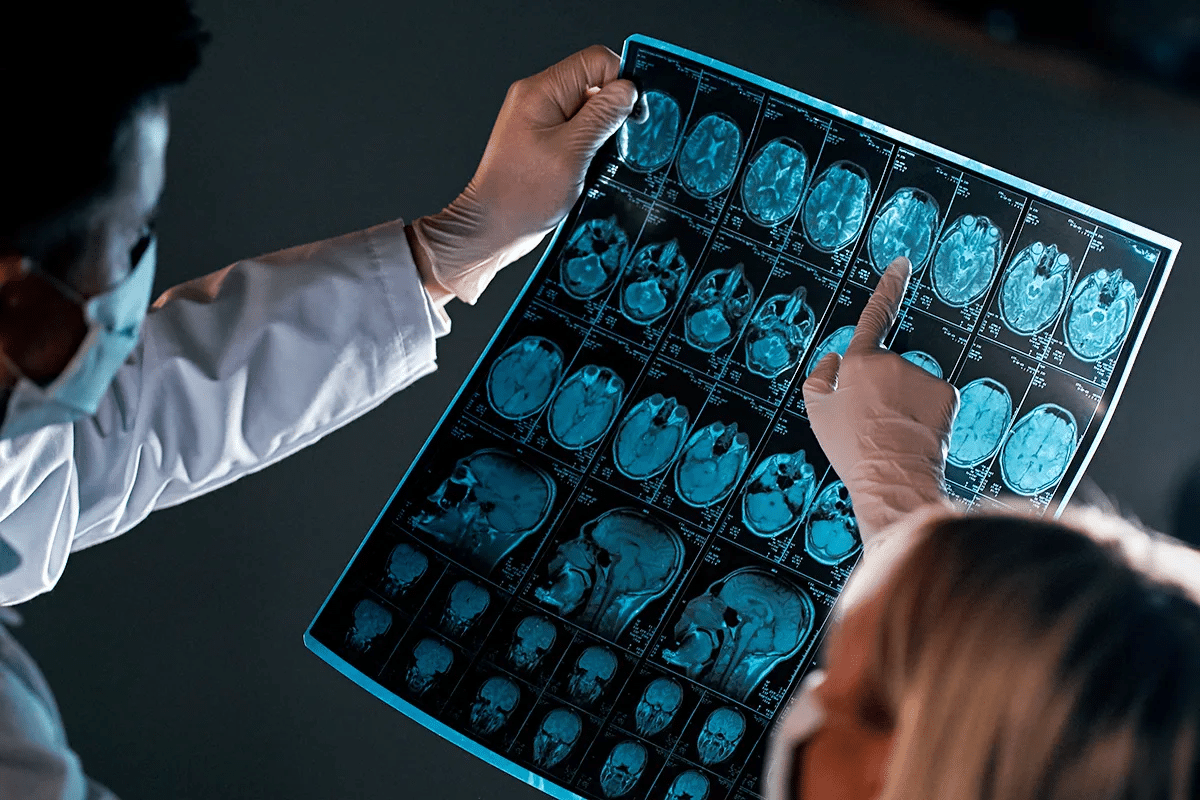
Diagnostic Methods for Visualizing Pathology
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease uses different methods to see plaques and tangles. Some key ways include:
- PET scans: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans can spot amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain.
- CSF analysis: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis checks beta-amyloid and tau protein levels. This gives clues about the disease’s progress.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) looks at brain atrophy and spots areas affected by Alzheimer’s disease.
FDA-Approved Anti-Amyloid Therapies
Two FDA-approved drugs, lecanemab and donanemab, have shown great promise. They reduce amyloid plaques and slow down cognitive decline. These drugs target the amyloid protein, a key part of Alzheimer’s disease.
The approval of these drugs is a big step forward in treating Alzheimer’s. They offer hope to patients and their families. The benefits include:
- Reduced amyloid plaque burden
- Slowed cognitive decline
- Potential for improved quality of life
Emerging Tau-Targeting Approaches
Researchers are also looking into tau-targeting approaches for treating Alzheimer’s disease. These therapies aim to reduce or eliminate the harmful effects of tau tangles on brain cells.
Some new tau-targeting methods include:
- Tau antibodies: Made to target and remove tau protein from the brain.
- Tau aggregation inhibitors: Try to stop tau tangles from forming.
- Tau-based vaccines: Aim to get the immune system to clear tau protein.
As research keeps moving forward, we will see better ways to diagnose and treat Alzheimer’s disease. This will lead to better outcomes for patients.
Conclusion: Progress and Promise in Alzheimer’s Research
We’ve looked into Alzheimer’s disease, focusing on its main features: plaques and tangles. These protein clumps are key to understanding and treating the disease.
Research has made big strides in understanding plaques and tangles. We now know they play a big role in memory loss and brain damage. This knowledge opens up new ways to treat Alzheimer’s.
New treatments targeting plaques and tangles give us hope. With ongoing research and better tests, we’re getting closer to managing Alzheimer’s. It’s vital to keep supporting research to make a real difference in fighting this disease.
FAQ
What are amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease?
Amyloid plaques are deposits of beta-amyloid protein that build up between nerve cells. Neurofibrillary tangles are clumps of tau protein inside neurons. These abnormal clumps are key signs of Alzheimer’s disease and harm brain function.
How do plaques and tangles affect brain cells?
Plaques and tangles disrupt how nerve cells talk to each other. They damage the transport systems within cells and cause cell death. This damage leads to brain shrinkage and the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
What is the role of tau protein in healthy neurons?
Tau protein helps keep neurons working right. But in Alzheimer’s, it becomes abnormal and forms tangles. These tangles are harmful to brain cells.
Are there any treatments available for Alzheimer’s disease that target plaques and tangles?
Yes, there are treatments approved by the FDA that aim to reduce amyloid plaques. They help slow down cognitive decline. Researchers are also looking into treatments that target tau protein.
How do plaques and tangles relate to cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease?
Studies show that tangles are more linked to cognitive problems than plaques. The buildup of these proteins leads to worsening cognitive function. Understanding this is key to finding better treatments.
What brain regions are affected by the pathological changes of Alzheimer’s disease?
The hippocampal formation and cerebral cortex are hit hard by Alzheimer’s. Damage here causes symptoms like memory loss and cognitive decline.
Can plaques and tangles be detected before symptoms appear?
Yes, imaging techniques can spot amyloid plaques and tangles in the brain. This lets doctors catch these changes early, which can lead to better treatment options.
What is the significance of understanding plaques and tangles in Alzheimer’s disease?
Knowing about plaques and tangles is vital for finding effective treatments. Research into these areas has helped us understand Alzheimer’s better and develop targeted therapies.
How do amyloid plaques form?
Plaques form when beta-amyloid protein builds up between nerve cells. This disrupts brain function and contributes to Alzheimer’s progression.
What is the relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and neurofibrillary tangles?
Tangles are a key feature of Alzheimer’s disease. Their buildup in neurons worsens cognitive decline. Studying tangles is essential for creating effective treatments.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Alzheimer’s Disease: Amyloid Plaques and Neurofibrillary Tangles. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2527075/