One in five Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70. This makes it one of the most common cancers in the U.S. Many know the risk, but few understand the symptoms and warning signs of this serious condition what does skin cancer look like.
Itching is a symptom of many health problems, including skin cancer symptoms. Knowing the signs of skin cancer is key to catching it early. Itching might mean there’s a problem that needs a doctor’s help.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding skin cancer symptoms is key to early detection.
- Itching can be a sign of skin cancer.
- Spotting skin cancer signs can save lives.
- Regular check-ups help find skin issues early.
- Knowing about skin cancer risks helps prevent it.
The Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Itching
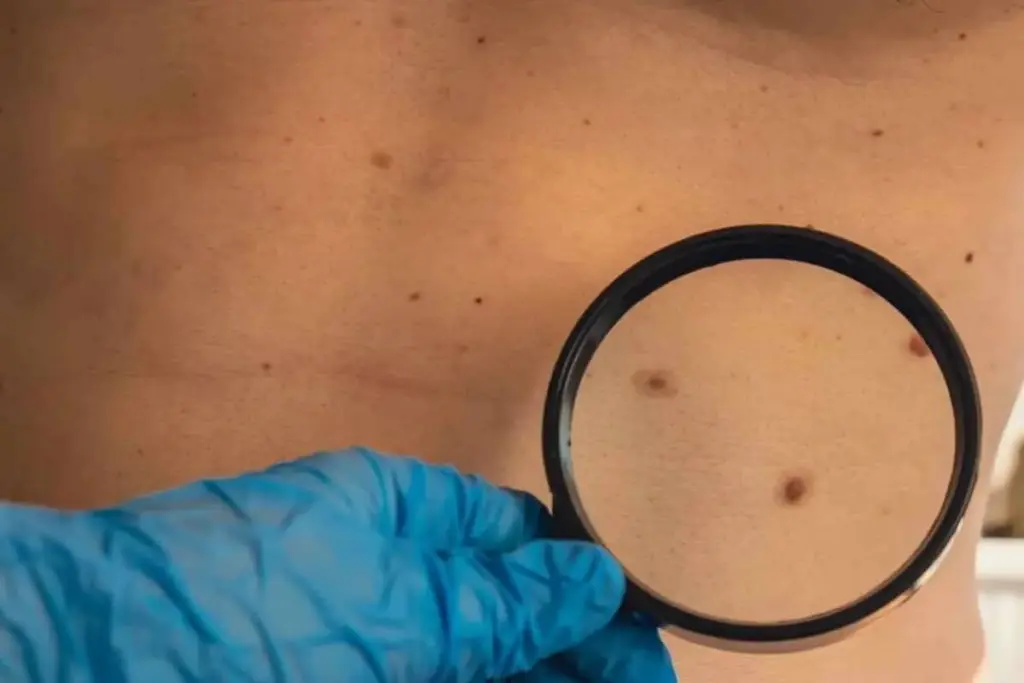
Itching is a symptom that can be linked to skin cancer. This connection is complex, with many factors at play. These factors can affect whether someone with skin cancer feels itchy.
How Common is Itching in Skin Cancer Cases?
Itching, or pruritus, is seen in many skin conditions, including some skin cancers. Studies show that itching’s frequency varies by skin cancer type. For example, itching is more common in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma than in basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma.
Why Certain Skin Cancers Cause Itching
The reasons behind itching in skin cancer are not fully known. Several factors are believed to play a role. These include chemicals released by tumor cells, nerve stimulation, and the immune system’s reaction to cancer. Some skin cancers can release substances that make nerve endings itch.
Itching as an Early or Late Symptom
Itching can appear early or late in skin cancer, depending on the cancer type and its growth. Sometimes, itching is an early warning sign, prompting people to see a doctor. Other times, it may show up later, suggesting the cancer is spreading.
Understanding the link between skin cancer and itching is key for patients and doctors. Spotting itching as a symptom can help catch skin cancer sooner. It also helps manage a patient’s comfort and quality of life, as itching can greatly affect well-being.
Types of Skin Cancer and Their Symptoms

Skin cancer comes in several types, each with its own symptoms. Knowing these differences helps spot health risks early.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer. It looks like a small, shiny bump or a pink patch. It can also show up as a sore that won’t heal or a scar-like area.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is another common skin cancer. It shows up as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore with scales or crust. SCC grows fast and might bleed or hurt.
It can spread, so catching it early is key.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer because it spreads fast. It starts in a mole or as a new mole. The ABCDE rule helps spot suspicious moles: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter increase, and Evolving shape or size.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is rare but aggressive. It looks like a firm, painless nodule or bump. It grows fast and can spread to other parts of the body.
Spotting these symptoms early is vital for treatment.
Knowing the signs of different skin cancers can help a lot. Regular skin checks and being aware of warning signs are key to keeping your skin healthy.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like? Visual Identification Guide
It’s important to know what skin cancer looks like to get help early. Skin cancer can show up in different ways, so it’s key to know the common signs.
Common Visual Characteristics
Skin cancer often shows up as unusual growths or changes. This can include new moles or changes in old ones, sores that won’t heal, or skin that turns red, scaly, or crusty. Spotting these changes early can help a lot.
Color Changes and Variations
A change in color or multiple colors in a lesion is a big warning sign. For example, a mole turning multicolored or showing irregular shades of brown, black, or pink, red, or white is a sign to watch. It’s very important to keep an eye on any new or changing colors.
Texture and Surface Abnormalities
Skin cancer can also change the skin’s texture or surface. This might mean lesions that are rough, scaly, or have an odd shape. Noticing these details can help tell if something is harmless or not.
Size and Growth Patterns
The size and how fast a skin lesion grows are also important. Skin cancers usually get bigger or change over time. Watching how big a mole or lesion is and if it’s changing is key to catching it early. A good rule is to worry about lesions bigger than a pencil eraser or those that are growing.
Knowing these signs can help people spot skin cancer symptoms early. This way, they can get medical help right away.
Skin Cancer Pictures: Early Stages vs. Advanced Stages
It’s important to know the difference between early and advanced skin cancer. This knowledge helps spot symptoms early. Early detection can lead to better treatment results.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Progression
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer. In the early stages, it looks like a small, shiny bump or a pink patch. Early detection is key to prevent serious damage.
As BCC grows, it can get bigger and look more irregular. Advanced BCC might turn into an open sore that bleeds or oozes. It can also form a flat, white, yellow, or waxy scar-like area.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is another common skin cancer. It looks different in its early and advanced stages. Early SCC is a firm, red nodule or a flat sore with a scaly or crusted surface.
Advanced SCC can grow large and spread if not treated quickly. It might look like a big, firm nodule or an open sore that doesn’t heal.
Melanoma Progression
Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer because it can spread fast. Early melanoma looks like a new mole or a change in an existing one, following the ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter, Evolving).
As melanoma gets worse, it can grow thicker and may ulcerate or bleed. Advanced melanoma can spread to lymph nodes and distant organs, making early detection critical.
Progression and Advanced Appearance
Skin cancer changes a lot as it progresses from early to advanced stages. Regular skin checks and knowing these changes are key for early detection.
Advanced skin cancers can greatly affect a patient’s quality of life. They may need more aggressive treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Beyond Itching: Complete List of Skin Cancer Symptoms
It’s important to know all the signs of skin cancer for early detection. Itching is one sign, but there are others. Knowing these signs helps catch skin cancer early.
Pain and Tenderness
Pain or tenderness in a skin area can be a sign of skin cancer. This discomfort can happen without any visible signs. It’s a sign to check further.
Bleeding and Crusting
Skin cancers may bleed or crust over, forming a scab. If a scab keeps coming back, it could be skin cancer. Watching for these changes is key.
Changes in Existing Moles
Changes in moles are a big warning sign. Look for changes in size, color, or shape. The ABCDE rule can help spot cancerous moles.
Non-Healing Sores
Sores that don’t heal can be a sign of skin cancer. These sores might bleed or crust over. If a sore won’t heal, see a doctor.
Knowing these signs can help catch skin cancer early. Regular self-checks and yearly dermatologist visits are important for skin health.
Red Spots and Bumps: When to Be Concerned
Red spots and bumps on the skin are common. But, it’s important to know the difference between harmless and serious issues. These changes can be from irritation, allergies, or even skin cancer.
Normal Red Spots vs. Suspicious Lesions
Most red spots or bumps are harmless. They might come from insect bites, minor irritations, or allergies. They are usually small, the same color, and can go away by themselves. But, suspicious lesions might be a sign of skin cancer. They often look irregular, have different colors, or feel odd.
|
Characteristics |
Normal Red Spots |
Suspicious Lesions |
|---|---|---|
|
Size and Shape |
Small, uniform |
Irregular, varied sizes |
|
Color |
Uniform red color |
Multiple colors or uneven color distribution |
|
Texture |
Smooth |
Uneven, scaly, or crusty |
Red Flags That Warrant Medical Attention
Some red spots or bumps need to be seen by a doctor right away. Look out for fast growth, odd shapes, different colors, or signs like itching, pain, or bleeding. If you see these signs, see a dermatologist.
- Rapid growth or changes in size
- Irregular or asymmetrical shape
- Multiple colors or uneven color
- Symptoms like itching, pain, or bleeding
Tracking Changes Over Time
Watching how red spots or bumps change is important. Keeping a record or taking pictures can help track their changes. This info is useful for doctors.
Being careful about skin changes and knowing when to worry can help keep your skin healthy. If you’re unsure, always talk to a healthcare professional.
Scabs and Skin Cancer: Important Connections
It’s key to know how scabs and skin cancer are linked. Scabs can hide skin cancers, making them hard to spot.
Formation of Scabs in Skin Cancer
Skin cancers can cause scabs for a few reasons. The cancer cells make the skin weak, leading to scabs. The body’s way of fighting off the cancer also causes scabs.
Key Factors Contributing to Scab Formation:
- Ulceration due to cancerous cell growth
- Body’s natural response to injury or abnormal cells
- Increased fragility of the skin
Distinguishing Between Normal Healing and Cancer
It’s important to tell normal scabs from those that might be cancer. Cancer scabs don’t heal or keep coming back.
|
Characteristics |
Normal Healing |
Potential Skin Cancer |
|---|---|---|
|
Duration |
Heals within a few weeks |
Persists or recurs |
|
Appearance |
Typically uniform, follows injury |
Irregular, may bleed or ooze |
|
Associated Symptoms |
Minimal discomfort, resolves with healing |
May be accompanied by pain, itching, or other symptoms |
When Scabs Should Raise Concern
Scabs that are big, don’t heal, or have other symptoms like bleeding or itching are a worry. Watch any changes in the scab or skin around it.
“If you notice a scab that doesn’t heal or is accompanied by other unusual symptoms, consult a dermatologist. Early detection is key to effective treatment of skin cancer.” – Dermatology Expert
Knowing about scabs and skin cancer can help catch it early. If you’re worried about a scab or skin lesion, get medical help.
Specific Body Areas and Skin Cancer Symptoms
Skin cancer can show up in different parts of the body. It’s not just about sun-exposed skin. Knowing where to look and what to watch for is key to catching it early.
Itchy Scalp and Skin Cancer
An itchy scalp might mean you have skin cancer, like scalp melanoma. If your scalp itches a lot and you see bleeding or a new mole, see a dermatologist. Getting your scalp checked often can spot problems early.
Lip Cancer: Signs and Symptoms
Lip cancer is a type of oral cancer. It can show up as sores, lumps, or color changes on the lips. Look out for sores that won’t heal, numbness, or pain. If your lips look different, get it checked out. Catching it early can make a big difference.
Lumps Under the Armpit: Possible Warning Signs
Lumps under the armpit could mean skin cancer. Sometimes, a lump there means cancer has spread from somewhere else. Watch for new or changing lumps and talk to a doctor if you’re worried.
Hidden Areas Often Overlooked
Skin cancer can hide in places like the scalp, behind the ears, or under the nails. Regular self-checks and doctor visits are important. Knowing your body and checking it often can help find cancer early.
Knowing where skin cancer can show up and what to look for helps fight it. Regular skin checks, by yourself and with a doctor, are essential for catching cancer early.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Stages and Progression
Knowing the stages of squamous cell carcinoma is key for early treatment. This skin cancer starts in the squamous cells. These are flat, thin cells on the skin’s outer layer.
Early Stage Identification
In the early stages, squamous cell carcinoma looks like a small, rough patch. It’s often red or pink and might bleed or crust. Catching it early is vital for treatment success.
“The sooner squamous cell carcinoma is found, the better the treatment options,” say dermatologists.
Middle Stage Characteristics
When it reaches the middle stage, the lesion grows and becomes more noticeable. It starts to go deeper into the skin, causing discomfort or pain.
- Increased size and thickness
- More pronounced symptoms
- Possible bleeding or oozing
Advanced Stage Symptoms
In advanced stages, squamous cell carcinoma can cause serious damage. It may lead to ulceration and destruction of surrounding tissue. It can also spread to other parts of the body, making treatment harder.
Advanced symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness
- Difficulty moving the affected area
- Swollen lymph nodes
Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma
When squamous cell carcinoma spreads, it goes to other parts of the body. This can be to the lymph nodes, bones, or internal organs. At this stage, treatment is aggressive and often involves several therapies.
“Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma is a serious condition that necessitates prompt and extensive medical care,” say oncology specialists.
The ABCDE Rule for Identifying Suspicious Skin Lesions
The ABCDE rule is a simple way to spot suspicious skin lesions. It’s a mnemonic device that helps people and doctors find moles or lesions that might be cancerous. It looks at the characteristics of these skin spots.
Asymmetry
The “A” in ABCDE means asymmetry. A normal mole looks symmetrical. If you draw a line through it, the two sides will match. But cancerous spots are often not symmetrical.
Border Irregularity
The “B” is for border irregularity. Benign moles have smooth, even edges. But cancerous moles have notched, ragged, or blurry edges.
Color Variation
The “C” is for color variation. A benign mole is usually one color, like brown. But cancerous moles can have many colors, like black, brown, red, pink, or white.
Diameter Concerns
The “D” is about diameter. Melanomas can be small, but they’re often bigger than a pencil eraser (about 6mm). Any mole that’s growing or changing size needs to be checked.
To better understand the ABCDE rule, let’s examine a comparison table:
|
Characteristic |
Benign Mole |
Malignant Mole |
|---|---|---|
|
Asymmetry |
Symmetrical |
Asymmetrical |
|
Border |
Smooth, even border |
Notched, ragged, or blurred edges |
|
Color |
Single shade of brown |
Multiple colors or shades |
|
Diameter |
Typically small |
Often larger than 6mm |
By using the ABCDE rule, people can find and treat skin cancer early. This makes treatment more likely to be successful.
Differentiating Skin Cancer from Benign Skin Conditions
It’s important to know the difference between skin cancer and benign skin conditions. This helps in catching problems early. Many skin issues look similar, making it hard to tell if a spot is cancerous.
Common Benign Conditions That Mimic Skin Cancer
Some benign skin conditions look like skin cancer. These include:
- Seborrheic keratoses: Benign growths that can appear as brown, black, or tan lesions.
- Dermatofibromas: Small, firm bumps that can be red or brown.
- Cysts: Closed sacs that can contain fluid or semi-solid material, sometimes appearing as lumps on the skin.
These conditions are usually harmless but can look like cancer.
Key Differences in Symptoms
Benign and cancerous lesions can look similar, but there are differences:
|
Characteristic |
Benign Conditions |
Skin Cancer |
|---|---|---|
|
Change Over Time |
Typically stable or changing slowly |
Often changing rapidly |
|
Border |
Usually well-defined |
Can be irregular or poorly defined |
|
Color |
Often uniform |
May have multiple colors or uneven pigmentation |
Knowing these differences can help spot cancerous lesions.
“The key to diagnosing skin cancer early is recognizing changes in the skin, whether it’s a new growth or a change in an existing mole.” –
A dermatologist’s insight
When Benign Conditions Become Concerning
Most benign skin conditions are not serious. But sometimes, they can become a problem or show an underlying issue. For example, a benign cyst can get infected, or a seborrheic keratosis can signal an underlying condition.
If you notice any unusual changes or have concerns about a skin lesion, it’s important to see a healthcare professional. They can evaluate and advise you properly.
Risk Factors for Developing Itchy Skin Cancers
Several factors can increase the risk of itchy skin cancers. These include UV radiation and genetic predispositions. Knowing these risks helps in prevention and early detection.
UV Exposure and Sun Damage
UV exposure is a big risk for skin cancer, including itchy types. Spending too much time in the sun or using tanning beds can cause skin damage and cancer.
Prevention Measures:
- Use sunscreen with a high SPF
- Wear protective clothing
- Seek shade, specially during peak sun hours
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a big part in skin cancer risk. People with a family history of skin cancer are more likely to get itchy skin cancers.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender are also important. Older people and men are more likely to get skin cancer.
Immunosuppression and Other Medical Factors
Being immunosuppressed, due to medical conditions or treatments, raises skin cancer risk. Certain medical conditions and treatments also increase this risk.
Here is a summary of the risk factors in a tabular form:
|
Risk Factor |
Description |
|---|---|
|
UV Exposure |
Increases risk through sun damage |
|
Genetic Predisposition |
Family history increases risk |
|
Age and Gender |
Older individuals and men are at higher risk |
|
Immunosuppression |
Weakened immune system increases risk |
Understanding these risk factors helps people take steps to lower their chance of getting itchy skin cancers. They should also see a doctor if they notice any symptoms.
Diagnosis Process: From Symptom Recognition to Confirmation
Diagnosing skin cancer takes several steps. It starts with recognizing symptoms and ends with confirmation. Spotting skin cancer early is key to effective treatment.
Initial Screening and Examination
A healthcare professional will examine your skin first. They look for any unusual spots or changes. They check the size, shape, color, and texture of these spots.
Tell your doctor about any new moles or changes in existing ones. Also, mention any itching or bleeding. This helps them assess the risk and decide what to do next.
Dermoscopy and Imaging
Dermoscopy uses a special microscope to look at your skin closely. It helps doctors see details they can’t see with the naked eye. This tool helps tell if a spot is harmless or not.
At times, tests like ultrasound or MRI might be needed. They help figure out how deep the cancer is or if it has spread.
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy is the main way to diagnose skin cancer. It involves taking a sample of the suspicious area for a microscope check. There are different types of biopsies, each for different situations.
The type of biopsy depends on the size, location, and depth of the spot. It also depends on your overall health.
Understanding Pathology Reports
After the biopsy, the sample goes to a lab for analysis. The pathology report will tell if the spot is cancerous, what type, and how thick the tumor is. This info is vital for figuring out the cancer stage and treatment.
Understanding your pathology report can be tricky. It’s important to talk to your doctor about it. They can explain what it means for your treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Different Types of Skin Cancer
Understanding skin cancer is key to treating it. The right treatment depends on the cancer type, size, and where it is. It also depends on the patient’s health.
Surgical Approaches
Surgery is a common treatment for skin cancer. This includes basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. The surgery might remove the tumor and some healthy tissue around it.
Mohs surgery is a special technique. It keeps more healthy tissue. The American Cancer Society says it’s great for the face and other sensitive areas.
Radiation and Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy rays. It’s used for cancers in hard-to-reach places like the eyelids, nose, or ears. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s used when cancer has spread.
“Radiation therapy is an effective treatment for skin cancer, even in areas where surgery would be disfiguring,” says Medical Expert, a dermatologist at XYZ Hospital.
Immunotherapy and Targeted Treatments
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Targeted treatments focus on specific cancer molecules. These are used for advanced skin cancers, like melanoma.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed immunotherapy helps advanced melanoma patients live longer.
Post-Treatment Symptom Management
After treatment, patients may face symptoms like pain, itching, or scarring. Managing these symptoms is important for quality of life. This can include medications, wound care, or other therapies.
- Pain management through medication or alternative therapies
- Itching relief using topical creams or oral medications
- Wound care to promote healing and minimize scarring
Conclusion: When to See a Doctor About Skin Changes
Knowing the signs of skin cancer is key for early treatment. We’ve talked about symptoms like itching, changes in moles, and sores that won’t heal. If you see new growths, sores, or mole changes, see a doctor.
Doing regular self-checks and yearly dermatologist visits can help catch skin cancer early. If you’re worried about your skin, don’t wait to get help. Early treatment is vital for beating skin cancer.
Understanding your risk and staying alert to your skin’s health can help prevent skin cancer. If you’re unsure about your skin or have concerns, talk to a healthcare expert. They can help you figure out your risks and when you should get checked.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of skin cancer?
Symptoms include itching, pain, and bleeding. Changes in moles and non-healing sores are also signs. Each type of skin cancer, like basal cell carcinoma and melanoma, has its own symptoms.
Does skin cancer always itch?
No, not all skin cancer itches. But, itching can be a sign, mainly in later stages. The itchiness can change based on the cancer type and how far it has spread.
What does skin cancer look like in its early stages?
Early skin cancer looks different for each type. Basal cell carcinoma might be a small, shiny bump. Squamous cell carcinoma could be a firm, red nodule.
Melanoma often looks like a new or changing mole. It should have uneven edges, different colors, and be large.
How can I differentiate between skin cancer and benign skin conditions?
Look for signs like uneven shapes and colors. Benign conditions like seborrheic keratoses have unique features. If unsure, see a dermatologist for a check-up.
What are the risk factors for developing skin cancer?
Risk factors include UV exposure and genetic predisposition. Age, gender, and weakened immune systems also play a part. People with fair skin or a family history of skin cancer are at higher risk.
How is skin cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis starts with a screening and possibly a dermatoscope. If needed, a biopsy is done to confirm the cancer type.
What are the treatment options for skin cancer?
Treatments depend on the cancer type and stage. Surgical options like excision or Mohs surgery are common. Other treatments include radiation, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.Managing symptoms after treatment is also important for patient care.
Can scabs be a sign of skin cancer?
Yes, scabs can be a sign, if they don’t heal or bleed easily. Certain cancers, like squamous cell carcinoma, may cause scabs.
What is the ABCDE rule for identifying suspicious skin lesions?
The ABCDE rule helps spot cancerous moles. It stands for Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter concerns, and Evolving. This rule helps detect melanoma early.
Are red spots and bumps always a cause for concern?
Not all red spots and bumps are cancer. But, new or changing ones need medical attention. Look out for rapid growth, bleeding, or itching.See a dermatologist to find out what’s causing them.
Can lip cancer be an itchy condition?
Lip cancer might cause discomfort or pain, but itching is rare. It often looks like a sore, lump, or discoloration on the lip.
What are the signs of skin cancer on the scalp?
On the scalp, skin cancer can look like a new growth or sore. It might be itchy or painful. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma can hide under hair.
How does squamous cell carcinoma progress?
Squamous cell carcinoma goes through stages. If not treated, it can spread to lymph nodes and other areas. Catching it early is key to effective treatment.
References
Profound Do Skin Cancers Itch: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like?
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4229457/









