At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to spot lip cancer early. Every year, about 40,000 people in the United States get diagnosed with it. It’s vital to know the signs that could mean you need to see a doctor fast.
Lip cancer usually shows up as squamous cell carcinomas. We’re here to help with quick medical checks, correct diagnoses, and treatment plans that meet global standards.
Spotting cancer early is the best way to treat it. In this article, we’ll share the seven main signs to watch for. This way, you can get help right away if you notice anything odd.
Key Takeaways
- Spotting early signs of lip cancer is key to good treatment.
- Lip cancer is often found as squamous cell carcinomas.
- About 40,000 cases are found each year in the United States.
- Good medical checks and correct diagnosis are vital for treatment.
- Our treatment plans are made just for you.
What Is Cancer Inside Lip?

It’s important to know about cancer inside the lip for early detection and treatment. This condition is when abnormal cells grow on the inner lip. It’s a serious form of oral cancer that needs quick action.
Definition and Medical Terminology
Cancer inside the lip is also called intraoral lip cancer or inner lip cancer. It happens when cancer cells grow on the inner lip. The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma.
The inner lip is a mucosal surface. Cancers here are part of oral cancers. The exact name depends on the location and type of cancer. But the main issue is the growth of abnormal cells that can spread.
Prevalence and Statistics in the United States
Lip cancer is a big health problem in the United States. Every year, thousands of new cases are found. The American Cancer Society says oral cancers, including lip cancers, are a big part of all cancer cases.
Here are some key statistics:
| Year | Estimated New Cases of Oral Cancer | Estimated Deaths from Oral Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 53,000 | 10,850 |
| 2021 | 54,000 | 10,900 |
| 2022 | 54,010 | 10,950 |
These numbers show why we need to be aware and catch cancer early. While not all oral cancers are inside the lip, the data stresses the importance of watching out for all types.
Types of Lip Cancer
It’s important to know about the different types of lip cancer. This knowledge helps in early detection and treatment. Lip cancer is classified based on the type of cells affected and the tumor’s nature.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common lip cancer, making up over 90 percent of cases. It starts in the squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells on the lip’s outer layer. This cancer can grow fast and spread if not treated quickly.
Squamous cell carcinoma is linked to tobacco use, too much sun, and HPV. Finding it early is key to successful treatment.
Other Types of Oral Cancers
While squamous cell carcinoma is common, other cancers can also affect the lip. These include:
- Basal cell carcinoma: A less common type that starts in the basal cell layer of the skin.
- Melanoma: A serious skin cancer that can happen on the lips, though it’s rare.
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma: A rare cancer that can occur in the salivary glands, including those in the lips.
Each cancer type has its own traits and needs a specific treatment. Knowing the exact type is vital for the right treatment plan.
Inside vs. Outside Lip Cancer: Important Distinctions
It’s key to know the difference between inside and outside lip cancer for the right treatment. Cancer inside the lip is called oral cancer. Cancer on the outside is often skin cancer. This difference affects how we treat and predict the outcome.
Oral Cancer vs. Skin Cancer
Oral cancer, found inside the lip, is usually more aggressive. It’s linked to tobacco, alcohol, and HPV. Skin cancer on the outside is mostly caused by the sun.
Oral Cancer vs. Skin Cancer: Key Differences
| Characteristics | Oral Cancer | Skin Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Inside the lip | Outside the lip |
| Risk Factors | Tobacco, alcohol, HPV | Sun exposure |
| Treatment Approach | Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy | Surgery, topical treatments |
Anatomical Differences and Implications
The lip’s anatomy is important for cancer type and behavior. The inside, with mucous membranes, is more at risk for oral cancer. The outside, exposed to the sun, is more likely to get skin cancer.
“The distinction between oral and skin cancer is not just semantic; it has significant implications for treatment and prognosis.” – Medical Expert, Oncologist
We must think about these differences when treating lip cancer. Knowing if the cancer is inside or outside helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Risk Factors for Developing Cancer Inside Lip
Lip cancer risk comes from lifestyle and demographic factors. Knowing these factors helps in prevention, early detection, and treatment.
Tobacco and Alcohol Use
Tobacco is a big risk for lip cancer, inside the lip. Smoking and smokeless tobacco harm lip tissue, leading to cancer.
Alcohol, with tobacco, raises the risk even more. Heavy drinking weakens the body’s defenses and DNA repair, making cancer more likely.
Sun Exposure
Sun’s UV rays are a major risk for lip cancer, mainly for the outer lip. UV radiation damages lip cells’ DNA, causing cancer. People who work outdoors or enjoy outdoor activities are at higher risk.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Some HPV strains increase lip and oral cancer risk. HPV infection can cause genetic changes in lip cells, leading to cancer. Safe sex and HPV vaccination can lower this risk.
Age and Gender Considerations
Lip cancer often hits older adults, over 60. Age increases risk due to long-term effects of tobacco and sun.
Men face higher lip cancer risk, mainly due to tobacco and alcohol use. But, more women are smoking and drinking, narrowing the gap.
Understanding these risks helps prevent lip cancer. Avoid tobacco, limit alcohol, protect from the sun, and keep good oral hygiene.
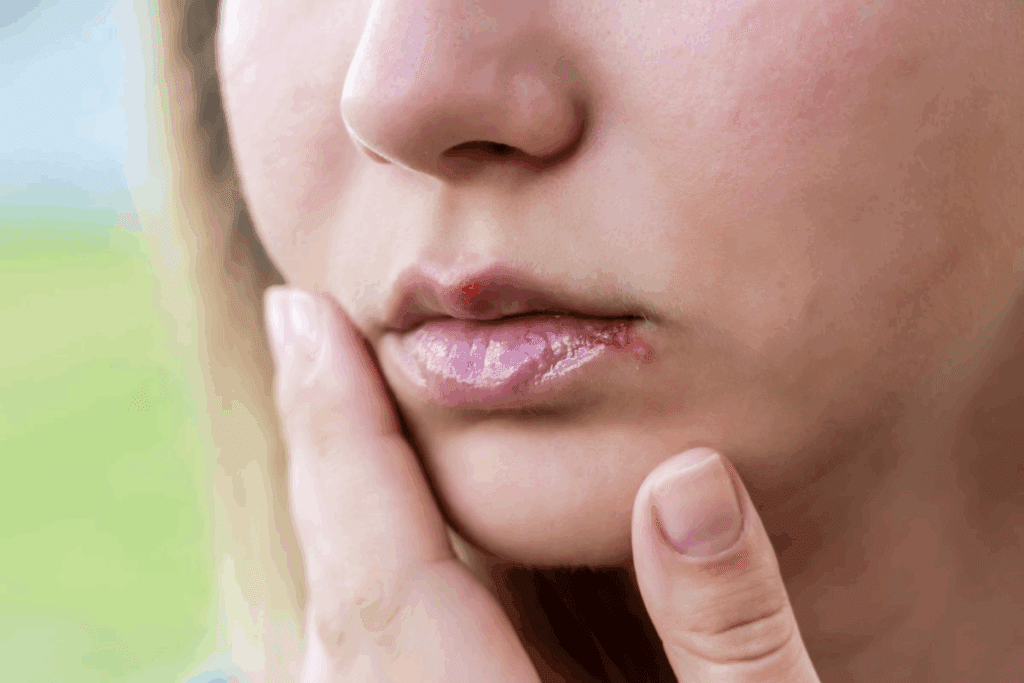
Sign #1: Persistent Sores or Ulcers
The first sign of lip cancer is often a persistent sore or ulcer inside the lip. We will look at what these sores are like, how they differ from common mouth ulcers, and when to see a doctor.
Characteristics of Cancerous Sores
Cancerous sores or ulcers from lip cancer have unique traits. They don’t heal in two weeks, unlike common mouth ulcers that heal in days. At first, they might be painless, but they can hurt as they grow.
Differentiating from Common Mouth Ulcers
It’s important to tell cancerous sores from common mouth ulcers. Common mouth ulcers heal in a week or so after minor trauma. But cancerous sores last longer and can grow. If a sore doesn’t heal, see a healthcare professional.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If a sore or ulcer inside your lip lasts over two weeks, see a doctor. Early detection is key to treating lip cancer well. We suggest seeing a doctor or dentist for any unusual lip changes, if you use tobacco or alcohol, or have been exposed to HPV.
Sign #2: White or Red Patches on Lips
White or red patches on the lips might mean you have lip cancer. This is a sign that needs quick action. These patches can look different and mean different things for your health.
Leukoplakia: Early Stage Cancer White Spots on Lips
Leukoplakia shows up as white patches or lesions on the lips or mouth. These spots are often a sign of something that could turn into cancer. If you have white patches that don’t go away, see a doctor to find out why and how to treat it.
Key characteristics of leukoplakia include:
- White or grayish patches that cannot be wiped away
- Patches that may be flat or slightly raised
- Possible presence of redness or inflammation around the patches
Erythroplakia: Red Patches and Their Significance
Erythroplakia shows up as red patches on the lips or inside the mouth. These red spots are less common but more likely to be cancerous. If you see any unusual red patches, get them checked by a doctor right away.
The significance of erythroplakia lies in its:
- High risk of being malignant
- Potential to be an early sign of oral or lip cancer
- Need for prompt medical assessment to determine the cause and appropriate treatment
Mixed Red and White Lesions
Sometimes, you might see both red and white patches together. These mixed spots are a mix of leukoplakia and erythroplakia. They need careful checking because they might mean a higher risk of cancer. Always see a doctor for a full check-up and diagnosis.
Knowing about the different types of patches on the lips is key for catching cancer early. By watching for these signs and getting medical help when needed, you can greatly improve your chances of beating cancer.
Sign #3: Pain, Numbness, or Tenderness
Feeling pain, numbness, or tenderness in your lip without a clear reason might mean you have lip cancer. These feelings can show up in different ways. It’s important to know what they mean and why they happen.
Localized Discomfort
Pain or discomfort in just the lip area could be a sign of lip cancer. This pain might feel like a dull ache or a sharp sting. It’s important to remember that this pain doesn’t go away easily.
“Don’t ignore pain or discomfort in your lip,” advises a top oncologist. “Seeing a doctor early can really help with treatment.”
Changes in Sensation
Numbness or changes in how you feel in your lip are also warning signs. You might feel tingling, burning, or even lose all feeling. This happens because cancer can mess with the nerves around your lip.
Numbness or feeling different in your lip can be scary. It might mean the cancer is touching nerves and tissues nearby. Seeing a doctor right away is important to figure out what’s going on and how to treat it.
Referred Pain Patterns
Sometimes, lip cancer pain can feel like it’s coming from other places, like your jaw, ear, or throat. This happens because nerves in your lip connect to other parts of your head and neck.
It’s key to understand where the pain is coming from. If you feel pain in your lip but it spreads to other areas, you should talk to a doctor. Referred pain can be tricky to figure out, but it’s a big clue for finding lip cancer.
Spotting signs of lip cancer, like pain, numbness, or tenderness, is key for catching it early and treating it well. If you’re feeling any of these symptoms, please get medical help right away.
Sign #4: Thickening or Lumps Inside the Lip
Thickening or lumps inside the lip can be a sign of lip cancer. It’s important to check them right away. Any unusual changes in the lip’s texture or structure need to be looked into.
Identifying Lip Tumors
Lip tumors can show up as lumps or thickening. They might not hurt or they might be painful. It’s important to watch for any new growths or changes in the lip area.
To spot lip tumors, knowing the normal lip and mouth anatomy is key. Any swelling, lumps, or thickening should be checked closely.
Characteristics of Cancerous Lumps
Cancerous lumps inside the lip often have specific signs. They are hard, fixed in place, and grow over time. At first, they might not hurt, but as they grow, they can become painful.
Not all lumps are cancerous. But, any lump that doesn’t go away or grows should be checked by a doctor. They can figure out the cause and what treatment is needed.
Benign vs. Malignant Growths
Telling the difference between benign and malignant growths is key. Benign growths are not cancerous and don’t spread. They don’t invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body.
Malignant growths, or cancer, can spread and invade nearby tissues. They grow fast, have irregular shapes, and stick to the tissues underneath. These signs might mean it’s a malignant growth.
Seeing a healthcare professional for a correct diagnosis and treatment plan is important. Early action is key to managing lip cancer well.
Sign #5: Bleeding or Unusual Discharge
Seeing unexplained bleeding or unusual discharge from your lip is a big warning sign. It’s important to understand what it might mean and get medical help.
Unexplained Bleeding from the Lip
Bleeding from the lip without a clear reason or injury could mean lip cancer. This bleeding might happen on its own or after a small injury.
It’s key to tell normal lip injuries from signs of cancer. If bleeding keeps happening, see a doctor right away.
Characteristics of Concerning Discharge
Lip cancer discharge can look different. It might be bloody, clear, or have other stuff in it. What matters most is that it’s not like anything else.
| Discharge Type | Possible Indications |
|---|---|
| Bloody Discharge | Potential bleeding from a tumor or ulcer |
| Clear Discharge | Possible infection or tissue reaction |
| Discharge with Debris | Possible necrotic tissue or tumor breakdown |
Associated Symptoms
Lip cancer can also cause other symptoms. These include pain, swelling, or changes in how the lip looks or feels.
Spotting these symptoms helps understand the problem better. It also guides the right medical check-up.
Key associated symptoms to watch for:
- Persistent pain or tenderness
- Swelling or thickening of the lip
- Changes in lip texture or appearance
Sign #6: Changes in Lip Appearance or Texture
A change in the lip’s look or feel is a warning sign that needs medical help. This sixth sign of lip cancer shows how the lip can change. These changes might mean there’s a problem.
Visual Changes to Watch For
Visual signs can be early warnings of lip cancer. These signs include:
- Discoloration: patches or areas that are noticeably different in color from the surrounding tissue
- Scaling or crusting: the development of scales or crusts on the lip surface
- Swelling: unexplained swelling or thickening of the lip
Texture Abnormalities
Texture changes in the lip can also signal lip cancer. These changes might be:
- Roughness: the lip surface becoming rough to the touch
- Thickening: the lip or parts of it becoming thicker than usual
- Numbness: a feeling of numbness or altered sensation in the lip
Progressive Nature of Changes
Cancerous changes get worse over time. Unlike harmless conditions, cancerous changes don’t go away by themselves. They keep getting worse.
| Characteristics | Benign Changes | Cancerous Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Often temporary | Typically persistent |
| Progression | May resolve or remain stable | Often worsen over time |
| Associated Symptoms | Usually minimal | May include pain, numbness, or bleeding |
Keep an eye on any lip changes. If you see anything odd or lasting, see a doctor right away.
Sign #7: Difficulty with Oral Functions
Lip cancer can make it hard to speak and swallow, showing the need for quick medical help. This seventh sign of lip cancer can show up in many ways. It can really change a person’s life.
Problems with Speaking
Advanced lip cancer often makes speaking hard. The tumor can mess with how the lips and tongue move. This can lead to slurred speech or trouble saying words clearly.
Experts say, “Being able to talk well is key for daily life. Any trouble can hurt social and work life a lot.” This problem can make it hard to share thoughts and connect with others.
Challenges with Eating or Swallowing
Lip cancer can also make eating and swallowing hard, known as dysphagia. As the cancer grows, it can block the food path. This makes it tough to eat even soft foods.
A study found, “Dysphagia can cause malnutrition and dehydration. This makes the patient’s health worse.” This symptom can really hurt a person’s diet and health.
Some people might feel pain when eating or swallowing. This can make them avoid eating enough. Doctors need to quickly help with these problems to keep patients healthy and recovering well.
Impact on Daily Life
Lip cancer’s effects on oral functions can deeply change daily life. Simple things like eating, talking, and socializing can become hard. This can make patients feel lonely or upset.
“The emotional side of lip cancer is very important,” experts say. It can hurt a person’s mental health and life quality.
Patients and their families should get help from doctors, speech therapists, and nutritionists. This can help manage these problems. It can also make life better for those with lip cancer.
Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
It’s important to know how to diagnose, treat, and prevent lip cancer. We’ll look at the different ways to find and treat this disease. We’ll also talk about how to avoid it.
Diagnostic Procedures
Doctors use several steps to find lip cancer. They start by checking the lip and mouth for any oddities. This is the first step in diagnosing.
Next, they might take a small piece of tissue for a biopsy. This helps confirm if cancer cells are present. The tissue is then checked under a microscope.
They might also use X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. These tests help see how big the cancer is and if it has spread.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Initial assessment of the lip and oral cavity |
| Biopsy | Confirmation of cancer cells |
| Imaging Tests (X-rays, CT, MRI) | Determining the extent and spread of cancer |
Treatment Approaches
The treatment for lip cancer depends on several factors. These include the tumor’s size, location, and the patient’s health. The main treatments are surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Surgery is often the first choice. It aims to remove the tumor and some nearby tissue. This helps get rid of all cancer cells.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or with surgery.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s usually used for more serious cases or with other treatments.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing lip cancer involves reducing risks and taking protective steps. Avoiding tobacco and alcohol is key. Also, protect your lips from the sun and keep your mouth clean.
Using lip balm with SPF helps shield your lips from UV rays. Regular dental visits are also important for catching any mouth problems early.
Knowing about human papillomavirus (HPV) and how to avoid it can also help prevent lip cancer.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the signs of lip cancer for early detection and treatment. We’ve talked about the different types of lip cancer, risk factors, and seven key signs. Understanding these can help people take care of their oral health.
Lip cancer awareness is key to finding it early, which helps a lot with treatment. Knowing about risks like tobacco, alcohol, sun, and HPV can help prevent it. Regular self-checks and dental visits are also important for catching problems early.
By staying informed and watching out, we can fight lip cancer together. Early detection is the best way to treat it. We urge everyone to look after their oral health and see a doctor if they notice anything odd.
FAQ
What are the common signs of lip cancer?
Signs include sores or ulcers that don’t heal, white or red patches, and pain or numbness. Thickening or lumps, bleeding, and changes in lip appearance are also signs. Difficulty with eating or speaking can also indicate lip cancer.
How can I differentiate between a common mouth ulcer and a cancerous sore?
Cancerous sores last longer, are often painless at first, and bleed easily. If a sore doesn’t heal in two weeks, see a doctor.
What is leukoplakia, and is it related to lip cancer?
Leukoplakia are white patches on the lips or inside the mouth. It’s not cancer but can lead to cancer if it doesn’t go away or has other symptoms.
Are there any specific risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing lip cancer?
Yes, risks include tobacco and alcohol use, sun exposure, HPV infection, and being older. Men are more at risk than women.
How is lip cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, biopsy, and sometimes imaging tests like CT or MRI scans. These tests check how far the cancer has spread.
What are the treatment options for lip cancer?
Treatments depend on the cancer’s stage and location. Options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a mix of these.
Can lip cancer be prevented?
While not all cases can be prevented, reducing risks helps. Avoid tobacco and alcohol, protect your lips from the sun, and keep your mouth clean.
What is the significance of HPV infection in lip cancer?
HPV, some strains of it, increase the risk of oral cancers, including lip cancer.
How does sun exposure contribute to the risk of lip cancer?
Long-term sun exposure, without protection, raises the risk of lip cancer, mainly on the lower lip.
What are the early signs of lip cancer that I should look out for?
Look for persistent sores, white or red patches, and changes in lip appearance or texture. Catching it early is key for effective treatment.
Can a tumor inside the lip be benign?
Yes, not all lumps or tumors inside the lip are cancerous. But, any new or changing growth should be checked by a doctor.
How does lip cancer affect daily life?
Advanced lip cancer can make eating, speaking, and swallowing hard. It may also require big lifestyle changes during treatment.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Lip Cancer: Early Signs and Symptoms. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10149798/



































