Testicular cancer often hits young men, making it a big concern. Knowing the symptoms early is key to treating it well. Studies show that spotting these signs early can greatly help those affected testicular cancer symptoms.
Spotting testicular cancer symptoms early can really help in treatment. We’ll look at the main signs that might mean you have testicular cancer. This way, you can get help fast.
Key Takeaways
- Testicular cancer is most common in young men aged 15-39 years.
- Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes.
- Awareness of testicular cancer symptoms is critical for young men.
- Recognizing the warning signs can lead to timely medical intervention.
- Understanding the symptoms is essential for effective treatment.
What is Testicular Cancer?
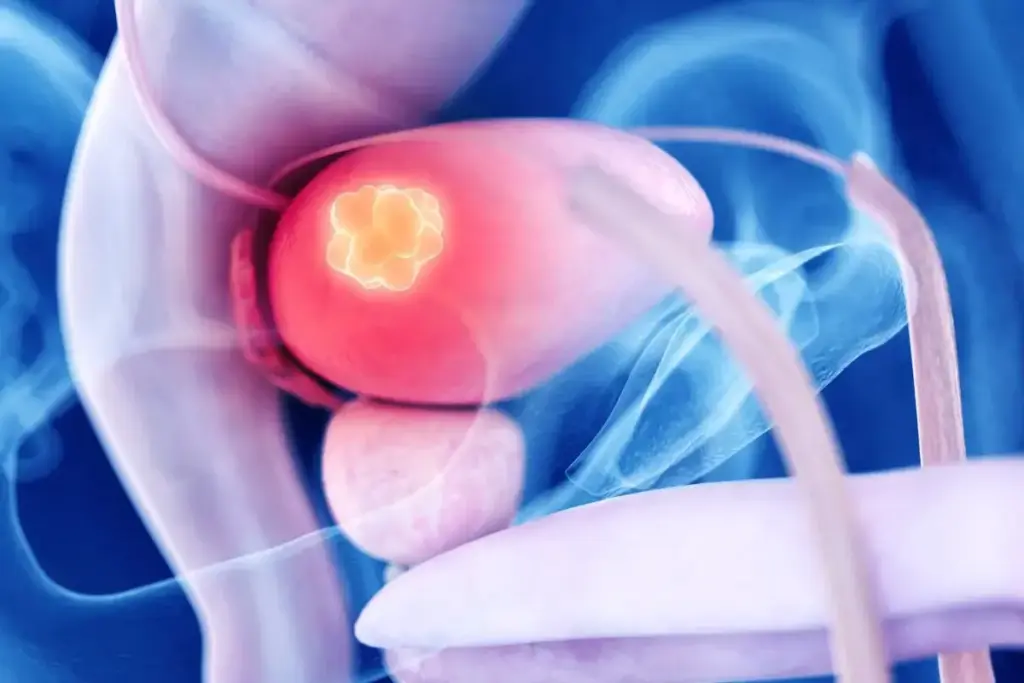
Testicular cancer is a rare condition but knowing about it is key for early treatment. It starts in the testicles, part of the male body. We’ll look at what it is, its types, and risk factors to understand it better.
Overview of Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer happens when abnormal cells in the testicles grow too much. It’s common in young and middle-aged men. The exact cause is unknown, but some factors can raise the risk.
Key Facts:
- Testicular cancer is rare compared to other cancers.
- It’s most often found in men aged 15 to 44.
- Finding it early can greatly improve treatment chances.
Types of Testicular Cancer
There are several types of testicular cancer, mainly based on where the cancer starts. The main types are:
- Seminomas: These grow slowly and are very sensitive to radiation.
- Non-Seminomas: This group includes several types like embryonal carcinoma and teratoma. They grow faster than seminomas.
Most testicular cancers are germ cell tumors, with seminomas being the most common. Knowing the type helps doctors choose the best treatment.
|
Type |
Description |
Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
Seminoma |
Slow-growing tumor |
Sensitive to radiation, common in men in their 30s and 40s |
|
Non-Seminoma |
Includes several subtypes |
Tends to grow more quickly, more common in men in their 20s |
Risk Factors
While the exact cause of testicular cancer is unknown, some risk factors have been found. These include:
- Cryptorchidism: A condition where one or both testicles haven’t moved down into the scrotum.
- Family History: Having a family history of testicular cancer, like in a father or brother.
- Age: It’s most common in young and middle-aged men.
“Knowing the risk factors and types of testicular cancer is key for early detection and effective management. Awareness can lead to better outcomes.”
— Medical Expert
Being aware of these factors helps men stay vigilant about their health. They should seek medical help if they notice any unusual symptoms, like a lump inside the testicle or changes in testicular size.
Common Symptoms of Testicular Cancer
Knowing the signs of testicular cancer can help improve treatment results. This type of cancer often shows clear signs that men should watch for.
Swelling or Lumps
A common symptom is a painless lump or swelling on the testicle. This can be as small as a pea or as big as a marble. It’s important to remember that not all lumps are cancerous. But, any unusual change should be checked by a doctor.
Key characteristics of a potentially cancerous lump include:
- A firm, painless swelling or lump
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- A change in the consistency of the testicle
Pain or Discomfort
Pain or discomfort in the testicle or scrotum is another symptom. This pain can feel like a dull ache or a sharp pain. It might be constant or come and go. If the pain lasts or is severe, seek medical help.
It’s worth noting that testicular cancer is often painless in its early stages. So, not feeling pain doesn’t mean there’s no problem.
Changes in Size or Shape
Changes in the size or shape of a testicle can also be a sign of cancer. Men should watch for any unusual changes, like one testicle getting bigger than the other. Or if a testicle feels different.
Doing regular self-exams can help men get to know their testicles. This makes it easier to spot any changes.
Physical Changes: What to Look Out For
Being aware of physical changes is essential for the early detection of testicular cancer, as it can present various symptoms that may seem minor but are significant.
Changes in the Testicle
A common sign of testicular cancer is a painless lump or swelling in the testicle. Men should watch for any unusual bumps or changes in testicle size. Remember, not all lumps are cancer, but any new or odd changes need a doctor’s check.
- A lump or swelling in the testicle
- A change in the size or consistency of a testicle
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
Unexplained Discomfort in the Groin
Men with testicular cancer might feel unexplained discomfort or pain in the groin or testicle. This pain can be a dull ache or sharp. Not all groin pain is cancer, but ongoing or severe pain should be checked by a doctor.
Breast Tenderness or Growth
Testicular cancer can also cause hormonal changes. This might lead to breast tenderness or growth (gynecomastia). This symptom is rare but serious and needs medical attention. Men with these symptoms should see a healthcare provider right away.
Being alert to these physical changes and talking to a healthcare provider can greatly help in early detection and treatment of testicular cancer.
Systemic Symptoms: Beyond the Testicles
Testicular cancer can spread and cause symptoms all over the body. Symptoms in the testicles are common, but other parts can be affected too. This shows the cancer has spread.
Fatigue and Weakness
Advanced testicular cancer can make you feel very tired and weak. This happens because your body is fighting the cancer. It can also affect how well your body works.
- Constant tiredness: Feeling extremely tired despite getting enough rest.
- Muscle weakness: Noticing a decrease in muscle strength, making everyday activities challenging.
These symptoms can really lower your quality of life. If you keep feeling tired or weak, you should see a doctor.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Advanced testicular cancer can also cause you to lose weight without trying. This happens when the cancer affects how your body uses food. Or when cancer cells take the nutrients meant for your body’s cells.
Key signs include:
- Losing weight without changing your diet or exercise routine.
- Noticing a decrease in appetite, which can further contribute to weight loss.
It’s important to know if weight loss is due to cancer or something else. If you’re losing weight and notice lumps in your testicles, see a doctor. They can help figure out what’s going on.
It’s also key to know the difference between a testicular cyst and cancer. Both can change the testicles, but they need different treatments. Always talk to a healthcare provider for the right diagnosis and care.
When to See a Doctor
Knowing when to see a doctor is key to avoiding serious issues. If you notice any unusual symptoms or changes, get medical help right away.
Warning Signs to Consider
There are several signs that mean you should see a doctor. These include:
- A lump or swelling in the testicle, which could be a sign of a testicular mass.
- Pain or discomfort in the testicle or scrotum.
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum.
- A sudden collection of fluid in the scrotum.
Importance of Early Detection
Finding testicular cancer early is very important. If you see any unusual changes, like a mass scrotum, see a doctor right away.
Early detection is critical. It helps doctors treat the cancer before it spreads. This can also mean less severe treatments.
|
Symptom |
Possible Indication |
Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Lump or swelling |
Testicular mass or tumor |
Consult a doctor |
|
Pain or discomfort |
Possible injury or infection |
Seek medical attention |
|
Heaviness or fluid collection |
Potential sign of testicular cancer |
Schedule a check-up |
Scheduling a Check-Up
If you notice any warning signs, make an appointment with your doctor. Your doctor will do a physical exam and might suggest more tests to find out what’s wrong.
Don’t wait to get medical help if you notice something odd. Early action can greatly improve your chances of a good outcome.
Risk Factors and Causes of Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer’s exact cause is unknown, but several risk factors are known. Knowing these can help spot the disease early. This might lower the chance of getting it.
Age and Ethnicity
Testicular cancer can hit at any age, but it’s common in young to middle-aged men. Men aged 15 to 35 are at higher risk. Also, Caucasian men are more likely to get it than men of other ethnicities.
Family History of Cancer
A family history of testicular cancer is a big risk factor. If a man has a father or brother with it, he’s at higher risk. This hints at a possible genetic link.
Conditions That May Increase Risk
Some medical conditions raise the risk of testicular cancer. For example, cryptorchidism, where testicles don’t drop, increases risk. Other conditions like testicular dysgenesis syndrome might also play a part.
To grasp the risk factors better, let’s look at the data in the table below:
|
Risk Factor |
Description |
Relative Risk |
|---|---|---|
|
Age |
Men between 15 and 35 years old |
Higher |
|
Ethnicity |
Caucasian men |
Higher |
|
Family History |
Having a father or brother with testicular cancer |
Significantly Higher |
|
Cryptorchidism |
Undescended testicles |
Higher |
Knowing these risk factors helps men understand their own risk. They can then talk to their doctor about any worries.
Diagnostic Tests for Testicular Cancer
Diagnosing testicular cancer involves several steps. These include a physical exam, imaging tests, and blood tests to check for tumor markers. We will explain the tests used to find testicular cancer. This will help you understand the process fully.
Physical Examination
A physical exam is the first step in diagnosing testicular cancer. A healthcare professional will look for any unusual lumps or swelling in the testicles. We check the testicles and the areas around them for any changes.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, like ultrasound, help confirm a tumor’s presence. They also show the tumor’s size and location. Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the inside. This helps us understand the tumor and plan the next steps.
Blood Tests
Blood tests look for tumor markers like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). These proteins are made by some testicular cancer cells. If these markers are high in the blood, it might mean cancer is present. We use these tests to track the disease and adjust treatment plans.
By combining physical exams, imaging tests, and blood tests, we can accurately diagnose testicular cancer. This allows us to create a good treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Testicular Cancer
When you’re diagnosed with testicular cancer, knowing your treatment options is key. The right treatment depends on the cancer’s stage and type, and your health.
There are many effective treatment strategies for testicular cancer. These include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Each treatment has its own role and is chosen based on your case.
Surgery: Orchiectomy
Surgery is often the first step in treating testicular cancer. It involves an orchiectomy, which is removing the affected testicle. This helps diagnose and treat the cancer by removing the source.
In some cases, a retroperitoneal lymph node dissection is done. This removes lymph nodes in the abdomen that might have cancer.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy rays. It’s very effective for some types of testicular cancer that are sensitive to it. This treatment is often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s a systemic treatment that can reach cancer cells in other parts of the body. Chemotherapy is great for treating cancer that has spread or is at a more advanced stage.
Choosing between these treatments, or using them together, depends on your cancer’s specifics and your health.
Coping Mechanisms and Support
Dealing with testicular cancer means finding ways to cope and getting support. This disease changes lives, affecting not just the person but their family too. It’s key to understand the emotional and mental effects of this diagnosis.
Emotional Support Resources
Getting emotional support is vital when facing testicular cancer. We offer counseling services and support hotlines. These help people deal with their feelings and find comfort.
Lifestyle Changes for Recovery
Changing your lifestyle can help with recovery. This might include eating better, being more active, and managing stress. A healthier lifestyle can boost well-being and help with healing.
Support Groups and Counseling
Support groups and counseling are great for sharing experiences. They offer a place to connect with others facing similar challenges. This can be very helpful during recovery.
|
Support Resource |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Counseling Services |
One-on-one or group counseling |
Emotional support, coping strategies |
|
Support Groups |
Meetings with others who have testicular cancer |
Shared experiences, community support |
|
Online Resources |
Access to information and forums |
Convenience, accessibility |
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Prepared
As we wrap up our talk on testicular cancer, it’s key to remember the importance of staying informed and proactive about your health. Knowing the warning signs and doing regular self-exams can help catch cancer early. This makes treatment more effective.
Watch out for swelling or lumps in your testicles, pain or discomfort, and any changes in size or shape. Being aware of these signs helps you get medical help fast.
Key Takeaways
Regular self-exams are vital for spotting any oddities. We suggest making self-exams a regular part of your routine. This way, you can catch any unusual changes in your testicles.
Empowering Yourself
By staying informed about testicular cancer and doing self-exams, you can take control of your health. If you notice any odd symptoms, don’t wait to see a doctor.
We stress the need for health awareness and urge you to stay alert about your well-being. This way, you can catch cancer early and get the right treatment. This leads to better health outcomes.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of testicular cancer?
Symptoms include a painless lump or swelling in the testicle. You might also notice changes in the size or shape of the testicle. Unexplained discomfort or pain in the groin or testicle is another symptom.
Is a painless lump on the testicle always a sign of cancer?
No, a painless lump doesn’t always mean cancer. But, it’s a symptom that needs medical attention. It could be cancer or another condition.
Can testicular cancer cause breast tenderness or growth?
Yes, some men with testicular cancer may feel breast tenderness or growth. This happens because of hormonal changes caused by the disease.
What are the risk factors for developing testicular cancer?
Risk factors include age and ethnicity. Family history of testicular cancer and certain medical conditions also play a role. These include undescended testes or testicular abnormalities.
How is testicular cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam and imaging tests like ultrasound. Blood tests are also used to check for tumor markers.
What are the treatment options for testicular cancer?
Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage and type. It may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Can testicular cancer be treated successfully if detected early?
Yes, early detection makes testicular cancer highly treatable. Early detection significantly improves outcomes.
What is the importance of self-exams in detecting testicular cancer?
Regular self-exams can spot changes or abnormalities in the testicles. This could lead to early cancer detection.
Are there any support resources available for individuals diagnosed with testicular cancer?
Yes, there are emotional support resources, support groups, and counseling services. They help individuals cope with a testicular cancer diagnosis.
Can lifestyle changes aid in recovery from testicular cancer?
Yes, making lifestyle changes can support recovery and overall health. These changes are important during and after treatment.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/testicular/basic_info/symptoms.htm






















