Nearly 900,000 Americans are affected by blood clots each year. Many cases are linked to lifestyle choices.
Some daily habits and choices can greatly affect clot formation. Knowing these factors is key to preventing clots and keeping our hearts healthy.What causes blood clots? Discover the essential lifestyle choices, like diet and inactivity, that pose a negative risk and how you can manage.
Looking into how lifestyle affects clot formation helps us find ways to improve.
Key Takeaways
- Lifestyle factors play a big role in blood clot formation.
- Our daily habits and choices can impact clot formation.
- Knowing the causes of blood clots is vital for prevention.
- Living a healthy lifestyle can lower blood clot risk.
- Being aware of blood clot risks is important for heart health.
Understanding Blood Clots and Their Formation
It’s important to know how blood clots form and when they’re a problem. Blood clotting helps stop bleeding when we get hurt. But, if it goes wrong, it can cause harmful clots.
The Normal Blood Clotting Process
The blood clotting process is complex but vital. It stops bleeding when a blood vessel is hurt. This process involves platelets and fibrin, which are key to forming clots.
When a blood vessel is damaged, the body first tries to stop the bleeding by constricting the vessel. Then, platelets stick to the injury, creating a plug. This plug is strengthened by fibrin, which is made through chemical reactions involving clotting factors.
When Blood Clotting Becomes Problematic
Blood clotting is a problem when it happens too much or in the wrong places. This can be due to genetics, lifestyle, or medical conditions. Clots in deep veins are called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). If they move to the lungs, they can cause a pulmonary embolism (PE), which is very dangerous.
- Genetic factors can make clotting disorders more likely.
- Lifestyle choices, like sitting too long or being overweight, raise clot risk.
- Certain health issues, like cancer or autoimmune diseases, can also affect clotting.
Types of Blood Clots
There are many types of blood clots, each with its own risks. The most common include:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Clots in the deep veins, usually in the legs.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Clots that travel to the lungs, causing a blockage.
- Arterial Thrombosis: Clots in arteries, which can lead to heart attacks or strokes.
Knowing about these clot types helps us spot warning signs and get the right medical help.
What Causes Blood Clots: The Fundamental Mechanisms
To understand blood clot formation, we must look at the key factors involved. Blood clots don’t come from one cause alone. They happen when several factors mess with normal blood flow and clotting.
Virchow’s Triad: The Three Main Factors
Virchow’s Triad is key to grasping blood clot formation. It points out three main factors: changes in blood flow, blood that clots too easily, and damage to the blood vessel lining.
- Changes in Blood Flow: Changes in blood flow can cause clots. For example, stasis, or slow blood flow, happens when we’re immobile for a long time.
- Hypercoagulability: This is when blood clots too easily. It can be due to genetics, cancer, or certain medicines.
- Endothelial Injury: Damage to the blood vessel lining can start clotting. It happens when the inner lining of blood vessels gets hurt.
How Lifestyle Choices Influence These Mechanisms
Lifestyle choices greatly affect blood clot formation. For instance, not moving much can change blood flow. Eating too much saturated fat can make blood clot more easily.
- Dietary Habits: Eating lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains keeps blood vessels healthy.
- Physical Activity: Exercise keeps blood flowing well and lowers clot risk.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Smoking harms the blood vessel lining and blood flow, raising clot risk.
Knowing about Virchow’s Triad and how lifestyle affects it helps us prevent blood clots. By choosing healthy foods, staying active, and avoiding smoking, we can greatly improve our blood vessel health.
Sedentary Lifestyle and Blood Clot Risk
Prolonged sitting is common in many jobs today. It can raise the risk of blood clots. We spend a lot of time sitting at desks or during commutes. It’s important to know how sitting affects our blood vessels.
The Dangers of Prolonged Sitting
Sitting for long can cause blood to pool in the legs. This increases the chance of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Even small leg injuries can lead to blood clots in people who don’t move much.
- Standing and stretching regularly can lower this risk.
- Doing simple exercises like ankle rotations and toe lifts while seated helps.
- Short walks during breaks can greatly improve blood flow.
How Inactivity Affects Blood Circulation
Inactivity can cause poor blood circulation. Without movement, veins don’t get the help they need to pump blood. This can lead to blood clots, mainly in the deep veins of the legs.
Being inactive makes blood flow slower. This makes it easier for clots to form. Regular exercise keeps blood flowing well and lowers clot risk.
Occupational Risks for Blood Clots
Jobs that involve a lot of sitting or standing can increase blood clot risk. For instance, office workers, drivers, and healthcare professionals often sit or stand for long hours. This raises their risk.
- Office workers can use ergonomic workstations and take breaks.
- Drivers should stop often to stretch and move.
- Healthcare professionals can fit stretching exercises into their busy days.
By knowing the risks of a sedentary lifestyle and taking action, we can lower blood clot risk. This helps keep our blood vessels healthy.
Obesity and Its Impact on Blood Clot Formation
It’s important to know how obesity affects blood clotting to prevent it. Obesity changes how our body works, raising the risk of heart diseases like blood clots.
Excess Weight and Clotting Risk
Being overweight, or obese, increases the chance of blood clots. This is because extra weight can cause inflammation and change how blood clots.
“Obesity is a major risk factor for venous thromboembolism, which includes both deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism,” says experts. They stress the importance of managing weight to lower clot risk.
Metabolic Changes Associated with Obesity
Obesity brings on metabolic changes that raise blood clot risk. These changes include insulin resistance, inflammation, and changes in lipid levels. All these can make blood more likely to clot.
Specifically, obesity is linked to:
- Increased levels of pro-coagulant factors
- Enhanced platelet activation
- Reduced fibrinolytic activity
Weight Management Strategies for Reducing Risk
Managing weight is key to lowering blood clot risk in obese people. This can be done through diet, exercise, and sometimes medical help.
Some good strategies are:
- Eating a balanced diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains
- Doing regular physical activity like walking or swimming
- Looking into weight loss programs or talking to a healthcare provider for advice
By understanding obesity’s link to blood clots and using effective weight management, people can lower their clot risk.
Smoking and Tobacco Use: Major Contributors to Blood Clots
Tobacco use, whether through smoking or vaping, greatly increases the risk of blood clots. It harms the heart and blood vessels. Knowing these risks is key to staying healthy.
How Nicotine and Toxins Affect Blood Vessels
Nicotine and toxins in tobacco harm blood vessel linings. This makes them more likely to block. It also makes blood clotting worse.
Health experts say smoking causes heart disease and raises the risk of blood clots. Quitting can greatly lower these risks. It’s a big step towards better heart health.
Vaping and New Tobacco Products
Vaping and new tobacco products bring new dangers. They may seem safer, but they contain harmful substances. Studies show vaping can harm the heart too.
Smoking Cessation Benefits for Clot Prevention
Quitting smoking is a top way to prevent blood clots. It cuts heart disease risk quickly. Support groups can help those trying to quit.
It’s never too late to quit smoking. Quitting today is better than waiting. It’s a big step towards avoiding blood clots and heart disease.
Dietary Factors That Influence Blood Clotting
Diet is key to keeping your heart healthy. Some foods can make blood clot more easily. This is because of the fats they contain.
Eating right helps keep blood vessels strong. It stops blood clots from forming. Some foods help, while others can increase the risk.
High-Fat Diets and Blood Clotting
Too much saturated and trans fat is bad. These fats are in many processed foods. They make blood more likely to clot.
The Impact of Dehydration
Drinking enough water is vital. It keeps blood flowing well. Without enough water, blood can thicken and clot more easily.
Nutritional Approaches to Reducing Blood Clot Risk
Some foods can lower the risk of blood clots. Omega-3s in fish like salmon help. Eating lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is also good for your heart.
| Dietary Factor | Effect on Blood Clotting |
| High-Fat Diets | Increases risk due to altered blood composition |
| Dehydration | Concentrates blood, increasing clotting risk |
| Omega-3 Rich Foods | Reduces clotting risk due to anti-clotting properties |
Stress, Sleep, and Their Effects on Blood Clot Risk
Chronic stress and lack of sleep are big risks for heart diseases, like blood clots. As we deal with today’s world, knowing how these affect our heart health is key.
Chronic Stress and Inflammatory Responses
Chronic stress sets off a chain of body responses, including stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones get us ready to fight or flee. But, if they stay high, they can cause inflammation and up the risk of blood clots. The inflammatory response is a key mechanism by which chronic stress contributes to cardiovascular disease.
“Cortisol, often referred to as the ‘stress hormone,’ has a profound impact on the body’s metabolic and cardiovascular systems,” notes a study on stress and cardiovascular health.
“Prolonged exposure to cortisol can lead to changes in blood pressure, lipid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity, all of which can contribute to an increased risk of blood clots.”
Sleep Deprivation and Cardiovascular Health
Lack of sleep also harms heart health. Sleep helps the body fix tissues, build bone and muscle, and boost the immune system. Not getting enough sleep can cause inflammation, high blood pressure, and a higher risk of blood clots.
Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining healthy blood circulation and preventing the formation of blood clots. Studies show people who sleep less than 7 hours a night face a higher risk of heart problems, including blood clots.
Stress Management Techniques for Better Circulation
Managing stress well is key to avoiding the risks of chronic stress and sleep loss. Activities like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can lower stress and help sleep better. Also, regular exercise and a healthy diet help keep the heart healthy.
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
- Yoga and tai chi for relaxation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Regular physical activity
- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
By using these stress management methods every day, people can lower their risk of blood clots and improve their heart health.
Hormonal Influences and Blood Clot Formation
Hormonal changes can greatly affect the risk of blood clots. Factors like birth control and pregnancy can change the body’s hormonal balance. This can increase the risk of clotting.
Birth Control and Hormone Replacement Therapy
Birth control and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can raise blood clot risks. Estrogen and progesterone, found in these treatments, can alter blood clotting factors.
Pregnancy-Related Clotting Risks
Pregnancy brings many changes, including blood clotting factor changes. These changes help the fetus grow and reduce bleeding during childbirth. But, they also raise the risk of blood clots.
Managing Hormonal Risk Factors
To lower blood clot risks from hormonal changes, knowing your risks is key. Talking to a healthcare provider about your risks is a vital step.
Travel-Related Blood Clots: Understanding and Preventing DVT
Traveling long distances, like by air, increases our risk of blood clots. This is because we sit for a long time. This condition is also known as “economy class syndrome,” but it’s not just for economy class or flying. Other factors like sitting too long, tight seats, and not drinking enough water also play a role.
Long-Distance Travel and “Economy Class Syndrome”
The term “economy class syndrome” was used to talk about the higher risk of DVT from long flights, mainly in economy seats. But, DVT can happen when we sit for a long time, like in cars or trains too.
Preventive Measures During Travel
There are ways to lower your risk of DVT when traveling far. Drinking lots of water, wearing loose clothes, and getting up to move are good steps. These actions help keep your blood flowing well.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water regularly.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing that can restrict blood flow.
- Take regular breaks to stand, stretch, and walk around.
- Consider wearing compression stockings to improve circulation.
When to Seek Medical Attention After Travel
After traveling, watch for signs of DVT. Look for swelling, pain, or tenderness in your legs. Also, check for redness or warmth. If you notice these, see a doctor right away.
Knowing the signs of DVT and taking steps to prevent it can greatly reduce risks from long trips. By understanding the dangers and taking action, travelers can lower their risk of this serious condition.
Medications and Supplements That Affect Blood Clotting
It’s important to know how some medicines and supplements can change blood clotting. This knowledge helps in managing and lowering the risk of blood clots. Both prescription and over-the-counter drugs, along with herbal supplements, can impact how blood clots. Knowing these effects helps in making better health choices.
Over-the-Counter Medications to Use with Caution
Many people use over-the-counter (OTC) medicines for different health problems. Some of these can change how blood clots. For example, NSAIDs like ibuprofen can inhibit platelet aggregation, which might raise the chance of bleeding. Also, some cold medicines with pseudoephedrine can constrict blood vessels, which could affect blood flow.
It’s key to stick to the right dose of OTC medicines. Always talk to a doctor, too, if you’re already taking blood thinners or have clotting issues.
Herbal Supplements That Influence Clotting
Herbal supplements are popular for their health benefits, but some can really change blood clotting. For instance, garlic supplements can make blood thinner and increase bleeding risk. Ginger can also affect how platelets work. Yet, some supplements like coenzyme Q10 might work against blood thinners.
Talking to your doctor about herbal supplements is very important. They can interact with your prescription medicines and affect blood clotting.
Discussing Medication Risks with Healthcare Providers
Talking about your medicines and supplements with your doctor is very important. They can tell you how to use them safely and what might happen when they mix with other drugs.
When you talk to your doctor, remember to:
- Share all the medicines and supplements you’re taking.
- Tell them about any clotting problems or bleeding risks you’ve had.
- Ask about any possible bad reactions with new medicines or supplements.
Being proactive and informed can help reduce risks from medicines and supplements that affect blood clotting.
Alcohol Consumption and Blood Clotting
Many of us enjoy drinking alcohol at social events and in our culture. But, it’s important to know how it affects our health, like blood clotting. Knowing the link between drinking and blood clotting helps us make better choices about our drinking.
Effects of Moderate vs. Excessive Drinking
Drinking in moderation means up to one drink a day for women and two for men. Studies show that moderate drinking might protect our hearts. But, drinking too much can harm our health, including raising the risk of blood clots.
Too much alcohol can mess with our blood’s clotting process. This is bad news for people already at risk for heart problems.
How Alcohol Affects Platelet Function
Alcohol changes how platelets work in our blood. Platelets are small cells that help form clots. Drinking too much can make them stick together more easily, leading to clots.
Research finds that heavy drinking boosts clotting factors, raising the risk of blood clots. But, drinking in moderation might help keep platelets healthy, lowering clot risk.
Guidelines for Safer Alcohol Consumption
To stay safe from alcohol’s effects on blood clotting, drink wisely. Here are some tips:
- Stick to moderate drinking (up to one drink a day for women, two for men).
- Avoid binge drinking to prevent serious health issues.
- Pay attention to how your body reacts to alcohol and adjust your drinking.
- Try water or low-calorie drinks to cut down on alcohol.
By being careful with our drinking, we can lower the risk of blood clots and keep our hearts healthy.
Medical Conditions That Increase Blood Clot Risk
It’s important to know which health issues can lead to blood clots. Many conditions can affect how our bodies clot blood. This makes some people more likely to get dangerous clots.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Heart problems are a big reason for blood clot risk. Issues like atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and coronary artery disease can cause clots. Atrial fibrillation, for instance, leads to irregular heartbeats that can cause blood to pool and clot.
Managing heart diseases with medicine, lifestyle changes, and treatments can lower this risk.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune diseases, where the body attacks itself, also raise blood clot risk. Conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis cause inflammation that can lead to clots. Some treatments for these diseases can also increase clot risk.
It’s key to monitor and manage these conditions with healthcare help.
Genetic Predispositions to Clotting
Some people are born with a higher risk of blood clots due to their genes. Conditions like Factor V Leiden and Prothrombin G20210A mutation affect how blood clots. Knowing your family history and getting genetic tests can help spot risks.
For those with genetic risks, taking preventive steps and staying under a doctor’s watch is essential.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of Blood Clots
Knowing the warning signs of blood clots is critical. Blood clots can form in deep veins, causing Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). They can also break loose and travel to the lungs, leading to Pulmonary Embolism (PE). Both are serious and need quick medical help.
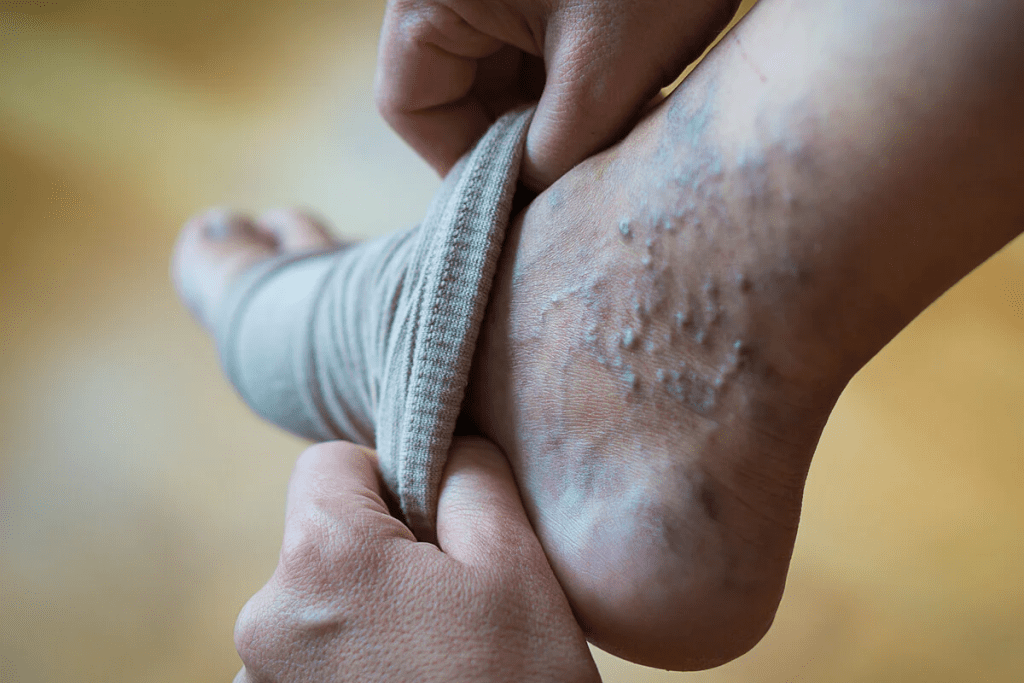
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT often happens in the legs. Its symptoms can be mild. You might notice swelling, pain, or tenderness in your leg. It could feel like a cramp or soreness.
The affected area might feel warm and the skin could look red or discolored. It’s important to watch for these signs. DVT can turn into a life-threatening PE if the clot moves.
Signs of Pulmonary Embolism
A Pulmonary Embolism happens when a blood clot blocks blood flow in the lungs. Symptoms can vary but often include sudden shortness of breath and chest pain. This pain gets worse when you breathe deeply.
Other signs include a rapid heart rate, coughing up blood, feeling lightheaded, or a sense of impending doom. These symptoms need immediate medical attention. PE can be fatal if not treated quickly.
“The sooner a pulmonary embolism is diagnosed and treated, the better the chances of survival.”
When to Seek Emergency Care
If you or someone you know has symptoms of DVT or PE, get medical help right away. Waiting too long can lead to serious problems, even death. Call emergency services or go to the emergency room if you have severe difficulty breathing, chest pain, or severe leg pain and swelling.
Key Takeaways:
- Be aware of the symptoms of DVT, including leg swelling and pain.
- Recognize the signs of PE, such as sudden shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Blood Clot Risk
Understanding what causes blood clots is the first step to lowering our risk. We’ve looked at how a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and some health issues can lead to blood clots. Making smart lifestyle choices can help a lot.
Changing our lifestyle is key to avoiding blood clots. Simple steps like exercising regularly, keeping a healthy weight, and managing stress can make a big difference. It’s also important to know the signs of blood clots and get help right away if we notice them.
Preventing blood clots starts with healthy habits and being mindful of our choices. We should talk to our doctors about our risk and make a plan to stay safe. Let’s all work together to lower our risk of blood clots.
FAQ
What are the main causes of blood clots?
Blood clots can be caused by genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions. Virchow’s Triad explains the main factors. These are changes in blood flow, hypercoagulability, and injury to the blood vessel lining.
How does a sedentary lifestyle contribute to blood clot risk?
Sitting for long periods can lead to blood clots. This is because blood flow is reduced, causing it to pool in the legs. This can result in deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Can obesity increase the risk of blood clots?
Yes, being overweight increases blood clot risk. Excess weight can cause inflammation and promote clotting. Eating well and exercising can help manage weight and reduce clot risk.
How does smoking affect blood clot formation?
Smoking damages blood vessel linings, making them more prone to clots. Nicotine and other toxins in smoke also raise blood pressure and increase platelet aggregation. This further raises the risk of blood clots.
What dietary factors can influence blood clotting?
A diet high in saturated fats and low in nutrients can make blood more viscous and prone to clotting. Dehydration also thickens blood, increasing clotting risk. Drinking water and eating a balanced diet can help keep blood flowing well.
Can stress and sleep deprivation contribute to blood clot risk?
Yes, stress and lack of sleep can increase blood clot risk. They promote inflammation and disrupt blood flow. Reducing stress and getting enough sleep can help lower this risk.
How do hormonal influences affect blood clot formation?
Hormonal changes, like those in pregnancy or with birth control, can raise blood clot risk. Managing these risks through medical supervision and lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk.
What are the risks associated with long-distance travel and DVT?
Long trips, like by air or car, can increase DVT risk due to sitting for long periods. Regular breaks to stretch, staying hydrated, and wearing compression stockings can help prevent DVT.
Can certain medications and supplements affect blood clotting?
Yes, some medications and supplements can affect blood clotting. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new medications or supplements to understand their effects.
How does alcohol consumption affect blood clotting?
Moderate alcohol use may not affect blood clotting much. But, too much drinking can increase bleeding and clotting risks. Drinking in moderation and knowing your limits can help minimize risks.
What are the warning signs of a blood clot?
Warning signs of a blood clot include leg swelling, pain, or tenderness (DVT). Shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood (pulmonary embolism) are also signs. If you have these symptoms, seek medical help right away.
References
- National Library of Medicine. (2001). Factor V Leiden thrombophilia. MedlinePlus Genetics.https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/factor-v-leiden-thrombophilia/



































