Nearly 900,000 Americans are affected by blood clots each year. Many experience symptoms that can be confused with other conditions. It’s important to know how to identify blood clots in legs correctly.
Leg pain and swelling are common signs of blood clots. But, they can also mean other serious health issues. Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help. At our institution, we stress the need for accurate diagnosis to give our patients the best care.
Key Takeaways
- Several conditions can mimic the symptoms of blood clots in legs.
- Accurate diagnosis is key for effective treatment.
- Leg pain and swelling are common symptoms that need medical check-up.
- Knowing the differences between blood clots and other conditions can save lives.
- Seeking medical attention quickly is vital for patients with symptoms.
Understanding Blood Clots in Legs
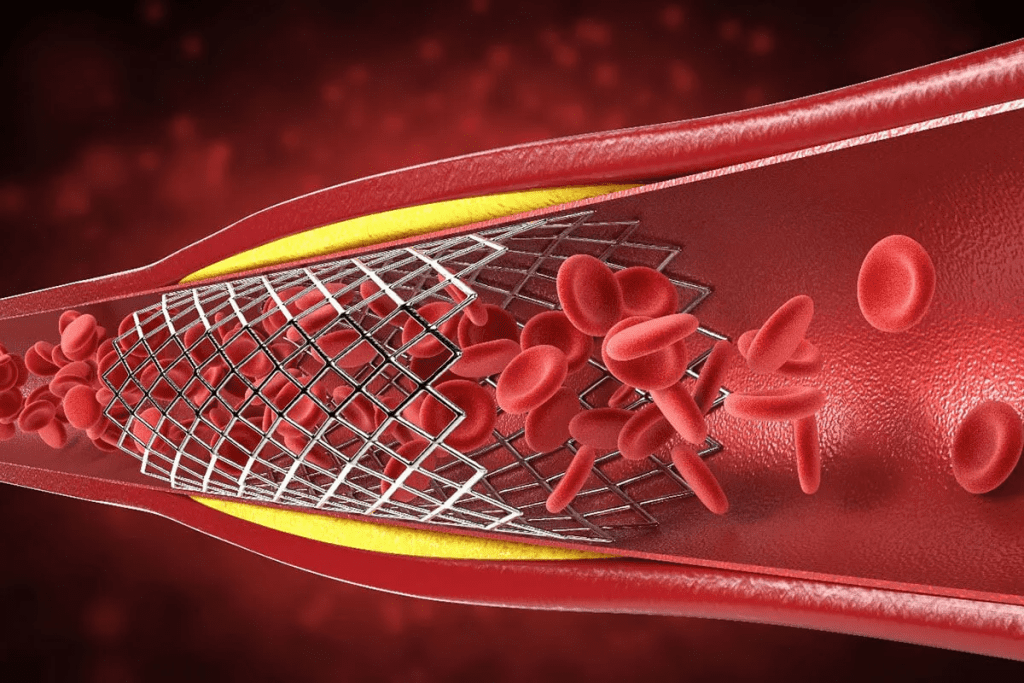
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
What Are Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Superficial Vein Thrombosis (SVT)?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in the deep veins, usually in the legs. DVT is a serious condition because it can cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism if it breaks loose and goes to the lungs. Superficial vein thrombosis (SVT), on the other hand, happens in veins closer to the skin’s surface.
Even though both involve blood clots, they are different in where they happen and how risky they are. The main differences between DVT and SVT are:
- Location: DVT is in deep veins, while SVT is in superficial veins.
- Risk: DVT is more dangerous because it can lead to a pulmonary embolism.
- Symptoms: Both can cause pain and swelling, but DVT’s symptoms are often more severe.
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
What Does a Blood Clot in the Leg Feel Like?

Having a blood clot in the leg can feel different for everyone. Symptoms can vary in how bad they are and what they feel like. We’ll look at the common feelings and symptoms of blood clots in the leg. This will help you know when to worry.
Common Sensations and Symptoms
Blood clots in the leg can cause a variety of sensations. These can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. Here are some common symptoms:
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, which may feel like cramping or soreness
- Swelling in the affected leg, sometimes accompanied by redness or warmth
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the leg
- Achiness or discomfort, specially when standing or walking
In some cases, you might not notice a blood clot at all. But when symptoms do show up, they can be clear. The pain from a blood clot is often a persistent, throbbing sensation. It doesn’t get better with rest or by elevating your leg.
Knowing these symptoms is key because they can mean a serious problem. If you feel any of these, and they’re bad or with other scary symptoms like trouble breathing or chest pain, get help right away.
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
Visual Appearance of Blood Clots in Legs
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
Typical Physical Signs
The look of a blood clot can change, but common signs are swelling, redness, and warmth. Swelling is a clear sign, caused by blocked blood flow. Redness and warmth show inflammation from the clot.
- Pain or tenderness in the affected leg
- Discoloration of the skin, which may appear blue or red
- Visible veins that are swollen or hardened
| Signs | Description |
| Swelling | Noticeable swelling due to obstructed blood flow |
| Redness and Warmth | Inflammation caused by the blood clot |
| Pain or Tenderness | Discomfort in the affected leg |
| Discoloration | Blue or red discoloration of the skin |
Spotting these signs early can help find blood clots quickly. If you think you have a blood clot, get medical help right away.
Blood Clots in Different Leg Locations
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
Lower Leg Blood Clot Symptoms
Blood clots in the lower leg, linked to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), show different symptoms. These include:
- Pain or tenderness in the calf or lower leg
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Warmth or redness of the skin
- A feeling of heaviness or aching in the leg
Some people might not feel any symptoms. So, knowing the risk factors for DVT is very important.
Blood Clot Symptoms Inner Thigh and Upper Leg
Blood clots in the inner thigh or upper leg have unique symptoms. These symptoms are:
- Pain or discomfort in the groin or upper thigh area
- Swelling or inflammation in the affected area
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- A palpable lump or cord-like structure in severe cases
It’s critical to seek medical attention if you notice these signs. Blood clots in these areas can be very dangerous. They can be life-threatening if they move to the lungs.
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
Bruising vs. Blood Clots in Legs
Bruising and blood clots in the legs can be confusing. It’s important to know the difference for proper diagnosis. When we notice leg injuries or unusual changes, we might wonder if it’s just a bruise or something more serious like a blood clot.
Both bruises and blood clots can happen in the thigh. A bruise is caused by trauma, leading to blood leakage into the tissues. On the other hand, a blood clot forms within a vein.
Blood Clot Bruise on Thigh: Is It Really a Clot?
To figure out if a bruise on the thigh is a blood clot, we need to look at symptoms and characteristics. Here are some key differences:
- Bruise: Results from trauma, with discoloration that changes over time, tenderness to the touch, and swelling that is usually limited.
- Blood Clot: May not have an obvious cause, can cause pain or tenderness not necessarily related to touch, and swelling that can be more pronounced and widespread.
To further clarify the differences, let’s examine a comparison table:
| Characteristics | Bruise | Blood Clot |
| Cause | Trauma or injury | Clot formation within a vein |
| Symptoms | Discoloration, tenderness | Pain, swelling, warmth |
| Swelling | Limited, localized |
Understanding these differences is key for getting the right medical attention. If you’re unsure between a bruise and a blood clot, always consult a healthcare professional.
Muscle Strains and Tears Mistaken for Blood Clots
It’s hard to tell the difference between muscle strains, tears, and blood clots when you have leg pain and swelling. These conditions often look the same because they share similar symptoms.
Symptoms of Muscle Injuries
Muscle strains and tears are common and can hurt a lot. They also cause swelling, just like blood clots do. A muscle strain happens when the muscle fibers get stretched or torn. A muscle tear is worse, where the muscle might be partially or fully broken.
The signs of muscle injuries include:
- Pain that gets worse when you move
- Swelling or bruising where it hurts
- Muscle weakness or stiffness
- A bump or lump in the muscle
Unlike blood clots, muscle injuries usually come from trauma or too much use. But, the pain and swelling can be mistaken for a blood clot if the injury isn’t seen right away.
To tell muscle injuries apart from blood clots, a doctor needs to check you carefully. They might use imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI. These tests help see what’s wrong and why you’re feeling pain.
Cellulitis: A Common Blood Clot Mimicker
Many patients are diagnosed with cellulitis, which looks like a blood clot in the leg. It’s a bacterial infection of the skin and the tissue just below it. This condition causes redness, swelling, and pain.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Cellulitis
Cellulitis symptoms are similar to those of a blood clot, making it hard to diagnose. Common signs include:
- Redness and swelling of the affected limb
- Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
- Pain or discomfort, specially when moving the affected limb
- Fever or chills in some cases
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor. Untreated cellulitis can cause serious problems.
Distinguishing Cellulitis from a Blood Clot
Both conditions share similar symptoms, but there are key differences. Cellulitis causes more widespread redness and swelling. A blood clot, on the other hand, causes more localized pain and swelling.
Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment. If you’re showing symptoms of either, seeing a healthcare professional is a must.
Baker’s Cysts and Their Similarity to Blood Clots
Baker’s cysts and blood clots in the leg share similar symptoms. This makes it hard to tell them apart. Both can cause a lot of discomfort and swelling, confusing patients and doctors.
What Is a Baker’s Cyst?
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling. It causes a bulge and tightness behind your knee. It might hurt when you extend your knee or when you’re active.
The cyst usually comes from a knee problem like arthritis or a meniscal tear. This leads to fluid buildup.
The symptoms of a Baker’s cyst can look like those of a blood clot. You might see swelling, pain, and a feeling of fullness or tightness in your leg. But, a Baker’s cyst is not the same as a blood clot. It needs different treatment.
Key differences between a Baker’s cyst and a blood clot include:
- The location of the swelling: A Baker’s cyst is usually behind the knee. A blood clot can be anywhere in the leg.
- The nature of the pain: Pain from a Baker’s cyst often gets worse when you extend your knee. Pain from a blood clot can be constant and gets worse with walking or standing.
- The presence of other symptoms: Blood clots can have warmth, redness, and discoloration. A Baker’s cyst might not have these symptoms.
Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment. If you have symptoms that could be from a Baker’s cyst or a blood clot, see a doctor. They can give you the right evaluation.
Peripheral Artery Disease vs. Venous Blood Clots
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
PAD is when arteries in the legs narrow. This is often due to plaque buildup. Venous blood clots, on the other hand, happen in veins and can be linked to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT).
Symptoms of PAD That Resemble Blood Clots
Symptoms of PAD can look like those of blood clots. Both can cause leg pain and discomfort. But the pain’s cause and how it feels are different.
PAD pain usually happens when you’re active, like walking, and goes away when you rest. Blood clots, though, cause pain that doesn’t stop and might also make the leg swell, feel warm, and look red.
| Symptom | Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) | Venous Blood Clots |
| Pain Characteristics | Intermittent claudication; pain during activity, relieved by rest | Constant pain; may be accompanied by swelling, warmth, redness |
| Location of Pain | Typically calf, thigh, or buttock | Usually in the leg, often associated with the area of the clot |
| Triggers | Physical activity | None specific; can occur at rest |
PAD and blood clots can happen together, making diagnosis harder. A detailed check-up is needed to tell them apart and treat them right.
When looking at leg symptoms, we must think about the whole vascular health. A good diagnosis includes looking at the patient’s history, doing a physical check, and sometimes, more tests like the ankle-brachial index (ABI) for PAD or ultrasound for blood clots.
Can Blood Clot Pain Come and Go?
Blood clot pain isn’t always steady; it can change, causing confusion. This change makes it hard to diagnose and treat blood clots well.
Patients often wonder if their leg pain is from a blood clot or something else. Blood clot pain can change a lot, and knowing its patterns is key.
Intermittent Symptoms of Blood Clots
Intermittent symptoms of blood clots include pain, swelling, and warmth or redness that change. These signs can be tricky because they might seem better before getting worse again.
Factors influencing intermittent blood clot pain include:
- Movement and activity levels
- Position of the affected limb
- Underlying health conditions
As one doctor says, “The pain from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can be tricky. It might seem to go away before coming back.”
“The changing symptoms make it hard for patients to know when to get medical help.”
People with intermittent leg pain or swelling should see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly help patients with blood clots.
Knowing that blood clot pain can change helps patients watch their symptoms closely. They should get medical help when needed.
Early Signs of Blood Clot in Leg
The early signs of a blood clot in the leg are often subtle. They can be easily overlooked but are critical to identify. Knowing the subtle initial symptoms is key to ensuring timely medical intervention.
Subtle Initial Symptoms Often Overlooked
A blood clot in the leg can show itself in different ways. Early signs include mild swelling, slight pain or tenderness, and warmth or redness in the affected area.
- Mild swelling that may not be immediately noticeable
- Slight pain or tenderness that can be mistaken for a muscle strain
- Warmth or redness in the affected area
These symptoms can be subtle and may develop gradually. This makes it challenging to diagnose a blood clot early. But knowing these signs can help in seeking medical attention promptly.
| Symptom | Description |
| Mild Swelling | Swelling that is not severe but noticeable upon comparison with the other leg |
| Slight Pain or Tenderness | Pain that is not sharp but can be felt when walking or standing |
| Warmth or Redness | The affected area may feel warmer or appear redder than the surrounding skin |
It’s essential to monitor these symptoms closely. Seek medical help if they persist or worsen. Early detection of blood clots can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Diagnostic Approaches for Suspected Blood Clots
Diagnosing blood clots in the legs involves several steps. These include a thorough check-up, looking at the patient’s medical history, and using advanced tests. When someone shows signs of a blood clot, doctors use a specific method to confirm it and check for other possible causes.
Medical Tests Used to Confirm Blood Clots
There are a few tests doctors use to find blood clots in the legs. These include:
- Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to see inside the blood vessels and find clots. It’s often the first choice because it’s safe and works well.
- D-dimer test: This blood test checks for D-dimer, a sign of clot breakdown. It’s helpful but not always enough on its own, mainly for low-risk patients.
- Venography: This X-ray test uses dye to show the veins and find clots. It’s very accurate but more invasive, used when ultrasound doesn’t work.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan: Good for finding clots in bigger veins, like in the pelvis or abdomen.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Useful for spotting clots in smaller veins or in tricky cases.
We pick the best test or tests based on the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and risk for blood clots.
Doctors also do a detailed physical exam and look at the patient’s medical history. They check for signs like swelling, pain, and warmth in the leg.
Getting the diagnosis right is key. It helps doctors treat the patient right and avoid serious problems like pulmonary embolism.
Superficial Thrombophlebitis vs. Deep Vein Thrombosis
It’s important to know the difference between superficial thrombophlebitis (SVT) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Both involve blood clots in veins, but they are different in location, symptoms, and treatment.
Key Differences in Presentation
SVT happens in veins near the skin. DVT, on the other hand, affects deeper veins, usually in the legs. The symptoms and how severe they are can differ.
SVT shows up as pain, redness, and swelling in the affected vein. It might feel warm and sore to the touch. DVT symptoms can be less obvious, but may include leg pain or swelling, warmth, and redness.
To understand SVT and DVT better, let’s look at their main features in the table below:
| Characteristics | Superficial Thrombophlebitis (SVT) | Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) |
| Location | Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help. | Deep veins, typically in the legs |
| Symptoms | Pain, redness, swelling along the vein | Leg pain or swelling, warmth, redness |
| Severity | Generally less severe than DVT | Can be severe, potentially life-threatening |
| Treatment Approach | Conservative management with NSAIDs and compression | Anticoagulation therapy to prevent clot progression |
Distinguishing between SVT and DVT is key because their treatments are different. SVT is usually treated with NSAIDs and compression stockings. DVT, though, needs anticoagulation therapy to stop the clot from getting worse.
It’s vital to accurately diagnose and treat these conditions to avoid complications.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Certain symptoms need quick action to avoid serious problems from blood clots. If you notice any of these red flag symptoms, act fast.
Red Flag Symptoms That Require Emergency Care
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
- Severe leg pain or swelling: Sudden, severe pain or swelling in one leg could mean a deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing: Chest pain, shortness of breath, or coughing up blood could signal a pulmonary embolism, a serious risk from DVT.
- Rapid heart rate: A sudden increase in heart rate might mean a blood clot has broken loose and is affecting your heart or lungs.
- Dizziness or fainting: Feeling dizzy or fainting could mean a blood clot is affecting your circulation or heart function.
- Confusion or difficulty speaking: Rarely, a blood clot can cause a stroke. Symptoms include confusion, trouble speaking, or weakness on one side of the body.
If you’re showing any of these symptoms, get emergency care right away. Waiting can lead to serious issues or even death.
| Symptom | Possible Indication | Action Required |
| Severe leg pain or swelling | Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Chest pain or difficulty breathing | Pulmonary Embolism | Call emergency services |
| Rapid heart rate | Cardiac complication from blood clot | Seek emergency care |
Medical experts stress the importance of quick action for blood clots.
“Time is of the essence when dealing with blood clots. Quick medical evaluation can greatly improve outcomes.”
Knowing these red flag symptoms helps you make smart health choices. If unsure about your symptoms, always seek medical advice.
Conclusion: Navigating Leg Pain and Swelling Concerns
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
Being aware of blood clot signs in the legs is important. This includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and superficial vein thrombosis (SVT). If you have ongoing or severe pain and swelling, see a doctor right away.
Understanding the differences is crucial for obtaining the right medical help.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a blood clot in the leg?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, and warmth. You might also feel a heavy or aching sensation.
How can I tell if I have a blood clot or just a muscle strain?
Blood clot symptoms are usually more severe and last longer. If unsure, it’s best to see a doctor.
Can a blood clot cause pain that comes and goes?
Yes, blood clot pain can be intermittent. It often comes with swelling and redness. If pain keeps coming back, see a doctor.
What is the difference between Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Superficial Vein Thrombosis (SVT)?
DVT happens in deep veins, usually in the legs. SVT is in superficial veins. DVT is more serious and needs quick medical help.
Can cellulitis be mistaken for a blood clot?
Yes, cellulitis, a skin infection, can look like a blood clot. It causes redness, swelling, and pain. A doctor’s diagnosis is key.
What are the red flag symptoms that require immediate medical attention for suspected blood clots?
Look out for severe pain, trouble breathing, chest pain, and sudden swelling. These are signs to get medical help right away.
How is a blood clot diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests like ultrasound or venography to diagnose.
Can a Baker’s cyst be mistaken for a blood clot?
Yes, a Baker’s cyst can look like a blood clot. It causes swelling and pain. A doctor’s diagnosis is needed to know the cause.
What is the difference between a bruise and a blood clot?
Bruises are from bleeding into soft tissues. Blood clots form in blood vessels. Both can cause color changes, but clots are more serious.
Can Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) be mistaken for a venous blood clot?
Yes, PAD can cause symptoms like pain and swelling, similar to blood clots. A proper diagnosis is needed to find the real cause.
References
NHS – Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)



































