Blood clots are a serious health issue. Knowing who to see is key. A hematologist, or a blood clot doctor, deals with blood clot problems like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism.
Key Takeaways
- A hematologist is a specialist who diagnoses and manages blood clot disorders.
- Blood clots can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism are common blood clot conditions.
- Specialists like hematologists and vascular surgeons are key in managing blood clot care.
- Understanding symptoms and getting medical help is vital for effective treatment.
Understanding Blood Clots: Types and Risk Factors
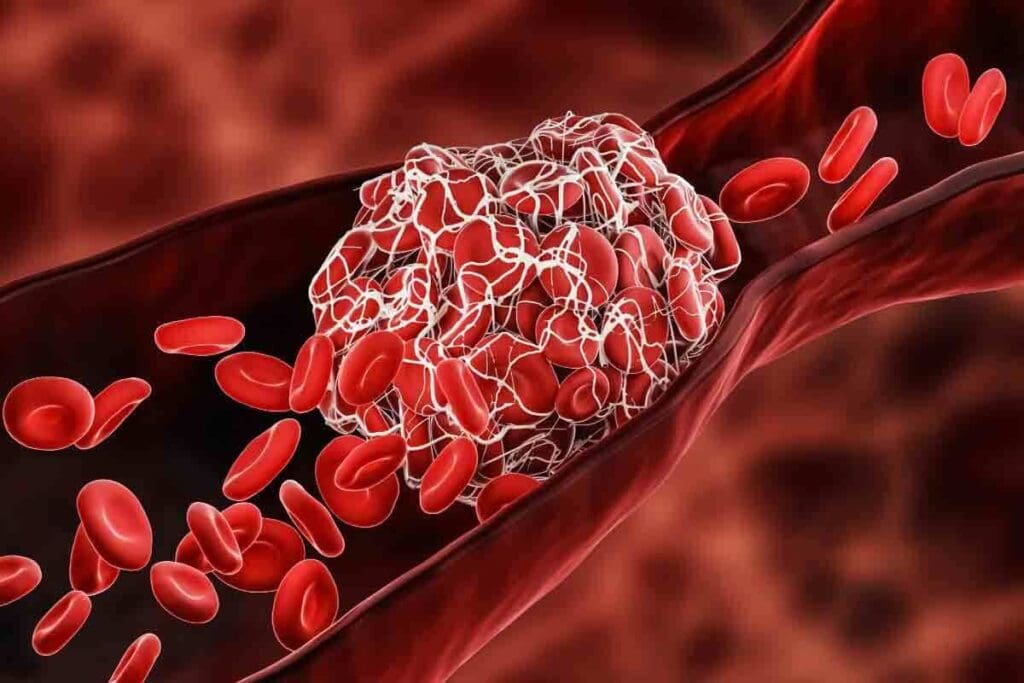
It’s important to know about blood clots to prevent and treat them. They can take many forms and affect different parts of the body. Blood clots are a group of disorders that need careful management.
Common Types of Blood Clots
Blood clots can be different based on where they form and how severe they are. The most common types are:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This happens when a clot forms in the deep veins, usually in the legs.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A serious condition where a clot travels to the lungs.
Knowing the risk factors for blood clots is key.
Risk Factors for Developing Blood Clots
Some main risk factors are:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Prolonged Immobility | Long periods of sitting or lying down, like on long flights or in bed. |
| Medical Conditions | Certain conditions like cancer, heart disease, and inflammatory disorders. |
| Hormonal Medications | Using hormonal contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy. |
Knowing these risk factors helps catch and prevent blood clots early. By understanding the types and risk factors, people can take steps to lower their risk. They should also get medical help when needed.
If you’re at risk, talk to a doctor about how to prevent and treat blood clots. Discussing anticoagulant medications, lifestyle changes, and other treatments is important. It’s all about finding what works best for you.
What Dr Treats Blood Clots: Primary Specialists

When you have blood clots, it’s important to know what dr treats blood clots and who to see for help. You need specialists who can find and treat the root cause of the problem.
Hematologists: Blood Disorder Specialists
Hematologists are doctors who deal with blood disorders, like blood clots. They know a lot about how blood clots form and can handle tough cases.
- Expertise in blood clotting disorders
- Ability to manage anticoagulation therapy
- Knowledge of bleeding disorders and their interaction with clotting conditions
Hematologists are key in managing blood clot disorders. They create treatment plans and provide ongoing care. Their training helps them tackle the complex issues of blood clotting.
Vascular Medicine Specialists
Vascular medicine specialists focus on vascular diseases, including blood clots. They also manage risk factors and prevent future clots.
Vascular medicine specialists work with other doctors to give patients the best care. Their knowledge of vascular health is vital in finding the cause of clots.
Hematologists and vascular medicine specialists are both important in treating blood clots. Together, they ensure patients get the care they need from start to finish.
Knowing the roles of these specialists helps patients make informed choices. It ensures they get the right care for managing blood clots.
Additional Medical Specialists for Blood Clot Treatment
Managing blood clots often requires a team effort. Hematologists are key in diagnosing and treating them. But other experts are also vital for full care.
Vascular Surgeons
Vascular surgeons handle vascular diseases, including blood clots. They do surgery when needed. This makes them a key part of the treatment team for serious cases.
Vascular surgeons do procedures like thrombectomy to remove clots. They’re very helpful when medicine alone isn’t enough or when there’s a risk of serious limb damage.
Interventional Radiologists
Interventional radiologists use imaging to guide minimally invasive treatments for blood clots. They can target treatments directly at the clot. This improves results and lowers risks.
They often do catheter-directed thrombolysis. This involves using a catheter to send clot-dissolving medicine to the clot. It’s very effective for big or dangerous clots.
Cardiologists and Pulmonologists
Cardiologists and pulmonologists are key for blood clots in the heart or lungs. Cardiologists are important for clots linked to heart issues, like atrial fibrillation.
Pulmonologists handle pulmonary embolism, where a clot goes to the lungs. They work with others to care for patients with this serious condition.
| Specialist | Role in Blood Clot Treatment | Common Procedures |
| Vascular Surgeons | Manage vascular diseases, perform surgical interventions | Thrombectomy, vascular surgery |
| Interventional Radiologists | Perform minimally invasive procedures using imaging guidance | Catheter-directed thrombolysis, angioplasty |
| Cardiologists | Manage cardiac-related blood clots and conditions | Anticoagulation therapy management, cardiac monitoring |
| Pulmonologists | Treat pulmonary embolism and related conditions | Pulmonary embolism management, oxygen therapy |
In conclusion, treating blood clots needs a team of experts. Knowing their roles helps patients understand the complexity of their care. It shows the value of a team approach.
Recognizing Blood Clot Symptoms
Knowing the signs of blood clots can help a lot. Blood clots can happen anywhere in the body. Their symptoms depend on where and how big the clot is.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is when a clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. You might notice:
- Swelling in the affected limb
- Pain or tenderness, more when standing or walking
- Warmth or redness in the affected area
Some people with DVT might not show any symptoms. It’s important to know the risk factors. If you see any signs, get medical help right away.
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms
A Pulmonary Embolism (PE) happens when a clot travels to the lungs. Look out for:
- Chest pain or discomfort that gets worse with deep breathing
- Shortness of breath or rapid breathing
- Rapid heartbeat
- Coughing up blood
These symptoms are serious and need immediate medical help.
When to Seek Emergency Care
If you or someone you know has blood clot symptoms, know when to act fast. Here’s a table of symptoms that mean you should get help right away:
| Condition | Symptoms | Action |
| DVT | Swelling, pain, warmth in one leg | Seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen |
| Pulmonary Embolism | Chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat | Call emergency services or go to the ER immediately |
In short, knowing the symptoms of blood clots is key for quick medical help. If you notice anything unusual or severe, get medical help without delay.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots: Tests and Procedures
Diagnosing blood clots involves several tests and procedures. These help confirm their presence and find the underlying causes.
It’s important to accurately diagnose blood clots for effective treatment. Healthcare providers use different tools to find out where and what the clots are like.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are key for diagnosing blood clots, like Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE).
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of blood vessels and detect clots.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body, helping to identify clots in various locations.
- Venography: Though less common, venography involves injecting contrast dye into the veins to visualize clots.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are vital for diagnosing blood clots and checking clotting disorder risks.
- D-dimer Test: This test measures a substance in the blood that is produced when a clot dissolves. It’s often used to rule out DVT or PE.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC can help identify abnormalities in blood cells that may contribute to clotting.
- Clotting Factor Tests: These tests measure the levels and activity of various clotting factors in the blood.
Genetic Testing for Clotting Disorders
Genetic testing may be recommended for some patients to identify inherited clotting disorders.
- Factor V Leiden Mutation: This genetic mutation increases the risk of developing blood clots.
- Prothrombin Gene Mutation: Another genetic mutation that can increase clotting risk.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Common Uses |
| Ultrasound | Detects clots in veins | DVT diagnosis |
| CT Scan | Provides detailed images of clots | PE diagnosis, DVT |
| D-dimer Test | Measures clot dissolution products | Ruling out DVT/PE |
Treatment Approaches for Blood Clots
Dealing with blood clots needs a plan that fits each person’s situation. The right treatment depends on the clot’s size and where it is, the patient’s health, and any other health issues.
Anticoagulation Therapy
Anticoagulation therapy is key in treating blood clots. It uses medicines to stop new clots from forming and to prevent existing ones from getting bigger. Anticoagulants don’t dissolve clots but stop them from growing. Common ones are warfarin, apixaban, rivaroxaban, and dabigatran. The right one depends on the patient’s kidney function, risk of bleeding, and other medicines they take.
Thrombolytic Therapy
Thrombolytic therapy is for serious cases of blood clots. It uses thrombolytic agents to break down the clot. This treatment is for severe clots because it can cause bleeding.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery might be needed for some blood clots. This includes removing the clot (thrombectomy) and putting in inferior vena cava (IVC) filters to stop clots from reaching the lungs. Surgery is considered when other treatments can’t be used or have failed.
The table below shows the main ways to treat blood clots:
| Treatment Approach | Description | Indications |
| Anticoagulation Therapy | Prevents new clot formation and growth of existing clots | Standard treatment for most blood clots |
| Thrombolytic Therapy | Dissolves existing clots | Severe clots, life-threatening conditions |
| Surgical Interventions | Removes clots or prevents clot migration | Contraindications to other therapies, failed other treatments |
In conclusion, treating blood clots is very specific and depends on many factors. Knowing the different treatments helps doctors make the best choices and patients get the best care.
The Role of a Hematologist in Blood Clot Management
Hematologists are key in managing blood clots. They are medical experts who deal with blood disorders, including clots. Their knowledge is vital for effective treatment.
Specialized Testing and Diagnosis
Hematologists use many tests to find blood clotting problems. These include:
- Blood tests to check clotting factors and platelet count
- Imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans to see clots
- Genetic testing for inherited clotting disorders
Getting the right diagnosis is essential. Hematologists use test results to figure out the cause of clots. They also check the risk of more clots happening.
Long-term Treatment Planning
Hematologists create detailed treatment plans for blood clot patients. This might include:
| Treatment Approach | Description | Benefits |
| Anticoagulation Therapy | Medications to stop new clots and prevent existing ones from growing | Less chance of more clots |
| Thrombolytic Therapy | Treatment to break down existing clots | Quick clot removal in emergencies |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Changes in diet, exercise, and habits to lower clot risk | Better heart health |
Managing Recurrent Clotting Events
Hematologists handle recurring clotting issues. They keep a close eye on patients and adjust treatments as needed. This helps lower the risk of more clots.
Key strategies for managing recurrent clotting events include:
- Regular check-ups to watch clotting risk factors
- Changing anticoagulation therapy as needed
- Finding and fixing the reasons for recurring clots
By taking a detailed approach, hematologists greatly improve patient outcomes and life quality.
What Kind of Doctor Treats Blood Clots in Legs
When you have a blood clot in your leg, you’ll need to see doctors who know a lot about blood and blood vessels. These experts are key in figuring out and treating blood clot problems.
Specialist Referral Patterns
First, your regular doctor might send you to see a specialist if they think you have a blood clot in your leg. The doctors you’ll usually see are:
- Hematologists: They deal with blood issues, like clotting. They can help with treatments like medicine to prevent more clots.
- Vascular Medicine Specialists: These doctors focus on blood vessel problems. They give full care for leg blood clots, sometimes with help from others.
Who you see might depend on how bad the clot is and if you have other blood vessel problems.
Collaborative Care Approaches
Handling blood clots in legs often means working together with different doctors. This team might include:
- Vascular Surgeons: They do surgery, like removing the clot, if needed.
- Interventional Radiologists: They use small procedures to find and fix blood clots without big surgery.
Working together, these doctors make sure you get the best care. They treat the clot and any other issues that might have caused it.
This team effort helps make a treatment plan that’s just right for you. It aims to make you better and lower the chance of more problems.
DVT Recovery Time: What to Expect
Knowing how long it takes to recover from DVT is key. It helps set realistic goals and treatment plans. Recovery from Deep Vein Thrombosis needs medical care, lifestyle changes, and watching your health closely.
Typical Recovery Timeline
The time it takes to get better from DVT can be weeks to months. How bad the clot is, how well treatment works, and if there are any problems all play a part.
Initial Recovery Phase: At first, usually the first week, doctors keep a close eye on you. They watch for clot growth and any serious issues. They start you on blood thinners to stop more clots.
How Long Should I Be Off Work With a DVT
How long you need to stay off work with DVT depends on your job, how bad the clot is, and how you’re doing. Most people take 1-2 weeks off, but it can be longer if your job is hard or if you have complications.
Factors to Consider:
- Nature of the job (sedentary vs. physically demanding)
- Severity of DVT symptoms
- Effectiveness of treatment and presence of complications
Factors Affecting Recovery Duration
Many things can change how long it takes to get better from DVT. These include where and how big the clot is, your health overall, and if you follow your treatment plan.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Recovery |
| Clot Location and Size | Clots in major veins (like the femoral vein) are usually worse. | Bigger clots or those in important places might need more time to heal. |
| Patient’s Overall Health | Having other health problems like heart disease or cancer. | People with serious health issues might take longer or have a harder time getting better. |
| Adherence to Treatment | Sticking to your blood thinner medicine as prescribed. | Not taking your medicine as you should can increase the risk of clotting getting worse or coming back. |
By knowing these factors and working with your doctor, you can manage your recovery better. This can help avoid any extra problems.
Blood Clots in Lungs Recovery Time
The time it takes to recover from blood clots in the lungs varies. It depends on how serious the clot is and the patient’s health.
Pulmonary Embolism Healing Process
The healing process for pulmonary embolism involves anticoagulation therapy. This therapy stops new clots from forming and helps dissolve existing ones. It’s also important to watch for any complications.
In the early stages, doctors closely watch for signs of clot dissolving. They also check for side effects of the medication. This is a key time for adjusting treatment to help the patient recover best.
Returning to Normal Activities
Going back to normal activities after a pulmonary embolism should be slow. It’s important to follow a doctor’s advice. The time it takes to start doing more depends on the patient’s health and how serious the embolism was.
- Light activities can usually be resumed within a few days to a week.
- More strenuous activities may need to be postponed for several weeks.
Long-term Lung Function Considerations
Long-term lung function after a pulmonary embolism can be affected by several things. These include the size and location of the clot, and the patient’s health before the embolism.
| Factor | Impact on Lung Function |
| Clot Size | Larger clots may result in more significant lung damage. |
| Pre-existing Conditions | Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can complicate recovery. |
| Anticoagulation Therapy | Effective anticoagulation can minimize long-term damage. |
Knowing these factors helps manage expectations and work towards better long-term lung health.
Living with Blood Clots: Long-term Management
Managing blood clots well needs a full plan. This includes keeping an eye on things and making lifestyle changes. People with blood clots must know how to manage their condition long-term. This helps avoid problems and improves their life quality.
Ongoing Monitoring Requirements
Keeping an eye on things is key for blood clot patients. This means:
- Regular blood tests to check if the medicine is working
- Imaging tests to see how big and where the clot is
- Watching for signs of post-thrombotic syndrome or pulmonary hypertension
Table: Ongoing Monitoring Tests for Blood Clots
| Test Type | Frequency | Purpose |
| Blood Tests (INR, aPTT) | Regularly, as advised by doctor | To monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy |
| Imaging Tests (Ultrasound, CT Scan) | Periodically, based on doctor’s recommendation | To assess clot size and location |
| Physical Examination | At each doctor visit | To check for signs of complications |
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle is important for managing blood clots. These changes include:
- Keeping a healthy weight to ease vein pressure
- Doing regular exercise, like walking, to help blood flow
- Avoiding sitting or lying down for too long, like on long flights
- Wearing compression stockings as your doctor suggests
When to Consult Your Blood Clot Specialist
Knowing when to get medical help is vital. If you have:
- More pain or swelling in the affected limb
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Unusual or heavy bleeding
- Signs of an allergic reaction to medication
By following these steps, people with blood clots can manage their condition well. This reduces the chance of serious problems.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Specialist for Blood Clot Treatment
Managing blood clots well needs a skilled specialist. Doctors like hematologists are key in diagnosing and treating these issues.
Finding the right specialist is key for good care. When facing blood clots, seeing a doctor with clotting disorder experience is vital. A specialist can handle everything from diagnosis to ongoing care.
Doctors like hematologists, vascular medicine specialists, and interventional radiologists work together. They create treatment plans that fit each patient. This teamwork helps improve care and lowers the chance of problems.
Knowing the importance of a specialist helps you manage your health better. If you have symptoms or a blood clot diagnosis, see a specialist. They can give you the care you need.
FAQ
What kind of doctor treats blood clots in legs?
Doctors like hematologists and vascular medicine specialists treat blood clots in legs. They might work with vascular surgeons for a full care plan.
What doctor treats blood clots?
Hematologists, who specialize in blood disorders, often treat blood clots. Other doctors, like vascular medicine specialists, cardiologists, and pulmonologists, might also help.
How long does it take a blood clot to heal?
Healing time for a blood clot varies. It depends on the clot’s location, severity, and treatment success. It can take weeks to months for a clot to dissolve.
How long should I be off work with a DVT?
Time off work with a DVT varies. It depends on your condition’s severity, job needs, and health. You might need a few days to weeks off to recover.
What are the symptoms of a blood clot in the lungs?
A blood clot in the lungs, or pulmonary embolism, shows as sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. Seek emergency care if you have these symptoms.
How long does it take to recover from a blood clot in the lungs?
Recovery from a lung blood clot takes weeks to months. It involves anticoagulation therapy, rest, and slowly getting back to normal activities.
What is the role of a hematologist in blood clot management?
Hematologists are key in managing blood clot disorders. They do tests, create treatment plans, and handle recurring clots.
What are the risk factors for developing blood clots?
Blood clot risks include family clotting history, recent surgery, long immobility, and certain conditions like cancer or genetic disorders.
How are blood clots diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans, blood tests, and genetic tests to diagnose blood clots.
What are the treatment approaches for blood clots?
Blood clot treatments include anticoagulation therapy, thrombolytic therapy, and surgery. Treatment choice depends on the clot’s location, severity, and cause.
How can I prevent blood clots?
Preventing blood clots means managing risks like staying active, avoiding long immobility, and maintaining a healthy weight. Sometimes, preventive therapy is recommended.
When should I consult my blood clot specialist?
See your blood clot specialist if you have symptoms like leg pain or swelling. Or if you have concerns about your treatment or ongoing care.
References
- Medical News Today. (2023, December 19). Blood Clot in Arm: Symptoms, Is It Dangerous, Causes, and Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325299


































