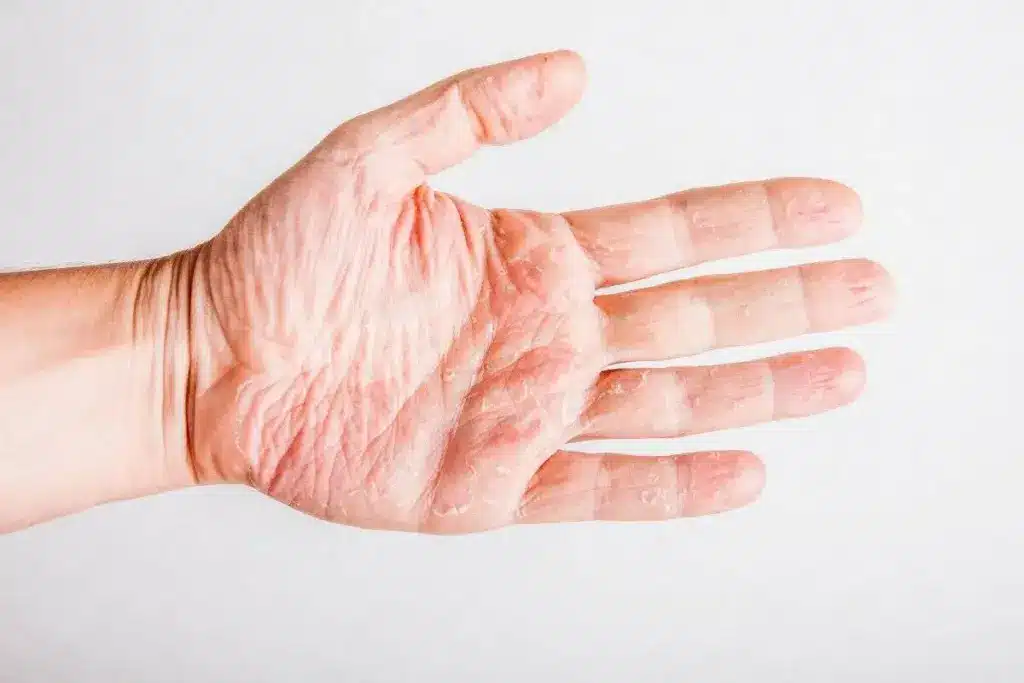
Eczema affects millions worldwide, causing discomfort, pain, and emotional distress. Research suggests that nutritional deficiencies may play a significant role in the development and severity of eczema what is good for eczema.
We know that living with eczema can be tough. Managing its symptoms is key to improving life quality. Our aim is to uncover the connection between eczema and nutritional deficiencies. We want to share effective eczema management strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Eczema is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including nutritional deficiencies.
- Understanding the causes of eczema is key to effective management plans.
- Nutritional deficiencies can make eczema symptoms worse.
- Managing eczema needs a complete approach.
- A balanced diet is vital for managing eczema.
Understanding Eczema: A Brief Overview
Eczema is more than just dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It’s a complex health issue affecting millions worldwide. Knowing about eczema is key to managing and treating it.
What is Eczema?
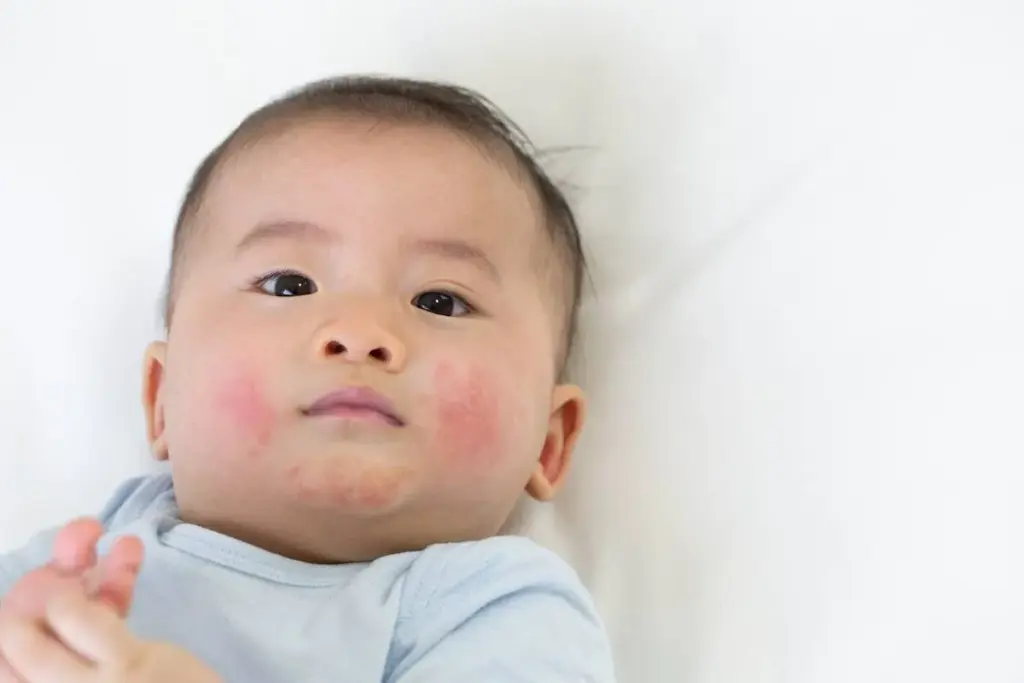
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, makes the skin inflamed, irritated, and itchy. The exact cause is unknown, but it involves genetics, environment, and the immune system.
People with eczema struggle to keep their skin’s natural barrier. This makes it easy for irritation and infection to set in. This leads to a cycle of inflammation and discomfort.
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, each with its own characteristics:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form, often linked to allergies and asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by irritants or allergens.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet.
- Nummular Eczema: Coin-shaped patches on the legs, arms, and back.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Scaly patches on oily areas like the scalp.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms vary but often include:
|
Symptom |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Dry Skin |
Feeling rough to the touch, often appearing before other symptoms. |
|
Itching |
Can range from mild to severe, often worse at night. |
|
Redness and Inflammation |
Affected areas become red, swollen, and warm to the touch. |
|
Crusting |
In severe cases, the skin may ooze and crust over. |
Understanding these symptoms and types of eczema is the first step. Recognizing signs and triggers helps find the right eczema care tips and eczema treatment options.
Looking for the best remedies for eczema can also help. It can offer comfort and reduce symptoms.
The Role of Nutrition in Skin Health
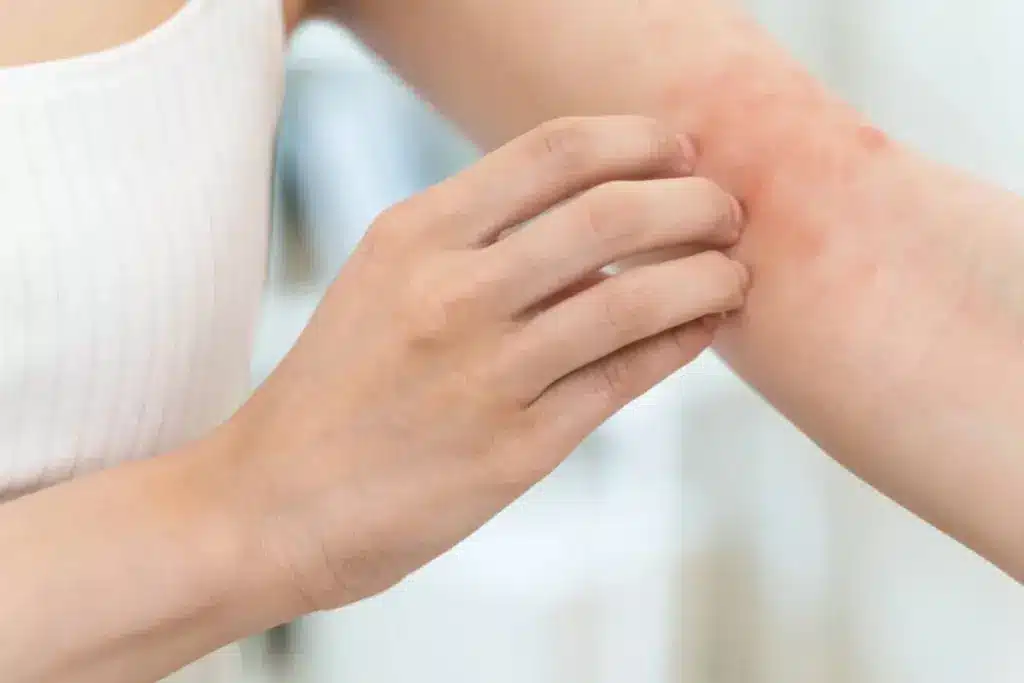

Nutrition is key to keeping our skin healthy. Eating well is important for fighting off eczema. The right foods can help or hurt our skin’s condition.
Essential Nutrients for Skin
Our skin needs many nutrients to stay in top shape. Vitamins A, C, and E, along with minerals like zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, are vital. They protect our skin, keep it strong, and help it heal.
Key Nutrients and Their Functions:
- Vitamin A: Important for skin regeneration and repair.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Helps reduce inflammation.
- Zinc: Crucial for wound healing and maintaining skin integrity.
How Deficiencies Affect Skin
Not getting enough nutrients can harm our skin, leading to eczema. For example, not enough vitamin A makes it hard for skin to heal. Not enough omega-3 fatty acids can cause more inflammation.
Not having enough nutrients can cause dryness, irritation, and make our skin more prone to infections. It’s important to eat enough of these nutrients to keep our skin healthy and manage eczema.
Food Sources of Key Nutrients
Eating foods full of essential nutrients helps our skin. Some top choices include:
|
Nutrient |
Food Sources |
|---|---|
|
Vitamin A |
Sweet potatoes, carrots, dark leafy greens |
|
Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
Salmon, walnuts, chia seeds |
|
Zinc |
Oysters, beef, chicken, pumpkin seeds |
Eating a balanced diet with these foods helps manage eczema and keeps our skin healthy. Along with other lifestyle changes, it can offer relief for eczema and improve our skin’s health.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies Linked to Eczema
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that can be made worse by nutrient deficiencies. Research shows certain nutrients are key for skin health. They may also play a role in eczema’s development or severity.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for healthy skin. They have anti-inflammatory effects that can lessen eczema’s inflammation. Not having enough omega-3s can increase inflammation and make eczema symptoms worse.
Eating foods high in omega-3s, like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help with eczema symptoms.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is also important for skin health. It helps regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation. People with eczema often have lower vitamin D levels.
Getting enough vitamin D through sun, diet, or supplements can help manage eczema.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that supports skin and immune health. It has anti-inflammatory effects and aids in wound healing. This is important for those with eczema.
Eating zinc-rich foods like oysters, beef, and chicken can help skin health. It may also reduce eczema symptoms.
Knowing about these nutrient deficiencies can help people with eczema manage their condition. It may also lessen the severity of their symptoms.
How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Help Eczema
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that help manage eczema. These essential fatty acids are not made by our bodies. So, we need to get them from food or supplements. Let’s see how they can ease eczema symptoms.
Sources of Omega-3s
Omega-3s are mainly found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds. Some top sources are:
- Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel
- Flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Walnuts
You can also find omega-3 supplements. They come in fish oil capsules and algal oil. Always talk to a doctor before taking any supplements.
Benefits of Omega-3 for Inflammation
Omega-3s can lessen inflammation, a big part of eczema. Eating foods rich in omega-3s can help. People might see:
- Less severe eczema flare-ups
- Better skin hydration
- Better skin health overall
A study in a Journal found omega-3s can reduce eczema severity.
Recommended Dosage
The right amount of omega-3s depends on the person and their eczema. A daily dose of 1000-2000 mg of EPA and DHA is often suggested. But, it’s important to talk to a doctor to find the right amount for you.
The Importance of Vitamin D for Skin
Vitamin D is key for healthy skin. It helps the immune system and keeps the skin barrier strong. This is important for preventing and managing skin issues like eczema. We’ll look at where to find vitamin D, its benefits for the skin, and how much sun is needed to keep levels up.
Sources of Vitamin D
You can get vitamin D from food, supplements, and sunlight. Foods like salmon and mackerel, fortified dairy, and some cereals are good sources. Adding these to your diet can naturally increase your vitamin D.
How Vitamin D Supports Immune Function
Vitamin D helps control the immune system, reducing inflammation and preventing autoimmune diseases. For skin, it helps manage the immune response, making eczema symptoms less severe. This makes vitamin D a key part of eczema treatment options and a source of relief for eczema sufferers.
Recommended Sun Exposure
While too much sun is bad, some sun is good for vitamin D. The right amount depends on your skin, where you live, and the time of day. Generally, 10-15 minutes of sun on your face, arms, and legs a few times a week is enough for most.
|
Source of Vitamin D |
Benefits for Skin Health |
Recommended Intake/Exposure |
|---|---|---|
|
Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel) |
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, supporting skin health and immune function. |
2 servings per week |
|
Fortified Dairy Products |
Provides vitamin D, supporting immune function and skin health. |
1-2 cups per day |
|
Sun Exposure |
Essential for vitamin D production in the skin. |
10-15 minutes, several times a week |
|
Supplements |
For individuals with deficiency or insufficient sun exposure/dietary intake. |
Consult a healthcare professional |
Keeping vitamin D levels up is key for skin health. It’s a valuable part of soothing eczema remedies. Knowing about vitamin D’s sources and benefits helps manage eczema and promotes healthier skin.
Exploring Zinc’s Influence on Eczema
Zinc is key for skin health. It helps fix skin problems, like eczema. This mineral is important for skin repair and keeping the immune system strong.
Importance of Zinc for Skin Repair
Zinc helps the body fix itself, mainly the skin. It aids in healing wounds, lowers inflammation, and keeps the skin’s barrier strong. For those with eczema, having enough zinc is vital to control symptoms and stop outbreaks.
Key benefits of zinc for skin health include:
- Enhancing wound healing
- Reducing inflammation
- Supporting the skin’s barrier function
Foods Rich in Zinc
Eating foods high in zinc can keep zinc levels right. Good sources include:
- Oysters
- Red meat
- Poultry
- Beans
- Nuts
- Whole grains
For those with eczema, eating a diet rich in zinc can help manage the condition.
Supplements and Dosage Guidelines
While food is best, supplements can help if you’re not getting enough zinc. Always follow the recommended amounts to avoid side effects.
Recommended daily intake of zinc:
- For adults: 8-11 mg
- For pregnant women: 11-13 mg
- For breastfeeding women: 12-14 mg
Always talk to a doctor before taking zinc supplements. They can help find the right amount for you.
Knowing how zinc helps skin health and adding zinc-rich foods or supplements to your diet can help manage eczema. It also improves your skin overall.
The Gut-Skin Connection
The link between our gut health and skin is clear, with eczema being a prime example. Research shows that our gut microbiome is key to managing eczema symptoms. This connection is known as the gut-skin axis.
How Gut Health Impacts Eczema
Gut health affects eczema in several ways. An imbalance in gut bacteria, or dysbiosis, can cause more inflammation. This inflammation makes eczema worse. Also, a weak gut barrier lets toxins into our blood, harming our skin.
To keep our gut healthy, we need to eat right and use supplements. This helps reduce inflammation and improves our skin.
Foods to Promote Gut Health
Some foods are great for our gut and skin. Here are a few:
- Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are full of probiotics. They help keep our gut balanced.
- Prebiotic-Rich Foods: Asparagus, bananas, and onions feed good bacteria in our gut.
- Omega-3 Rich Foods: Fatty fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are good for our gut and fight inflammation.
Probiotics and Their Role
Probiotics are live bacteria that help our health. They’re important for our gut and can help with eczema.
Probiotics do many good things for eczema, like:
- Reducing inflammation
- Improving our gut barrier
- Helping our immune system
|
Probiotic Strain |
Potential Benefits for Eczema |
|---|---|
|
Lactobacillus rhamnosus |
Reduces inflammation and improves gut barrier function |
|
Bifidobacterium lactis |
Enhances immune system modulation and reduces eczema severity |
By understanding the gut-skin connection, we can use foods and probiotics to help eczema. This natural approach is a promising way to manage eczema and improve our skin health.
The Impact of Allergies on Eczema
For those with eczema, knowing and managing allergies is critical. Allergies can make eczema worse. Understanding this link is key to better eczema care tips.
Common Allergens Triggering Eczema Flare-Ups
Dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and some foods can set off eczema. Knowing what these are is the first step to controlling symptoms. For example, dust mites live in dust and are common in bedding and furniture.
Testing for Allergies
Testing for allergies involves looking at your medical history and doing tests like skin prick tests. These tests find out what’s causing your eczema. This way, you can get the right eczema treatment options.
Managing Allergies to Reduce Symptoms
Handling allergies means avoiding what you’re allergic to and using medicines. You also need to make lifestyle changes to lower your exposure. This can greatly lessen your eczema symptoms and improve your life, using some of the best remedies for eczema.
|
Allergen |
Common Sources |
Tips for Avoidance |
|---|---|---|
|
Dust Mites |
Bedding, carpets, upholstered furniture |
Use allergen-proof bedding, wash fabrics in hot water weekly |
|
Pet Dander |
Pets, specially cats and dogs |
Bathe pets often, keep them out of bedrooms |
|
Pollen |
Trees, grasses, weeds |
Stay inside when pollen is high, use HEPA filters |
|
Certain Foods |
Many foods, often dairy, nuts, soy |
Avoid foods that trigger it, check food labels |
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Eczema
For those with eczema, making lifestyle changes can help a lot. Simple changes in daily life can manage eczema better. This improves life quality a lot.
Staying Hydrated
Drinking water is key for healthy skin. It keeps skin moist from the inside, lowering dryness and irritation risks. Aim for eight glasses of water daily, adjusting for your needs and activity.
Tips for Staying Hydrated:
- Drink water regularly throughout the day
- Avoid sugary drinks that can trigger inflammation
- Incorporate hydrating foods like watermelon and cucumbers into your diet
Effective Stress Management
Stress can make eczema worse. Using stress management can help. Try meditation, yoga, and deep breathing to lower stress.
Stress Management Techniques:
|
Technique |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Meditation |
Practice mindfulness and focus on the present moment |
Reduces stress and anxiety |
|
Yoga |
Combine physical postures with deep breathing exercises |
Improves flexibility and reduces stress |
|
Deep Breathing |
Focus on slow, deliberate breaths to calm the mind |
Lowers stress levels and promotes relaxation |
The Importance of Moisturizers
Moisturizers are vital for eczema care. They keep moisture in, protect from irritants, and hide dry, inflamed skin. Picking the right moisturizer is key; choose fragrance-free and hypoallergenic ones.
Key Ingredients in Moisturizers:
- Ceramides: Help repair the skin’s barrier
- Hyaluronic Acid: Provides intense hydration
- Glycerin: Attracts moisture to the skin
Over-the-Counter Treatments for Eczema
Over-the-counter treatments are a good start for fighting eczema. They can ease symptoms and help control the condition.
Topical Steroids vs. Non-Steroidal Options
There are two main types of over-the-counter eczema treatments: topical steroids and non-steroidal options. Topical steroids help reduce inflammation and itching. They come in creams, ointments, and lotions, in different strengths.
Non-steroidal options moisturize the skin, reduce itching, and protect against irritants. They’re great for mild eczema or keeping skin healthy between outbreaks.
|
Treatment Type |
Benefits |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Topical Steroids |
Reduce inflammation and itching |
Hydrocortisone cream |
|
Non-Steroidal Moisturizers |
Hydrate the skin, reduce itching |
CeraVe, Eucerin |
|
Topical Immunomodulators |
Modify the immune response locally |
Calcineurin inhibitors (though often prescription) |
When to Consider OTC Treatments
OTC treatments work well for mild to moderate eczema. If your symptoms are severe or don’t improve, see a doctor for advice.
- Mild eczema symptoms
- Maintenance between flare-ups
- As part of a complete treatment plan
Tips for Effective Use
To make the most of over-the-counter eczema treatments, follow these tips:
- Always read and follow the product instructions.
- Apply topical treatments as directed, usually after bathing.
- Moisturize regularly to keep the skin hydrated.
- Be patient; it may take some trial and error to find the right product.
Understanding your options and using over-the-counter treatments wisely can help manage your eczema. This can improve your life quality.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
Knowing when to see a dermatologist is key to managing eczema well. Mild cases can be handled with self-care and over-the-counter treatments. But, severe or ongoing cases need a doctor’s help.
Signs You Need Professional Help
If you notice any of these, it’s time to see a dermatologist:
- Persistent or severe eczema symptoms that don’t improve with self-care
- Significant impact on your quality of life due to eczema
- Uncertainty about the diagnosis or the best course of treatment
- Signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus
Early intervention by a dermatologist can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
What to Expect During a Consultation
During your visit, the dermatologist will:
- Conduct a thorough examination of your skin
- Ask about your medical history and symptoms
- Discuss your current treatments and lifestyle
This detailed approach helps create a treatment plan that fits your needs.
Treatment Options Dermatologists Recommend
Dermatologists suggest various treatments based on your eczema’s severity and type. These can include:
- Prescription topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators
- Phototherapy
- Systemic medications for severe cases
- Lifestyle and skincare recommendations
By working with a dermatologist, you can create an effective eczema management plan. This plan will improve your skin health and overall well-being. For more information on eczema care tips and management strategies, we recommend exploring resources from reputable health organizations.
Building a Long-Term Management Plan
Managing eczema well means using natural treatments, making lifestyle changes, and keeping up with new research. A long-term plan can really help reduce eczema symptoms.
Tracking Progress
Keeping a symptom diary is very helpful. It lets you see how things like diet and stress affect your eczema. This way, you can make better choices for your care.
Achieving Realistic Goals
It’s important to set goals that are achievable. Working with a healthcare professional helps you create a plan. This plan includes natural remedies and lifestyle changes that fit your needs.
It’s also key to stay updated on new research and treatments. This way, you can adjust your plan as needed. This ensures you’re always getting the best care possible.
FAQ
What are the most common nutrient deficiencies linked to eczema?
Omega-3 fatty acid, vitamin D, and zinc deficiencies are often seen in people with eczema. Eating foods rich in these nutrients or taking supplements can help manage symptoms.
How can omega-3 fatty acids help alleviate eczema symptoms?
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory effects. They can reduce inflammation and ease eczema symptoms. Adding foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, or walnuts to your diet is recommended.
What is the role of vitamin D in maintaining healthy skin?
Vitamin D is key for immune function and healthy skin. It’s important to keep vitamin D levels up through sun exposure, diet, and supplements.
How does zinc influence eczema?
Zinc is vital for skin repair. A zinc deficiency can make eczema worse. Eating foods like oysters, beef, or chicken can help.
What is the gut-skin connection, and how does it impact eczema?
The gut-skin connection shows how gut health affects skin health. A healthy gut microbiome, achieved through probiotics and a balanced diet, can help with eczema symptoms.
Can allergies trigger eczema flare-ups?
Yes, allergies can cause eczema flare-ups. Identifying and managing allergens can help reduce symptoms. Testing for allergies and avoiding triggers is recommended.
What lifestyle changes can help manage eczema?
Staying hydrated, managing stress, and using moisturizers are helpful. These changes can ease symptoms and improve life quality.
When should I consult a dermatologist for eczema treatment?
If eczema symptoms don’t improve or get worse, see a dermatologist. They can offer personalized treatment and a long-term plan.
What are the benefits of keeping a symptom diary for eczema management?
A symptom diary helps track symptoms and identify patterns. It aids in making informed treatment decisions. Keeping a diary is useful for monitoring progress and adjusting treatment plans.
What are some effective over-the-counter treatments for eczema?
Topical steroids and non-steroidal creams are good over-the-counter options. Always follow instructions and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist.
How can I stay informed about new research on eczema management?
Stay updated with reputable health sources and research institutions. This helps in making informed decisions about your treatment plan.
References
What Is Good For Eczema: Crucial Deficiency Link Fact https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5006549/





