Knowing the difference between a bulging disc and a herniated or slipped disc is key for good spine care. AtLiv Hospital, we help international patients with advanced medical treatments. We offer clear, caring advice.
A bulging disc happens when the disc’s outer layer bulges out but doesn’t tear. This keeps the jelly-like center inside. On the other hand, a herniated or slipped disc has a tear or rupture. This lets the inner material leak or push out.
Dealing with these conditions can be tough. Our team is here to give you top-notch healthcare. We make sure you get the care you need.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the difference between bulging and herniated discs is essential for effective treatment.
- A bulging disc protrudes outward without tearing, while a herniated disc involves a tear or rupture.
- Liv Hospital offers expert, patient-centered spine care for international patients.
- Clear diagnosis is key for the right treatment and care.
- Our team is committed to giving compassionate and complete healthcare services.
Understanding Spinal Disc Anatomy
The spine’s structure is supported by spinal discs. These discs are key to our back health. To grasp bulging and herniated discs, we must explore their anatomy and function.
Structure of a Healthy Spinal Disc
A healthy spinal disc has two main parts: the nucleus pulposus and the annulus fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus is soft and gel-like, acting as a shock absorber. The annulus fibrosus, a tough outer layer, is made of collagen fibers. Together, they absorb shock, help with movement, and support the spine.
Function of Spinal Discs
Spinal discs are vital for our spine. They act as shock absorbers, spreading out stress and load. They also make the spine flexible and movable. Plus, they keep the space between vertebrae right, avoiding bone-on-bone contact.
- Absorbing shock and distributing loads
- Facilitating spinal flexibility and movement
- Maintaining intervertebral space
Importance of Disc Health for Overall Spine Function
Healthy spinal discs are essential for a healthy spine. They keep the spine aligned, prevent degenerative conditions, and avoid bulging discs and herniated discs. Healthy discs support the spine’s natural shape and allow for smooth movement. But, disc problems can cause pain and limit movement.
Knowing how important disc health is can help prevent issues like slip disc bulge. A healthy lifestyle, including exercise and good posture, supports disc health and overall well-being.
Bulging Vs Slipped Disc: Key Differences Explained
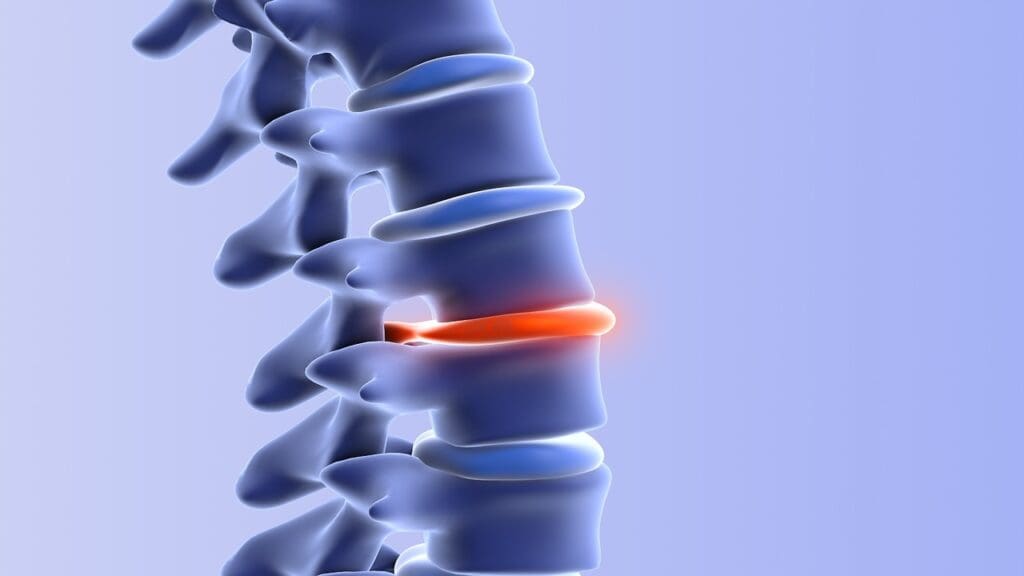
The terms “bulging disc” and “herniated disc” are often mixed up, but they mean different things for spinal health. We’ll look into these differences to clear up the confusion between these two common spinal issues.
Definition of a Bulging Disc
A bulging disc happens when the disc pushes out beyond its usual shape, but its outer layer stays whole. This can happen because of aging or injury. The main thing about a bulging disc is that it doesn’t have a tear in the outer layer. Instead, the disc just bulges out, which might press on nerves nearby.
Definition of a Herniated/Slipped Disc
A herniated disc, or slipped disc, is when the outer layer of the disc tears, letting the soft inside out. This can cause a lot of pain and might press on nerves, leading to more symptoms. It’s important to know that a “slipped disc” doesn’t really “slip” out of place; it herniates because of the tear.
Visual Comparison of Both Conditions
To get a better idea of the difference between bulging and herniated discs, let’s look at a picture. A picture can show how a bulging disc pushes out without tearing, while a herniated disc has a tear that lets the inside out.
Knowing these differences is key for figuring out what’s wrong and how to treat it. Even though both can hurt, how you deal with them might change based on the disc problem.
Common Terminology: Clearing Up the Confusion
The world of spinal disc conditions is full of confusing terms. It’s important for patients to understand these terms to grasp their diagnosis. This clarity is key for those seeking to understand their spinal health.
Many people get confused by the different names for disc conditions. Let’s look at some common terms and what they mean.
Why “Slipped Disc” Is a Misnomer
The term “slipped disc” is often mixed up with “herniated disc.” But, it’s actually a misnomer. Discs don’t slip out of place. Instead, they can bulge or herniate.
This confusion comes from thinking a disc has moved, which isn’t true. The real issue is that the disc’s structure is damaged, causing a bulge or herniation. Knowing this is key to understanding the condition and the right treatment.
Difference Between Herniated, Ruptured, and Extruded Discs
Terms like herniated, ruptured, and extruded are used when talking about disc damage. They all describe different levels of damage but are connected.
- A herniated disc happens when the outer layer cracks, letting the gel-like center bulge out.
- A ruptured disc is more serious, with the outer layer torn, causing a big leak of disc contents.
- An extruded disc is when the disc material breaks through the outer layer but is not fully outside the disc space.
Knowing these differences helps figure out how serious the condition is and what treatment is best.
Understanding Disc Prolapse Terminology
Disc prolapse is a term for when a disc bulges or herniates, pressing on nearby nerves. It covers a range of disc displacement, from mild bulging to severe herniations.
Getting clear on these terms helps patients understand their condition better. It also helps doctors explain treatment options more clearly.
Degenerative Disc Disease and Its Relationship to Disc Problems
It’s important to know about degenerative disc disease to understand bulging and herniated discs. This disease affects the spine, causing the discs to wear down. This wear can lead to bulging and herniated discs.
What Is Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is when the spinal discs wear out. These discs are the cushions between the vertebrae. As we get older, these discs lose height, dry out, and become less flexible.
This wear and tear can cause cracks in the disc’s outer layer. This can lead to bulging or herniation. The discs’ degeneration is a natural part of aging but can be sped up by lifestyle, genetics, and injuries.
Prevalence Across Age Groups
Degenerative disc disease is common, affecting many as they age. By 50, almost 90% of adults have some disc degeneration. But not everyone with it will show symptoms.
The condition becomes more common with age. It’s also more likely in those who lift heavy, bend a lot, or have spinal injuries. Knowing how common it is helps in managing it.
Progression From Degeneration to Bulging or Herniation
The move from degenerative disc disease to bulging or herniation is gradual. As the disc weakens, it’s more likely to bulge or rupture. This can happen from injury or strain, or over time.
When a disc bulges or herniates, it can press on nerves. This can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the back or limbs. Knowing how it progresses helps in preventing and managing disc problems. Early action on degenerative disc disease can help avoid more serious issues.
Causes and Risk Factors of Bulging Discs
Bulging discs are caused by age, lifestyle, and genetics. As we age, our spinal discs change, leading to bulging. Knowing these factors helps in prevention and management.
Age-Related Degeneration
Age is a big factor in bulging discs. Our spinal discs lose water and become drier with age. This can cause them to bulge, pressing on nerves. By 50, most people’s spinal discs have worn down a lot. Experts say the aging spine is more prone to disc issues.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices also affect bulging disc risk. These include:
- Poor posture, which can put uneven stress on the spine
- Lack of exercise, making back muscles weak
- Smoking, which harms disc health
- Obesity, adding extra weight on the spine
Living a healthy lifestyle can lower bulging disc risk. Exercise, a good diet, and not smoking help keep the spine healthy.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a big role in bulging discs. If your family has disc problems, you might too. Studies show genetics can affect disc health, making some more likely to bulge. Knowing your family’s health history helps understand your risk.
While we can’t change age and genetics, being aware helps us act. Healthy choices and caring for our spine can lower bulging disc risk. It also helps manage them if they happen.
Causes and Risk Factors of Herniated Discs
Knowing what causes herniated discs is key to preventing and treating them. We’ll look at how injuries, repeated strain, and health issues can lead to herniated discs.
Traumatic Injuries
Getting hurt in an accident or fall can cause a herniated disc. Lifting heavy things the wrong way is another common cause. When the spine gets hit hard, the disc’s outer layer can crack, letting the soft inside spill out.
Repetitive Strain
Doing the same thing over and over can hurt your spine. Repetitive lifting, bending, or twisting can wear out your discs. Jobs that involve a lot of lifting or bending, like construction or warehouse work, are risky. Even sitting for long periods without moving can be harmful if you’re not careful.
“Repetitive strain injuries are a common occupational hazard, and herniated discs are among the most significant risks.” – Occupational Health Expert
Underlying Medical Conditions
Some health issues can make you more likely to get a herniated disc. Degenerative disc disease weakens discs, making them more likely to herniate. Other problems, like scoliosis or spinal stenosis, can also raise your risk by changing your spine’s shape.
| Risk Factor | Description | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Traumatic Injuries | Sudden impact or force on the spine | Proper lifting techniques, safety gear |
| Repetitive Strain | Repeated stress on the spine | Regular breaks, proper posture, exercise |
| Underlying Conditions | Pre-existing spinal conditions | Monitoring, management of underlying conditions |
By knowing what causes herniated discs, you can take steps to avoid them. Stay healthy, lift right, and manage any health problems you have.
Symptoms of Bulging Discs
The symptoms of bulging discs can differ a lot from person to person. Some might not feel any pain, while others might have mild to severe pain. Knowing these symptoms is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Asymptomatic Bulging Discs
Many people with bulging discs don’t show any symptoms. These discs are often found by chance during tests for other reasons. Even though they don’t cause pain, it’s important to keep an eye on them to make sure they don’t get worse.
Mild to Moderate Pain Patterns
When symptoms do show up, they can be mild or moderate. The pain usually happens in the lower back or neck. It might stay the same or get worse with certain activities or positions.
It’s important to remember that the pain level doesn’t always match the size of the bulge. Some people with small bulges might feel a lot of pain, while others with bigger bulges might not feel much.
When Bulging Discs Become Problematic
Bulging discs can become a problem if they cause a lot of pain or nerve symptoms. This happens when the bulge presses on or irritates nearby nerves. Patients might feel pain that spreads, numbness, tingling, or weakness in their limbs.
Getting an early diagnosis and the right treatment is key to managing these symptoms.
| Symptom | Description | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Localized or radiating pain | Mild to Severe |
| Numbness/Tingling | Numbness or tingling sensation in limbs | Moderate to Severe |
| Weakness | Muscle weakness in affected areas | Moderate to Severe |
In conclusion, the symptoms of bulging discs can vary a lot. While some might not feel any pain, others might have a lot of discomfort or nerve symptoms. It’s important to understand these symptoms to get the right medical care and avoid further problems.
Symptoms of Herniated Discs
Knowing the symptoms of herniated discs is key for getting the right treatment. These discs, also called slipped discs, can lead to many symptoms. These symptoms can really affect how well you live your life.
Radiating Pain Patterns
Radiating pain is a big sign of a herniated disc. This happens when the disc presses on nerves, causing pain to spread. For example, a disc in the lower back can send pain down to the legs. This is often called sciatica.
Neurological Symptoms
Herniated discs can also lead to other symptoms. You might feel numbness, tingling, or weakness in certain areas. In serious cases, you could lose reflexes or muscle strength. This shows why seeing a doctor quickly is important.
Sciatica and Herniated Discs
Sciatica often goes hand in hand with herniated discs, mainly in the lower back. It’s when pain spreads along the sciatic nerve, from the back to the legs. This pain happens when the sciatic nerve gets compressed or irritated, usually by a herniated disc.
Emergency Warning Signs
While many herniated discs can be treated without surgery, some signs need urgent care. Look out for sudden, severe pain, loss of bladder or bowel control, and weakness or numbness in the legs. If you notice these, get medical help right away.
Dealing with herniated disc symptoms can be scary. It’s vital to talk to doctors who can figure out what’s wrong and suggest the best treatment. By knowing the symptoms and getting help fast, you can manage your condition better and live a better life.
Diagnostic Approaches for Disc Problems
Diagnosing disc problems needs a detailed approach. We use physical exams, imaging, and neurological tests. These methods help us understand the extent of the problem, like a bulging or herniated disc.
Physical Examination Techniques
A thorough physical exam is the first step. We check the patient’s movement, muscle strength, and reflexes. Tests like the straight leg raise test help spot nerve issues, common with herniated discs.
- Palpation to identify areas of tenderness
- Range of motion assessment to evaluate flexibility and pain
- Muscle strength testing to detect weakness
- Reflex testing to assess nerve function
Imaging Options
Imaging is key to confirming disc problems. We use different imaging methods, each with its own benefits.
- X-rays: Good for bone structures and degenerative changes.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Best for soft tissues like discs, nerves, and the spinal cord.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans: Detailed bone images, useful with myelography for the spinal canal.
Neurological Testing
Neurological tests are vital for checking nerve function. We check sensory and motor functions to see if nerves are compressed or damaged.
When Imaging Findings Don’t Match Symptoms
At times, imaging doesn’t match symptoms. This can happen for many reasons, like asymptomatic discs or timing issues. We use clinical judgment and more tests to decide on treatment.
By combining physical exams, imaging, and neurological tests, we get a clear diagnosis. This helps us create a good treatment plan for disc problems, like bulging or herniated discs.
Treatment Options for Bulging Discs
Bulging discs can be treated in many ways. This includes simple steps and more complex methods. The right treatment depends on how bad the condition is, the patient’s health, and what they prefer.
Conservative Management Approaches
For bulging discs, starting with simple treatments is common. This means trying to reduce symptoms and improve function without surgery. We suggest making lifestyle changes like staying healthy, improving posture, and exercising regularly.
Activity modification is also key. This means avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or twisting. These actions can make the condition worse. By changing these habits, patients can often feel better and stop the condition from getting worse.
Physical Therapy Interventions
Physical therapy is very important for treating bulging discs. A physical therapist creates a special exercise plan. This plan helps strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and better posture. Core strengthening exercises are very helpful because they help keep the spine stable and reduce pressure on the disc.
Physical therapists also use techniques like massage and joint mobilization. These help manage pain and improve how well the spine moves.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain is a big part of treating bulging discs. We might suggest using over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs. These help with inflammation and pain. Sometimes, more advanced pain management like corticosteroid injections is needed to reduce swelling and pain.
When to Consider More Advanced Treatments
While simple treatments and physical therapy work for many, some cases need more help. If symptoms don’t get better or get worse, or if there are signs of nerve problems, more serious treatments might be needed.
These could include minimally invasive procedures or surgery. Deciding on these treatments depends on the patient’s specific situation and health.
Treatment Options for Herniated Discs
Understanding the treatment options for herniated discs is key for those seeking relief. A herniated disc, also known as a slipped disc, can cause a lot of pain. We will look at the different treatments, from non-surgical methods to more invasive procedures.
Non-Surgical Approaches
First, treatment often starts with non-surgical methods. These include:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen back muscles and improve flexibility.
- Pain Management: Medications like NSAIDs or epidural steroid injections to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Changes in daily activities, posture, and exercise routines to alleviate symptoms.
These methods can help manage symptoms and work for many patients.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For those not helped by non-surgical treatments, minimally invasive procedures are considered. These include:
- Epidural Steroid Injections: To reduce inflammation around the herniated disc.
- Nerve Root Blocks: To target specific nerves causing pain.
- Laser Discectomy: A procedure using laser technology to remove the herniated portion of the disc.
These procedures aim to reduce pain and avoid more invasive surgery.
Surgical Interventions
If conservative and minimally invasive treatments fail, surgery may be needed. Surgical options include:
| Procedure | Description | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Discectomy | Removal of the herniated disc portion | Several weeks |
| Microdiscectomy | A less invasive version of discectomy | Several weeks |
| Spinal Fusion | Fusing the vertebrae to stabilize the spine | Several months |
Recovery Expectations
Recovery from surgery for a herniated disc varies. Generally, patients can expect:
- Initial recovery at home for a few weeks
- Gradual return to normal activities over several weeks to months
- Physical therapy to strengthen the back and improve flexibility
Following post-operative instructions carefully is key for a smooth recovery.
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between a bulging disc and a herniated or slipped disc is key for good spinal health. We’ve looked at the anatomy of spinal discs, what causes bulging and herniated discs, and their symptoms and diagnosis.
Bulging vs slipped disc or herniated vs slipped disc shows they’re not the same. A bulging disc just bulges out a bit. But a herniated or slipped disc is worse, causing nerve pain and serious discomfort.
How to manage these issues varies. Some treatments are simple, like physical therapy and pain relief. Others might need surgery. Knowing the details helps doctors give the right treatment for each person.
We aim to help you understand the differences between bulging and herniated discs. This knowledge lets you take care of your spine better. By knowing the signs and getting the right medical help, you can lessen the effects of disc problems and keep your spine working well.
Is a slipped disk the same as a herniated disk?
Yes, both terms describe the same issue. It happens when the outer layer of the disk tears or ruptures. This lets the inner material leak or push out.
What is the difference between a bulging disc and a herniated disc?
A bulging disc means the outer layer bulges out but doesn’t tear. A herniated disc has a tear or rupture. This lets the inner material leak or push out.
Are bulging discs and slipped discs the same?
No, they are not the same. A bulging disc bulges out without tearing. A slipped disc, or herniated disc, has a tear or rupture.
What are the symptoms of a herniated disc versus a bulging disc?
Herniated discs cause more severe symptoms. These include radiating pain, numbness, and neurological symptoms. Bulging discs might be painless or cause mild to moderate pain.
Can a bulging disc become a herniated disc?
Yes, a bulging disc can turn into a herniated disc. This happens if the outer layer tears or ruptures. Then, the inner material leaks or pushes out.
How are bulging and herniated discs diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and neurological tests. These help find and measure disc problems.
What are the treatment options for bulging and herniated discs?
Treatment varies. It can include conservative management, physical therapy, and pain management. Sometimes, minimally invasive procedures or surgery are needed, depending on the case.
Is degenerative disc disease related to bulging or herniated discs?
Yes, it can lead to bulging or herniated discs. Degenerative disc disease weakens the disc’s structure.
Can lifestyle factors contribute to the risk of developing bulging or herniated discs?
Yes, certain lifestyle factors increase the risk. These include age, genetics, repetitive strain, and traumatic injuries.
What is the difference between a herniated disc and a ruptured disc?
Both terms describe a tear in the disk. But, a ruptured disc usually means a bigger tear. A herniated disc might have a smaller tear or protrusion.
Are there any emergency warning signs associated with herniated discs?
Yes, watch for severe pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs. Also, look out for loss of bladder or bowel control, and difficulty walking. These signs need immediate medical help.

































