Thyroid disorders are a big health issue for millions worldwide. The thyroid gland makes two key hormones, T3 and T4. These hormones control how our body uses energy and feels overall. If the thyroid gland doesn’t make the right amount of these hormones, it can cause hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Knowing the difference between these conditions is key for the right treatment. Hartford Healthcare says knowing the symptoms and causes helps a lot with treatment.
The main difference is in hormone levels. Hypothyroidism means the thyroid doesn’t make enough hormones. Hyperthyroidism means it makes too much. This difference leads to different symptoms and treatments for each condition.
Key Takeaways
- Thyroid disorders affect millions worldwide, impacting metabolism and energy.
- Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism represent opposite states of thyroid hormone production.
- Understanding the differences is key for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Symptoms and causes vary a lot between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
- Proper treatment depends on accurate diagnosis and can greatly improve quality of life.
Understanding Thyroid Function and Disorders
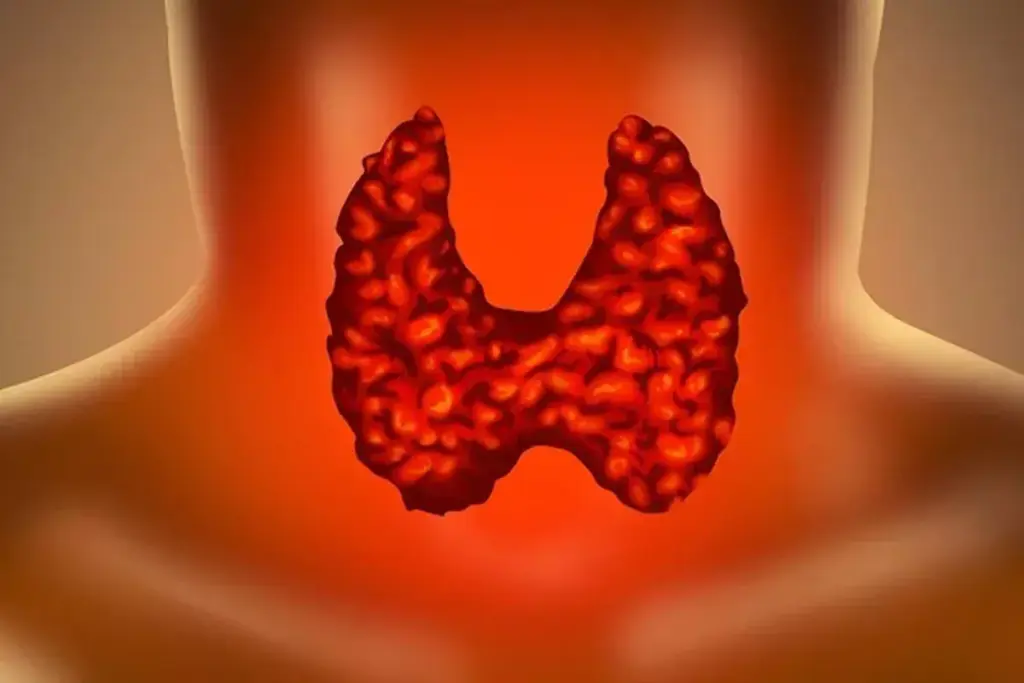
The thyroid gland is a small but vital organ in the neck. It produces hormones that control our metabolism, digestion, heart rate, and energy levels. Knowing about thyroid disorders is important.
The Role of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly. It makes two main hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are key to our metabolic rate, energy levels, and metabolic health.
When the thyroid works right, our body functions well. But, if it gets out of balance, health problems can arise.
About 20 million people in the United States have thyroid disease. Many cases go unnoticed. Thyroid issues can hit anyone, at any age or gender. So, knowing about the thyroid gland and its disorders is key.
Prevalence of Thyroid Disorders in the United States
Thyroid disorders are more common than you might think. Around 12% of the U.S. population will get a thyroid condition at some point. The main types are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid doesn’t make enough or too much hormone.
| Thyroid Disorder | Characteristics | Prevalence |
| Hypothyroidism | Underproduction of thyroid hormones | More common, mostly in women |
| Hyperthyroidism | Overproduction of thyroid hormones | Less common than hypothyroidism |
For more details on hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, check out UCLA’s article. It offers a deep dive into both conditions.
The Difference Between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism
The thyroid gland can be out of balance, leading to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism means the gland doesn’t make enough hormones. Hyperthyroidism means it makes too many. Both conditions affect millions, so knowing the difference is key.
Hypothyroidism: When the Thyroid Underproduces
Hypothyroidism happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormones. These hormones are vital for energy and metabolism. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
The main cause is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. This is when the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
Hyperthyroidism: When the Thyroid Overproduces
Hyperthyroidism is when the thyroid gland makes too many hormones. This leads to anxiety, weight loss, and rapid heartbeat. Graves’ disease is the main cause. It’s when the immune system mistakenly tells the thyroid to make more hormones.
Diagnosis Methods for Thyroid Disorders
To diagnose hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, doctors use several methods. They look at your medical history and do lab tests. The main test is a thyroid function test. It checks TSH, T3, and T4 levels in your blood.
They might also do thyroid antibody tests and thyroid ultrasound. These help find the cause and check the gland’s health.
It’s important to know the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. This helps doctors give the right treatment. It improves patients’ lives by balancing their thyroid hormones.
Treatment Approaches and Management
It’s important to know how hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are treated differently. Each condition needs its own special care. This ensures the best treatment for each patient.
Medication and Therapies for Hypothyroidism
The main treatment for hypothyroidism is synthetic thyroid hormone. Levothyroxine is the most used medicine. It’s taken by mouth to replace the missing thyroid hormone.
The doctor will check your blood often. This helps find the right amount of medicine for you.
“The goal of treatment is to restore normal thyroid hormone levels, which helps ease symptoms and improves life quality.”
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism treatment options are more varied. They include medicines, radioactive iodine, or surgery. Antithyroid medications like methimazole help lower hormone production.
Radioactive iodine therapy uses a special iodine to shrink the thyroid gland. Surgery might be needed to remove part or all of the gland.
Lifestyle Considerations for Thyroid Health
Living a healthy lifestyle is key for thyroid health. Eating foods rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc helps. Stress-reducing activities like yoga and meditation can also help.
| Treatment Aspect | Hypothyroidism | Hyperthyroidism |
| Primary Treatment | Synthetic thyroid hormone replacement (Levothyroxine) | Antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery |
| Lifestyle Considerations | Balanced diet, stress management |
Knowing how to treat hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism helps doctors give better care. This tailored approach improves health and life quality for patients.
Conclusion
It’s key to know the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism for the right treatment. We’ve looked at how these thyroid issues are different. This shows why getting the right diagnosis and treatment is so important.
Figuring out if someone has hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism starts with their symptoms and what causes them. This helps doctors create treatment plans that really work for each person.
Understanding hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism is essential for managing thyroid health. By knowing the differences, we can take better care of our thyroid. This improves our overall health and well-being.
By focusing on the unique needs of each patient, we can offer better care. This targeted approach leads to better health outcomes for everyone.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
The main difference is how much thyroid hormone the gland makes. Hypothyroidism means the gland doesn’t make enough. Hyperthyroidism means it makes too much.
What are the common symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include feeling very tired, gaining weight, and dry skin. You might also lose hair, feel cold easily, and feel depressed. These happen because the gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormones.
What are the typical symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include losing weight, having a fast heartbeat, and feeling anxious. You might also feel hot, shake, and have changes in your menstrual cycle. These happen because the gland makes too many thyroid hormones.
How are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam, your medical history, and blood tests to diagnose these conditions. They check the levels of thyroid hormones in your blood.
What is the difference between hypo and hyperthyroidism in terms of treatment?
For hypothyroidism, you might take medication to replace the missing hormones. For hyperthyroidism, treatments can include medicines, radioactive iodine, or surgery to reduce hormone production.
Can lifestyle changes help manage thyroid disorders?
Yes, making lifestyle changes can help with both conditions. This includes eating right, managing stress, exercising regularly, and avoiding substances that harm thyroid function.
Are there any differences in the prevalence of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is more common than hyperthyroidism. But, how common each is can change based on where you live, iodine intake, and other factors.
How do hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism affect overall well-being?
Both conditions can really affect how you feel and function. They can change your energy, mood, and how your body works. Getting the right treatment is key to feeling better.
What’s the difference between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism in terms of metabolic effects?
Hyperthyroidism speeds up your metabolism, causing weight loss and more energy. Hypothyroidism slows it down, leading to weight gain and less energy.
Can hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism be differentiated based on their causes?
Yes, the causes are different. Hypothyroidism often comes from autoimmune thyroiditis, surgery, or radiation. Hyperthyroidism usually comes from Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, or thyroiditis.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.thyroid.org/hypothyroidism/























