A bone marrow transplant is a big deal in medicine. It’s used to fight serious diseases like some cancers and blood problems.This treatment swaps out bad bone marrow with good one. It’s called bm transplantation.There are two ways to do this transplant. You can use your own stem cells or get them from someone else. Knowing the risks and what it means is key for those thinking about it.
Key Takeaways
- A bone marrow transplant is a serious procedure used to treat life-threatening diseases.
- The treatment involves replacing diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow.
- There are two main types of bone marrow transplants: autologous and allogeneic.
- Understanding the risks is crucial for patients considering this treatment.
- Bone marrow transplants are used to treat certain cancers and blood disorders.
Understanding Bone Marrow and Its Function
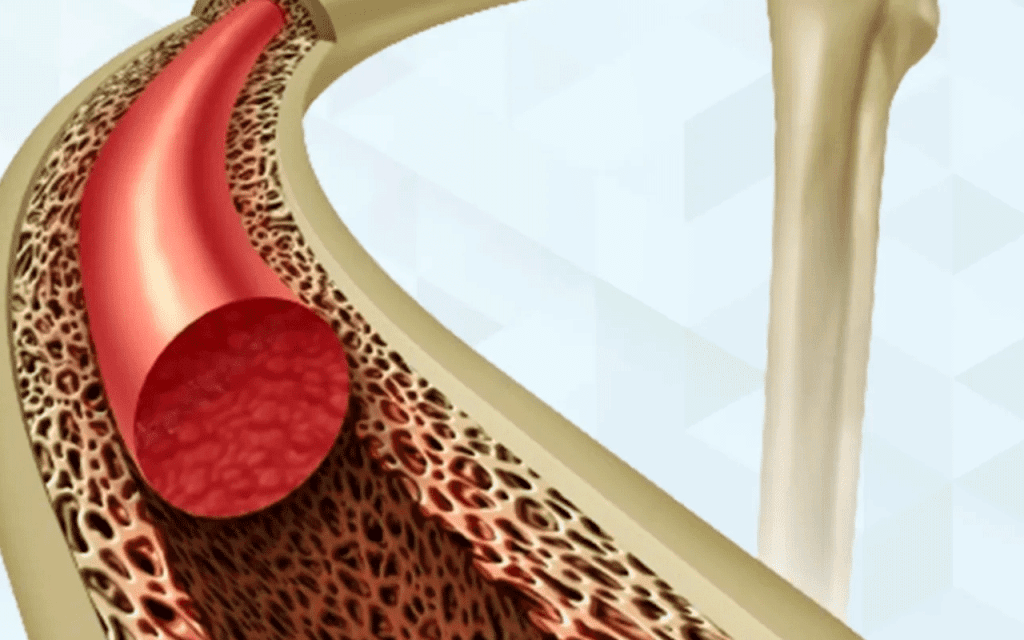
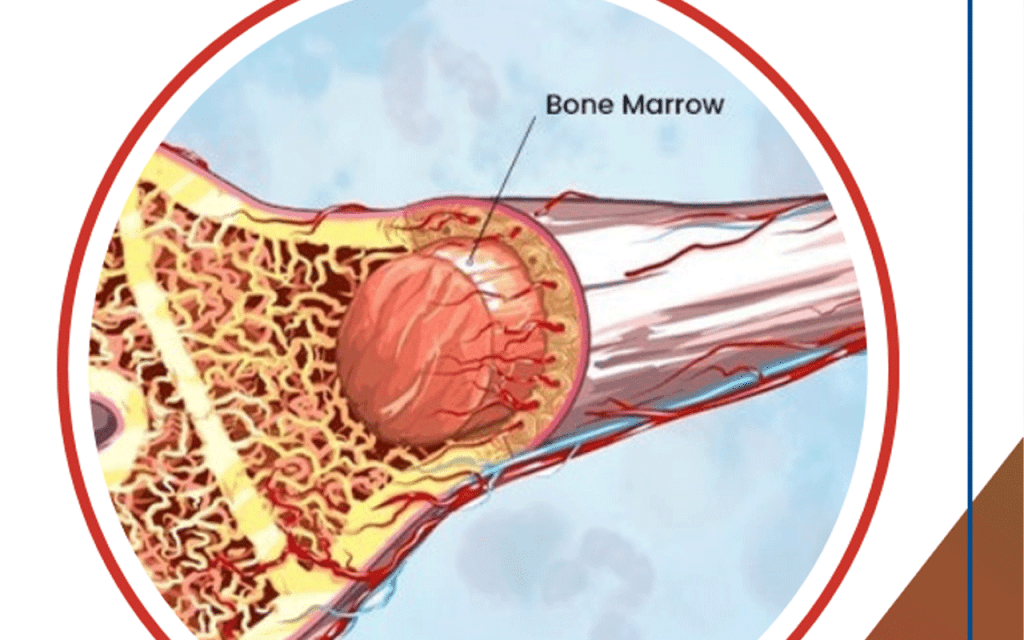
Bone marrow is key in making blood cells. It’s the soft tissue inside bones like hips and thighbones. It makes blood cells vital for our life.
What is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow is a complex tissue with blood vessels, nerves, and cells. It mainly has hematopoietic stem cells. These cells can turn into different blood cells.
The Role of Bone Marrow in the Body
Bone marrow’s main job is to make blood cells. It creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infections, and platelets help blood clot.
Types of Cells Produced in Bone Marrow
The bone marrow makes several cell types. They fall into three main groups:
- Myeloid lineage: This includes red blood cells, platelets, and some white blood cells like neutrophils and monocytes.
- Lymphoid lineage: This group makes lymphocytes, a key white blood cell for the immune system.
- Other cells: Bone marrow also produces other cells that help our body’s health.
Knowing about bone marrow is key to understanding hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. This is a procedure that replaces a patient’s bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
What is BM Transplantation?
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, also known as bone marrow transplant, is a treatment for serious diseases. These include leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
Definition and Purpose
A bone marrow transplant replaces damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. This helps the body make healthy blood cells. It treats conditions that harm the bone marrow.
BMTs can be based on the stem cell source and the donor-recipient genetic match. Knowing the types and purposes of BMT is key for patients and doctors.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplants
There are different bone marrow transplants, like autologous and allogeneic. An autologous transplant uses the patient’s own stem cells. These are collected, stored, and then given back after treatment.
An allogeneic transplant uses stem cells from a donor. The donor can be a relative or someone else, and matching is key for success.
It’s important to know the differences between these transplants. This helps choose the best treatment for a patient’s condition.
Medical Conditions Requiring Bone Marrow Transplants
Bone marrow transplantation is used to treat many medical conditions. This includes cancer and blood disorders. The choice to have a bone marrow transplant depends on the condition, its severity, and the patient’s health.
Leukemia and Lymphomas
Leukemia is a blood and bone marrow cancer. Bone marrow transplants replace the diseased marrow with healthy one. Lymphomas, cancers of the lymphatic system, may also need bone marrow transplants. This is especially true for aggressive or relapsed cases.
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow. Bone marrow transplants can treat multiple myeloma. They are most effective for those who can handle high-dose chemotherapy and a transplant.
Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is a rare condition where the bone marrow doesn’t make blood cells. A bone marrow transplant can cure aplastic anemia. It replaces the damaged marrow with healthy cells from a donor.
Other Conditions
Bone marrow transplants can also treat other diseases. This includes some genetic disorders and immune system deficiencies. Whether a transplant is suitable depends on the disease’s severity and the patient’s health.
The Bone Marrow Transplant Procedure
The bone marrow transplant procedure is a complex process with several key steps. It’s important for patients and their families to understand these steps. This helps them navigate the transplant process effectively.
Pre-transplant Evaluation and Testing
Before a bone marrow transplant, patients go through a detailed evaluation and testing. They check the patient’s health, disease status, and if they’re a good candidate for the transplant. Tests include blood work, imaging, and heart checks to make sure the patient can handle the transplant.
Donor Matching Process
For allogeneic transplants, finding a compatible donor is key. The donor matching process types the patient’s HLA and looks for a match. This can be a family member, an unrelated donor, or umbilical cord blood. The closer the HLA match, the lower the risk of GVHD.
Harvesting Bone Marrow
Bone marrow can be harvested through surgery or apheresis. In surgery, bone marrow is taken from the hip bones under general anesthesia. Apheresis collects stem cells from the blood after they’re mobilized from the bone marrow with medications.
The Transplantation Process
The actual transplant involves putting the stem cells into the patient’s bloodstream through a catheter. This is like a blood transfusion. The stem cells then go to the bone marrow to make new blood cells.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| Pre-transplant evaluation | Assessing patient health and disease status | Overall health, disease severity |
| Donor matching | Finding a compatible donor | HLA typing, donor availability |
| Harvesting bone marrow | Extracting stem cells | Method of harvest (surgical or apheresis) |
| Transplantation | Infusing stem cells into the patient | Central venous catheter, stem cell quality |
Each step of the bone marrow transplant procedure is crucial for success. Understanding these steps helps patients prepare for the challenges and opportunities ahead.
Preparation for a Bone Marrow Transplant
Getting ready for a bone marrow transplant is key. It involves making the body ready for the transplant. This means getting rid of old cells and weakening the immune system to stop it from rejecting the new marrow.
Conditioning Regimens
The conditioning regimen is a vital part of the transplant process. It uses chemotherapy and radiation therapy to kill cancer cells. This makes room for the new bone marrow. The exact regimen depends on the patient’s health, the transplant type, and other factors.
Chemotherapy and Radiation
Chemotherapy kills cancer cells and gets the bone marrow ready for the transplant. The choice and amount of chemotherapy drugs vary based on the patient’s condition and transplant type. Radiation therapy is also used to destroy cancer cells and weaken the immune system.
Central Venous Catheter Placement
A central venous catheter is placed before the transplant. It’s a safe way to give medications and blood products during treatment. The catheter goes into a large vein in the chest or neck.
Mental and Emotional Preparation
Preparing for a bone marrow transplant is not just physical. It also needs mental and emotional preparation. Patients should get support from family, friends, and mental health experts. This helps them deal with the stress and uncertainty of the transplant.
Understanding the preparation for a bone marrow transplant helps patients. It makes them better prepared for this complex medical procedure and increases the chances of a successful outcome.
Immediate Risks and Complications
Bone marrow transplants come with serious risks and complications. This procedure replaces a patient’s bone marrow with healthy stem cells. It’s a complex process that needs careful management.
Infection Risks
Patients face a high risk of infections after a bone marrow transplant. The treatment weakens the immune system. This makes them more likely to get sick.
- Bacterial infections: Patients are at risk of developing bacterial infections, particularly during the neutropenic phase.
- Viral infections: Viral infections, such as cytomegalovirus (CMV), can be a significant concern for patients after a bone marrow transplant.
- Fungal infections: Fungal infections, such as aspergillosis, can be life-threatening in immunocompromised patients.
Graft Failure
Graft failure is a serious issue after a bone marrow transplant. It happens when the new stem cells don’t work. This leads to a lack of blood cells.
Graft failure can be caused by several factors, including:
- Inadequate donor cell count
- Poor donor-recipient HLA matching
- Infection or graft-versus-host disease
Organ Damage
The treatment before a bone marrow transplant can harm organs. This includes the liver, lungs, and heart.
Organ damage can lead to long-term complications, such as:
- Liver dysfunction
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Cardiac dysfunction
Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a serious complication. It happens when the donor immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues.
The symptoms of acute GVHD can include:
- Skin rash
- Liver dysfunction
- Gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea and diarrhea
Long-term Side Effects of BM Transplantation
Bone marrow transplantation can have lasting side effects that affect a person’s life quality. While it saves many lives, it’s important for patients and their caregivers to know about these complications. These can happen years after the treatment.
Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) is a common long-term side effect. It happens when the donated immune cells attack the body’s tissues. cGVHD can affect organs like the skin, liver, mouth, and eyes, causing rashes, dry mouth, and vision issues. Managing cGVHD often requires ongoing immunosuppressive therapy.
Secondary Cancers
Another risk of BMT is secondary cancers. The treatment’s immunosuppressive nature can lead to new cancers. Patients should watch for signs like unusual bleeding, persistent fatigue, or unexplained weight loss. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are key for early detection and treatment.
Fertility Issues
The conditioning regimen before BMT can harm fertility. Both men and women may face infertility or reduced fertility as a result. It’s vital for patients to talk about fertility preservation with their healthcare team before BMT.
Organ Dysfunction
Organ dysfunction is another possible long-term issue after BMT. The treatment can damage vital organs like the heart, lungs, and liver. Patients may face heart failure, pulmonary fibrosis, or liver cirrhosis. Regular monitoring and management are crucial to prevent further problems.
In summary, while bone marrow transplantation can cure many diseases, it comes with significant long-term side effects. Knowing these risks and working closely with healthcare providers can help manage and reduce these complications. This improves the quality of life for BMT survivors.
Recovery Process After a Bone Marrow Transplant
After a bone marrow transplant, patients face a tough recovery journey. This journey has several stages, each important for their health and happiness.
Hospital Stay Duration
Patients start their recovery in the hospital, where they are watched closely for weeks after the transplant. How long they stay in the hospital depends on their health and the transplant details.
Key factors influencing hospital stay duration include:
- The patient’s overall health before the transplant
- The type of bone marrow transplant performed
- The presence of any complications or infections
Engraftment Process
Engraftment is a key moment in recovery. It’s when the new stem cells start making blood cells. This usually happens 2-4 weeks after the transplant.
During engraftment, patients are closely monitored for signs of:
- Increasing white blood cell counts
- Improving platelet counts
- Resolution of transplant-related complications
Immune System Recovery Timeline
Recovering the immune system takes time, often months to a year or more. During this time, patients are more likely to get sick and may need medicines to prevent infections.
Key aspects of immune system recovery include:
- Reconstitution of immune cells
- Recovery of immune function
- Gradual tapering of immunosuppressive medications
Physical Rehabilitation
Physical rehab is crucial for recovery. It helps patients get their strength and function back. A personalized rehab plan can greatly improve their life after the transplant.
“Rehabilitation is an essential component of the recovery process, enabling patients to achieve their full potential and return to their normal activities.” – Expert in Bone Marrow Transplantation
Psychological Impact of Bone Marrow Transplants
Getting a bone marrow transplant is more than just a physical challenge. It deeply affects the mind, impacting not just the patient but also their family and caregivers.
Emotional Challenges for Patients
Patients face many emotions during a bone marrow transplant. They might feel anxious, scared, depressed, or isolated. The treatment, which includes strong medicines and sometimes radiation, can make them very tired and emotionally open.
One patient said, “The hardest part was not knowing what the future held and feeling completely at the mercy of my treatment.”
Impact on Family and Caregivers
The effects of bone marrow transplantation don’t stop with the patient. Their family and caregivers also face significant stress and emotional challenges. They have to handle a lot, like managing medicines, going to doctor’s appointments, and supporting the patient emotionally.
It’s vital for families to get support too. This can include counseling, support groups, and resources for caregiving. A caregiver shared, “We didn’t realize how much we needed support until we were in the midst of it. Having a network of other families going through the same thing was invaluable.”
Coping Strategies and Support Systems
It’s crucial for patients and their families to have good coping strategies and strong support systems. This can include:
- Access to mental health professionals for counseling and therapy
- Support groups, either in-person or online, to connect with others who are going through similar experiences
- Educational resources to understand the transplant process and what to expect
- Family and friend support networks to help with practical needs and emotional support
By using these resources, patients and their loved ones can better handle the challenges of bone marrow transplantation.
Post-Transplant Psychological Care
After a transplant, care goes beyond just physical recovery. It also includes ongoing mental support. Patients might need counseling and therapy to deal with any emotional or psychological issues. This support is key to helping them adjust to life after the transplant.
Survival Rates and Prognosis
Survival rates after bone marrow transplantation have gotten better. But, how well a patient does depends on several important factors. Knowing these factors helps both patients and doctors make better choices about treatment and care after the transplant.
Factors Affecting Survival
Many things can affect how well a patient does after a bone marrow transplant. The main ones are the disease itself, the patient’s health, and the type of transplant. Disease status at the time of transplant is very important. Patients who are in remission or have little disease left tend to do better.
Other key factors include patient age and donor-recipient matching. Younger patients usually do better, and a closer match between donor and recipient can lower the risk of serious problems like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Disease-Specific Outcomes
Outcomes after bone marrow transplantation vary a lot depending on the disease. For example, patients with acute leukemia in remission at transplant time have a better chance of survival than those with active disease.
On the other hand, patients with multiple myeloma or lymphoma face different survival rates. This depends on how well their disease responded to previous treatments and the transplant method used.
Quality of Life After Transplant
Quality of life after bone marrow transplantation is very important. While the transplant can cure many, it also comes with big risks and possible long-term side effects. These can include chronic graft-versus-host disease, organ problems, and secondary cancers.
Survivors often need ongoing care to deal with these issues and improve their life quality. Rehabilitation programs and supportive care are key in helping patients recover and get back to their daily lives.
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers
- Monitoring for signs of complications
- Adherence to prescribed medications and therapies
- Lifestyle adjustments to promote overall health
By understanding what affects survival rates and prognosis, patients can better navigate their treatment journey. This helps them make informed decisions about their care.
Conclusion
Bone marrow transplantation is a major medical treatment. It gives hope to patients with serious diseases. It’s important for patients and doctors to know the risks, benefits, and results of this complex process.
Planning carefully and taking good care after the transplant can lead to better results. Knowing the process, risks, and benefits helps patients make smart choices about bone marrow transplants.
The success of a transplant depends on many things. These include the patient’s health, the match with the donor, and the care after the transplant. Understanding these factors helps patients get through the transplant process successfully.
FAQ
What is a bone marrow transplant?
A bone marrow transplant replaces a patient’s bad bone marrow with good one.
What is the purpose of a bone marrow transplant?
A bone marrow transplant treats diseases like cancer and blood disorders.
What are the types of bone marrow transplants?
There are two types: autologous (using the patient’s own stem cells) and allogeneic (using donor stem cells).
What is the difference between autologous and allogeneic bone marrow transplants?
Autologous uses the patient’s own stem cells. Allogeneic uses stem cells from a donor.
What are the risks associated with bone marrow transplantation?
Risks include infection, graft failure, organ damage, and graft-versus-host disease.
What is graft-versus-host disease?
Graft-versus-host disease happens when donor immune cells attack the patient’s tissues.
How long does it take to recover from a bone marrow transplant?
Recovery takes months to a year or more.
What is the engraftment process?
Engraftment is when new stem cells start making blood cells.
What are the long-term side effects of bone marrow transplantation?
Side effects include chronic graft-versus-host disease, secondary cancers, fertility issues, and organ dysfunction.
How does a bone marrow transplant affect fertility?
It can make patients infertile or reduce fertility.
What is the survival rate for patients after a bone marrow transplant?
The survival rate depends on the disease, patient’s health, and transplant type.
What is the quality of life after a bone marrow transplant?
Quality of life varies based on health and long-term side effects.
References
- American Cancer Society. (2024). Bone marrow and stem cell transplants. Retrieved September 25, 2025, from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/managing-cancer/treatment-types/stem-cell-transplant.html
- Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. (2024). Bone marrow transplant. Retrieved September 25, 2025, from https://www.lls.org/treatment/types/bone-marrow-transplant
- National Cancer Institute. (2024). Stem cell transplantation: Questions and answers. Retrieved September 25, 2025, from https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/stem-cell-transplant/stem-cell-transplant-questions
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. (2024). Bone marrow transplant. Retrieved September 25, 2025, from https://medlineplus.gov/bonemarrowtransplantation.html









